adrenal glands, GI system, & interventional radiology
1/309
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
310 Terms
What is the acronym for the structures in the intraperitoneal?
FOULS JARS
What is the acronym for the structures in the retroperitoneal?
SAD PUCKER
List out what each letter of the intraperitoneal acronym stands for.
Fallopian tubes
Ovaries'
Uterus
Liver
Spleen
Jejunum
Appendix
Rectum
Stomach
List out what each letter of the retroperitoneal acronym stands for.
Suprarenal glands
Aorta/IVC
Duodenum
Pancreas
Ureter
Colon
Kidneys
Esophagus
Rectum
Is the stomach considered an intra- or retroperitoneal organ?
Intraperitoneal
Is the jejunum considered an intra- or retroperitoneal organ?
Intraperitoneal
Is the 1st part of the duodenum considered an intra- or retroperitoneal organ?
Intraperitoneal
Is the appendix and cecum considered an intra- or retroperitoneal organ?
Intraperitoneal
Is the spleen considered an intra- or retroperitoneal organ?
Intraperitoneal
Is the transverse and sigmoid colon considered an intra- or retroperitoneal organ?
Intraperitoneal
Is the liver considered an intra- or retroperitoneal organ?
Intraperitoneal
Is the gallbladder considered an intra- or retroperitoneal organ?
Intraperitoneal
Are the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries considered an intra- or retroperitoneal organ?
Intraperitoneal
Is the adrenal gland considered an intra- or retroperitoneal organ?
Retroperitoneal
Is the aorta & IVC considered an intra- or retroperitoneal organ?
Retroperitoneal
Is the duodenum considered an intra- or retroperitoneal organ?
Retroperitoneal
Is the pancreas considered an intra- or retroperitoneal organ?
Retroperitoneal
Is the ureter considered an intra- or retroperitoneal organ?
Retroperitoneal
Is the ascending and descending colon considered an intra- or retroperitoneal organ?
Retroperitoneal
Is the kidney considered an intra- or retroperitoneal organ?
Retroperitoneal
Is the esophagus considered an intra- or retroperitoneal organ?
Retroperitoneal
Is the rectum considered an intra- or retroperitoneal organ?
Retroperitoneal
When scanning for the adrenal glands, they are more likely to be seen on children or adults?
Children
List the 3 anatomical areas where the adrenal glands can be found to the upper pole of the kidney.
Superior
Anterior
Medial
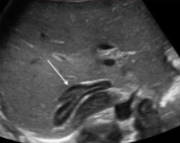
What is the structure seen at the white arrow?
Adrenal gland
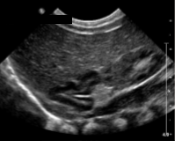
What is the prominent structure seen here?
Adrenal gland
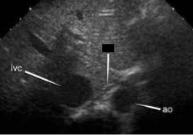
What is the name of the structure crossed out?
Crus of the diaphragm
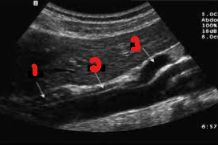
Label the structures seen in this image.
Gastro-esophageal junction
Crus of the diaphragm
Celiac Axis
What is another term for retroperitoneal fibrosis?
Ormond’s disease
Ormond’s disease is another term for what?
Retroperitoneal fibrosis
Name the pathology:
“Abnormal formation of fiber-like tissue (fibrosis) occurs within the retroperitoneal space”
Retroperitoneal fibrosis (Ormond’s disease)
Retroperitoneal fibrosis is a rare ___________ disorder.
Inflammatory
Retroperitoneal fibrosis is the abnormal formation of ______-like tissue fibrosis.
Occurs within the ____________ space.
Fiber-like
Retroperitoneal
Retroperitoneal fibrosis is abnormal tissue ________.
Growth
Retroperitoneal fibrosis often spreads to affect what other structure?
Ureter
Retroperitoneal fibrosis is generally located where?
Aortic bifurcation
Retroperitoneal fibrosis will resemble what other pathology?
Horseshoe kidney
In this lecture, a horseshoe kidney is similar in appearance to what pathology?
Retroperitoneal fibrosis (Ormond’s disease)
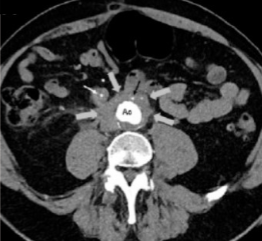
What pathology is seen at the arrow?
Retroperitoneal fibrosis (Ormond’s disease)
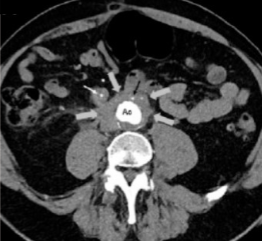
What imaging modality is seen here?
CT
List the 7 sonographic findings of retroperitoneal fibrosis (Ormond’s disease).
Hypoechoic midline mass
Bilateral ureteral obstruction
Hydronephrosis
Decreased renal function
IVC and lymphatic compression
Lower extremity edema
Scrotal swelling
How does retroperitoneal fibrosis affect the kidneys? (2)
Bilateral ureteral obstruction
Hydronephrosis
Compression of the IVC and lymphatic system from retroperitoneal fibrosis can lead to what 2 clinical findings?
Lower extremity edema
Scrotal swelling
How does lower extremity edema cause scrotal swelling?
Compression of the gonadal veins
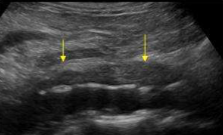
What pathology is seen here in this sagittal image of the aorta?
Retroperitoneal fibrosis (Ormond’s disease)
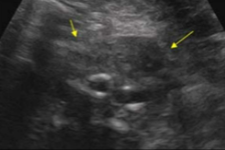
What pathology is seen here in this transverse image of the aorta?
Retroperitoneal fibrosis (Ormond’s disease)
The adrenal gland will produce hormones in response to signals from what other structure?
Pituitary gland
The pituitary gland will send signals to what other structure to produce hormones?
Adrenal glands
All cortical hormones fall under what category of hormones?
Adrenal-cortical
All medullary hormones fall under what category of hormones?
Catecholamines
Adrenal-cortical hormones are __________ hormones.
Cortical
Catecholamine hormones are __________ hormones.
Medullary
List the 3 hormones that are considered cortical hormones.
Mineralcorticoids
Glucocorticoids
Androgens
Mineralcorticoids are also referred to as…
Aldosterone
Glucocorticoids are also referred to as…
Cortisol
Aldosterone is also referred to as…
Mineralcorticoids
Cortisol is also referred to as…
Glucocorticoids
Aldosterone is produced from which layer of the adrenal gland?
Cortex
Glucocorticoids (cortisol) is produced from which layer of the adrenal gland?
Cortex
Mineralcorticoids (aldosterone) is produced from which layer of the adrenal gland?
Cortex
Epinephrine is also referred to as…
Adrenaline
Adrenaline is also referred to as…
Epinephrine
List the 2 hormones that are considered medullary hormones.
Epinephrine (adrenaline)
Norepinephrine
Epinephrine (adrenaline) is produced from which layer of the adrenal gland?
Medulla
Norepinephrine is produced from which layer of the adrenal gland?
Medulla
Adrenocortical hormones are regulated by what other hormone?
Adrenocorticotropic hormone
Adrenocorticotropic hormone regulates what other hormone?
Adrenocortical
What does ‘ACTH’ stand for?
Adrenocorticotropic hormone
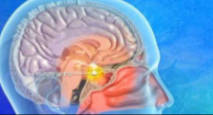
What hormone is released from the anterior pituitary gland?
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
Adrenocorticotropic hormone is released from what structure?
Anterior pituitary gland
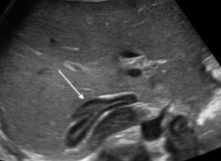
What structure is seen at the white arrow?
Adrenal gland
List the 2 sonographic findings of an adrenal gland.
Hypoechoic cortex
Echogenic medulla
Adrenal adenomas can have which 2 ‘functions’?
Hyperfunctioning
Non-functioning
Majority of adrenal adenomas are _______-functioning.
Non-
Adrenal adenomas are ________ findings.
Incidental
Define a ‘hyperfunctioning adrenal adenoma.’
Adenomas will produce hormones, causing symptoms to occur
Define a ‘non-functioning adrenal adenoma.’
Hormones are not affected
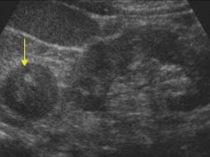
What is the pathology seen here?
Adrenal adenoma
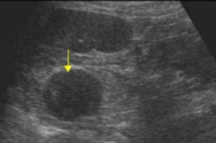
What is the pathology seen here?
Adrenal adenoma
Name the pathology:
“Excessive cortisol secretion (hypercortisolism)”
Cushing’s Syndrome
What is Cushing’s Syndrome?
Excessive cortisol secretion (hypercortisolism)
What is the term for excessive cortisol secretion?
Hypercortisolism
Define ‘hypercortisolism.’
Excessive cortisol secretion
Adrenal adenomas can lead to what 2 pathologies?
Cushing’s Syndrome
Conn Syndrome
List the 5 causes of Cushing’s Syndrome.
High doses of corticosteroid medicine over time
Adrenal adenoma
Pituitary gland tumor
Adrenal gland disease
Hereditary
List the 6 clinical symptoms of Cushing’s Syndrome.
Thin arms and legs
Large belly
Fat pad on the back of the neck
Abnormal stretch marks
Bruise easily
Hirsutism
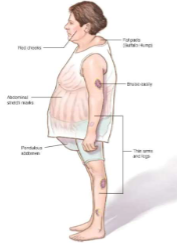
A patient who has been using high doses of corticosteroid medication mentions seeing changes in their body. Based on the clinical symptoms, what can be assumed here?
Cushing’s Syndrome
What is another term for Conn Syndrome?
Primary aldosteronism
Primary aldosteronism is another term for what pathology?
Conn Syndrome
Name the pathology:
“Excess production of aldosterone”
Conn Syndrome
Conn syndrome is the excess production of what hormone?
Aldosterone
Conn syndrome is most often caused by what pathology?
Adrenal adenoma
Why would an adrenal adenoma lead to Conn Syndrome?
Excess production of aldosterone, leading to a hyperfunctioning adrenal adenoma
What kind of adrenal adenoma can be seen with Conn syndrome?
Hyperfunctioning
List the 5 clinical symptoms of Conn’s Syndrome.
High blood pressure
Low blood potassium
Polyuria
Fatigue
Increase aldosterone
Why does aldosterone increase with Conn’s Syndrome?
Due to stimulating the secretion of potassium by the kidneys
List the 7 clinical symptoms of Addison’s disease.
Hair loss
Blurry vision
Abdominal pain
Decreased appetite
Darkening of the skin (hyperpigmentation)
Shaking or tremors
Depression
Addison’s Disease is an adrenal ___________.
Insufficiency
Name the pathology:
“When the adrenal glands are not producing enough cortisol and/or aldosterone”
Addison’s Disease
Addison’s Disease is when the adrenal glands are not producing enough of which 2 hormones?
Cortisol
Aldosterone