Art of Film Midterm
1/72
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
At its base, what is a movie?
Short for motion picture
Popular entertainment
What is cinematic language?
The systems, methods, or conventions by which movies communicate with the viewer. Techniques and concepts that connect the viewer to the story, such as camera angles, editing, sound design, and mise-en-scène.
What does the word Cinema mean?
Greek word “kinesis” —> means “movement”
What does the word Film derive from?
derives from celluloid strip on which the images that make up motion pictures were originally captured, cut, and projected.
What do fiction films strive for?
Cause and effect, sequential progression
How many images per second is in an average film?
24 images per second
What is a shot?
an unbroken span of action captured by an uninterrupted run of a motion-picture camera.
What is editing?
Process by which editor combines and coordinates individual shots into a cinematic whole; the basic creative force of cinema.
What is film analysis?
Film analysis involves breaking down a sequence, scene, or entire movie to identify the tools and techniques that compose it.
What is culture invisibility?
An unbroken span of action captured by an uninterrupted run of a motion-picture camera.
What does the term invisible describe in context of film form?
an unbroken span of action captured by an uninterrupted run of a motion-picture camera.
Which of the following describes the relationship between “invisibility” and the term cinematic language?
Cinematic language is so familiar to viewers it seems invisible.
What is explicit meaning?
Everything that a movie presents on the surface.
What is implicit meaning?
An association, connection, or inference that a viewer makes based on the given (explicit) meaning conveyed by the story and form of a film.
Implicit meaning is closest to our everyday understanding of the word 'meaning’.
What is a storyboard?
A shot-by-shot breakdown that combines sketches or photographs of how each shot is to look and written descriptions of the other elements that are to go with each shot, including dialogue, sound, and music.
What is blocking?
The actual physical relationships among figures and settings. Additionally, the process of establishing those relationships during rehearsal.
What is the role of the showrunner?
The person who provides for the creative vision and management of a television show, including supervision of the writing, direction, and design.
Top of TV series creative hierarchy
What is formal analysis?
Film analysis that examines how a scene or sequence uses formal elements—narrative, mise-en-scène, cinematography, editing, sound, and so on—to convey the story, mood, and meaning.
What is cultural analysis?
Film analysis that examines how a movie reflects the culture that produced and consumed it. Cultural analysis looks at movies more as cultural artifacts than as expressive works of art.
What is Mise-en-scene?
The composition, staging, of all the elements within the frame, including setting, costumes, and makeup, actors, lighting, and figure movement
What is Narrative?
Structured into acts that establish, develop, and resolve character conflict.
What is Content?
Subject of artwork (what the work is about). Content provides something to express.
What is Form?
The means by which that subject is expressed/experienced. Form supplies the methods and techniques necessary to present it to the audience.
What is Cinematic Language?
The systems, methods, or conventions by which the movie communicates with the viewer. Includies the lighting, mise-en-scène, cinematography, performance, editing, and sound.
What is the difference between the content and the form of a movie?
Whereas content is the subject of an artwork, form is the means by which that subject is expressed and experienced.
What is the relation between form and expectations when watching a movie?
the viewer's desire to see a film that meets the expectations they had before entering the theater.
the viewer's desire to escape the "normal" world.
the viewer's desire to encounter special effects.
the viewer's desire to learn the answers to questions posed by story elements.
How do patterns relate to expectations when watching a movie?
Patterns create expectations by familiarizing viewers with storytelling conventions, such as the three-act structure, which leads to anticipation of a setup, conflict, and resolution.
What is a MacGuffin?
An element that is vital to the characters (motivates them) but turns out to be surprisingly less significant to the overall narrative than initially predicted.
What is parallel editing?
Technique that makes different lines of action appear to be co-occurring (also called cross-cutting)
What are the fundamental aspects of film form?
Movies depend on light.
Movies provide an illusion of movement.
Movies manipulate space and time in unique ways.
What is the relation between space and time in a film?
On the movie screen, space and time are relative to each other
Movies can move seamlessly from one space to another, make space move, or fragment time in many different ways.
What is mediation?
When an agent transfers something from one place to another (in this case, the camera transferring aspects of space to the viewer), it is known as mediation
What is it realism?
Realism —> In cinematic terms, an approach to narrative filmmaking that employs naturalistic performances and dialogue
modest, unembellished sets and settings; wide-angle compositions and other unobtrusive framing and story lines that portray “ordinary” people.
What is anti realism?
Anti-realism —> Opposite of realism, however, not polar opposite to realism. Distorting or abstracting reality for thematic expression or artistic effect.
What is formalism?
Similar to anti realism, an approach to style and storytelling that values conspicuously expressive form over the unobtrusive form associated with realism.
What is verisimilitude?
Appearance of being true or real. Movies are verisimilar when they convince you that the things on the screen—people, places, and so on, no matter how fantastic or antirealistic—are “really there.”
What does the term “narrative” mean or refer to?
Narrative can be…
Story
Type of movie
Structuring fictional/fictionalized stories presented in narrative films, movie stories are constructed and presented to engage, involve, and orient an audience.
What makes narrative films distinct from documentary and experimental films?
Narrative films are directed toward fiction.
What does narrative organization involve?
Narrative organization involves the selection and arrangement of content in a cause-and-effect sequence of events occurring over time.
What are the four forms of documentaries?
Factual, instructional, persuasive, and propaganda.
What are factual films?
Documentary that presents people, places, or processes straightforwardly, meant to entertain and instruct without unduly influencing audiences. (like
What are Instructional films?
Seek to educate viewers about common interests rather than persuade them to accept particular ideas (ex: cooking, yoga, etc.)
What are Persuasive films?
Address social injustice, or corporate, and governmental injustice.
What are propaganda films?
Documentary film that systematically disseminates deceptive or distorted information.
What categories of documentary are there according to Bill Nichols?
Expository, Observational, Poetic, Participatory, Performative, and Reflexive. (*define each??…)
What tools are used in most documentaries?
narrative, interviews, archival footage, voice-over narration, and reenactments.
What are some aspects, goals, and criteria of experimental cinema?
Experimental films are not commercial, rather personal; they do not conform to conventional expectations of story and narrative cause and effect, exploit the possibilities of the cinema, critique culture and media, and invite individual interpretation.
What is the term originally applied to experimental filmmaking?
avant-garde
What are some aspects, goals, and criteria of documentary cinema?
Key aspects include gathering real-world evidence, shaping a narrative from authentic material, and creating an emotional and intellectual connection with the audience.
Represent reality, differentiating it from fictional films by focusing on real events, people, and issues
At its base, what is an animated movie?
Drawings or other graphical images are placed in a series of photography–like sequences to portray movement.
What are the different types of animation?
Hand-drawn, stop-motion, and anime.
What is cel animation?
Using clear celluloid sheets to create single backgrounds that could serve for multiple exposures of a main character.
What makes anime unique in terms of the animation process?
emphasis on static or limited animation, expressive art styles (including large eyes), detailed backgrounds, and the use of "camera effects" to create a cinematic feel
What does the term genre mean?
Refers to the categorization of narrative films by the stories they tell and the ways they tell them. (Ex: musical, science fiction, horror, western).
What is the categorization of narrative films by the stories they tell and the ways they tell them?
genre
Which of the following is a function of genre?
Genres enforce fundamental beliefs and passively perform cultural rituals.
Which genre convention refers to the way a movie’s story is structured?
story formula
What are the various uses of genre?
Genre allows the story formulas, theme, character types, setting, presentation, and stars to become a predictable factor that viewers can expect. Genres can also capture a specific type of audience and craft a certain emotional experience based on these predictions.
What conventions are part of genres?
Story formula, Theme, Character Types, Setting, Presentation, and Stars
What is generic transformation?
Process by which a particular genre is adapted to meet the expectations of a changing society.
What are the main genres out there?
Gangster, Film Noir, Science Fiction, Horror, Western, and Musical (other genres exist obviously).
What is the difference between a “narrative,” the “narration,” and the “narrator”?
Narrative —> A story
Narration —> Act of telling a story
Narrator —> Who or what tells the story
What narratorial role does the camera play?
In every movie, the camera is the primary narrator
What types of narrators are there?
First-person narration —> narrator is a character who typically imparts information in the form of voice-over narration
Direct address narration —> form of narration in which an on-screen character looks and speaks directly to the audience (breaks the fourth wall).
Third-person narrator —> Narration delivered from outside the diegesis by a narrator who is not a character in the movie.
Omniscient narrator —> allows character to travel freely within the world of the film, showing us the narrative’s events from a godlike, unlimited perspective that no single character in the film could have.
Restricted narration —> reveals information to the audience only as a specific character learns of it.
What is the diegesis?
a narrative or plot, typically in a movie.
How do we understand the relation between the narration of a camera versus that of a character?
A character’s voice is internal to the story’s participant, while a camera’s voice is external (visual framing of the story itself).
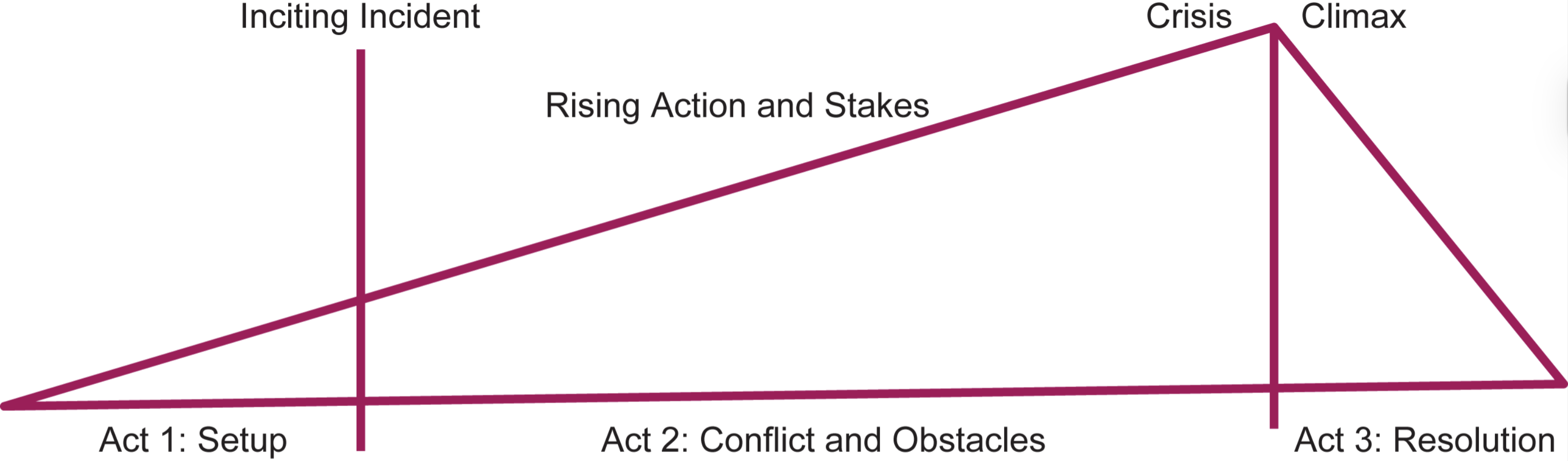
What is the basic narrative structure of most Hollywood cinema? What usually happens in each act?
The three-act format.
First act: establishes character, setting, and tone, and then introduces the goal with an inciting incident
Second act: Protagonist’s pursuit of the goal, and the conflict and obstacles that must be confronted before the goal is gained or lost at the peak of rising action and stakes.
Third act: Resolves conflict, wraps up ongoing storylines, and gives the viewer a chance to process the resolution.
What is the difference between plot and story?
A movie’s plot —> consists of all actions and events that filmmakers present on-screen.
A movie’s story —> consists of all the narrative events that are explicitly presented on screen/all the events are implicit or we infer something happened without it being shown.
What is the difference between story duration, plot duration, and screen duration?
Story duration: the amount of time that the implied story takes to occur.
Plot duration: elapsed time of those events that the film explicitly presents.
Screen duration: movie’s running time on screen.
What possible relations are there between plot time and screen time? What motivates these relations?
Summary relationships (plot duration > screen duration)
Real-time relationships (screen duration = plot duration)
Stretch relationships (screen duration > plot duration)
These relations are motivated by time concerns, and can show meaning and significance, and can provide insight into how critical events are.
What is the difference between suspense and surprise in a film?
Surprise —> shocking
Suspense —> More drawn out
What is the difference between the setting and scope of a film?
Setting —> Time and place in which the story occurs. (place, date, etc.)
Scope —> Overall range in time and place of the movie’s story. (like period of time)
What are the three common character types in film?
Round character —> complex character possessing numerous subtle, repressed, or contradictory traits. Usually end up developing over the course of the story.
Flat character —> Relatively uncomplicated character exhibiting few distinct traits. Usually do not change significantly as the story progresses.
Antihero —> Outwardly unsympathetic protagonist pursuing a morally objectionable or otherwise undesirable goal.