IB Physics SL ALL
1/129
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
130 Terms
What are the 6 fundamental quantities you much know?
Mass, length, time, temperature, current, mol
What is an absolute uncertainty?
The actual uncertainty of a given measurement
What is an fractional uncertainty?
The absolute uncertainty divided b the measured quantity
What is an percentage uncertainty?
The fractional uncertainty expressed as a percentage
If values are multiplied/divided, what do you do with the uncertainties?
percentage uncertainty is added
If values are added/subtracted, what do you do with the uncertainties?
adding the absolute uncertainty
Does a constant affect the percentage uncertainty in a calculated value?
no
What do you do when you square a quantity to the percentage uncertainty?
it doubles
When square rooting a quantity, its percentage uncertainty _____?
Halves
definition of distance travelled?
Length of path taken
Definition of displacement?
The position of an object relative to a defined starting position
Definition of speed?
Rate at which distance is covered/changes
Definition of velocity?
Rate at which displacement changes
Definition of relative velocity?
The velocity of one object as seen from another
Definition of acceleration?
rate at which velocity changes (with time)
What does the gradient of a displacement v time graph represent?
Velocity
What does the gradient of a velocity vs time graph represent?
Acceleration
The area under a velocity vs time graph is what?
Displacement
The area under an acceleration verses time graph is what?
change in velocity
The time for the _____ motion is always the same as the time for the ____ motion for a trajectory.
Horizontal, vertical
What is translational equilibrium?
Vector sum of all the forces acting on the body is equal to zero. (Moving at constant velocity)
What is newtons first law?
A body will continue in its current state of motion unless acted on by a resultant force
What is newtons second law?
the acceleration of a body is proportional to the resultant force acting on the body (F=ma)
What is static friction?
The force between the object and the surface
What is dynamic friction?
The force between the object and the surface that attemps to refuce the movement of one relative to the other.
Definition of power?
Rate at which work is done
What is the principle of conservation of energy?
Energy cannot be created or destroyed, only converted from one form to another
What is the definition of linear momentum?
The product of mass of an object and its velocity. P=mv
What is the equation for impulse?
impulse = average force x time
what does the area of a force vs time graph represent?
Impulse
What is the conservation of linear momentum ?
Total momentum of objects in an isolated system remains constant
What is conserved in elastic collisions?
Kinetic energy is conserved
What is an Inelastic collision?
There is a maximum loss of kinetic energy (Stick together upon impact)
What is temperature?
The average kinetic energy of the particles within a substance
Equation of internal energy?
Internal energy = potential energy + Kinetic energy
Definition of specific heat capacity?
The energy required to increase the temperature of 1kg of a substance by 1c
Definition of specific latent heat?
The energy needed to melt one kg of a substance at constant temperature
If you increase the volume at connstant temperature of an ideal gas what happens?
The pressure decreases
If you increase the temperature at constant volume of an ideal gas what happens?
pressure increases
If you increase the temperature at constant pressure of an ideal gas?
Volume increases
what does R represent in PV=nRT?
molar gas constant
What is the definition of a mole?
Same number of particles as there are atoms in 12g of carbon -12
Definition of molar mass?
The mass of one mole of a particular substance
What are the factors of behaving like an ideal gas?
1) particles occupy zero volume 2) no intermolecular forces between particles
Where is the direction of acceleration on simple harmonic motion?
Always acting towards the centre
Definition of oscillation
Movement of a particle to and fro from its original position
Definition of medium
The "material" through which a wave travels
Definition of amplitude
Maximum displacement of a particle from equilibrium position. (Usually measured in meters)
Definition of frequency
The number of waves/oscillations produced/observed per second (f=1/t)
Definition of phase difference
The phase difference between two sources is the fraction of a cycle bu which one source moves behing the other
Definition of simple harmonic motion
SHM is defined as motion where the acceleration of the particle is proportional to but in the opposite direction to the displacement of the particle (a-x) ( a=acceleration, x=displacement)
What direction are particles moving in a longitudinal wave?
"Particle" oscillations (vibrations) are parallel to direction of wave
What direction are particles moving in a transverse wave?
"Particle" oscillations are perpendicular to direction of wave motion
What does the wavelength of a displacement / time graph represent?
Period
What does the wavelength of a displacement / position graph represent?
Wavelength
At what speed do EMS waves travel at?
Speed of light
What are the the waves in order of wavelength?
Gamma, X rays, UV, Visible, IR, Micro, Radio GAXUVIMR
Sound waves are generated by vibrating objects. The obkect then exerts a series of push-pulls on air particles. This causes regular pulses of high pressure air (_____) and low pressure air (_______).
Compressions / Rarefactions
Definition of wavefront
A wavefront shows a line of points all in phase with eachother. Distance between two wavefronts = wavelength
A ray is always ______ to the wavefronts
perpendicular
angle of incidence =
angle of reflection
Does the frequency remain the same for refraction?
yes
Does the wavelength remain the same for refraction?
No
Does the speed remain the same for refraction?
No
If a wave enters a medium in which it travels slower what happens?
Speech decreases, Wavelength decreases, Frequency remains the same, bends towards the normal
What is the definition / equation for the refractive index?
Ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum to the speed of light in the material
What is the charge of: Electron / Proton?
Negative / Positive
What is the S.I unit for charge?
Coulomb (C)
What is coulomb's law?
like charges repel and opposite charges attract
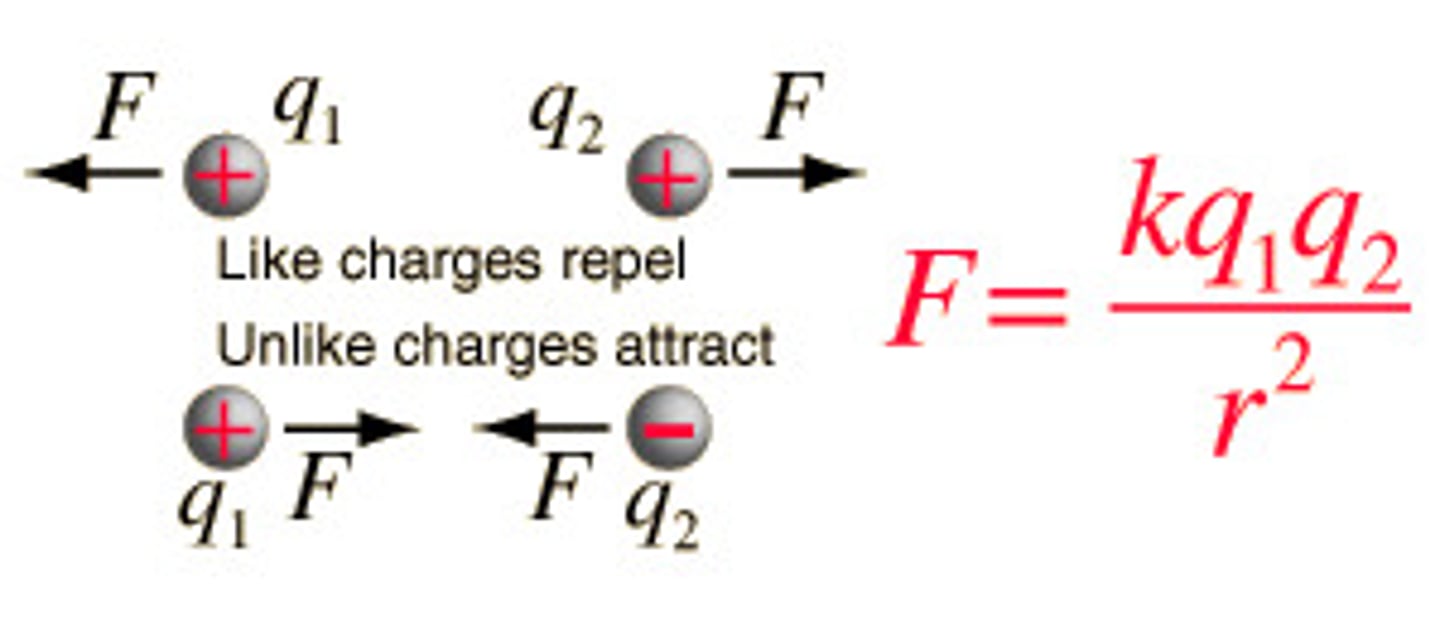
What is the equation for force of electric field?
Force = field strength x charge
What is the equation for electric force between two plates?
E=v/d (NOT IN EQUATION BOOKLET)
What is the definition of electric current?
Current is defined to be the rate of flow of charge
Direct current is produced by ___-cell batteries
dry
Potential difference is also known for?
Voltage
Potential difference is defined to be?
The work done per unit charge when charge moves from one place to another
(Kirchhoff's law) The current flowing into the junction is equal to the current flowing ____
out
In any complete loop in any part of a circuit, the ___ of all the potential differences across all components and power sources is equal to zero.
sum
If the current in a conductor increases =
The temperature increases
The greater the resistance of a material, the more ________ _______ must be applired to produce a certain current.
potential difference
Definition of resistance?
The ratio of potential difference across a conductor to the current flowing through the conductor
Resistance is measured in?
Ohms
What is Ohm's law?
The current through a wire is proportional to the potential difference across it, provided the temperature is unchanged.
Generally ______ conductors obey Ohm's law
Metallic
An ohmic conductor has what sort of line on a graph of VxI?
Straight passing through 0,0 point
If light increases, the resistance of the LDR ______
decreases
The speed (Drift velocity) of electrons in a conductor depends on:
Cross sectional area of a conductor, Length of a conductor, material from which a conductor is made from, temperature of conductor, potential difference across conductor
Equation for power?
Work done/time taken
Cells can be categorised as ___-cells or ___-cells
dry, wet
What is a primary cell?
Is a disposable, non-rechargeable cell
What is a secondary cell?
May be rechargeable. Can be cheaper in the long term.
What is the definition for emf?
The electrical energy produced per unit charge inside the source
What is the equation for the size of force on a current carrying conductor?
F=BILsin(Theta)
What is the equation for the size of the force on a charge moving with velocity?
F=Bqvsin(Theta)
What direction is acceleration in circular motion?
Towards the centre
What is the circular motion acceleration called?
Centripetal acceleration
What direction is the resultant force on an object in circular motion?
Towards the centre of the circle
What is Newton's law of gravitation?
F=G(mm/r^2)
Equation for gravitational field strength?
g=F/m
What is the equation for energy of photon?
E=hf (H being Planck's constant)
What must be put in to move an electron from one energy level to a higher energy level?
Energy