BM Topic 3.3: Costs & Revenues
1/11
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
4 main types of costs
fixed
variable
direct
indirect (overhead)
What are ‘costs’ & some examples?
costs are the charges that an organisation incurs from its operations.
purchase of raw materials & components for production
purchase of stocks (inventory) of components or finished goods from suppliers
rent for hiring the commercial premises or mortgage payments for financing land, premises & buildings
insurance payments for public liability, buildings insurance & vehicle insurance
salaries & wages to employees
payment for utility bills for gas, electricity & telephone charges
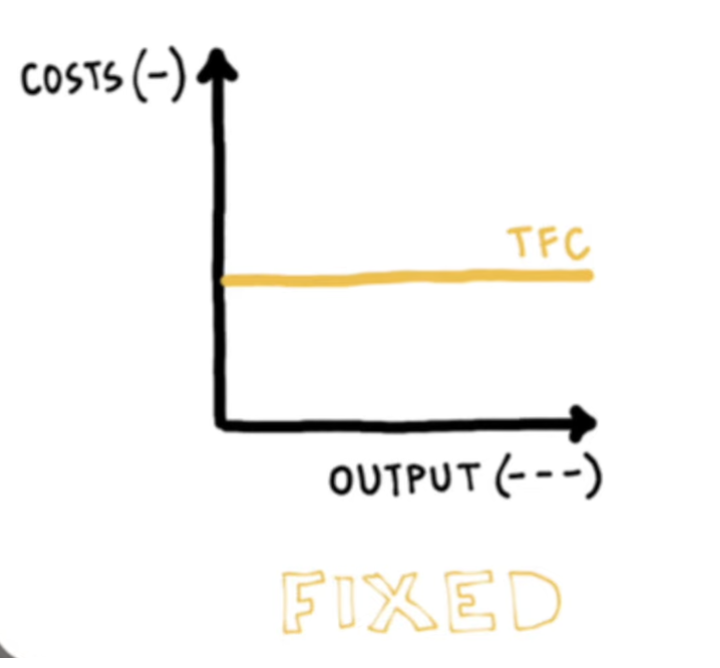
Define ‘fixed costs’ & some examples
costs that do not change depending on the level of output or quantity. have to be paid irrespective of how much is produced or sold.
rent payments
salaries to management
internet
*sometimes referred to as total fixed costs (TFC)
Define ‘variable costs’ & some examples
costs that change in proportion with the level of output. these costs rise when the firm’s output or sales volume increases
purchasing of raw materials & components for productions
commission paid to sales staff
piece-rate wages
***when a firm’s fixed costs are combined with its variable costs, the total cost of production can be determined
What is the ‘total cost of production’ & how to calculate it?
the aggregate amount of money spent on the output of a business
total costs = total fixed costs + total variable costs
What are the ‘average costs (AC) (or average total costs (ATC))’ & how to calculate it?
average cost (AC) refers to the cost per unit
average cost (AC) = total cost (TC) ÷ quantity (Q)
average cost (AC) = average fixed cost (AFC) + average variable cost (AVC)
a decline in average total cost as output rises shows the organization experiences economies of scale
a rise in average cost as output rises shows the organisation experiences diseconomies of scale
average fixed cost will always fall when the level of output increases because total fixed cost is spread over an increasingly larger level of output
Define ‘direct costs AKA cost of sales’ & some examples
expenses that can be directly tied (evidently & explicitly associated) to the output or sale of a certain good, service, or business operation.
e.g. direct costs for a hair salon include money spent on hair products like shampoo, conditioner, hair dyes
Define ‘indirect costs AKA overhead’ & some examples
costs that are not easily identifiable with the sale or output of a specific good, service, department, or business operation
rent on premises
salaries for administrative staff
fees paid for legal & accounting services
general insurance for third parties, fire & theft
costs involved with maintaining & running the organisation
Define ‘revenue’ & how to calculate it
the money coming into a business from the sale of goods and services
total revenue = price of product x quantity sold
Define ‘revenue streams’ & examples
the various sources of revenue for a business (other than trading activity) OR means, other than trading activity, used to generate income for an organisation
dividends
interest on deposits (bank deposits)
merchandise
donations
sponsorship deals
advertising revenue
subscription
rental income
licensing fees
royalties
leasing charges
recurring grants & subsidies from the government
Define ‘total revenue’
the sum of income received by a business from its trading activities