Respiratory
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/114
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:09 PM on 4/27/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
115 Terms
1
New cards
Briefly outline asthma- definition, symptoms
Heterogenous disease characterised by chronic airway inflammation
Reversible airflow limitation
SSx:
- wheeze
- breathlessness
- chest tightness
- cough
- worse at night
- triggered by allergen/exercise/cold air/aspirin/BB
- atopic features
Reversible airflow limitation
SSx:
- wheeze
- breathlessness
- chest tightness
- cough
- worse at night
- triggered by allergen/exercise/cold air/aspirin/BB
- atopic features
2
New cards
List 5 different phenotypes of asthma
Allergic
Non-allergic
Adult-onset
Asthma with persistent airflow limitation
Asthma with obesity
Non-allergic
Adult-onset
Asthma with persistent airflow limitation
Asthma with obesity
3
New cards
Which clinical features make an asthma diagnosis LESS likely?
Dizziness, light-headedness or peripheral tingling
Productive cough in absence of wheeze/breathlessness
Normal examination when breathless
Voice disturbance
Smoking history (>20 pack years)
Cardiac disease
Normal PEF or FEV1 when symptomatic
Productive cough in absence of wheeze/breathlessness
Normal examination when breathless
Voice disturbance
Smoking history (>20 pack years)
Cardiac disease
Normal PEF or FEV1 when symptomatic
4
New cards
List the differential diagnoses of wheeze
Asthma
COPD
Obstruction e.g. foreign body
Anaphylaxis
Pulmonary oedema
COPD
Obstruction e.g. foreign body
Anaphylaxis
Pulmonary oedema
5
New cards
Outline the management of acute asthma
*O*xygen (high flow, aim for >92%
*S*albutamol
**H**ydrocortisone/prednisolone
**I**pratropium bromide
**T**heophylline
**!** Magnesium sulphate
*S*albutamol
**H**ydrocortisone/prednisolone
**I**pratropium bromide
**T**heophylline
**!** Magnesium sulphate
6
New cards
Define chronic bronchitis
Presence of chronic productive cough and sputum for at least 3 months in each of two successive years
7
New cards
Define emphysema
Enlarged alveolar spaces and loss of alveolar walls
8
New cards
Define COPD
Common, preventable and treatable disease
Characterised by persistent respiratory symptoms + airflow limitation
Due to airway and/or alveolar abnormalities caused by significant exposure to noxious particles or gases
Risk factors- over 35 yrs, smoke/ex-smoker
Characterised by persistent respiratory symptoms + airflow limitation
Due to airway and/or alveolar abnormalities caused by significant exposure to noxious particles or gases
Risk factors- over 35 yrs, smoke/ex-smoker
9
New cards
How do you calculate pack years?
Number of packs (20) per day x years smoked
e.g. 1 pack a day for 30 yrs= 30
e.g. 1 pack a day for 30 yrs= 30
10
New cards
Describe the pathophysiology of COPD
***Chronic bronchitis***
* hypertrophy of mucus secreting glands :. more mucus= sputum cough
* infiltration of bronchial walls with inflammatory cells :. airway narrowing
***Emphysema***
* loss of elastic recoil :. airflow limitation + air trapping
* bulla formation (air filled space after alveoli walls break down)
* hypertrophy of mucus secreting glands :. more mucus= sputum cough
* infiltration of bronchial walls with inflammatory cells :. airway narrowing
***Emphysema***
* loss of elastic recoil :. airflow limitation + air trapping
* bulla formation (air filled space after alveoli walls break down)
11
New cards
Compare the inflammation in asthma and COPD
*ASTHMA:*
- triggered by sensitising agent
- CD4+ and t lymphocytes
- presence of eosinophils, macrophages + mast cells
- mostly REVERSIBLE
*COPD:*
- triggered by noxious agent
- CD8+ and T lymphocytes
- presence of macrophages + neutrophils
- mostly IRREVERSIBLE
- triggered by sensitising agent
- CD4+ and t lymphocytes
- presence of eosinophils, macrophages + mast cells
- mostly REVERSIBLE
*COPD:*
- triggered by noxious agent
- CD8+ and T lymphocytes
- presence of macrophages + neutrophils
- mostly IRREVERSIBLE
12
New cards
Describe the classic symptoms of COPD
Exertional breathlessness
Chronic cough
Regular sputum production
Frequent winter bronchitis
Wheeze
Chronic cough
Regular sputum production
Frequent winter bronchitis
Wheeze
13
New cards
Outline the clinical features of COPD
Tachypnoea
Use of accessory muscles
Hyperinflation
Reduced cricosternal distance (
Use of accessory muscles
Hyperinflation
Reduced cricosternal distance (
14
New cards
How is the severity of COPD assessed?
Using MRC dyspnoea scale
Ranges from grade 0 (only breathless with strenuous exercise) to grade 4 (too breathless to leave house or when dressing)
\
FEV1
Ranges from grade 0 (only breathless with strenuous exercise) to grade 4 (too breathless to leave house or when dressing)
\
FEV1
15
New cards
What is Dahl's sign?
Hyperpigmentation seen above knees/elbows in COPD patients
16
New cards
List the smoking cessation drugs
Vareniciline (Champix)
- selective nicotine receptor partial agonist
Nicotine replacement therapy (patches, gums, spray, inhaler)
Bupropion (Zyban)
- atypical antidepressant
- selective nicotine receptor partial agonist
Nicotine replacement therapy (patches, gums, spray, inhaler)
Bupropion (Zyban)
- atypical antidepressant
17
New cards
Outline the pharmacological treatment of stable COPD
Flu vaccines
SABA (salbutamol, terbutaline)
Anti-cholinergics (ipratropium bromide, aclidinium)
LABA (salmeterol, indacterol)
ICS
Phosphodiesterase inhibitors (theophyllines, roflumilast)
SABA (salbutamol, terbutaline)
Anti-cholinergics (ipratropium bromide, aclidinium)
LABA (salmeterol, indacterol)
ICS
Phosphodiesterase inhibitors (theophyllines, roflumilast)
18
New cards
Outline the non-pharmacological treatment of stable COPD
Exercise training programmes
Long-term O2 therapy (>15 hrs a day)
Lung volume reduction surgery
Lung transplant
Long-term O2 therapy (>15 hrs a day)
Lung volume reduction surgery
Lung transplant
19
New cards
Outline the complications of COPD
Respiratory failure
(PaO2
(PaO2
20
New cards
List the investigations used to diagnosed COPD
O2 saturation
ABG
Sputum + blood cultures
CXR
ECG
Bloods- eosinophil count, U&E, CRP, theophylline, cardiac enzymes
CT/CTPA (rule out PE)
ABG
Sputum + blood cultures
CXR
ECG
Bloods- eosinophil count, U&E, CRP, theophylline, cardiac enzymes
CT/CTPA (rule out PE)
21
New cards
List the differentials for COPD
Pneumonia
Pneumothorax
Malignancy
PE
HF/ACS
Pneumothorax
Malignancy
PE
HF/ACS
22
New cards
Define pneumonia
Symptoms and signs consistent with an acute lower respiratory tract infection associated with new radiographic shadowing
British Thoracic Society
British Thoracic Society
23
New cards
Outline the symptoms of pneumonia
Fever
Shivers
Malaise
Dyspnoea
Cough
Sputum
Pleuritic pain
Haemoptysis
Shivers
Malaise
Dyspnoea
Cough
Sputum
Pleuritic pain
Haemoptysis
24
New cards
Outline the signs of pneumonia
Pyrexia
Cyanosis
Confusion (elderly)
Tachypnoea/tachycardia
Consolidation (reduced expansion, dull percussion, increased fremitus, bronchial breathing)
Pleural rub (raspy breathing)
Cyanosis
Confusion (elderly)
Tachypnoea/tachycardia
Consolidation (reduced expansion, dull percussion, increased fremitus, bronchial breathing)
Pleural rub (raspy breathing)
25
New cards
List the lung defence mechanisms
Filtration in upper airways
Cough reflex
Mucociliary clearance
Alveolar macrophages
Humoral and cellular immunity
Oxidative metabolism of neutrophils
Cough reflex
Mucociliary clearance
Alveolar macrophages
Humoral and cellular immunity
Oxidative metabolism of neutrophils
26
New cards
Outline the different investigations for pneumonia
Diagnosis:
- CXR
- FBC/CRP
Severity:
- U&E
- FBC/CRP/LFT
- ABG
Target therapy:
- blood + sputum cultures
- Pneumococcal urinary antigen
- Legionella urinary antigen + sputum culture
- viral PCR
- CXR
- FBC/CRP
Severity:
- U&E
- FBC/CRP/LFT
- ABG
Target therapy:
- blood + sputum cultures
- Pneumococcal urinary antigen
- Legionella urinary antigen + sputum culture
- viral PCR
27
New cards
What is CURB65?
A scoring system for pneumonia
Confusion
Urea (>7mmol/l)
Respiratory rate (>30/min)
Blood pressure (
Confusion
Urea (>7mmol/l)
Respiratory rate (>30/min)
Blood pressure (
28
New cards
How does the CURB65 scoring affect the management of pneumonia?
0-1: treat at home
2: short admission, oral antibiotics
3: senior urgent review
4-5: critical care
2: short admission, oral antibiotics
3: senior urgent review
4-5: critical care
29
New cards
Outline the general management of pneumonia
O2 (aim for 94-98%)
Antibiotics
IV fluids, analgesia, DVT prophylaxis
Chest physio
Nutritional support
Smoking cessation
Antibiotics
IV fluids, analgesia, DVT prophylaxis
Chest physio
Nutritional support
Smoking cessation
30
New cards
Name the pathogen that causes Tb
Mycobacterium Tuberculosis
31
New cards
Outline the risk factors of Tb
Immunosuppression e.g. HIV infection, silicosis (inhaling silica dust), substance abuse, severe kidney disease, low BMI, transplant, cancer, diabetes
Homelessness
Imprisonment
Homelessness
Imprisonment
32
New cards
Outline the presentation of Tb
Respiratory:
- cough
- sputum
- haemoptysis
Systemic:
- fever
- malaise
- loss of appetite
- night sweats
- weight loss
- lymphadenopathy
- cough
- sputum
- haemoptysis
Systemic:
- fever
- malaise
- loss of appetite
- night sweats
- weight loss
- lymphadenopathy
33
New cards
Describe the pathogenesis of Tb
Inhaled particles deposited in alveoli →
invade and replicate in alveolar macrophages →
epithelial reaction to bacteria →
encapsulation of bacteria (tubercle) →
bacteria continue to replicate or become latent →
causes destruction and fibrosis of tissue
invade and replicate in alveolar macrophages →
epithelial reaction to bacteria →
encapsulation of bacteria (tubercle) →
bacteria continue to replicate or become latent →
causes destruction and fibrosis of tissue
34
New cards
Compare primary and post-primary Tb
*Primary:*
- Tb with no pre-existing immunity
- non-infectious
- high mortality in vulnerable (children, elderly)
- often outside lung
- HIV coinfection
*Post-primary:*
- with pre-existing immunity
- infectious
- forms cavities in lungs
- young adults
- immunocompetent immune system
- Tb with no pre-existing immunity
- non-infectious
- high mortality in vulnerable (children, elderly)
- often outside lung
- HIV coinfection
*Post-primary:*
- with pre-existing immunity
- infectious
- forms cavities in lungs
- young adults
- immunocompetent immune system
35
New cards
Outline the diagnosis of Tb
*Sputum*- PCR, culture
*CXR*- segmental/lobar consolidation, hilar or mediastinal lymphadenopathy, pleural effusion
*Inflammatory markers*- ESR, CRP
*Histology*- granuloma, caseation, histocytes, giant cells, lymphocytes
*CXR*- segmental/lobar consolidation, hilar or mediastinal lymphadenopathy, pleural effusion
*Inflammatory markers*- ESR, CRP
*Histology*- granuloma, caseation, histocytes, giant cells, lymphocytes
36
New cards
Outline the treatment of Tb
4 antibiotics for 2-4 months intensive
Rifampicin
Isoniazid
Pyrazinamide
Ethambutol
Rifampicin
Isoniazid
Pyrazinamide
Ethambutol
37
New cards
What is sarcoidosis? Who does it affect?
A multisystem granulomatous disorder of unknown cause
Highest prevalence in Northern Europe
Adults 20-40yrs
Caucasians
HLA-DRB1 + DBQ1 alleles
Highest prevalence in Northern Europe
Adults 20-40yrs
Caucasians
HLA-DRB1 + DBQ1 alleles
38
New cards
Outline the clinical features of sarcoidosis
Fever
Erythema nodosum
Polyarthralgia
Bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy
Dry cough
Dyspnoea
Low exercise tolerance
Chest pain
Red eyes
Thirst, polyuria (hypercalcaemia)
Skin lesions
Erythema nodosum
Polyarthralgia
Bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy
Dry cough
Dyspnoea
Low exercise tolerance
Chest pain
Red eyes
Thirst, polyuria (hypercalcaemia)
Skin lesions
39
New cards
How is sarcoidosis diagnosed?
Bloods: high ESR, lymphopenia, high Ca2+, high Ig,
Biopsy: non-caseating granuloma
Bone XR: 'punched out' lesions in distal phalanges
Biopsy: non-caseating granuloma
Bone XR: 'punched out' lesions in distal phalanges
40
New cards
Why do oxygen prescriptions need to be monitored?
Oxygen toxicity leads to free radicals
:. seizures + unconsciousness
Also results in constriction of pulmonary circulation
:. seizures + unconsciousness
Also results in constriction of pulmonary circulation
41
New cards
What's the O2 saturation target for COPD patients?
88-92%
42
New cards
What's the general O2 saturation target?
Above 94%
43
New cards
Briefly outline the 4 ways O2 is administered
***Venturi mask:*** delivers fixed O2 concentration
5-10 L/min, 35-60% FIO2, type 1 resp failure
\
***Non-rebreather reservoir bag:*** critical/trauma patients, 70-80% FIO2, effecting for short term treatment
\
***Nasal cannulae:*** 2-5L/min, 24-50% FIO2, suitable for most patients with type 1 and 2 resp failure, comfortable
5-10 L/min, 35-60% FIO2, type 1 resp failure
\
***Non-rebreather reservoir bag:*** critical/trauma patients, 70-80% FIO2, effecting for short term treatment
\
***Nasal cannulae:*** 2-5L/min, 24-50% FIO2, suitable for most patients with type 1 and 2 resp failure, comfortable
44
New cards
What is humidified O2 and when is it prescribed?
Reduces dryness in upper airways
Should be humidified if O2 is being delivered for more than 24hrs
Should be humidified if O2 is being delivered for more than 24hrs
45
New cards
How does the BTS classify acute asthma?
Life-threatening asthma mnemonic
\
==**33, 92 CHEST:**==
\
PEFR **
\
==**33, 92 CHEST:**==
\
PEFR **
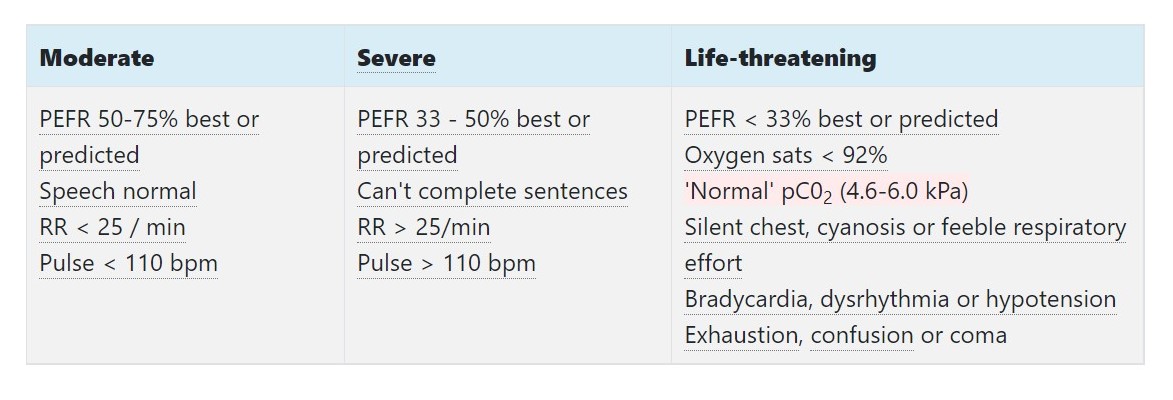
46
New cards
Define a pneumothorax
Air in the pleural space leading to lung collapse
47
New cards
Outline the different types of pneumothoraxes
**Spontaneous:** primary (normal lung) or secondary to pre-existing lung disease
\
**Non-spontaneous:** traumatic or iatrogenic
\
**Non-spontaneous:** traumatic or iatrogenic
48
New cards
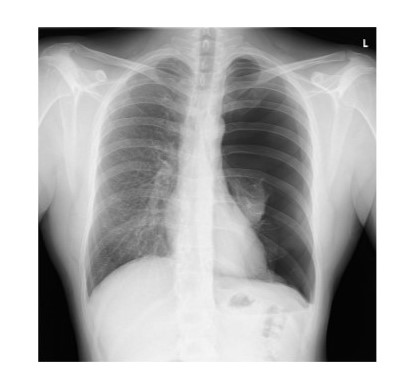
Diagnosis?
Large left pneumothorax
49
New cards
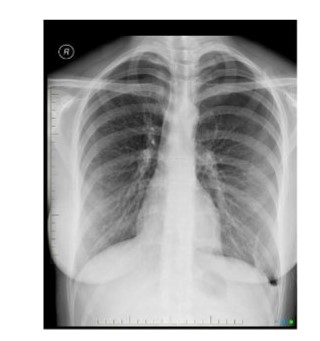
Diagnosis?
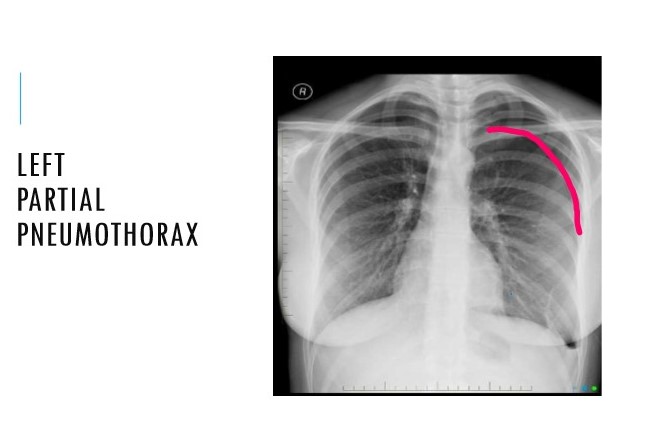
50
New cards
Outline the causes of secondary pneumothorax
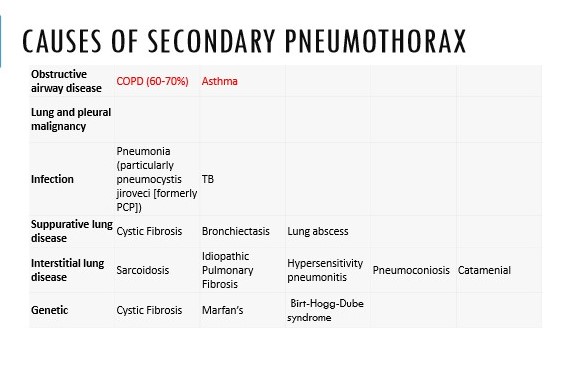
51
New cards
Outline the symptoms of pneumothorax
**Sudden** onset/ acute
\
Pleuritic chest pain
\
SOB
\
Cough
\
Pleuritic chest pain
\
SOB
\
Cough
52
New cards
Outline the differentials of pneumothorax
==Respiratory==- __PE__, pneumonia, acute exacerbation of respiratory disease
\
%%Cardiovascular%%- __ACS, MI__, pericarditis, aortic dissection, aneurysm rupture, cardiac tamponade
\
Other- MSK, GORD, panic attack
\
%%Cardiovascular%%- __ACS, MI__, pericarditis, aortic dissection, aneurysm rupture, cardiac tamponade
\
Other- MSK, GORD, panic attack
53
New cards
Outline the signs of pneumothorax
**Reduced** expansion
\
**Hyper-resonant** percussion
\
**Quiet** breath sounds
\
Tachycardia
\
**Hyper-resonant** percussion
\
**Quiet** breath sounds
\
Tachycardia
54
New cards
Outline the management of a pneumothorax
A-E assessment
History and examination
\
\
History and examination
\
\
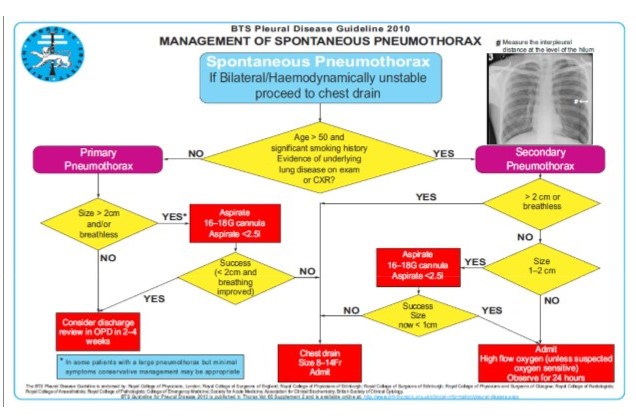
55
New cards
Where is the safe triangle?
Location used when aspirating pneumothorax
\
Needle inserted right above rib to avoid neurovascular bundle
\
Boundaries: latissimus dorsi, pec major, line superior to nipple + apex at axilla
\
Needle inserted right above rib to avoid neurovascular bundle
\
Boundaries: latissimus dorsi, pec major, line superior to nipple + apex at axilla
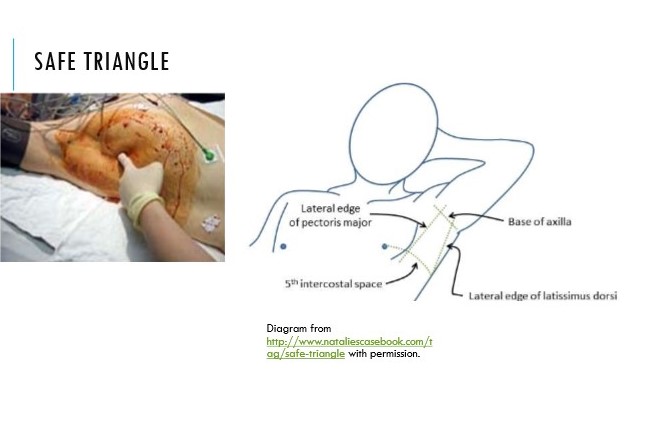
56
New cards
Describe tension pneumothorax
Increasing pressure in thoracic cavity
\
Hole in visceral pleura is letting air in on inspiration
\
On breathing out, air isn’t being let out :. one-way valve
\
Hole in visceral pleura is letting air in on inspiration
\
On breathing out, air isn’t being let out :. one-way valve
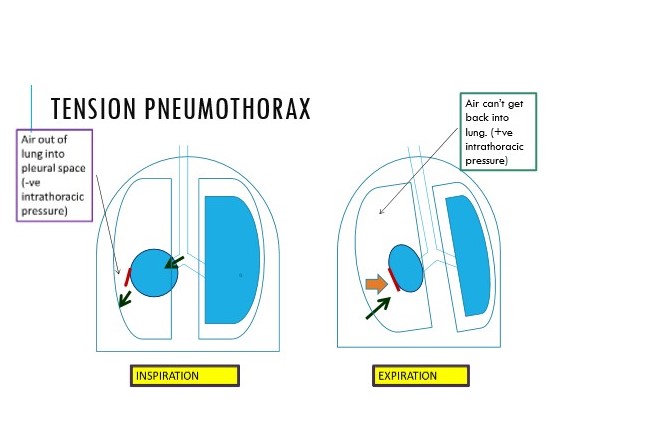
57
New cards
Outline the clinical features of tension pneumothorax
Severe breathlessness
\
Tachycardia
\
Pulsus paradoxus (exaggerated fall in systolic pressure during inspiration >10mm/Hg)
\
Distended jugular veins
\
Tracheal deviation (AWAY)
\
Ipsilateral reduced/absent breath sounds
\
Tachycardia
\
Pulsus paradoxus (exaggerated fall in systolic pressure during inspiration >10mm/Hg)
\
Distended jugular veins
\
Tracheal deviation (AWAY)
\
Ipsilateral reduced/absent breath sounds
58
New cards
Outline the emergency management of a tension pneumothorax
No CXR
\
Needle decompression
\
Large bore cannula in MCL 2nd ICS
\
Needle decompression
\
Large bore cannula in MCL 2nd ICS
59
New cards
Advice to prevent recurrence of pneumothorax
No diving
\
Stop smoking
\
No aeroplane travel for 2-6 weeks
\
Pregnancy can increase risk
\
Return immediately if SOB
\
Stop smoking
\
No aeroplane travel for 2-6 weeks
\
Pregnancy can increase risk
\
Return immediately if SOB
60
New cards
Epidemiology of PE

61
New cards
Outline the risk factors for VTE- major and non major

62
New cards
Outline the clinical features of a minor PE
**Symptoms:**
* May be asymptomatic
* SOB
* Pleuritic chest pain
* Haemoptysis
\
**Signs:**
* Tachypnoea
* Low grade fever
* Sinus tachycardia or new AF
* Hypoxia
* Localised pleural rub
* DVT
* May be asymptomatic
* SOB
* Pleuritic chest pain
* Haemoptysis
\
**Signs:**
* Tachypnoea
* Low grade fever
* Sinus tachycardia or new AF
* Hypoxia
* Localised pleural rub
* DVT
63
New cards
Outline the clinical features of a massive PE
Hypotension
\
Collapse
\
Cardiac arrest
\
Sudden death
\
Hypoxia
\
Acute right heart strain
* loud P2, wide splitting of 2nd heart sound, gallop rhythm, tricuspid regurgitation
\
RHF
* low cardiac output, raised JVP, low BP
\
Collapse
\
Cardiac arrest
\
Sudden death
\
Hypoxia
\
Acute right heart strain
* loud P2, wide splitting of 2nd heart sound, gallop rhythm, tricuspid regurgitation
\
RHF
* low cardiac output, raised JVP, low BP
64
New cards
Outline the diagnostic tests for PE
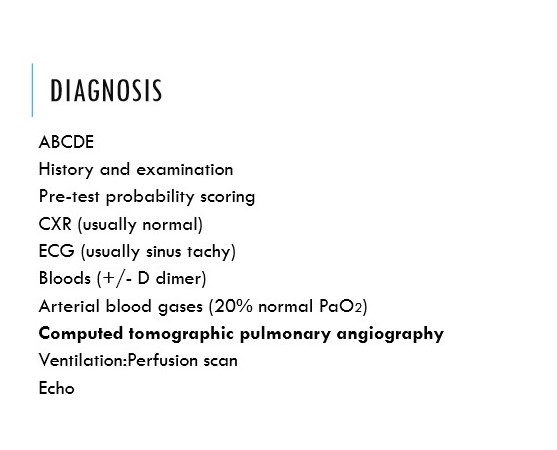
65
New cards
Describe the Well’s score for PE

66
New cards
How does a PE present on a CXR?
Usually normal
\
May be signs of:
* pulmonary hypertension (enlarged vessels)
* pleural effusions
* Westermark’s sign- focal hyperlucency
* Hampton’s hump- wedge-shaped infarcts
\
May be signs of:
* pulmonary hypertension (enlarged vessels)
* pleural effusions
* Westermark’s sign- focal hyperlucency
* Hampton’s hump- wedge-shaped infarcts
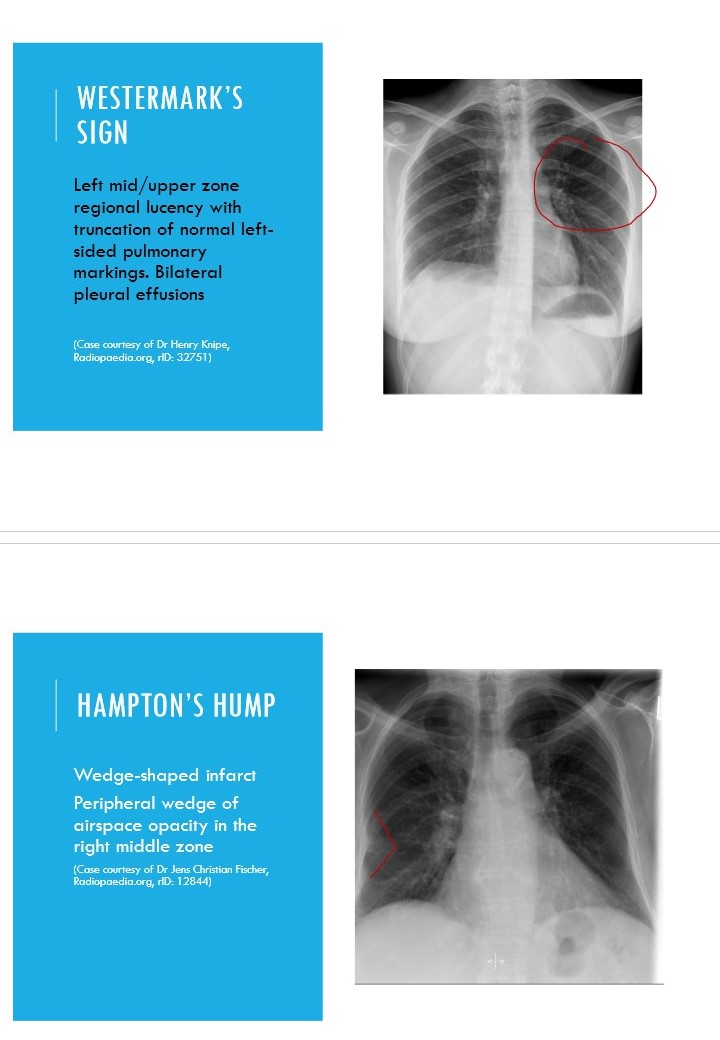
67
New cards
How does PE present on an ECG?
Non-specific ST and T wave abnormalities
\
Sinus tachycardia
\
New AF
\
Right axis deviation
\
RBB
\
S1Q3T3 (large S wave in lead I, Q wave in III, inverted T in III- classic cor pulmonale presentation)
\
Sinus tachycardia
\
New AF
\
Right axis deviation
\
RBB
\
S1Q3T3 (large S wave in lead I, Q wave in III, inverted T in III- classic cor pulmonale presentation)
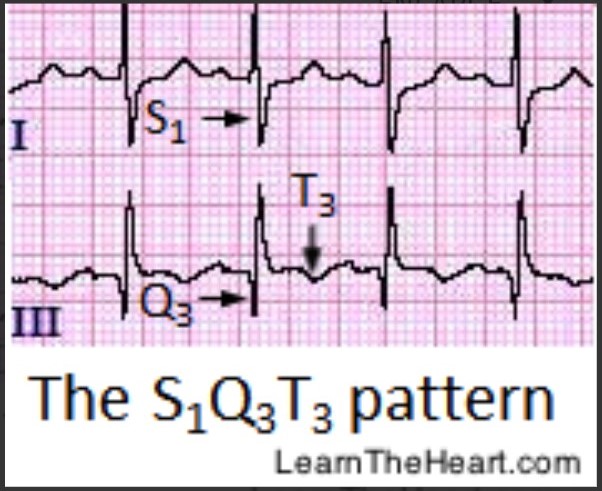
68
New cards
When is a V/Q scan indicated in suspected PE?
Only used if:
* normal CXR
* no concurrent symptomatic CVD
* inconsistent with clinical suspicion
* normal CXR
* no concurrent symptomatic CVD
* inconsistent with clinical suspicion
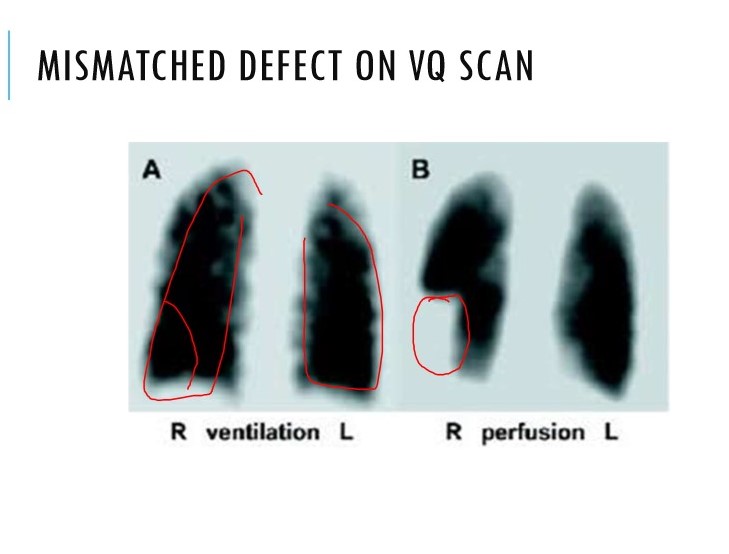
69
New cards
How is PE managed in pregnancy?
Well’s score and D-dimer unhelpful
\
1. Start LMWH (continue for 6 wks postnatal)
2. CXR (with lead protection for foetus)
3. ECG
4. Bilateral leg ultrasound
5. Half-dose VQ scan
\
1. Start LMWH (continue for 6 wks postnatal)
2. CXR (with lead protection for foetus)
3. ECG
4. Bilateral leg ultrasound
5. Half-dose VQ scan
70
New cards
Outline the general management of PE
LMWH or fondaparinux or UFH
\
If major PE:
* open pulmonary embolectomy (surgical removal)
* IVC filter (traps fragmented thromboemboli on way to pulmonary circulation)
\
If major PE:
* open pulmonary embolectomy (surgical removal)
* IVC filter (traps fragmented thromboemboli on way to pulmonary circulation)
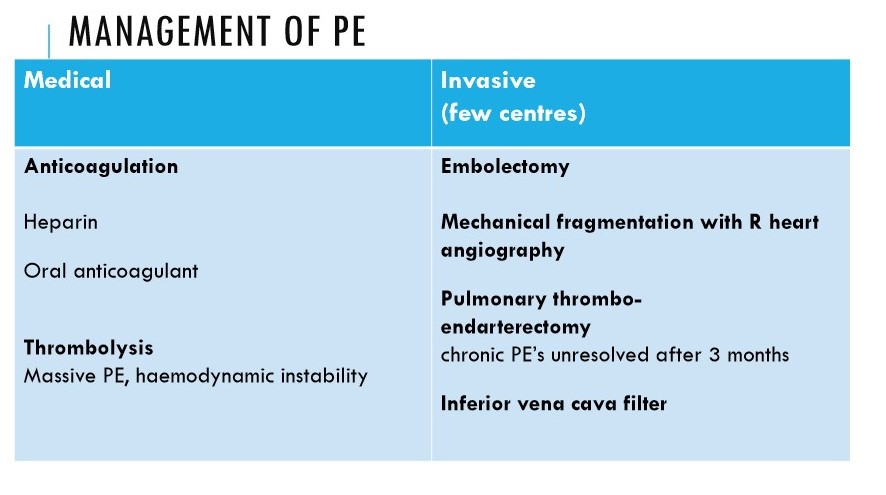
71
New cards
Briefly outline the features of the different types of lung cancer
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC)- 10%
\
Non small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)
* Squamous cell carcinoma 20-30%
* adenocarcinoma 40-50%
* large cell carcinoma 10-15%
\
Non small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)
* Squamous cell carcinoma 20-30%
* adenocarcinoma 40-50%
* large cell carcinoma 10-15%
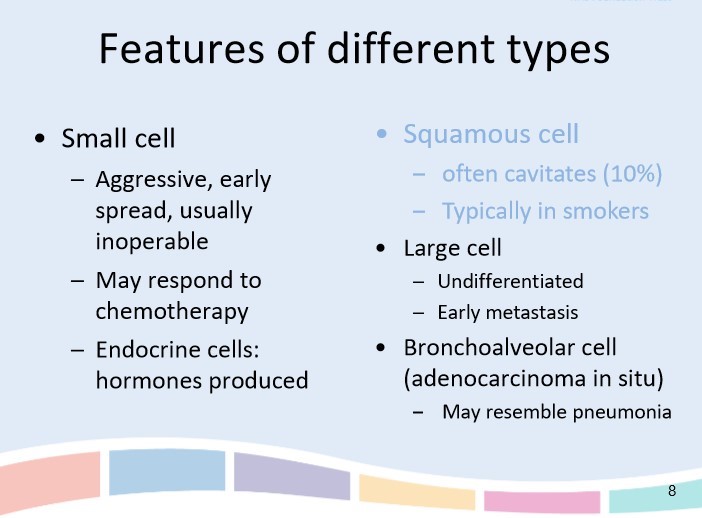
72
New cards
Outline the staging and diagnostic investigations of lung cancer
* staging CT of chest and upper abdomen
* blood tests
* bronchoscopy
* CT guided biopsy
* PET scan
* MRI scan for Pancoast tumours
* bone scan
* brain CT/MRI
* blood tests
* bronchoscopy
* CT guided biopsy
* PET scan
* MRI scan for Pancoast tumours
* bone scan
* brain CT/MRI
73
New cards
Describe the TNM staging of lung cancer
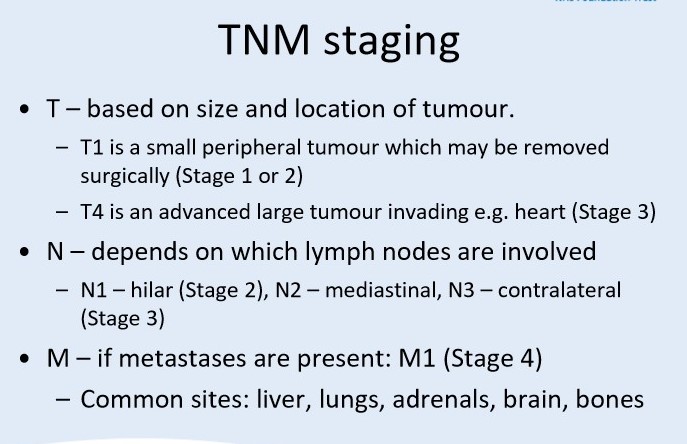
74
New cards
List the treatment options for lung cancer
1. ==Surgical== (for localised tumours that have not metastasised)
\
2. ==Radical Radiotherapy== (useful in squamous cell carcinoma where surgery is not possible)
\
3. ==Palliative Radiotherapy== (to relieve symptoms)
\
4. ==Chemotherapy or immunotherapy==
\
5. ==Adjuvant/neo-adjuvant chemotherapy== (chemo given __after surgery__ to reduce recurrence OR chemo given __before surgery__ to ensure cancer is well controlled)
\
6. Other ==palliative measures== and counselling
\
\
75
New cards
List the paraneoplastic syndromes of SCLC
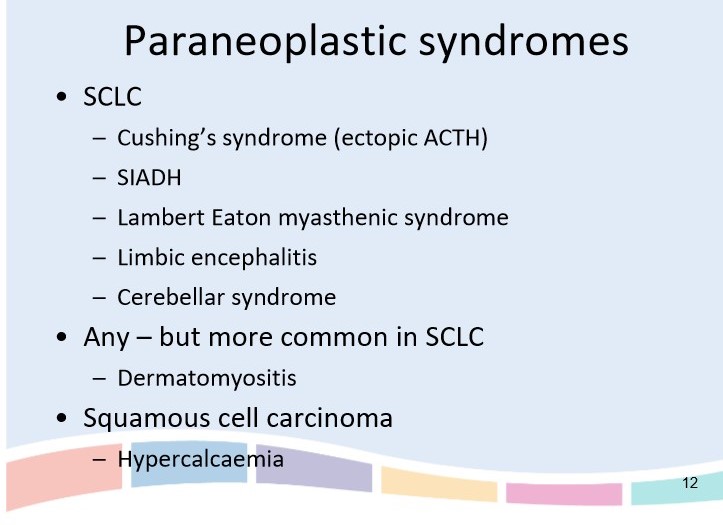
76
New cards
Outline the paraneoplastic features of squamous cell carcinoma
1. PTH- related protein secretion causing hypercalcaemia
2. clubbing
3. hypertrophic pulmonary osteoarthropathy (HPOA)
1. proliferative periostitis affecting long bones
4. hyperthyroidism due to ectopic TSH
77
New cards
Outline the paraneoplastic features of adenocarcinoma
1. gynaecomastia
2. hypertrophic pulmonary osteoarthropathy (HPOA)
78
New cards
Define Type 1 RF
A partial pressure of oxygen below 8 kPa
79
New cards
Define Type 2 RF
A partial pressure of O2 below 8 kPa
\
AND PaCO2 greater than 6.5 kPa
\
AND PaCO2 greater than 6.5 kPa
80
New cards
Describe the mechanisms of hypoxia
**Hypoventilation** (asthma, COPD, motor neurone disease, obesity)
\
**Diffusion abnormality** (pulmonary fibrosis, sarcoidosis, COPD)
\
**V/Q mismatch** (lobar pneumonia, asthma, PE, pneumothorax)
\
**Right to left cardiac shunt** (patent truncus arteriosus)
\
**Low inspired O2** (high altitude, air-flight)
\
**Diffusion abnormality** (pulmonary fibrosis, sarcoidosis, COPD)
\
**V/Q mismatch** (lobar pneumonia, asthma, PE, pneumothorax)
\
**Right to left cardiac shunt** (patent truncus arteriosus)
\
**Low inspired O2** (high altitude, air-flight)
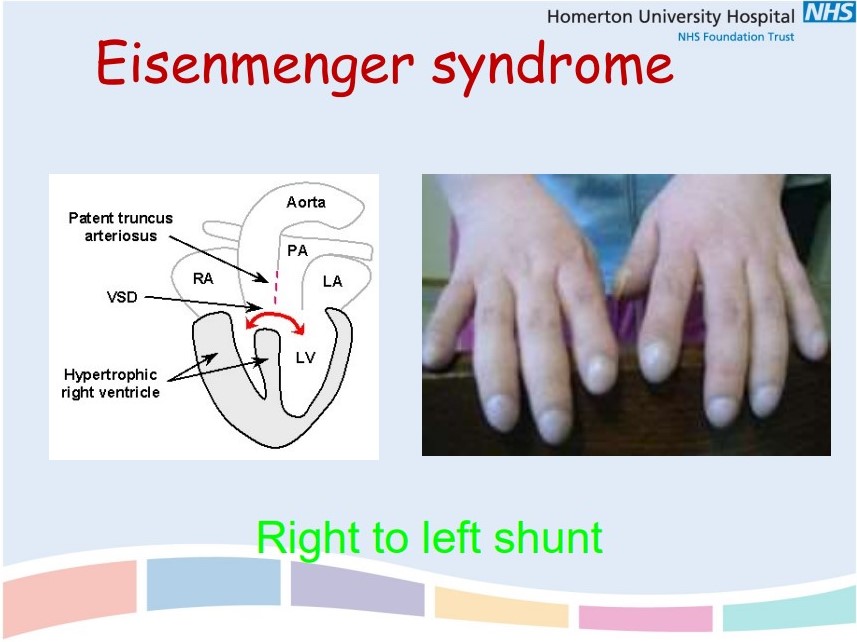
81
New cards
Describe LTOT

82
New cards
Describe CPAP

83
New cards
Define Obstructive Sleep Apnoea
Repetitive episodes of partial or complete upper airway obstruction during sleep
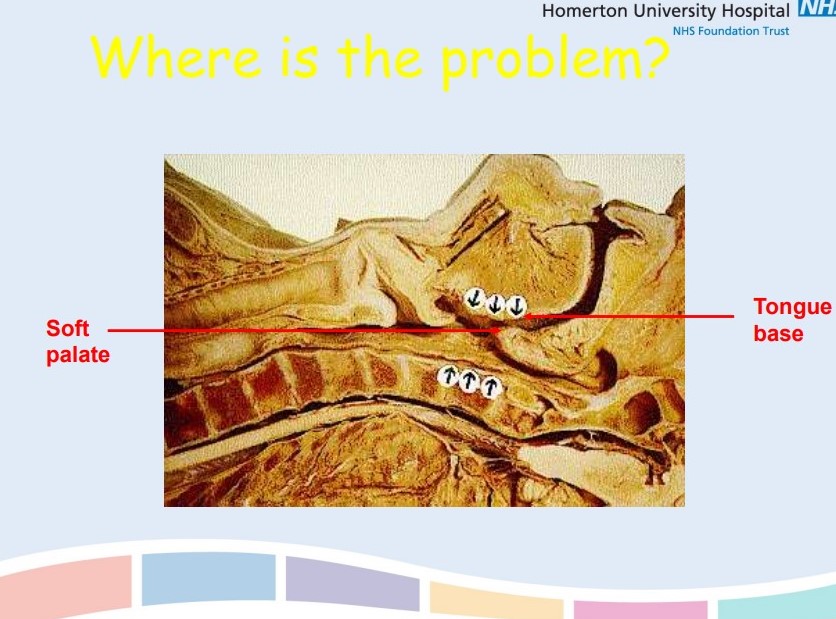
84
New cards
Outline the details needed in a sleep history for OSA
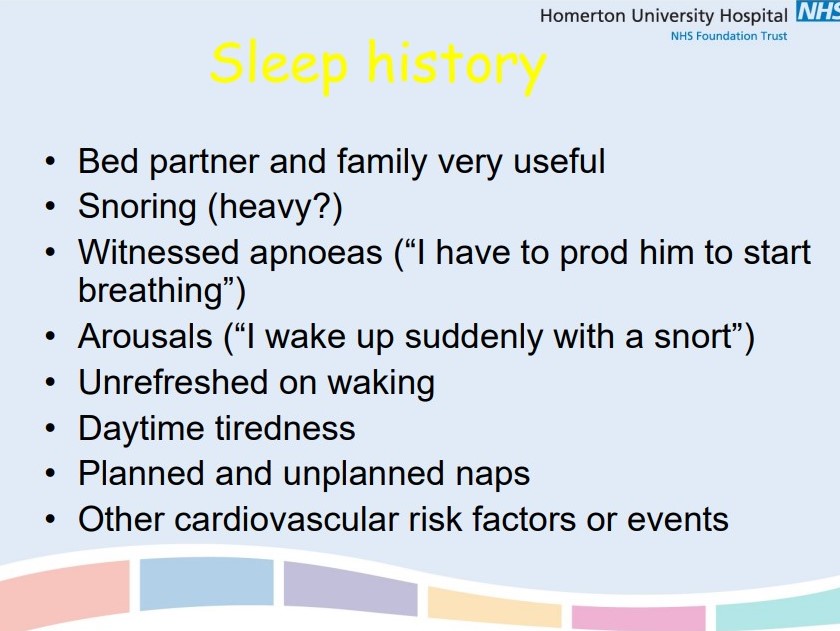
85
New cards
How is the severity of OSA assessed?
AHI
\
RDI
\
Epworth Sleepiness Scale (OSA= score >10/24)
\
RDI
\
Epworth Sleepiness Scale (OSA= score >10/24)
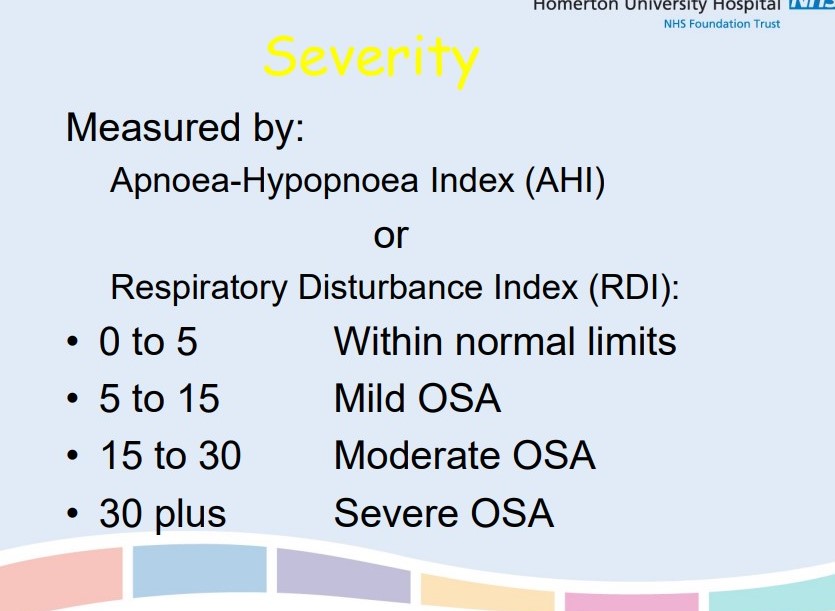
86
New cards
Outline the treatment options for OSA
Weight loss
\
CPAP (for moderate-severe OSA)
\
Avoiding alcohol and sedatives
\
Non-supine sleep
\
Tonsillectomy
\
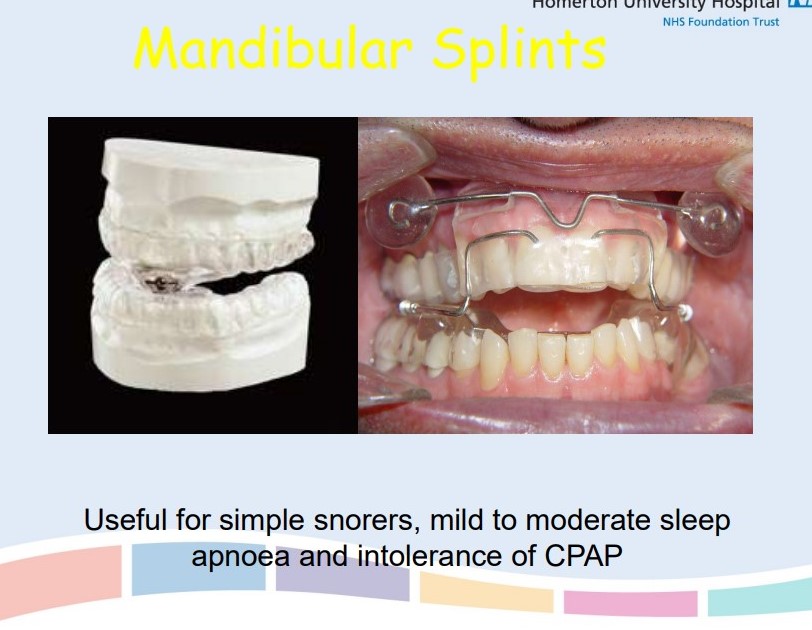
Mandibular advancement splints
\
Maxillofacial splints
\
Treat underlying cause e.g. Cushing’s
\
CPAP (for moderate-severe OSA)
\
Avoiding alcohol and sedatives
\
Non-supine sleep
\
Tonsillectomy
\
Mandibular advancement splints
\
Maxillofacial splints
\
Treat underlying cause e.g. Cushing’s
87
New cards
Briefly outline the steps in asthma management (adults)
1. Newly diagnosed→ SABA
2. Not controlled or more symptoms→ SABA + low dose ICS
3. SABA + low dose ICS + LTRA
4. SABA + low dose ICS + LABA
5. SABA +/- LTRA
1. switch ICS/LABA for maintenance and reliever therapy (includes ICS)
6. SABA +/- LTRA + medium dose ICS MART
7. SABA +/- LTRA plus one of
1. high dose ICS
2. LAMA or theophylline
3. seek specialist advice
\
88
New cards
Describe bronchiectasis and its causes
Permanent __dilatation of the airways__ secondary to chronic infection or inflammation
\
**Causes:**
* post-infective e.g. Tb, measles, pertussis, pneumonia
* CF
* bronchial obstruction e.g. lung cancer, foreign body
* immune deficiency e.g. selective IgA, hypogammaglobulinemia
\
ECG showing tramlines (bronchial wall thickening), prominent in left lower zone
\
**Causes:**
* post-infective e.g. Tb, measles, pertussis, pneumonia
* CF
* bronchial obstruction e.g. lung cancer, foreign body
* immune deficiency e.g. selective IgA, hypogammaglobulinemia
\
ECG showing tramlines (bronchial wall thickening), prominent in left lower zone
89
New cards
List the causes of upper zone fibrosis
Fine inspiratory crackles on auscultation
\
==**CHART**==
\
**C**oal worker’s pneumoconiosis
**H**istiocytosis/ hypersensitivity pneumonitis
**A**nkylosing spondylitis
**R**adiotherapy
**T**b
**S**ilicosis/ sarcoidosis
\
==**CHART**==
\
**C**oal worker’s pneumoconiosis
**H**istiocytosis/ hypersensitivity pneumonitis
**A**nkylosing spondylitis
**R**adiotherapy
**T**b
**S**ilicosis/ sarcoidosis
90
New cards
List the causes of lower zone fibrosis
==**I Don’t Care Actually**==
\
**I**PF
\
**D**rug-induced e.g. amiodarone, methotrexate
\
**C**onnective tissue disorders e.g. systemic lupus erythematous (SLE)
\
**A**sbestosis
\
**I**PF
\
**D**rug-induced e.g. amiodarone, methotrexate
\
**C**onnective tissue disorders e.g. systemic lupus erythematous (SLE)
\
**A**sbestosis
91
New cards
List 3 consequences of OSA
Daytime somnolence
\
Compensated respiratory acidosis
\
Hypertension
\
Compensated respiratory acidosis
\
Hypertension
92
New cards
Name the most likely causative agent of an infective exacerbation of COPD
Haemophilus influenzae
93
New cards
Outline the inhaler technique guideline recommended by the BTS
1. Remove cap and shake
\
2. Breathe out gently
\
3. Put mouthpiece in mouth and as you begin to breathe in, which should be slow and deep, press canister down and continue to inhale steadily and deeply
\
4. Hold breath for 10 seconds, or as long as is comfortable
\
5. For a second dose wait for approximately 30 seconds before repeating steps 1-4
\
Only use the device for the number of doses on the label, then start a new inhaler.
94
New cards
Briefly outline the management of low-severity CAP
==**Amoxicillin**== first-line
\
If penicillin allergic, then use macrolide (erythromycin) or tetracycline
\
**5 day course** of antibiotics
\
Repeat CXR at 6wks
\
If penicillin allergic, then use macrolide (erythromycin) or tetracycline
\
**5 day course** of antibiotics
\
Repeat CXR at 6wks
95
New cards
Briefly outline the management of moderate and high-severity CAP
==**Dual antibiotic therapy**== with amoxicillin and a macrolide
\
**7-10 day course**
\
NICE recommend considering beta-lactamase stable penicillin such as **co-amoxiclav, ceftriaxone or piperacillin with tazobactam and a macrolide** in high-severity CAP
\
Repeat CXR at 6wks
\
**7-10 day course**
\
NICE recommend considering beta-lactamase stable penicillin such as **co-amoxiclav, ceftriaxone or piperacillin with tazobactam and a macrolide** in high-severity CAP
\
Repeat CXR at 6wks
96
New cards
List the indications for a chest drain insertion
(Tube inserted into pleural cavity which creates a one-way valve, allowing movement of air or liquid out)
\
* pleural effusion
* pneumothorax not suitable for conservative management or aspiration (therapeutic and diagnostic)
* empyema
* haemothorax
* haemopneumothorax
* chylothorax (accumulation of lymph from GIT in lungs)
\
* pleural effusion
* pneumothorax not suitable for conservative management or aspiration (therapeutic and diagnostic)
* empyema
* haemothorax
* haemopneumothorax
* chylothorax (accumulation of lymph from GIT in lungs)
97
New cards
List the contraindications of a chest drain insertion
* **INR > 1.3** (greater risk of bleeding and complications)
* platelet count
* platelet count
98
New cards
Outline the staging of COPD
1. Mild: FEV1 >80%
2. Moderate: FEV1 50-79%
3. Severe: FEV1 30-49%
4. Very severe: FEV1
99
New cards
Outline the LTOT criteria for COPD patients
lungS POP
\
Secondary polycythaemia
Peripheral oedema
Oxygen 7.3-8
Pulmonary hypertension
\
Secondary polycythaemia
Peripheral oedema
Oxygen 7.3-8
Pulmonary hypertension
100
New cards
Describe bronchiectasis and what its most common organism is
==**Permanent dilatation of airways**== secondary to chronic infection
\
Commonly caused by **Haemophilus influenzae**
\
Commonly caused by **Haemophilus influenzae**