Chapter 5: Economic Growth, The Financial System, and Business Cycle
1/53
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapter 5 of Econ 104 Final Exam
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
long-run economic growth
the change in GDP over time. It is the increase in the economy’s capacity to produce goods and services
how is economic growth measured
by the changes in GDP or GDP per capita over a long period of time.
GDP per capita equation
Real GDP
────────
Population
Economic growth equation (% change)
gdp (x) - gdp (y)
growth in x = ────────────── * 100
gdp (y)
Economic growth over a long period of time equation (annual avg. growth rate)
GDP(x)
( --------------------- )1/n − 1 × 100
GDP(y)
Rule of 70
if a country’s real GDP per capita grows at a constant rate of (g) percent, GDP per capita will double its current value
Rule of 70 equation
70
( --------------------- )
growth rate
Determinants of long-run growth
labor productivity
property rights
Labor productivity
the amount of output per hour of work; it is made up of capital (equipment/machinery) per worker and technological change
Property rights
rules that govern ownership and use of resources
The business cycle
cycle that tells us that we are not always performing at our maximum
Potential GDP
the value of GDP when all firms are producing at capacity
Maximum GDP
The level of GDP that an economy can attain and sustain over a long period of time; determined by resources and technology
The financial system
enables businesses to borrow and invest in new capital, research, and innovation, hire workers, and train existing workers; it matches savers and borrowers
Financial system components
capital markets and financial intermediaries
Capital markets
where firms raise funds by selling stocks and bonds (financial securities)
Financial intermediaries
banks that borrow money from savers at a lower interest rate and lend it borrowers like firms at a higher interest rate
Why do we need financial systems?
risk sharing, liquidity, and information
Risk-sharing
financial systems make it possible for low-income people to invest in diversified investment portfolios like mutual funds
liquidity
Refers to the ease of converting an asset into cash; this incentives savers to invest through the financial system
information
financial intermediaries have access to skill and info that you don’t when it comes to risk assessment
What is total savings equal to
total investments
why does total savings=total investments
S=Y-C-G and I=Y-C-G in a closed economy
Private savings
savings by households
Public savings
savings by the government
Private savings equation
S= Y + TR - C - T
Public Savings Equation
S = T - G - TR
national savings
sum of private and public savings
national savings equation
S = Y - C - G
Government budget balance
refers to the difference between tax revenues (T) and its total expenditure (G + TR)
When is there a budget balance
government expenditure = total tax revenues (G + TR = T), and public savings is 0
when is there a budge deficit
when government expenditure > total tax revenue (G+TR > T), and public savings are negative
when is there a budget surplus
when government expenditure < total tax revenues (G + TR < T), and public savings are positive
How does a budget surplus increase total savings
it adds to government savings, which gets added to private savings
The market for loanable funds
illustrates the equivalence of savings and investment in a closed economy (savers loaning to borrowers)
savers role in the market for LF
suppliers
borrowers in the market of LF
buyers
Demand for loanable funds
comes from businesses willingness to borrow and invest
supply of loanable funds
comes from households’ desire to save and governments budget balance
Graph of loanable funds units
Y = real interest rate X=loanable funds per dollar
graph of loanable funds
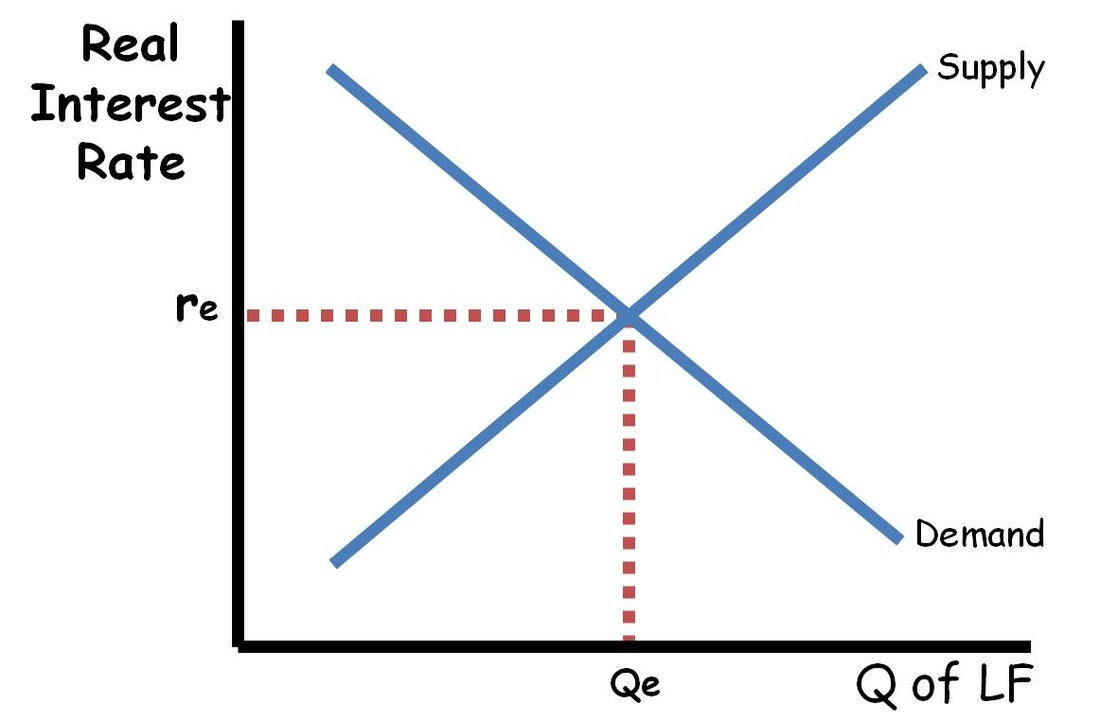
What do changes in savings and investment lead to
Shifts in supply and demand, which leads to a change in the interest rate
the effect of budget deficit on loanable funds
supply shifts left, real interest rate increases, and investment decreases
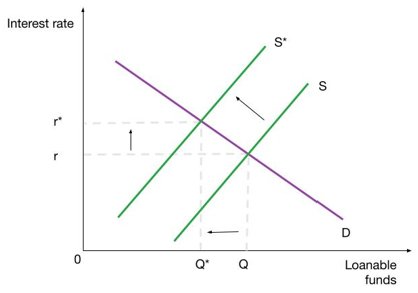
The effect of budget surplus on loanable funds
Supply shifts right, the real interest rate decreases, and investment increases
The business cycle
alternating periods of expanding and declining economic activity, measured by real GDP
phases of the business cycle
Expansion, peak, recession, trough
expansion phase
production is increasing and so is employment and average incomes
the peak
real gdp had reached its highest short-term level, and signals the end of the expand is on phase
recession phase
follows the peak and its a period of declining production, employment, and average incomes
the trough
at the bottom of the business cycle and signals the end of the recession phase and the start of expansion
the national bureau of economic research (NBER)
publishes business cycle data/dates
when does the inflation rate increase during the business cycle
toward the end of the expansion phase and into the beginning of the next recession
when does the inflation rate decreases during the business cycle
during the recession phase
what is the effect of recessions on the inflation and unemployment rate
inflation rate falls and unemployment rate rises