ESS chap 7. Climate change and energy production
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Energy security
Ability to secure affordable, reliable, and sufficient energy supply for the needs of a particular country
why it is important → national security
Case study - energy security issues in Ukraine, the US, Denmark
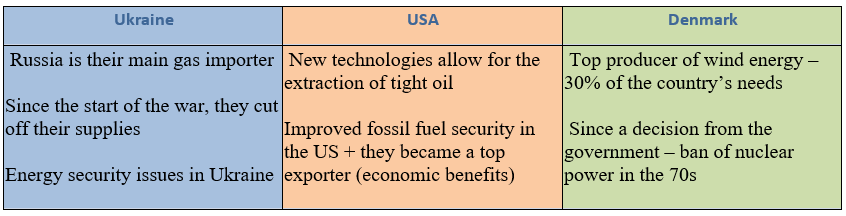
Strategies to ensure energy security
diversify the sources of energy (decrease vulnerability)
do not only rely on importation of energy
Consequences of fossil fuel combustion
air pollution
acid deposition
photochemical smog
What are fossil fuels? (what, formation, advantages, inconvenients)
Main types:
coal
oil
natural gas
formed by dead plants and animals under pressure over millions of years
Advantages: high-energy content, infrastructures already in place, relatively cheap, currently abundant
Inconvenients: non-renewable, destruction of species habitat (decrease biodiversity), emits greenhouse gases (air pollution)
Coal
Where
found in China, the US, Russia, India
Issues
can cause lung or respiratory health problems
Natural gas
What
mostly methane but also ethane, butane, propane, pentane
Where
found in Russia, Iran, Qatar, and Turkmenistan (natural reserves)
the top producers are the US, Russia, and Iran
hard to detect because it is odorless, colorless, and tasteless (adding hydrogen sulfide to notice it)
fracking
Nuclear power
Where
North America, Europe, and Asia (nuclear power plants)
75% of electricity in France and 20% of electricity in the US from nuclear power
for waste: underground repositories (dispersal of radioactive materials and contamination of groundwater)
Advantages: minimal carbon dioxide emission, potential advancements in technology
Disadvantages: high levels of radioactive waste, risk of catastrophic nuclear accidents, high costs associated with the building and decommissioning power plants
Climate/weather
Climate is the ‘average’ weather over the long term (e.g. years) often at a regional level, whereas weather refers to the conditions over a short time scale (e.g. day to day) at a local level
Factors affecting climate
outside the earth
solar radiation
tilting and orbit of the earth
within the earth
atmospheric and ocean circulation systems
greenhouse gases
volcanic activity
feedback cycles
Significance of the Earth’s axial orbit
Impacts solar radiation and creates seasons
Northern hemisphere tilted toward the sun
Summer in the Northern Hemisphere (more sunlight)
Winter in the Southern Hemisphere (tilted away from the Sun)
Southern hemisphere tilted toward the sun
Summer in the Southern Hemisphere (more sunlight)
Winter in the Northern Hemisphere (dark in the North Pole until Spring)
The Tri-Cellular Model of Air circulation
El Nino
Positive/Negative feedback loop of climate change
Positive: global warming → melting of ice → decrease in the albedo effect → increases temperatures (less reflection)
Negative: global warming → increased creation of clouds → increase in the albedo effect → decreases temperatures
Opposed perspectives on climate change
Climate-skeptic
the US government under Donald Trump (withdrew the US from the Paris Agreement, rolled back environmental regulations, and encourages fracking, coal, oil, and gas industries)
Pro-Climate
the EU (global effort, committed to the Paris Agreement, investments in renewable energies)
Greta Thunberg (environmental activist and advocate)