EB.5 Vet Path
1/524
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
525 Terms
What do somatic spinal nerves do?
Transmit sensory and motor information
What cranial nerves are considered to be part of the CNS because they are myelinated by oligodendrocytes rather than schwann cells?
CN1 and CN2
Which part of the enteric nervous system is located in the submucosa and aids in digestion, fluid secretion, absorption, and blood flow?
endoneurium
surrounds individual nerve fibers
perineurium
ensheathe nerve fascicles
epineurium
surrounds groups of fascicles
schwann cells
myelinates PNS axons
trophic support for axons
endoneurium fibroblasts
phagocytic abilities in the endoneurium to remove exonal debris
Satellite glial cells
found in neurons but dont know what they do
Dorsal nerve root
sensory information
Ventral nerve root
Motor information
What are dysautonomias?
failure of the autonomic nervous system
How do dysautonomias present in dogs and cats?
GI upset, urinary incontinence, mydriasis, prolapsed 3rd eyelids, bradycardia
What part of the PNS are affected by peritonitis?
enteric, myenteric and submucosal
edematous nerves and hyperplastic support cells
What breed is most likely to have genetic Congenital Hypomyelinating Polyneuropathy due to a mutation in the myelin protein zero (MPZ) gene?
Golden Retrievers
What cells are most likely affected in young hopping golden retrievers?
Schwann Cells > demyelination disorder
What plant has the toxic substance karwinol A and is found in SW USA where it effects ruminants?
Coyotillo
What cells does karwinol A target?
Schwann cells are targeted by the plant Coyotillo
What endocrine disorders cause a plantigrade stance in cats?
diabetes mellitus and hypothyroidism
How does Vitamin A deficiency cause a peripheral neuropathy in calves and pigs?
Vitamin A deficiency causes continued bone deposition and decreased resorption that results in compression of the optic nerves, wallerian degeneration, and blindness
What vitamin is responsible for Riboflavin deficiency or curled toe paralysis in pountry?
Vitamin B deficiency that causes endoneuronal edema
What does lead cause in the CNS?
neuronal necrosis
What does lead cause in the PNS?
demyelination
What toxins target neuronal cell bodies?
organomercurial compounds
doxorubicin
What chemical toxin causes distal axonal degeneration?
Vincristine
neuroparaxia
mild traumatic injury that leaves the axon intact and can result in a temporary conduction block followed by total recovery of function
Axonotmesis
Severe trauma damage that destroys that axon but spares the connect tissue framework, so regeneration and reinnervation is possible
Neurotmesis
Traumatic severance of the nerve with destruction of the supporting framework
What is neurogenic shock?
When traumatic injury causes immediate vasoconstriction followed by vasodilation causing a loss of blood pressure
What are the three types of nerve sheath neoplasms?
schwannoma
neurofibroma
perineurioma
What species can get schwannomas?
DOGS, cats, horses, cows
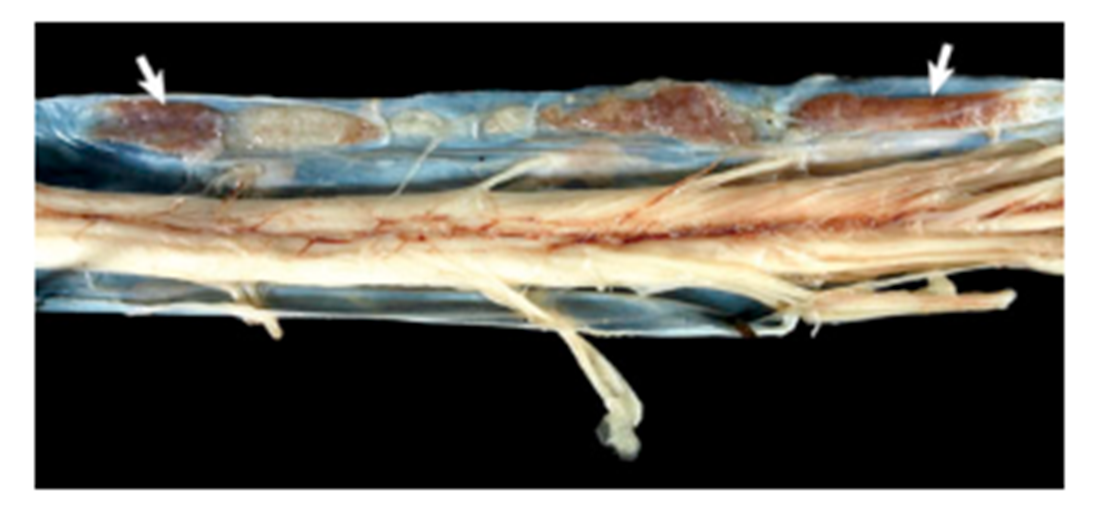
Where do dogs most commonly get schwannomas?
trigeminal nerve, spinal nerve roots of the brachial plexus, and nerve roots at the thoracic and lumbar areas
What pathology is shown in this image?
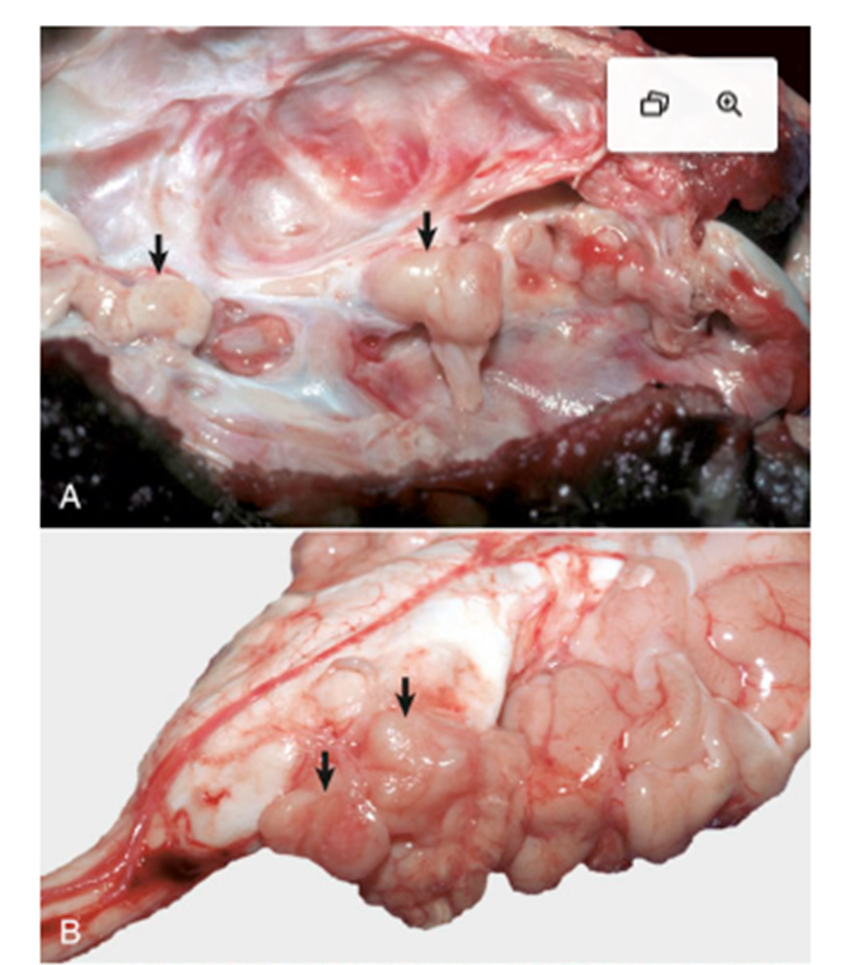
Trigeminal nerve schwannoma
What pathology is shown in this image?
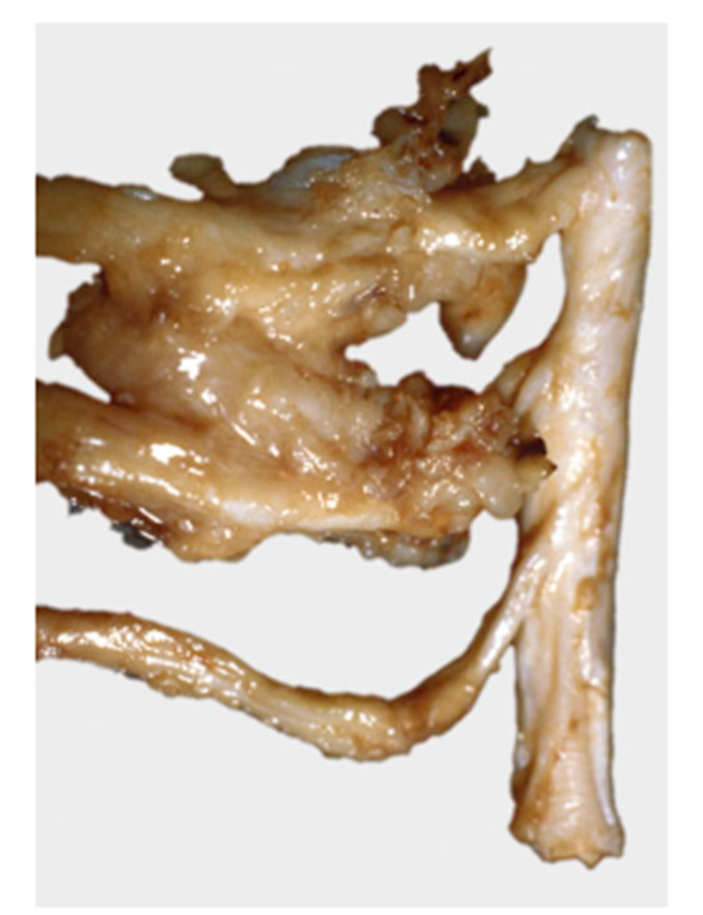
Spinal nerve schwannoma
What is colonic aganglionosis?
a lethal disorder involving the development of the enteric division of the PNS that most commonly affects foals with overo markings
What is the mutation associated with colonic aganglionosis?
autosomal recessive mutation of the endothelin B receptor that is required for the development of the
What age equines are most likely to be affected by equine grass sickness, aka equine dysautonomia?
2-7 yr
What are the predisposing conditions of equine dysautonomia?
pasture grasses stressed by rapid growth or sudden cold weather resulting in reduced concentrations of antioxidants and increased concentrations of glutamate and aspartate
What is the only way to diagnose equine grass sickness antemortem?
full thickness biopsy of the ileum
What animals are most likely to have recurrent laryngeal paralysis?
2-7 yr old tall, male horses, usually the left side
What equine condition causes urinary incontinence, fecal retention, muscle atrophy over pelvis and hindlimbs due to inflammation on the sacrococcygeal nerves?
Polyneuritis equi
What pathology is shown in this image?
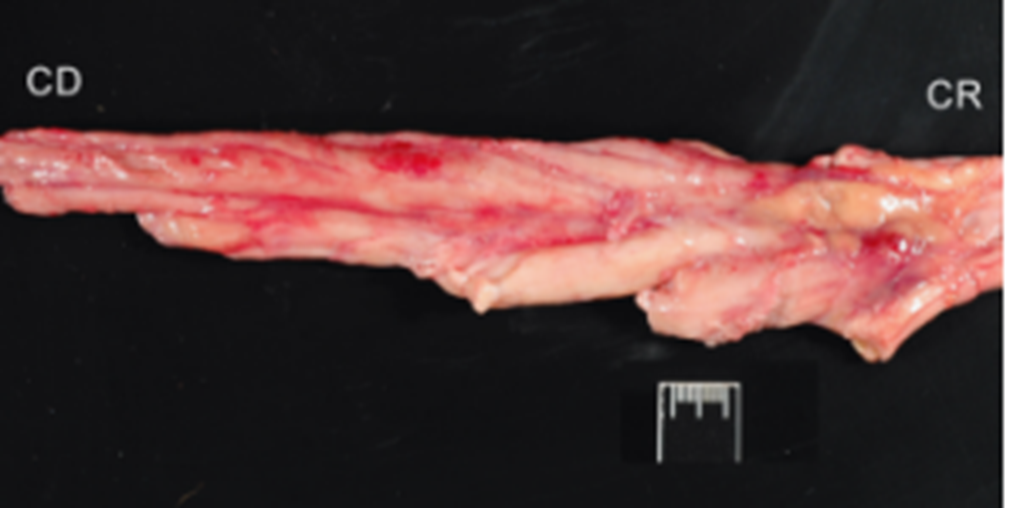
Polyneuritis equi (image)
What canine condition is an acute fulminating polyradiculoneuritis with inflammation in the ventral spinal nerve roots that causes paralysis from a few days to months but recovery is common?
Acute idiopathic polyneuritis aka coonhound paralysis
What pathology is shown in this image?
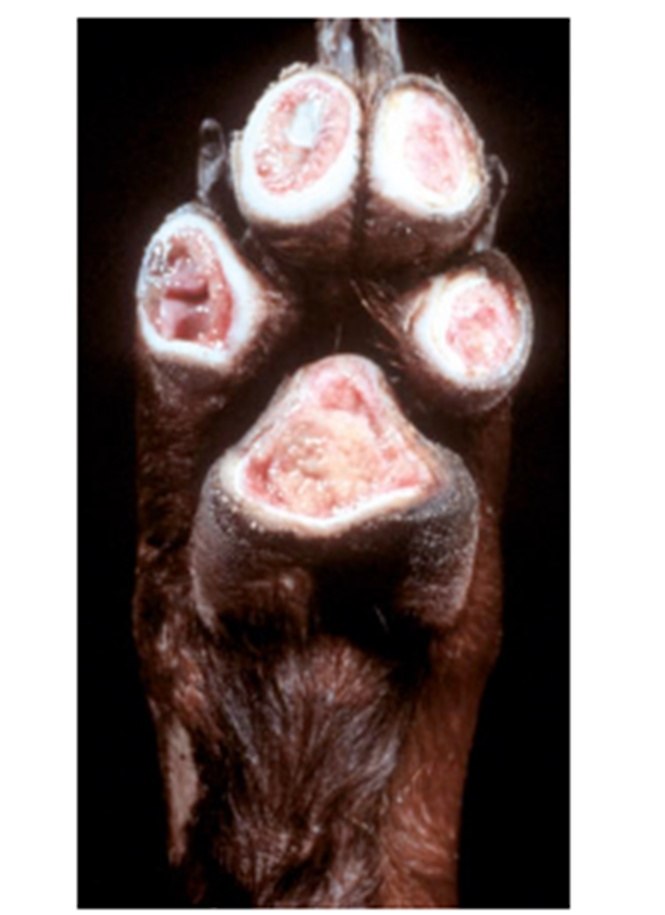
Sensory neuropathy of english pointers
Where are the lesions of sensory neuropathy of english pointers commonly found?
Dorsal root ganglia and dorsal spinal nerves
At what pH does listeriosis proliferate?
>5.4 in silage
What nerve does listeriosis target in order to perform retrograde axonal transport to the brainstem? Hint: It is tied to the clinical sign of drooling
Trigeminal nerve
What pathology is shown in this image of the brainstem of a cow?
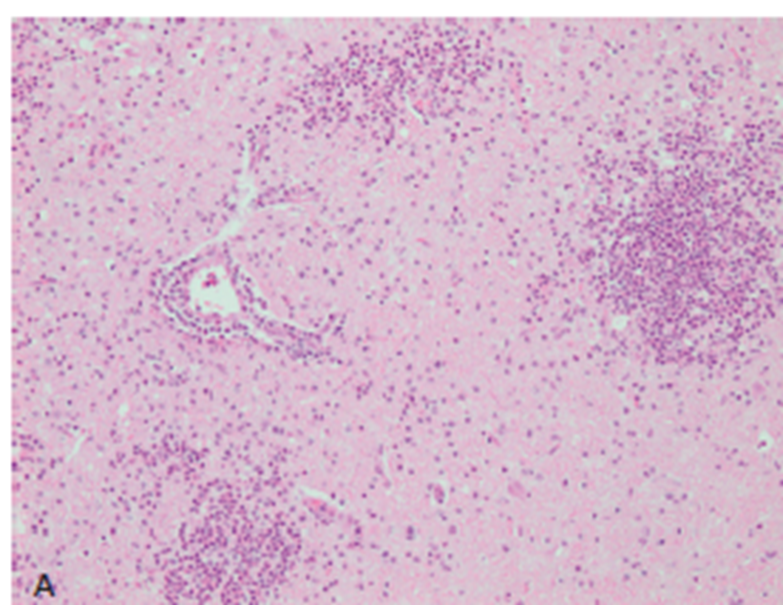
microabcesses with listeriosis
What is one of the key pathogens responsible for meningoencephalitis in cattle?
Histophilus somni
What cattle are most commonly affected by Thrombotic Meningoencephalitis due to Histophilus somni?
6-12 mo old feedlot cattle
After Histophilus somni replicated in the respiratory system, how does it spread to the CNS to induce TME?
Hematogenously
Which pathogen is associated with vasculitis and vascular necrosis causing randomly scattered irregular foci of hemorrhage and necrosis throughout the cerebrum at the grey-white interface?
Thrombotic meningoencephalitis (description)
What pathogen is shown in this image?
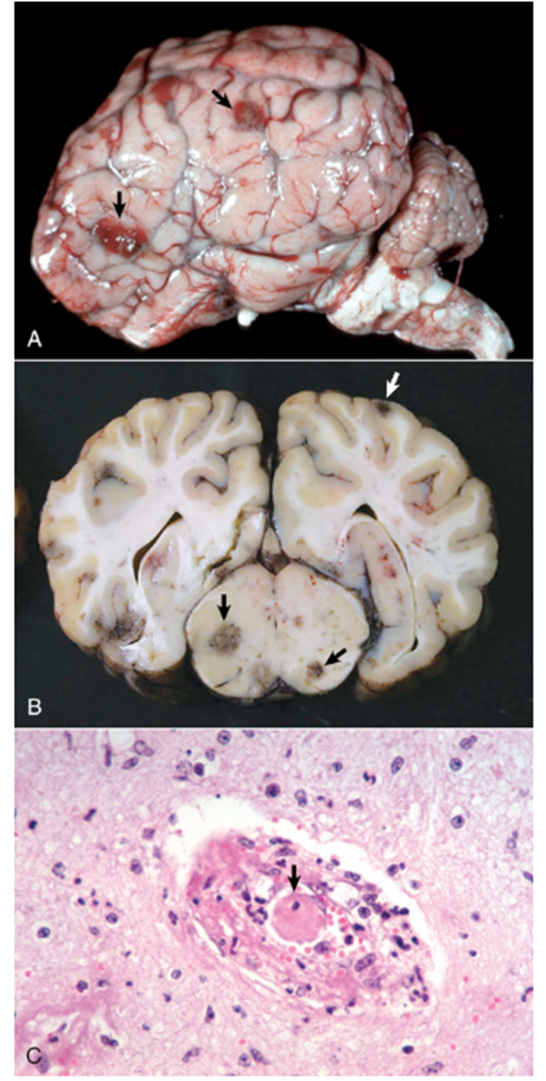
TME (image)
What pathology is shown in this image?
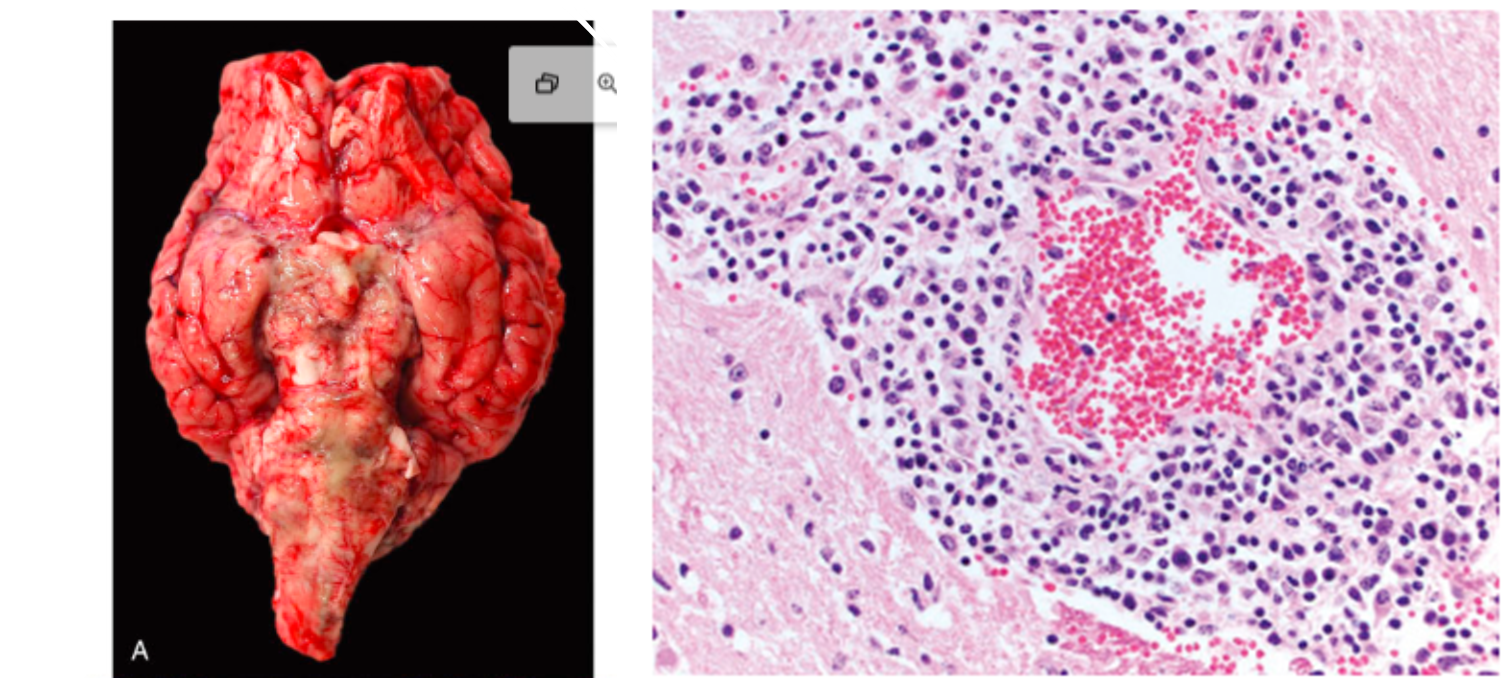
Malignant Catarrhal Fever
a gammaherpes virus - fatal
Caprine Arteritis Encephalitis is a readily transmissible virus between dam and baby. How do you recognize it grossly?
tan-salmon brain and spinal cord necrosis
White Matter
What age of animal is prone to developing the arthritis portion of the disease?
Adults only
What pathology is shown in this image?
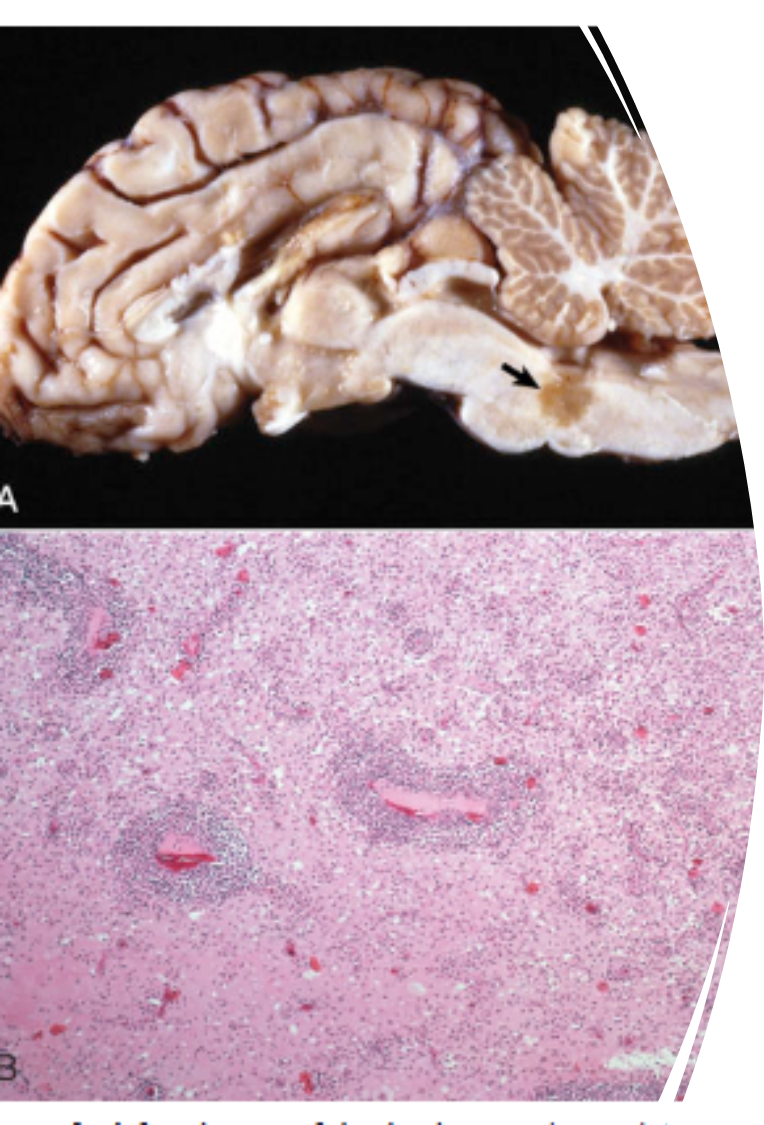
Caprine Arthritis Encephalitis
The bacteria in the rumen digest carbohydrates that release what key amino acid?
Thiamine
Why do we see a thiamine deficiency in young ruminants?
because the rumen has not matured yet
Why do we see thiamine deficiency in adult ruminants?
because grain overload causes an overgrowth of thiaminase producing bacteria
What pathology is described as having a yellow discoloration and softening of the cerebrocortical grey matter and is autofluorescent under UV?
Polioencephalomalacia (description)
What pathology is shown in this image?
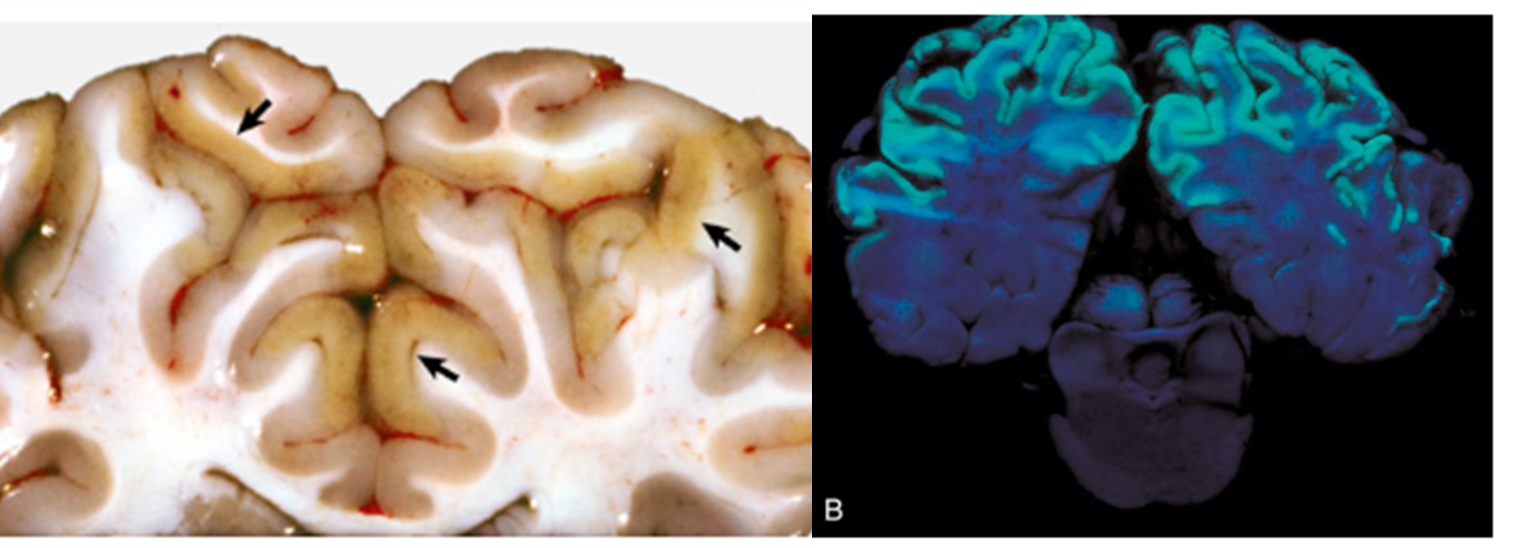
Polioencephalomalacia (image)
What are causes of polioencephalomalacia in ruminants?
thiamine deficiency
sulfur toxicosis
lead toxicity
water deprivation/salt toxicity
What is the congenital form a copper deficiency in small ruminants called?
Swayback
What pathology is shown in this image?
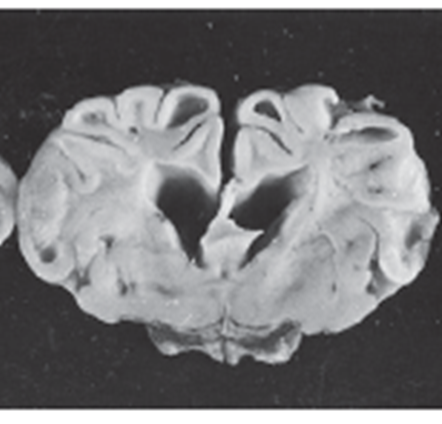
bilateral cerebrocortical lesions in a small ruminant indicating copper deficiency
What kind of lesions are seen in the CNS with infections of Clostrudium perfringens type D, aka overeating disease?
bilaterally symmetric foci of malacia and cavitation, yellow-grey-red, prefers to target white matter
What pathology is shown in this image?
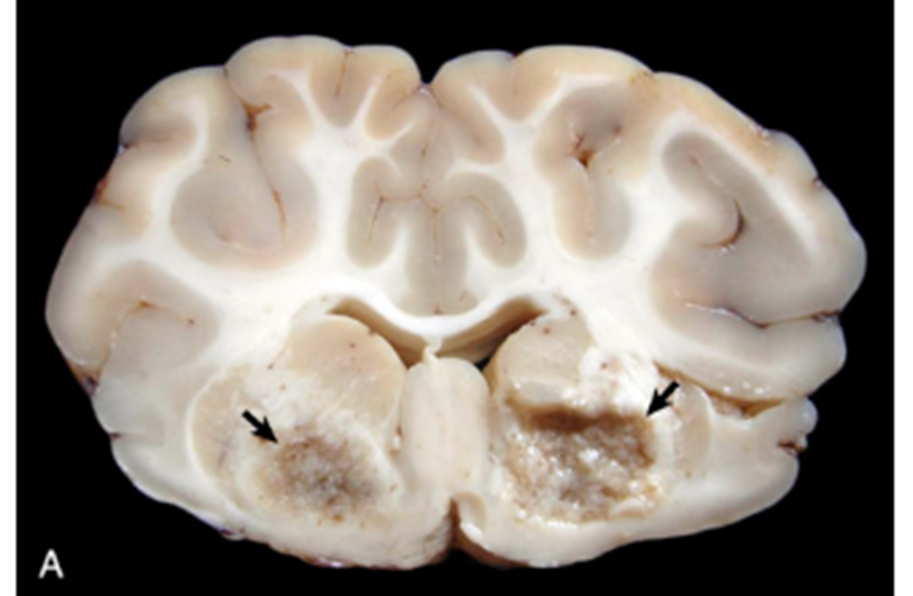
Focal symmetric encephalomalacia associated with Clostridium perfringens
What are the effects of distemper virus in the CNS?
all cells in the CNS are susceptible to infections that cause encephalomyelitis and demyelination due to the virus targeting oligodendricytes
What breeds are most commonly affected by degenerative myelopathy because of a mutation in the superoxide dismutase 1 gene (SOD1)?
German Shepherds, usually over 8 yr
What part of the CNS does degenerative myelopathy most commonly target?
Thoracic spinal cord, axonal degeneration
What pathology is shown in this image?
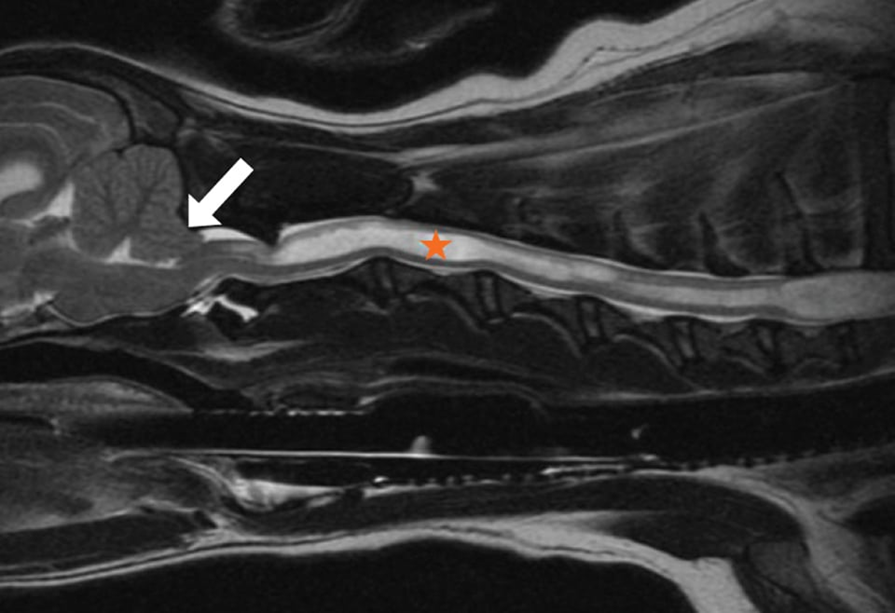
Chiari like malformation
What breeds are predisposed to chairi like malformation?
Cavalier King Charles Spaniel
What pathology is shown in this image?
dural ossification
What are the lesions of granulomatous meningoencephalitis like?
polka-dot gelatinous or granular irregular areas of grey-white-red lesions in the white matter of the brainstem
What cells are suspected to be involved in granulomatous meningoencephalitis?
t lymphocytes
What pathology is shown in this image?
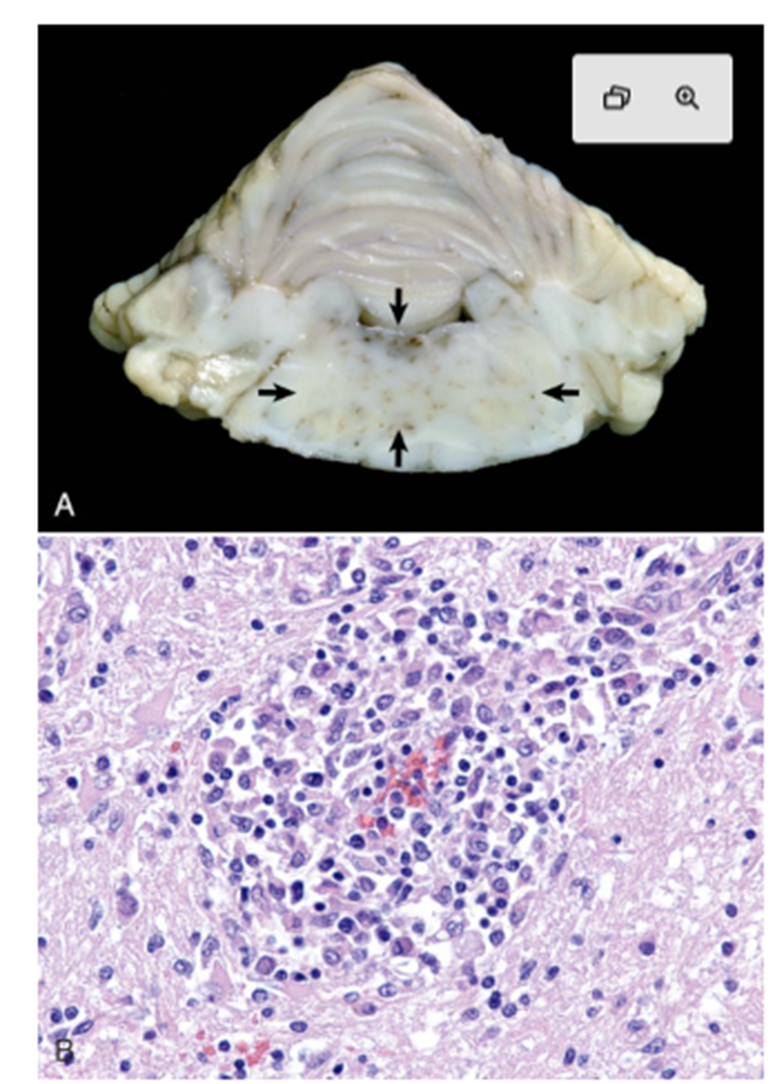
granulomatous meningoencephalitis
What dogs are predisposed for necrotizing meningoencephalitis?
young to middle aged pugs, shih tzu, Chihuahua and Maltese
What part of the CNS does NME specifically target?
Cerebral cortex
What breeds are predisposed for necrotizing meningoencephalitis?
Yorkies
Where are lesions of NLE most commonly found?
Cerebral white matter and brainstem
What pathology is shown in this image?
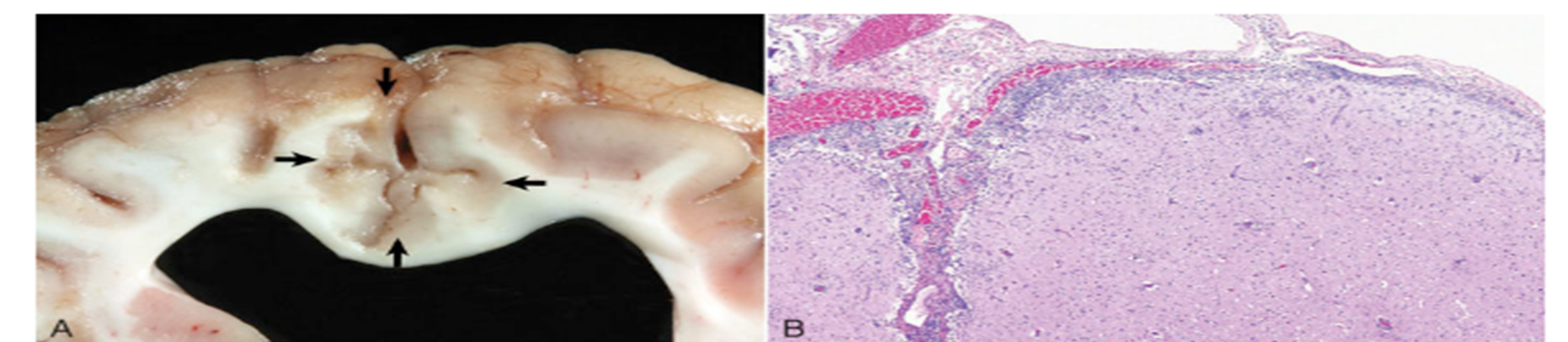
Necrotizing meningoencephalitis
What pathology is shown in the image?
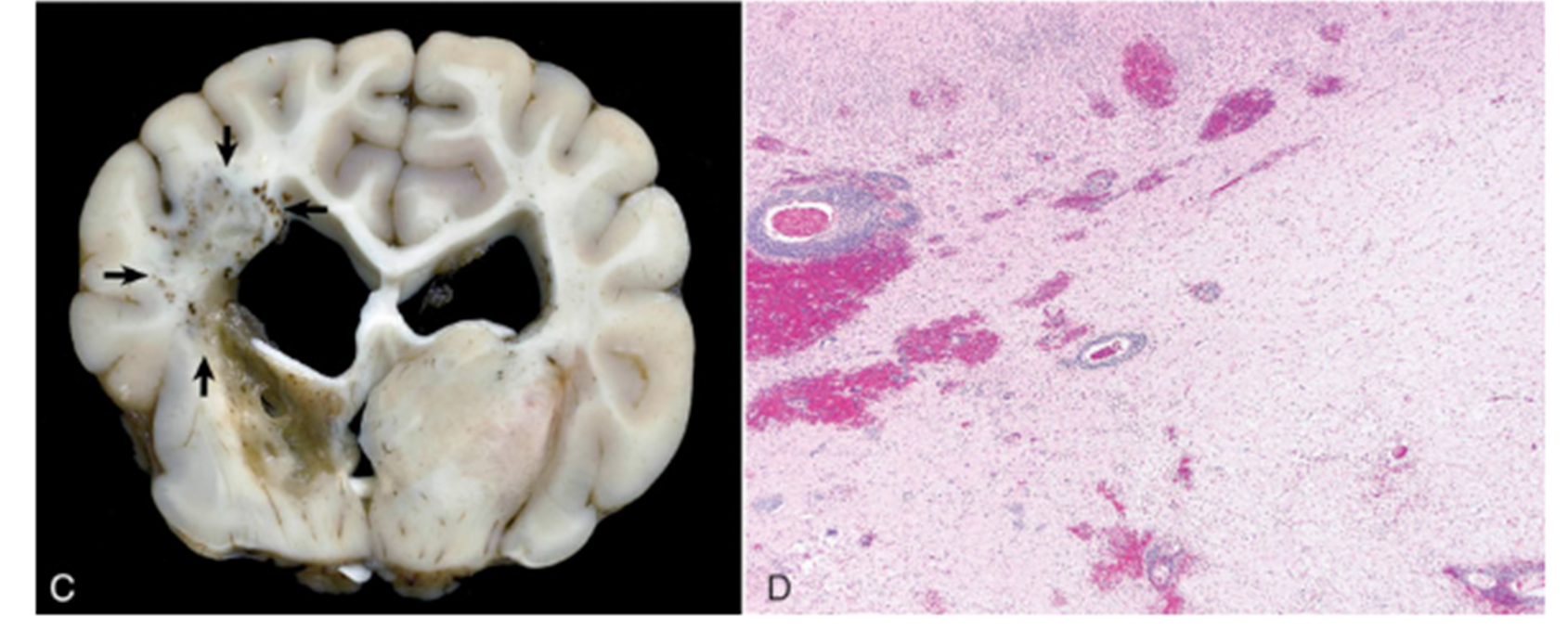
Necrotizing leukoencephalitis
What is the actual name of beagle pain syndrome?
Steroid-responsive megingitis-arteritis is also known as beagle pain syndrome
How do dogs with steroid-responsive meningitis-arteritis present?
Severe cervical hyperesthesia, hunched posture, fever, neutrophilia, neutrophilic pleocytosis on CSF, and leptomeningeal hemorrhage in the cervical spinal cord and brainstem
What breeds are predisposed to IVDD due to their collagen deficiency?
Chondrosydtrophic breeds
Type 1 Herniation
more sever, acute, large breed dogs
Type 2 herniation
chronic, small breed dogs
What pathology is shown in this image?
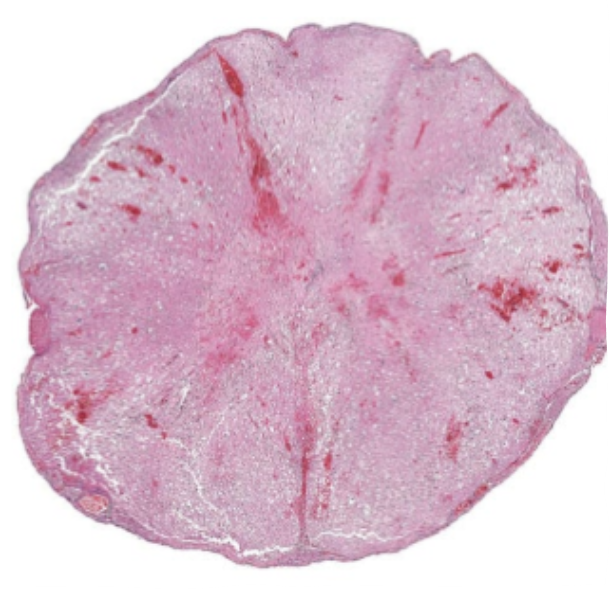

Myelomalacia of the spinal cord following IVDD, probably a small dog, poor prognosis
What disease is similar to human alzheimers and is associated with abnormal protein deposition in the brain?
Canine Cognitive Dysfunction (CCD)
What pathology is shown in this image?
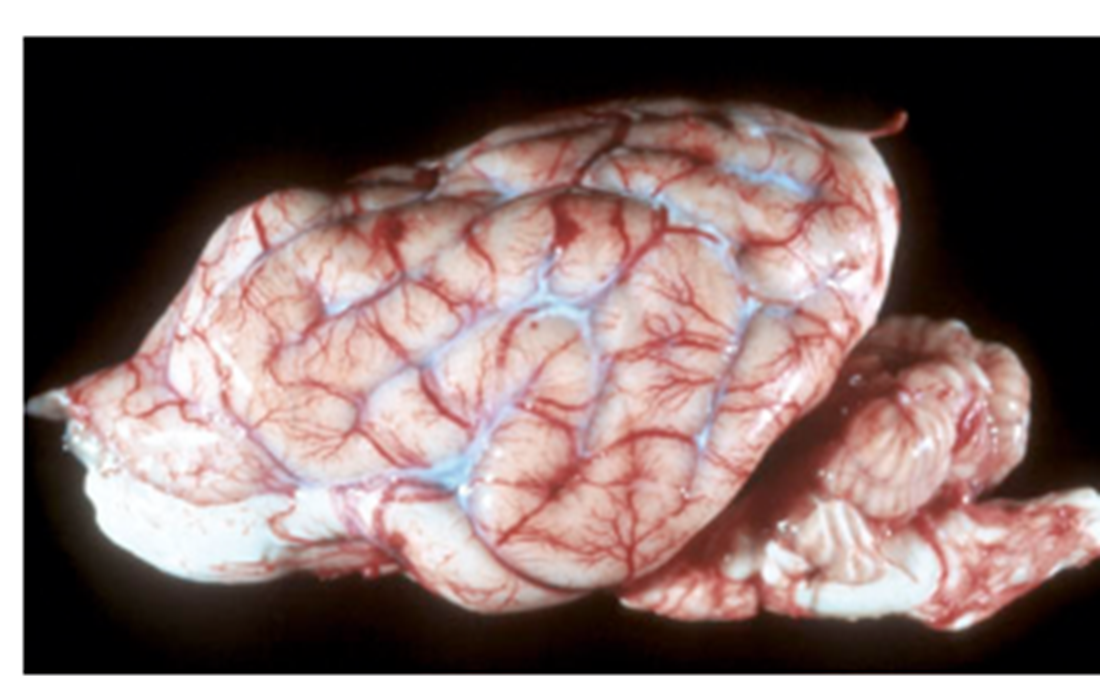
Leptomeningeal fibrosis, particularly in the sulci
What causes the CSF to be cloudy in cats with FIP?
fibrin rick exudate within the ventricles
What pathology is shown in this image?
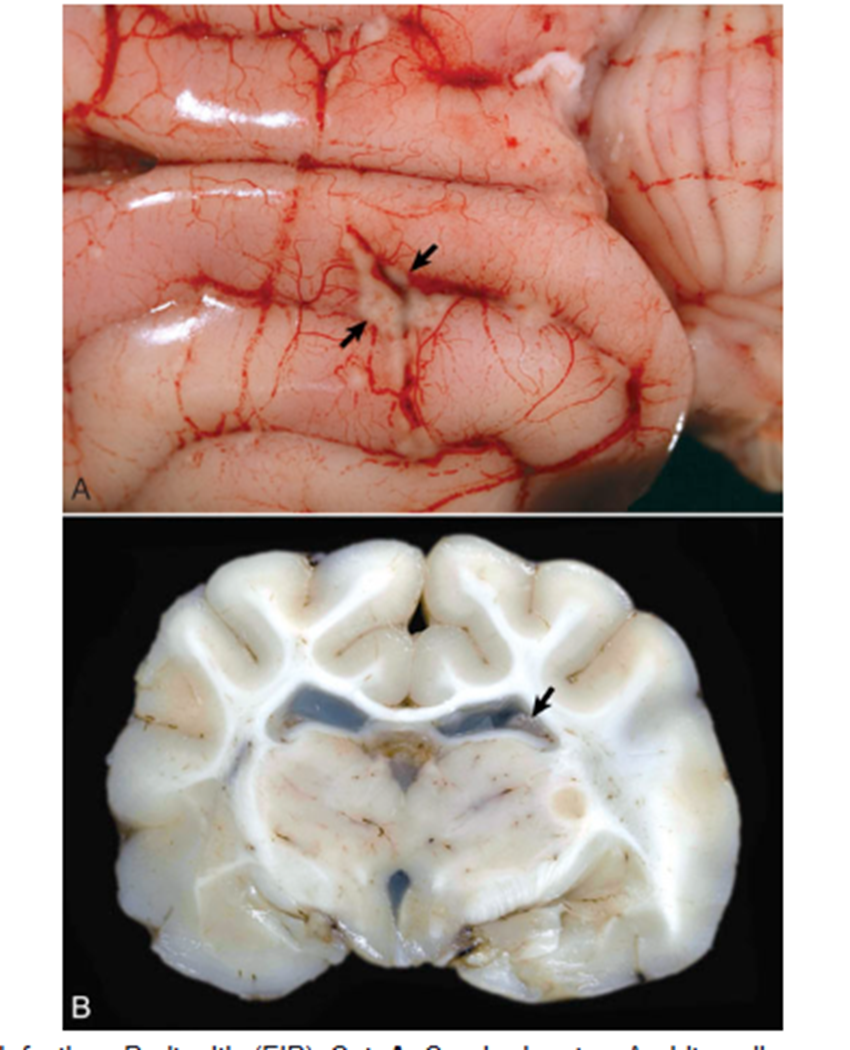
FIP
What condition occurs when a Cuterebra fly larvae enters the brain via the nasal cavity?
Feline Ischemic Encephalitis is because of fly larvae
What pathology is shown in this image?
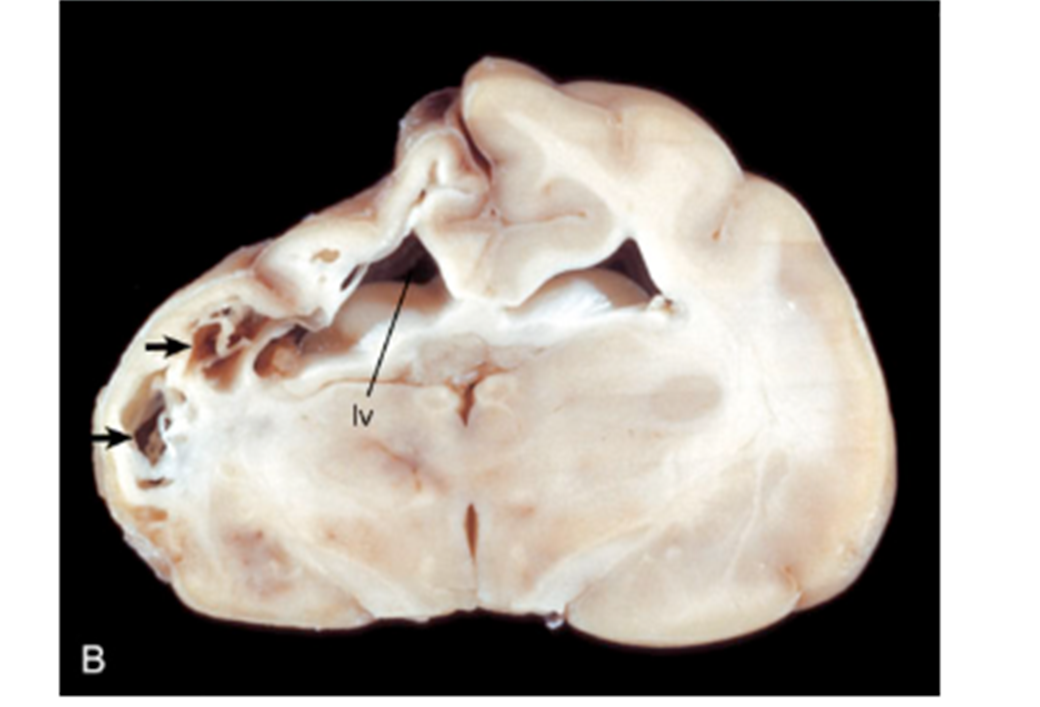
collapsed cerebral cortex most likely due to necrosis following larval invasion
What pathology is shown in this image?
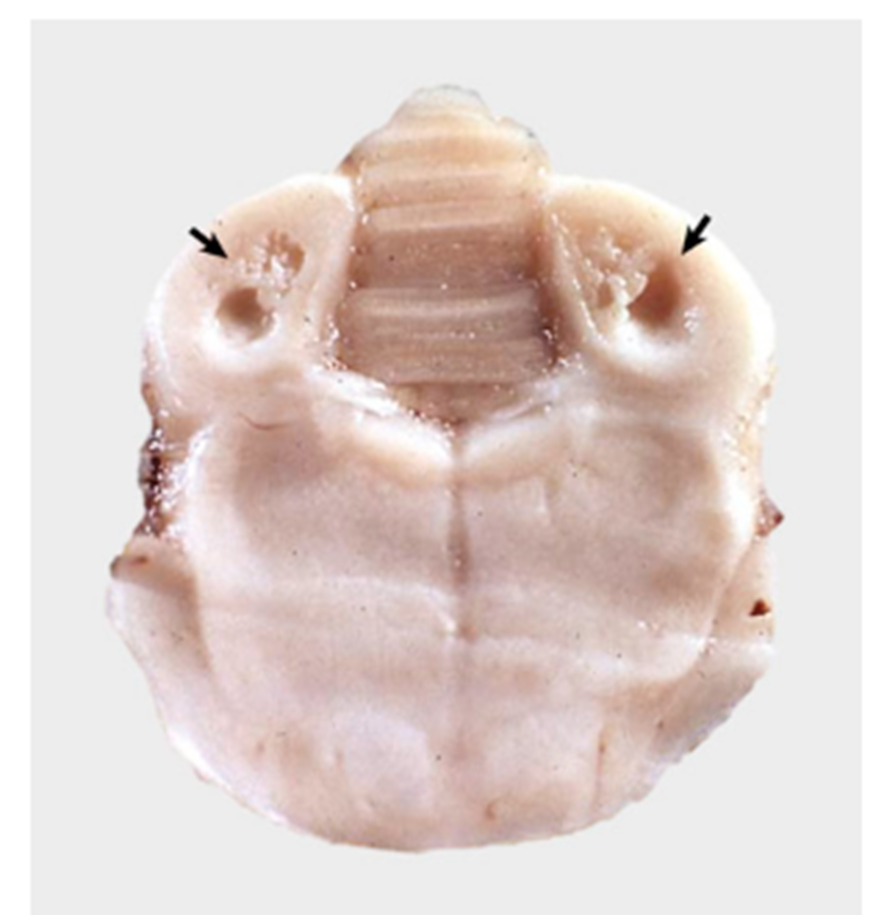
feline thiamine deficiency
How do cats become thiamine deficient?
ingestion of fish containing thiaminase or dietary deficiency
What domestic species most frequently gets primary neoplasms of the CNS?
Dogs
What are examples of embryonal tumors?
medulloblastoma
ependymoblastoma
neuroblastoma
primitive neuroectodermal tumors (PNET)
Which embryonal tumor is most common in young animals, arises in the cerebellum and usually does not cause hemorrhage, necrosis or cysts?
medulloblastomas
What pathology is shown in this image?
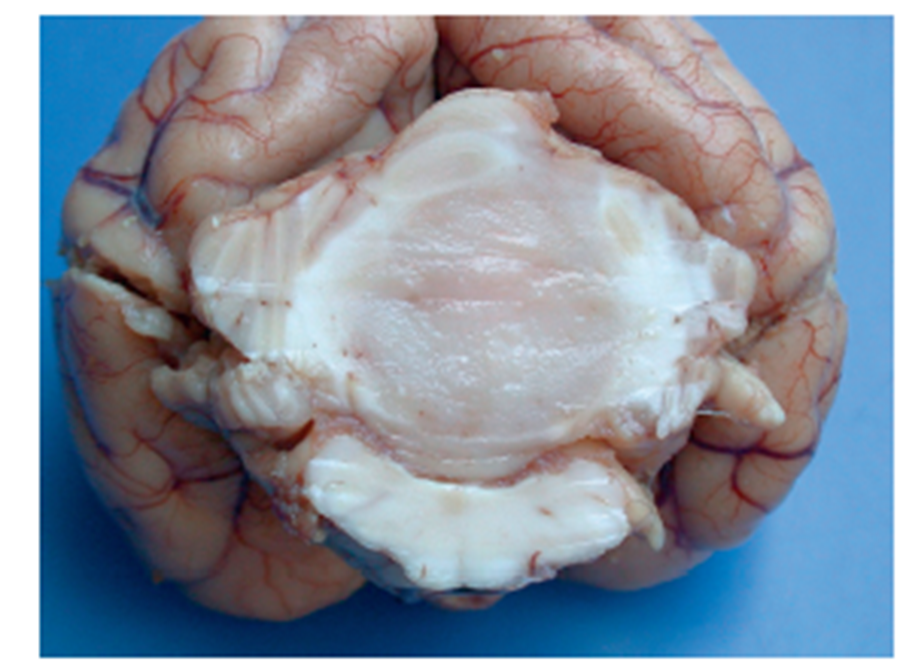
medulloblastoma (image)
well circumscribed, soft, gray - pink mass that compresses the fourth ventricle