Photosynthesis
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
Photosynthesis
Process whereby green plants convert the radiant energy of light into chemical energy that is then stored in food molecules
light, carbon dioxide, and water
What do plants utilize to produce oxygen and carbohydrates?
Chloroplasts
Where does photosynthesis take place in?
Glucose
What is the main product of photosynthesis?
6 carbon dioxide, 12 water, and light energy
What are the reactants in the photosynthesis equation?
6 glucose, 6 oxygen, and 6 water
What are the products in the photosynthesis equation?
Chromatography; chromatogram
_______________ is a method of separating closely related compounds, as in the case of pigments, by allowing the mixture of substances to diffuse through an absorbent called _______________
Thylakoid membrane
Where does the light-dependent reaction happen?
Stroma
Where is the site of the Calvin cycle?
Light Dependent Reaction and Light Independent Reaction (Calvin Cycle)
What are the two stages of Photosynthesis
light and water
What is needed in the light-dependent reaction?
oxygen, atp, nadph
what are the outputs of the light-dependent reaction?
because it requires light to excite electrons
Why is it called a light-dependent reaction?
True
True or False
Photosystem II (PSII) occurs before Photosystem I (PSI), even if PSI was discovered first.
Photosystems
Composed of either integral or peripheral proteins embedded in the phospholipid bilayer.
Integral proteins
proteins that are embedded within the phospholipid bilayer of cell membranes; typically involved in transport and structural functions
Peripheral proteins
proteins found on the surface of the membrane; signaling and enzymatic activities.
Chlorophyll
absorbs light
PQ (Plastoquinone)
transfers electrons from PSII to Cytochrome complex.
Cytochrome complex
acts like a turbine, helps create a proton gradient
PC (Plastocyanin)
carries electrons to PSI
Ferredoxin (FD)
carries electrons to NADP+ reductase
NADP+ Reductase
enzyme that converts NADP+ to NADPH
Splitting of Water (Photolysis) Process
2 electrons go to PSII.
4 protons contribute to the gradient.
O₂ is released via stomata (must combine two ½ O₂).
O₂ diffuses out because it's a gas and can escape through the phospholipid bilayer.
Energy Transfer Process
Light excites electrons at PSII → PQ → Cytochrome → PC → PSI.
Electrons lose energy along the way and need re-excitation at PSI.
Energy from excited electrons drives protons (H⁺) into the lumen, creating a proton gradient.
ATP Synthase uses the proton gradient to convert ADP + Pi → ATP.
Chemiosmosis
Movement of H⁺ through ATP synthase to produce ATP.
Z-scheme
What is the flow of electrons from water → PSII → PSI → NADP+
atp, nadph, carbon dioxide
What is needed in the calvin cycle?
carbohydrates (glucose, starch)
What is the output of the calvin cycle
rubisco (RuBP)
What is the enzyme used during carbon fixation
Carbon Fixation Process
CO₂ attaches to RuBP (5-carbon compound) to form unstable 6-carbon.
Splits into two 3-carbon compounds (3-PGA).
Carbon Fixation
Reduction
Regeneration
What are the steps in Calvin Cycle?
Reduction Process
3-PGA → G3P (Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate).
Requires: ATP and NADPH.
From 3 CO₂ molecules → 6 G3P molecules.
1 G3P is used to make glucose.
5 G3P regenerate RuBP (cycle continues).
Regeneration Process
Uses ATP to convert G3P back to RuBP.
To make 1 glucose:
6 CO₂, 18 ATP, 12 NADPH are needed.
False
True or False
Glucose can enter the mitochondria without being broken down to pyruvate
To remove chlorophyll pigments
Why do we soak the mayana leaves (Coleus sp.) in ethanol?
to soften the tissues and stops cellular activity or deactivate cellular processes
Why do we boil the mayana leaves (Coleus sp.) in water?
True
True or False
Iodine test detects starch, not glucose directly.
the more the intense the light, the higher the rate of photosynthesis and vice versa
What is the relationship between the intensity of light and photosynthesis?
the longer the wavelength, the less the energy and vice versa
What is the relationship between the wavelength of light and photosynthesis?
violet light
Which wavelength carries the most energy?
red light
Which wavelength carries the least energy?
thylakoid and intergranal lamella
Where is photosynthetic pigment found?
Photosynthetic Pigment
A coloured biological compound that is present in chloroplasts and photosynthetic bacteria, and which captures light energy for photosynthesis.
chlorophylls and carotenoids
What are the type of pigments present in chloroplasts?
Chlorophyll
pigment that gives plants their green colour by reflecting green light.
Carotenoids
pigment that gives plants their warm colour by reflecting red, orange, or yellow light.
to absorb visible light
What is the function of photosynthetic pigments?
380nm to 750nm
What is the range of the wavelength that photosynthetic pigments absorb light?
Phaeophytin
A yellow-gray band color on the chromatogram
It primarily functions as an electron acceptor, receiving electrons from the P680 phase after absorbing light.
Xanthophyll
A yellow-brown band color on the chromatogram
absorbs blue-violet light wavelengths and also transfers the energy to chlorophyll a
it is also a pigment for light absorption.
Chlorophyll a
A bright green/blue green band color on the chromatogram
Used in the light phase of photosynthesis where it absorbs the photons and converts it to chemical energy.
Absorbs blue and red light the most efficiently along with chlorophyll b.
Chlorophyll b
A yellow green/olive green band color on the chromatogram
accessory pigment used for absorbing light wavelengths that chlorophyll a has difficulty in absorbing
A. Carotene
B. Xanthophyll
C. Chlorophyll a
D. Chlorophyll b
Identify A, B, C, and D
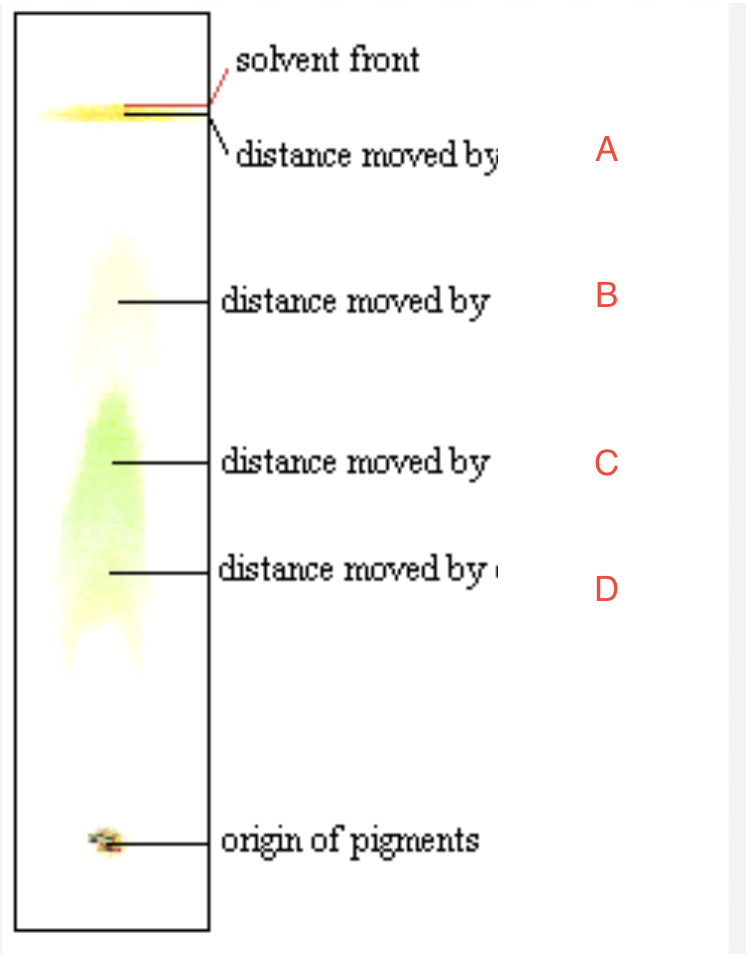
By the distance they travel through the chromatogram (Rf)
Aside from band color, how else can pigments be identified?
Retention factor (Rf)
This value is the ratio that can be calculated and compared to identify unknown compounds
distance of pigment from origin / distance of solvent front from origin
How to compute for Rf
Carotene – 0.95
Phaeophytin – 0.83
Xanthophyll – 0.71
Chlorophyll a – 0.65
Chlorophyll b – 0.45
What are the known Rf values for each pigment?
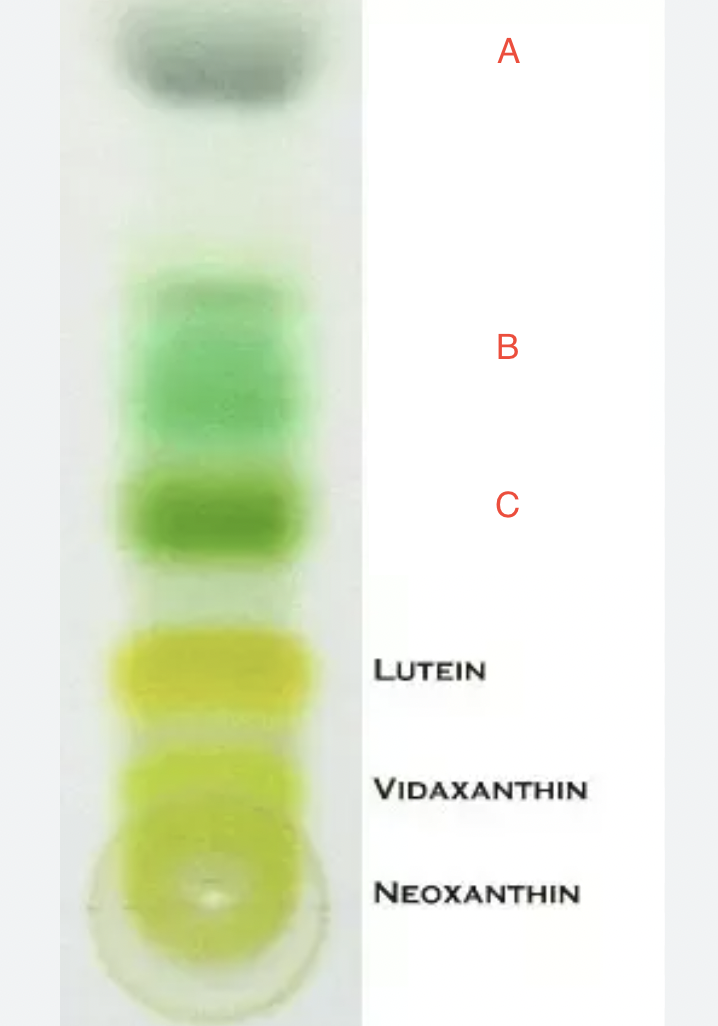
A. Phaeophytin
B. Chlorophyll a
C. Chlorophyll b
Identify A. B, and C
Identifies the solubility of the pigment and the molecular weight
What does the distance travelled say about the pigment?
True
True or False
More soluble pigments and lighter molecular weighted pigments travel faster
Carotene
yellow band color on the chromatogram
used for photoprotection by reflecting excessive light towards the plant
False
True or False
ATP is produced during the Calvin cycle.
2 G3P molecules (carbohydrates or your glucose)
When carbon dioxide is fixed during the calvin cycle, what will be the product?
Iodine solution
What was the solution used to detect the presence of the product of Calvin cycle?
Carbonic Acid
What product was produced when you blew the straw in a phenol red solution?
False
True or False
In paper chromatography, Xanthophyl is the top/highest pigment observed.
True
True or False
Water > Ethanol > Iodine
False
True or False
The product of Calvin cycle is produced in the roots
NADP+
What is the final electron acceptor during photosynthesis?
Phenol Red
pH indicator that changes from yellow to red over pH below 6.8 (more acidic), and then turning a bright pink color above pH 8.2 (more basic)
the higher the distance, the lesser the intensity, the lower the photosynthetic rate
What is the relationship between the distance of light and photosynthesis?
It was reflected. Chlorophyll gives plants their green color because it does not absorb the green wavelengths of white light
Why was green color not absorbed by chlorophyll?