P1 : Energy
1/103
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
104 Terms
What is a system?
An object or group of objects
What happens when a system changes?
Energy is transferred
What is the difference between an open system and a closed system?
An open system can gain and lose energy to the surroundings whereas a closed system can only transfer energy within the system and cannot gain or lose energy (the overall change in energy is always 0)
What are the 8 energy stores?
Gravitational potential energy store
Electrostatic energy store
Thermal energy store
Magnetic energy store
Elastic potential energy store
Nuclear energy store
Chemical energy store
Kinetic energy store
Explain gravitational potential energy store
The energy an object has in relation to its position in a gravitational field/earths surface
Explain electrostatic energy store
Energy of negative and positive ions
Explain thermal energy store
Related to temperature, basically heat energy
Explain magnetic energy store
Energy in a magnetic field
Explain elastic potential energy store
Energy when something is stretched or squashed
Explain nuclear energy store
Energy from breaking atoms apart
Explain chemical energy store
Held in chemical bonds
Explain kinetic energy store
Movement or motion of an object
What are the 4 ways energy is transferred?
Heating
Electrically
Radiation
Mechanically
What happens when energy is transferred by heating to an object?
The object changes temperature
What happens when energy is transferred electrically to an object?
A current flows through the object
How is energy transferred by radiation?
Energy transferred as a wave, e.g. light and infrared
What happens when energy is transferred mechanically to an object?
The object moves or a force has been applied to it
In terms of kinetic energy, when is energy transferred to an object?
When it speeds up
In terms of kinetic energy, when is energy transferred away from an object?
When it slows down
What 2 factors does kinetic energy store depend on?
Mass
Speed
What is the formula for kinetic energy?
½ x m x v²
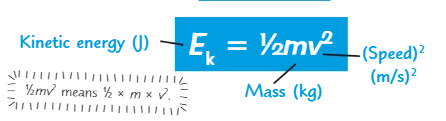
When is energy transferred to an object in terms of gravitational potential energy?
When an object is being lifted
What 3 factors does gravitational potential energy depend on?
Mass
Height
Gravitational field strength
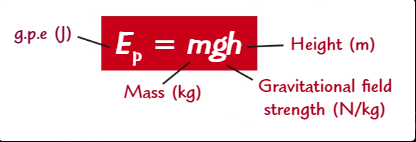
What is the formula for gravitational potential energy?
m x g x h
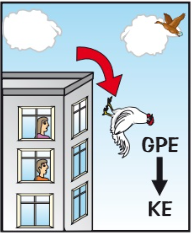
When a falling objects has no air resistance what is the formula in terms of g.p.e and k.e

What is the formula for elastic potential energy?
½ x k x e²
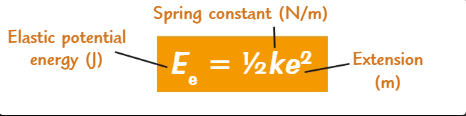
What is work done?
When a force moves an object through a distance, energy is transferred and work is done
What is the formula for work done?
f x s
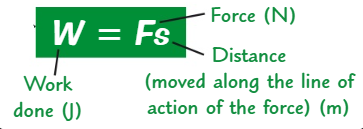
Explain the energy transfer of a ball being thrown upwards + when work is done (2)
The initial force of a person to throw a ball does work.
Energy is transferred mechanically from the chemical energy store of the arm to the kinetic energy store of the ball.
Explain the energy transfer of a moving car hitting an obstacle + when work is done (3)
The normal contact force between the car and the object does work.
Energy is transferred from the kinetic energy store of the car to the other energy stores of the object and the car body.
Some energy could be transferred as sound waves.
Explain the energy transfer of an object being accelerated by a constant force
Energy is transferred from the chemical energy store of the fuel in the car to the kinetic energy store of the car
Explain the energy transfer of a vehicle slowing down + when work is done (2)
The friction between the car’s brakes and wheels does work as it slows down
Energy is transferred from the wheels kinetic energy store to the thermal energy store of the surroundings
Explain the energy transfer of a ball falling down + when work is done (3)
A ball dropped from its height is accelerated by gravity
The gravitational force does work
Energy is transferred from the ball’s gravitational potential energy store to its kinetic energy store
Explain the 2 energy transfers of a kettle heating water
Energy is transferred to the water by heating into the water’s thermal energy store
Energy is transferred electrically (when a current flows) from the plug to the thermal energy store of the heating element of the kettle
What is specific heat capacity?
The amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of 1kg of substance by 1°C
What is the equation for specific heat capacity?
ΔE=m x c x ∆θ
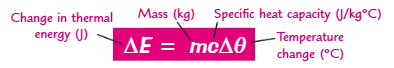
What are the units for specific heat capacity?
J/kg°C
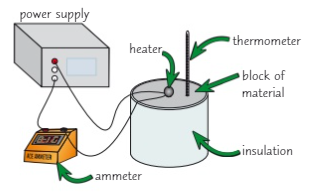
Explain how to investigate specific heat capacity (9)
Get a block of the desired material with 2 holes in it (one for the heater and one for the thermometer)
Measure the mass of the block, then wrap it in an insulating layer (like newspaper) to reduce energy transferred to the surroundings
Insert the heater and thermometer into the 2 holes
Measure the initial temperature of the block and set the potential difference of the power supply to 10V
Turn on the power supply and start a stopwatch
As the block heats up take readings of the temperature and current every minute
After 10 minutes turn the power supply off and calculate power using P=VI then use E=Pt to calculate the energy transferred to the heater
plot a graph and find the gradient. This would be ∆θ/ΔE then the shc is 1/(gradient x mass of the block)
Repeat this experiment with different materials
What is the conservation of energy principle?
Energy cannot be created or destroyed, only stored or transferred
What is dissipated energy?
Wasted energy that wasn’t transferred to the desired energy store
What is the energy transfer in a mobile phone? (useful and dissipated in an open system) (2)
Energy is usefully transferred to the chemical energy store of the battery in the phone
But some of the energy is dissipated in this transfer to the thermal energy store of the phone causing it to heat up
What is power?
The rate of energy transfer or work done
What is the equation for power in terms of energy transfer?
P = E/t
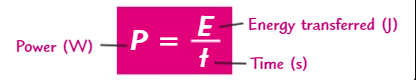
What is the equation for power in terms of work done?
P=W/t
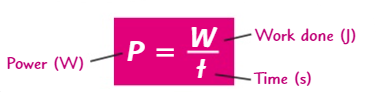
What does one watt equal to?
1 Joule of energy transferred per second
What does a powerful machine do?
Transfer a lot of energy in a short space of time
What state of matter does conduction take place in?
Solids
What is the definition of conduction?
The process where vibrating particles transfer energy
Explain conduction (5)
Energy is transferred to the thermal energy store of the object by heating
This energy is shared across the kinetic energy stores
The particles vibrate more and collide with each other
Collisions lead to energy being transferred between particles’ kinetic energy stores
This process continues until the whole object has been warmed up
What is thermal conductivity?
The measure of how quickly energy is transferred through a material
What state of matter does convection take place in?
Liquids and gases
What is the definition convection?
When energetic particles move away from hotter regions into cooler regions
Explain convection? (5)
Energy is transferred to the thermal energy store of the particles by heating
This energy is shared across the kinetic energy store of the particles
The particles start to move faster and the space between the particles increase + density decreases
The warmer, less dense particles will then move to the cooler, dense regions
This process repeats leading to a convection current
What are the 2 ways to reduce unwanted energy transfers?
Lubrication
Thermal insulation
Why is friction bad in terms of unwanted energy transfers?
Because friction causes energy to be dissipated to the thermal energy store of objects and surroundings
What do lubricants do?
Reduce friction
Give an example of a lubricant
Liquids (oil)
What does thermal insulation do?
Prevent thermal energy from escaping
Explain 6 examples of thermal insulation in houses + how they work
Thick walls - made from a low thermal conductivity material keep heat in
Loft Insulation - reduce currents created in lofts
Cavity walls - have an air gap between 2 walls which reduce amount of energy transfer by conduction
Cavity wall insulation - cavity wall are which are filled with foam to reduce energy transfer by convection
Double glazed windows - have an air gap between between 2 sheets of glass which prevent energy transfer by conduction
Draught excluders - reduce energy transfers by convection
Explain how to investigate the effectiveness of materials as thermal conductors (6)
Boil water and put it into a beaker and measure the mass of the water using a top pan balance
Use a thermometer to measure the initial temperature of the water
Put a lid on the beaker and leave it for 5 minutes then measure the temperature of the water
Pour away the water and allow the beaker to cool
Repeat this again but with the beaker wrapped in different materials, make sure to use the same mass of water + same initial temperature
The lower the temperature difference the better the material is as an insulator
What is energy efficiency?
When more energy is transferred to a useful energy store then dissipated
What are the 3 ways in which energy can be more efficient?
Lubrication
Insulation
Streamlined
What is the equation for efficiency in terms of energy transfer?
Efficiency = useful output energy transfer/total input energy transfer

What is the equation for efficiency in terms of power?
Efficiency = useful power output/total power input

What 2 things can efficiency be calculated as?
Decimal (efficiency is always less than 1 because nothing is 100% efficient)
Percentage (efficiency is always less than 100% because nothing is 100% efficient)
What one device is 100% efficient?
Electrical heaters

What are the 2 types of energy sources?
Non-renewable energy sources
Renewable energy sources
What is the difference between non-renewable and renewable energy sources?
Non-renewable energy sources will run out one day whereas renewable energy sources won’t
What are the 2 types of non-renewable energy sources?
Fossil fuel
Nuclear fuel
Give 3 examples of fossil fuels
Oil
Coal
Gas (Natural)
What are the properties of non-renewable energy sources? (3)
Reliable (produce a lot of energy)
Will run out one day
Harmful to the environment
What does burning coal and oil release + what does this lead to + what are the effects?
Burning coal and oil releases sulfur dioxide which leads to acid raid
Acid rain is harmful to trees and buildings
What is a big risk with oil production + what does this effect?
Oil spillages which cause harm to the sea and those at sea (animals)
What are the pros + cons for nuclear power? (5)
Nuclear power is clean
Does not cause pollution when generating electricity
Is extremely reliable
Decommissioning a run down power plant is expensive + takes years
Nuclear power produces nuclear waste which is very dangerous (radioactive material) + radioactive waste is difficult to dispose of (stored for thousands of years before it is safe)
What do nuclear power plants run on?
Uranium and plutonium
Give 7 examples of renewable energy sources
Solar
Wind
Water waves
Hydro-electricity
Bio-fuel
Tides
Geothermal
What are the pros + cons of renewable energy sources? (3)
They will never run out
Most of them do damage to the environment but less than non-renewable energy
They are unreliable (don’t produce as much energy)
What are the 3 primary uses of energy sources?
Transport
Heating
Generating electricity
What non-renewable energy sources are used in transport + for what? (2)
Petrol + diesel are used for cars and are created from oil
Coal is used in some old-fashioned steam trains to boil water and produce steam
What renewable energy sources are used in transport + for what?
Some vehicles use biofuel or a mix of biofuel and petrol or diesel
What non-renewable energy sources are used in heating + for what? (3)
Natural gas is used to heat water which is then pumped into radiators in homes
Coal is burnt in fireplaces
Electric heaters used non-renewable sources to function
What renewable energy sources are used in heating + for what? (3)
A geothermal heat pump uses geothermal energy resources to heat buildings
Solar water heaters which use solar energy to heat water which heats water which is then used into radiators
Burning bio-fuel can be used as heating
How does wind power generated electricity?
Via wind turbines which have generators that rotate to produce electricity
What are the pros + cons of wind energy? (7)
There is no pollution
Not reliable (rely on wind + some days there isn’t wind)
Ruin the view
Noisy
No fuel costs + minimal running costs
Don’t cause permanent damage
Doesn’t produce an immediate response for high demand
How does solar power generate electricity?
By using the energy released from the sun in the form of solar panels
What are the pros + cons of solar energy? (5)
Located in remote areas
No pollution
Not reliable (rely on sun + at night are useless)
No running costs and free to maintain
Doesn’t produce an immediate response for high demand
How does geothermal power generate electricity?
By using heat from the earth
What are the pros + cons of geothermal energy? (4)
Reliable
Does very little damage to the earth
Aren’t many suitable locations for power plants
Cost of building power plants is really high (compared to the energy it produces)
How does hydro-electricity power generate electricity?
Flooding of a valley by building a big dam
What are the pros + cons of hydro-electrical energy? (6)
There is no pollution
Habitats are destroyed when dams are built + valleys are flooded
Produces an immediate response for high demand
Not reliable (needs a country with a lot of lakes and no droughts)
There are no fuel costs and minimal running costs
How does wave power generate electricity?
Wave powered turbines generate electricity using a generator
What are the pros + cons of wave energy? (6)
There is no pollution
Disturbs the sea bed and the habitats of sea animals
Spoil the view
Are a hazard to boats
Not reliable (rely on waves + when there is no wind for waves are useless)
No fuel costs and minimal running costs
How does tidal power generate electricity?
Through tidal barrages which are big dams built across rivers, with turbines in them
How are tides formed + how many times a day?
Are produced twice a day via the gravitational pull of the sun and the moon
What are the pros + cons of tidal energy? (6)
No pollution
Reliable
Prevent boats from crossing bodies of water
Spoil the view
Disturb wildlife
No fuel costs and minimal running costs
How do bio-fuels generate electricity?
Made from plant products or animal waste and are burnt to produce electricity
What are the pros + cons of bio-fuel energy? (6)
Are carbon neutral (when burnt produce CO2 but the plants that are being burnt used CO2)
Reliable
Doesn’t produce an immediate response to high demand
Can be stored
Expensive to produce
Large area of forest is removed to make space for it + this leads to increased CO2 + methane emissions
Why are fossil fuels bad?
Produce greenhouse gases which lead to global warming
What are the 3 reasons people wanted to use renewable energy resources?
Fossil fuels are damaging to the environment
Non-renewables will run out and we need to learn how to survive without them before they do
Pressure from other countries led to the gov to set targets
How have car companies contributed to a more greener environment?
By producing electric cars that don’t need fossil fuels to run