APHUG Key Terms
5.0(2)Studied by 18 people
0%Unit Mastery
0%Exam Mastery
Build your Mastery score
Supplemental Materials
Card Sorting
1/84
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:21 PM on 4/19/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
85 Terms
1
New cards
Culture
Beliefs, customs, and traditions of a specific group of people.
2
New cards
Density
The population of a country or region expressed as an average per unit area.
3
New cards
Diffusion
The spread of an idea through physical movement from one place to another.
4
New cards
Distribution
The arrangement of features in space.
5
New cards
Crude Birth Rate
The total number of live births in a year for every 1000 people alive in society.
6
New cards
Crude Death Rate
The total number of deaths in a year for every 1000 people in society.
7
New cards
Demography
The scientific study of population characteristics.
8
New cards
Infant Mortality Rate
The total number of annual deaths among infants under 1 year old for every 1000 live births in a society.
9
New cards
Natural Increase Rate
The percentage growth of a population in a year computed as the CBR - CDR.
10
New cards
Population Pyramid
A bar graph that displays a country's population by age and gender.
11
New cards
Asylum Seeker
A person who has left their home country as a political refugee and is seeking asylum in another.
12
New cards
Chain Migration
The social process by which immigrants from a particular town follow one another to a different city.
13
New cards
Immigration
Migration to a location.
14
New cards
Pull Factor
Positive conditions that induce people to new locations from other areas.
15
New cards
Push Factor
Negative conditions that induce people to leave their abode and migrate to a new location.
16
New cards
Refugees
People who have fled their country because of political persecution and seek asylum in another country.
17
New cards
Custom
The frequent repetition of an act to the extent that it becomes characteristic of the group of people performing the act.
18
New cards
Folk Culture
Culture practiced by a small homogenous rural group living in isolation.
19
New cards
Popular Culture
Culture found in a large heterogenous society that shares certain habits despite differences in other personal characteristics.
20
New cards
Habit
Repetitive act performed by an individual.
21
New cards
Dialect
A regional variety of a language distinguished by vocabulary, spelling, and pronunciation.
22
New cards
Lingua Franca
a common language used by speakers of different languages
23
New cards
Official Language
language adopted for use by the government for conduct of business and publication of documents
24
New cards
Fundamentalism
The strict adherence to a particular doctrine.
25
New cards
Universalizing Religion
A religion that attempts to appeal to all people, not just those living in a particular location.
26
New cards
Ethnic Religion
a religion that is particular to one culturally distinct group of people
27
New cards
Apartheid
a policy or system of segregation or discrimination on grounds of race.
28
New cards
Ethnicity
A social division based on national origin, religion, language, and often race.
29
New cards
Genocide
Deliberate extermination of a racial or cultural group
30
New cards
Race
Identity with a group of people descended from a common ancestor.
31
New cards
Autocracy
A system of government in which the power to rule is in the hands of a single individual
32
New cards
City-State
a city that with its surrounding territory forms an independent state.
33
New cards
Democracy
A form of government in which citizens govern themselves
34
New cards
Federal State
An internal organization of a state that allocates most powers to units of local government.
35
New cards
Gerrymandering
Process of redrawing legislative boundaries for the purpose of benefiting the party in power.
36
New cards
Nation State
A country who's population share a common identity.
37
New cards
Self Determination
the right of people to choose their own form of government
38
New cards
Sovereignty
Supreme or independent political power
39
New cards
State
a nation or territory considered as an organized political community under one government.
40
New cards
Unitary State
places most power in the hands of central government officials
41
New cards
Fairtrade
A system of trading that ensures fair prices for produce from LEDCs
42
New cards
Fossil Fuels
a nonrenewable energy resource that forms in the Earth's crust for millions of years
43
New cards
Gender Inequality Index (GII)
A measure of the extent of each country's gender inequality
44
New cards
Gross Domestic Product
A measurement of the total goods and services produced within a country.
45
New cards
Human Development Index (HDI)
the UN's index used to rank standards of living in its member countries
46
New cards
Primary Sector
the part of the economy that draws raw materials from the natural environment
47
New cards
Secondary Sector
he part of the economy that transforms raw materials into manufactured goods
48
New cards
Tertiary Sector
the part of the economy that involves services rather than goods
49
New cards
Value Added
The gross value of the product minus the costs of raw materials and energy.
50
New cards
Millennium Development Goals
Eight international development goals that all members of the UN have agreed to achieve by 2015
51
New cards
Agribusiness
agriculture conducted on commercial principles, especially using advanced technology.
52
New cards
Commercial Agriculture
Agriculture undertaken primarily to generate products for sale off the farm.
53
New cards
Desertification
the gradual transformation of habitable land into desert
54
New cards
Green Revolution
Rapid diffusion of new agricultural technology, especially new high-yield seeds and fertilizers.
55
New cards
Milkshed
The area surrounding a city from which milk is supplied.
56
New cards
Subsistence Farming
farming in which only enough food to feed one's family is produced
57
New cards
Transhumance
The seasonal migration of livestock between mountains and lowland pastures.
58
New cards
Break of Bulk Point
A location where transfer is possible from one mode of transportation to another
59
New cards
Bulk Gaining Industry
An industry in which the final product weighs more or comprises a greater volume than the inputs
60
New cards
Bulk Reducing Industry
An industry in which the final product weighs less or comprises a lower volume than the inputs.
61
New cards
Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
Geographic Information Systems are used to analyze data on maps using layers
62
New cards
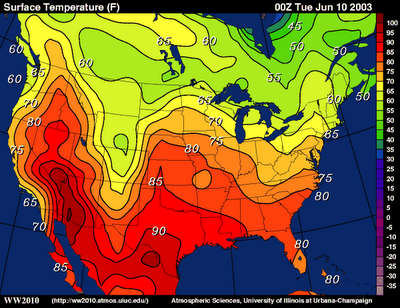
Isoline Map
Maps that show lines that join points of equal value. (For example, a topographic map is an isoline map on which lines join points of equal elevation.)
63
New cards
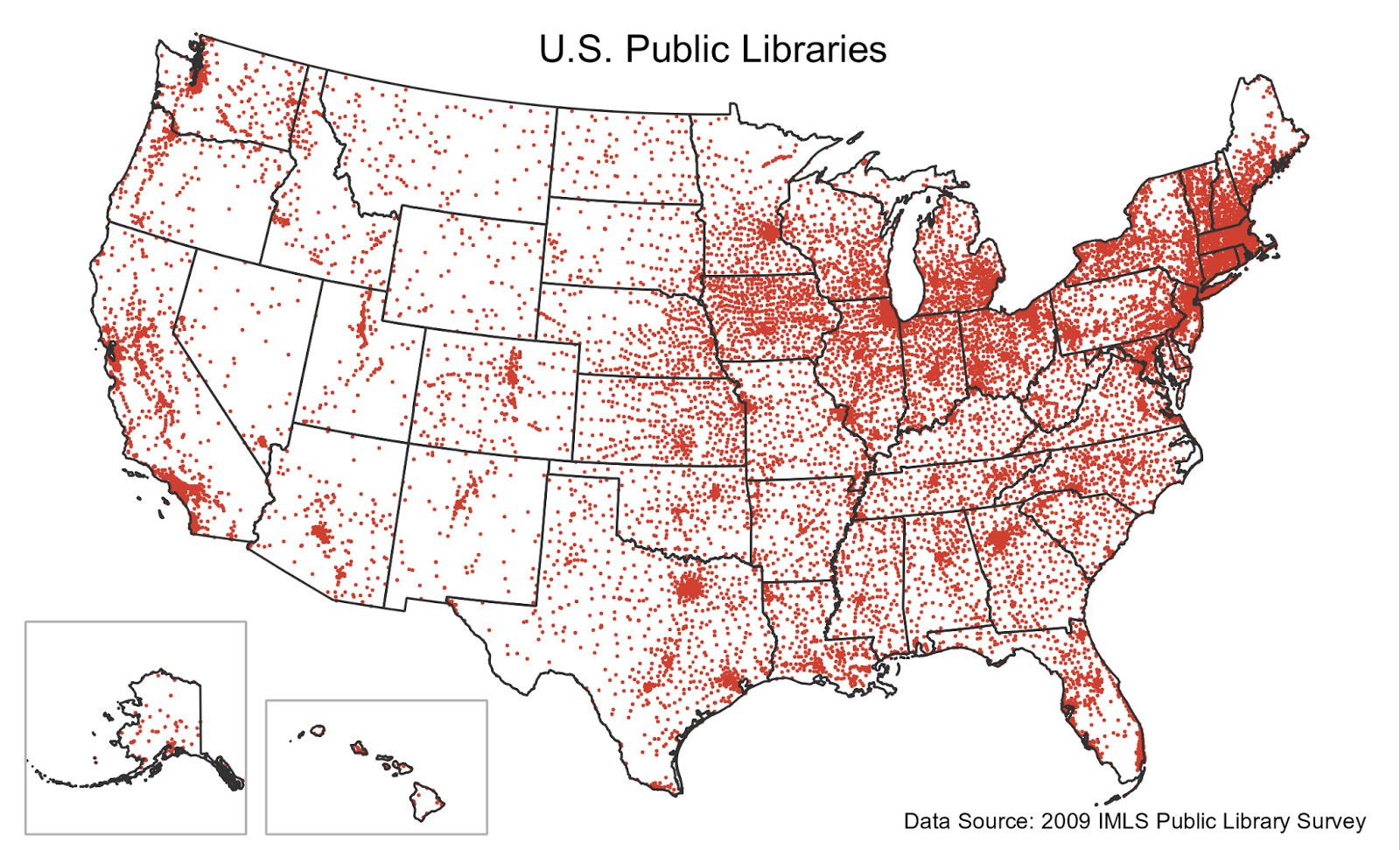
Dot Map
\
Dot maps are a type of unit visualizations that rely on a visual scatter to show spatial patterns, especially variances in density. The dots may represent the actual locations of individual phenomena, or be randomly placed in aggregation districts to represent a number of individuals.
Dot maps are a type of unit visualizations that rely on a visual scatter to show spatial patterns, especially variances in density. The dots may represent the actual locations of individual phenomena, or be randomly placed in aggregation districts to represent a number of individuals.
64
New cards
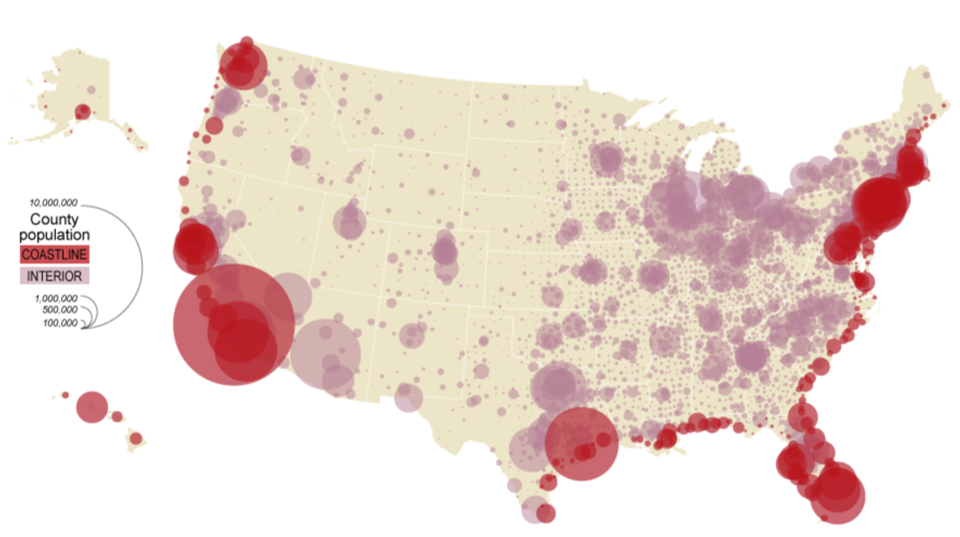
Proportional Symbol Map
\
A Proportional symbol map is a type of Thematic map that uses map symbols that vary in size to represent a quantitative variable. Symbols vary in height, length, area, or volume from place to place depending on the variable that they represent.
A Proportional symbol map is a type of Thematic map that uses map symbols that vary in size to represent a quantitative variable. Symbols vary in height, length, area, or volume from place to place depending on the variable that they represent.
65
New cards
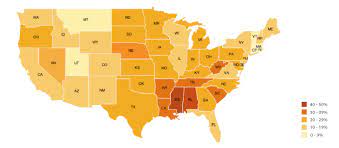
Chloropleth Map
A map that uses differences in shading, coloring, or the placing of symbols within predefined areas to indicate the average values of a property or quantity in those areas.
66
New cards
Demographic Transition Model
A process with 4 steps in which every country moves through, once a country enters a new stage it will not go back to a previous stage. \n Stage 1: Low Growth (high CBR&CDR, low NIR) \n Stage 2: High Growth (high CBR&NIR, low CDR)(happened due to industrial revolution)ex:Cape Verde, Nicaragua \n Stage 3: Moderate Growth(decreasing CBR,CDR,NIR)(happens when people decide to start having less kids) ex:Chile, \n Stage 4:Low Growth(CBR=CDR, has ZPG) ex: USA, England, Luxemburg \n Stage 5:unofficial stage (low CBR, increasing CDR) ex: Russia
67
New cards
Von Thunen Model
Hearth-1826, Germany, by Johann Heinrich Von Thunen \n says- What farmers produce varies upon distance from market \n -takes into account cost of tranportation (which governs use of land) \n -assumes no natural features (land uniformity) \n -model places market in middle surrounded by dairy, then forestry (lumber), then grains and field crops, and lastly ranching and livestock
68
New cards
Rostow’s Development Model
Hearth-W.W. Rostow, 1950 \n says- all countries move through 5 steps to development and modernization through selling resources and global participation (productive) \n Step 1: Traditional Society:high in agriculture but unproductive and developed \n Step 2:Preconditions of Takeoff:development begins with innovative leader who starts to buy technology \n Step 3:Takeoff:Same areas start to produce and become productive and bring in $ \n Step 4:Drive to Maturity: Technology diffuses and workers become more specialized \n Step 5:High Mass Consumption: More specialized jobs and become consumers
69
New cards
Central Place Theory
Hearth-Walter Christaller \n says- where central places in the urban hierarchy would be functionally and spatially distributed (hexagon shaped areas) \n -hierarchy: city,town,village, hamlet \n -assumes that all land is the same (equal, no valleys mnts) \n ex: Iowa
70
New cards
Concentric Zone Model
hearth-1923, E.W. Burgess \n says-cities grow outwards from the CBD in rings \n 1st inner ring-CBD \n 2nd-Transiton Zone (poorer, immigrants) \n 3rd-Working Class Homes \n 4th-Newer spacious homes \n 5th-commuters
71
New cards
Multiple Nuclei Model
hearth-1945, E.L. Ulman \n says-cities are a complex structure w/ more than 1 center \n -also says certain things are more attracted to certain areas \n ex: airports attract hotels and universities attract pizzerias
72
New cards
Peripheral Model
\-good ex for N. America \n says- an urban area consists of a central area surrounded by other districts and places and enclosed by a major road \n -model points to problems of segregation that characterizes many suburbs
73
New cards
Hoyt
Sector Model
74
New cards
Burgess
Concentric Zone Model
75
New cards
Sector Model
hearth-1939, homer hoyt \n says-city develops in sections or wedges not rings \n -grows outwards in wedges \n -best housing is on edges \n ex of model:chicago
76
New cards
Wallerstein World Systems Theory
says-the world economy has a 3 tier structure \n Core: generates wealth in economy, high levels of education, technology, and salaries(RICH) \n ex:USA \n Periphery:generates less wealth in world economy lower level of education, technology, and salaries(POOR) \n ex:congo \n Semi-periphery: a buffer zone between Core&periphery both can exist \n ex: brazil, india, china, mexico
77
New cards
Losch’s Location Theory
says- manufacturing plants choose locations where they can maximize profit \n -can maximize profit when income is higher than the cost to make it \n ex:fur stores in vail, co
78
New cards
Hotelling’s Location Theory
says-location of an industry cannot be understood w/o references to other industrys of the same kind \n ex:gas stations are always next to each other
79
New cards
Weber’s Location Theory
says- says-manufacturing plants will be where costs are the least \n ex:cheap labor, maquiladoras
80
New cards
Lee’s Migration Theory
Divides factors causing migrations into two groups of factors, push and pull. The factors are either economic, cultural, or environmental \n push- things that are unfavorable about the area that one lives in \n pull-things that attract one to an area
81
New cards
Ravenstein’s Migration Theory
says-majority of migrants move short distances and if they migrate long distances its' to cities. \n -urban residents migrate less than inhabitants of rural land. \n -families migrate less than individuals and men will travel further
82
New cards
Gravity Model
says-Distance and population size effect receiving and sending countries \n -people will travel closer than far but large populations send more people. \n ex:china and india to US
83
New cards
Migration Transition Model
says-countries in stage 1 of DTM have internal migration \n -most sending countries are in stages 2-3 (international emigration) \n -most receiving countries are in stages 3-4(int'l immigration)
84
New cards
Malthusian Theory
claims-that worlds population is growing much more quickly than earth's food supply (1798)
85
New cards
Core-Domain-Sphere Model
says- a culture is more homogenous and intense in the core