AP Biology Unit 4 "Cell Communication and the Cell Cycle" Quizlet
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Cell Communication
The process through which cells can detect and respond to signals in their environment
Signal Transduction Pathway
The process by which a signal on a cell's surface is converted into a specific cellular response.
Phosphorylation
The metabolic process of introducing a phosphate group into an organic molecule.
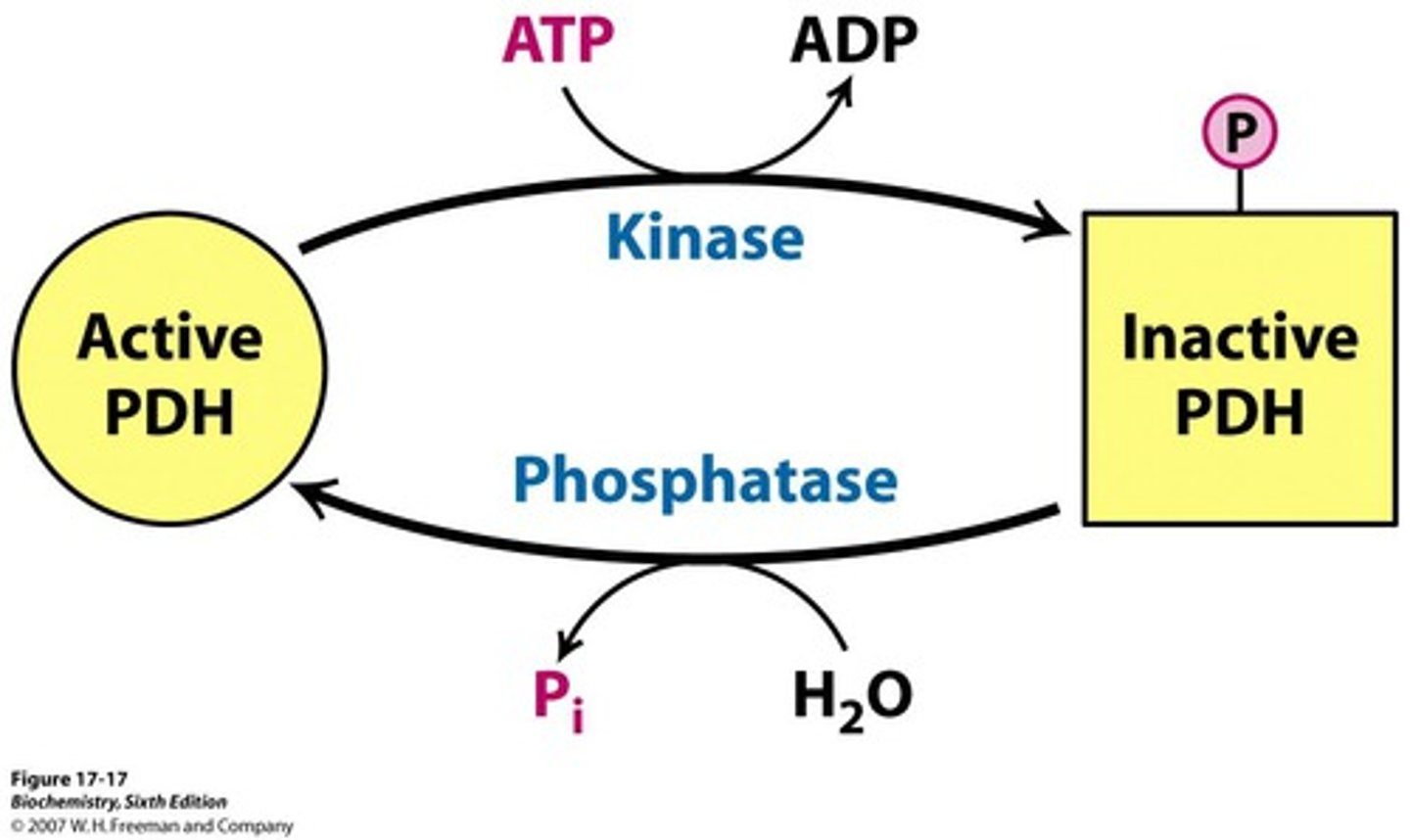
Kinase
An enzyme that transfers phosphate ions from one molecule to another
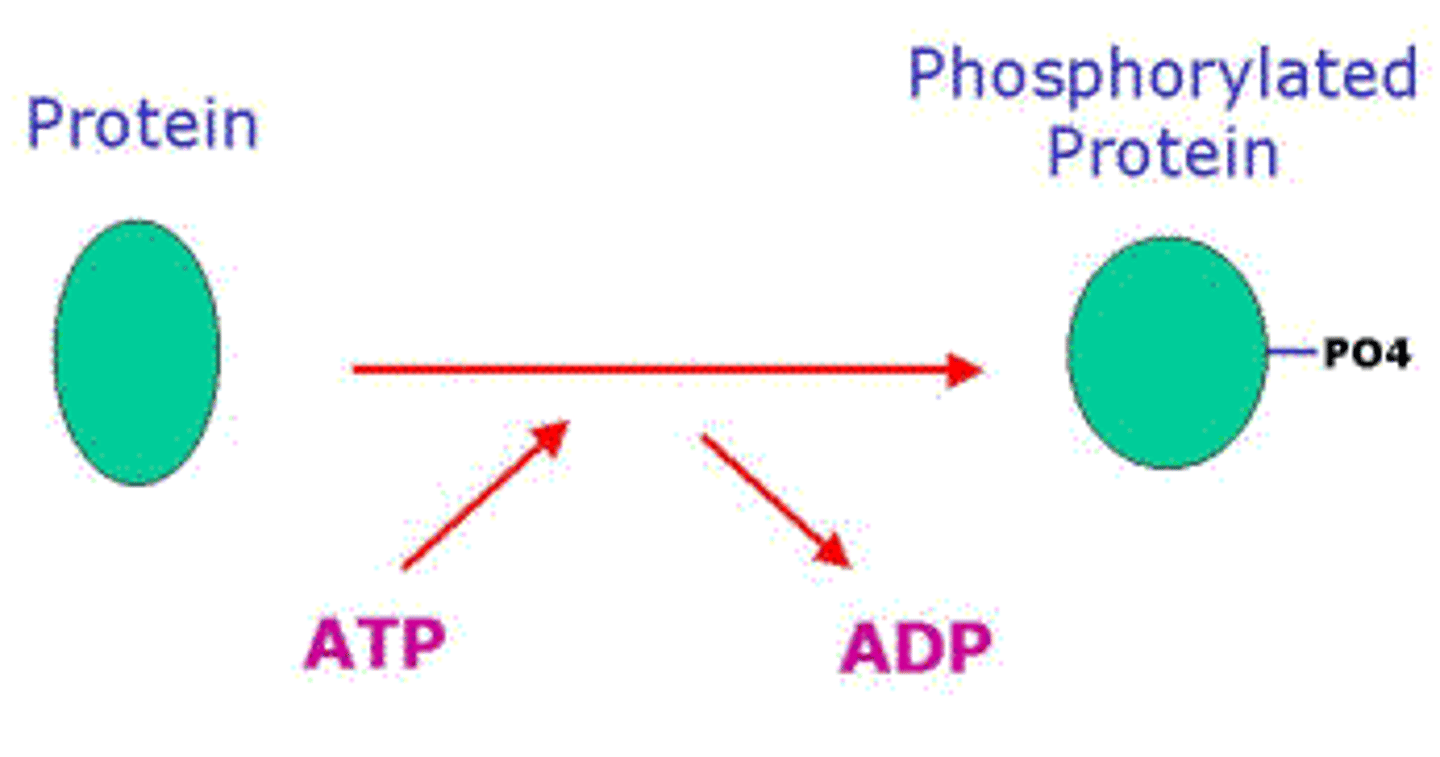
Phosphatase
An enzyme that removes a phosphate group from a molecule
Ligand
A molecule that binds specifically to a receptor site of another molecule.
G protein-coupled receptor
A signal receptor protein in the plasma membrane that responds to the binding of a signaling molecule by activating a G protein.
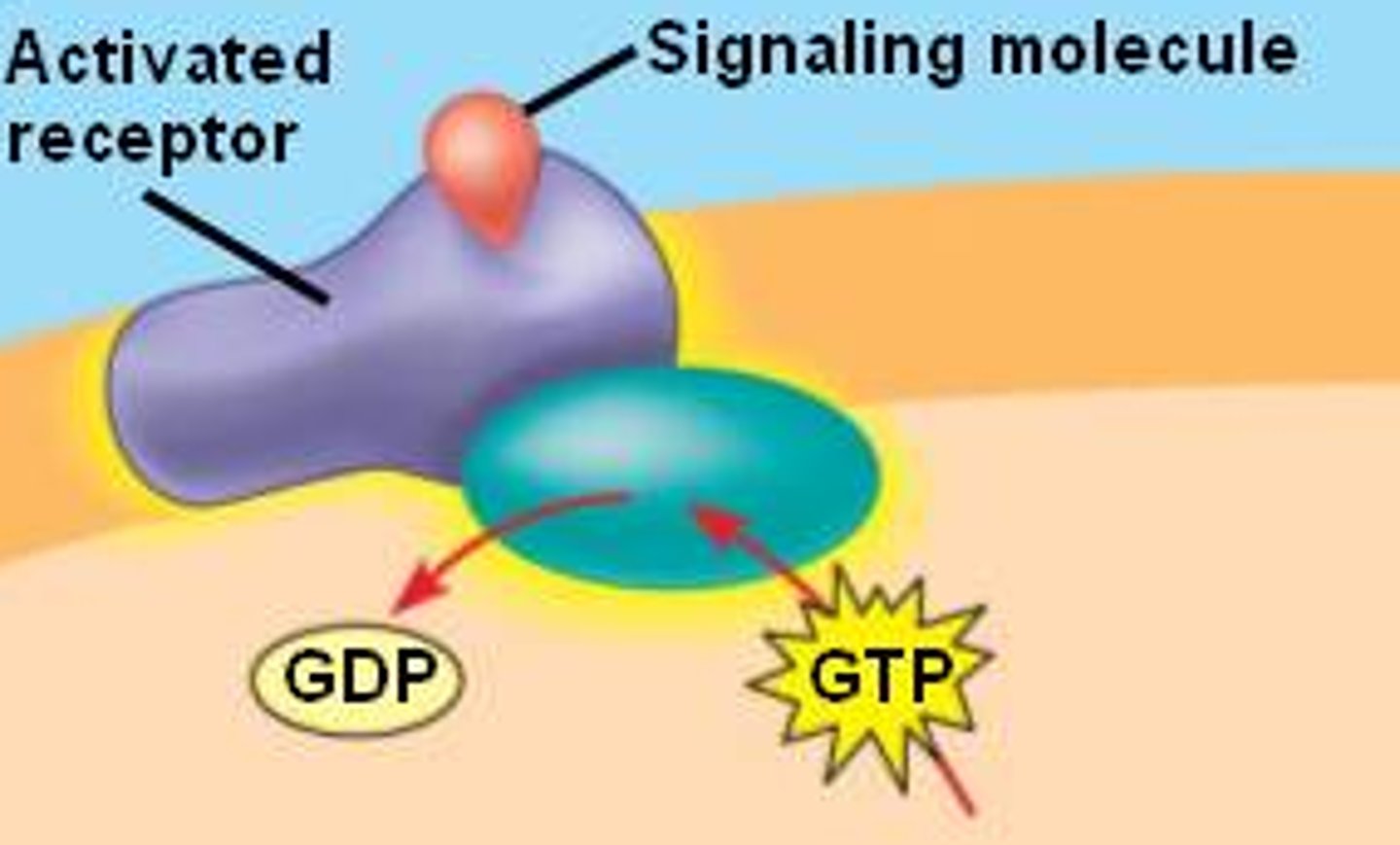
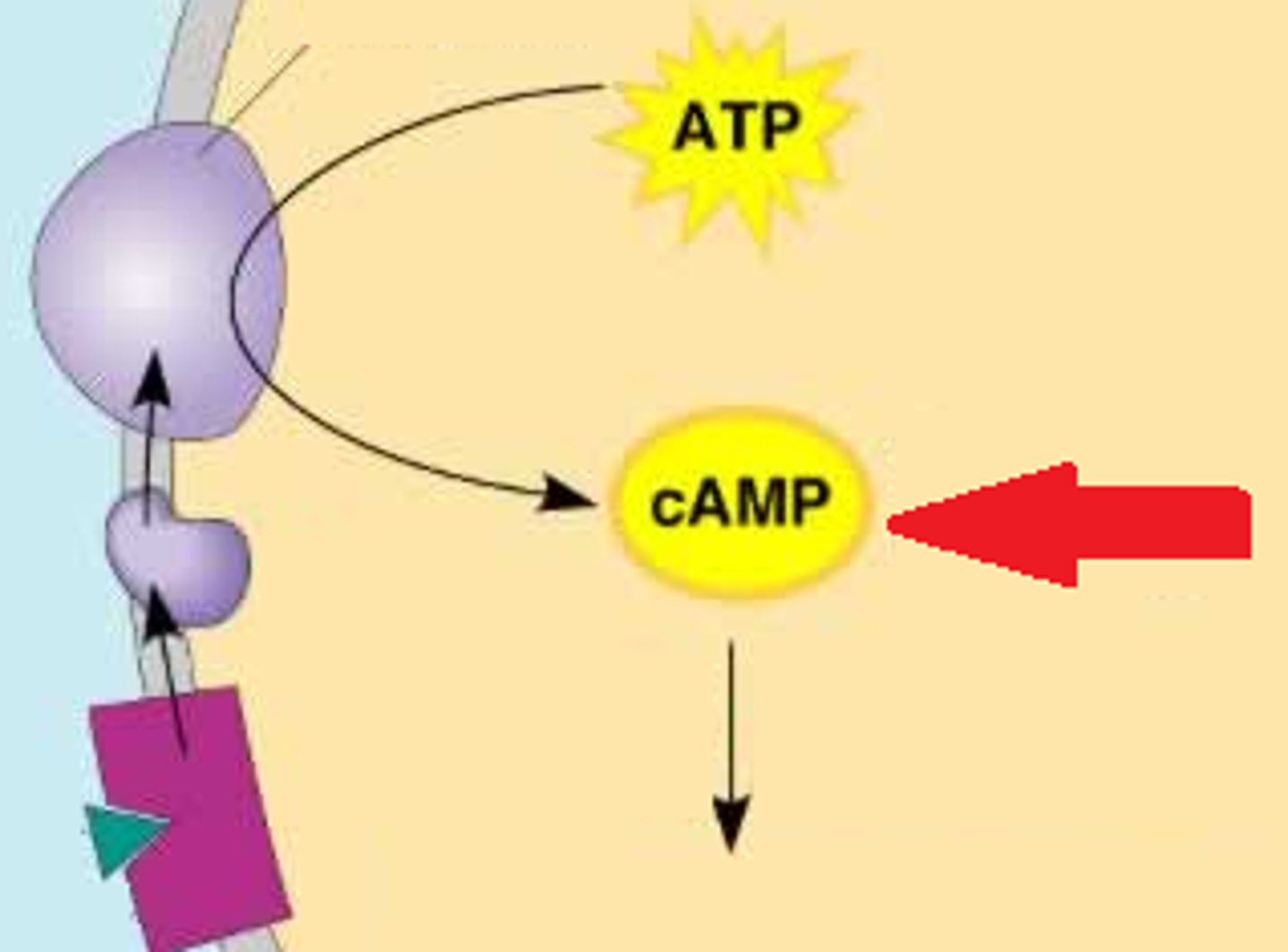
Second messengers
A small, nonprotein, water-soluble molecule or ion, such as calcium ion or cyclic AMP, that relays a signal to a cell's interior in response to a signal received by a signal receptor protein.
Apoptosis
Programmed cell death
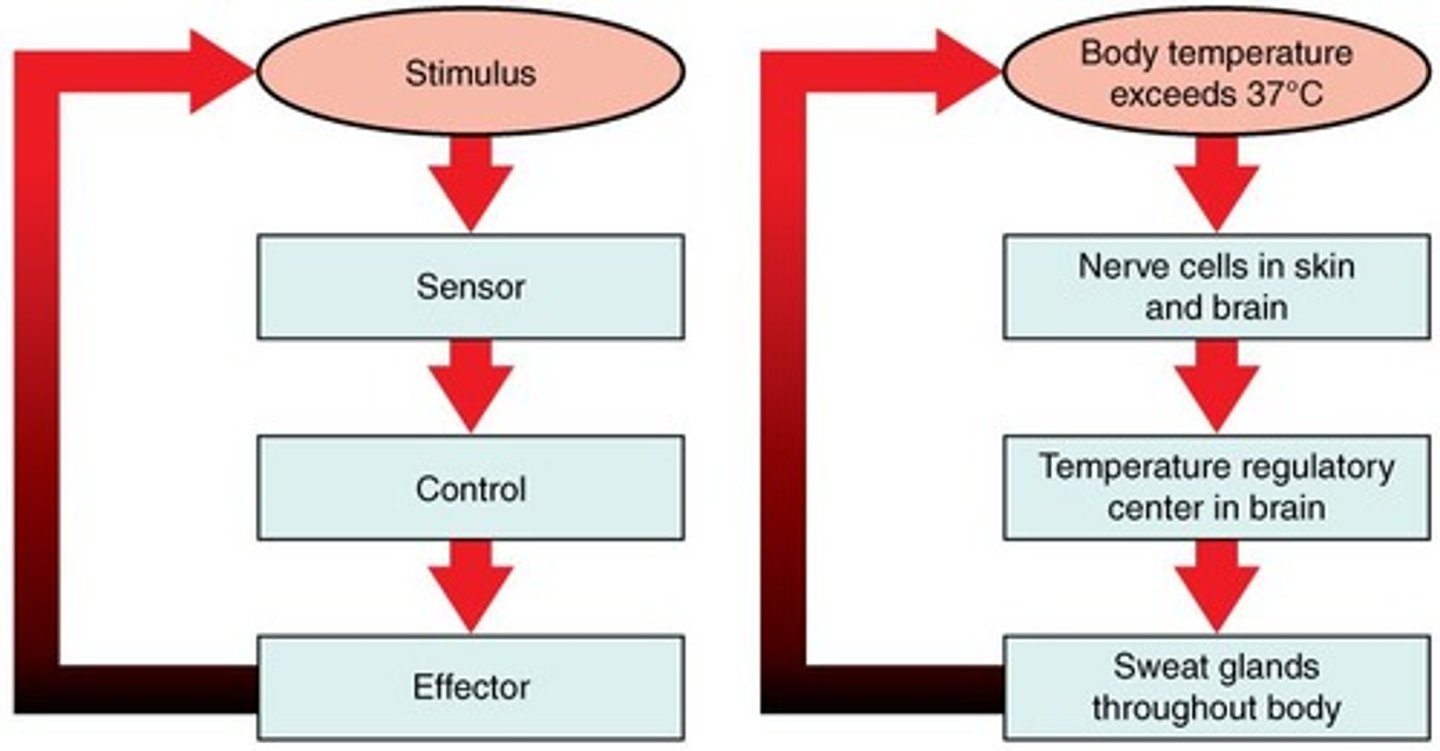
Negative feedback
A primary mechanism of homeostasis, whereby a change in a physiological variable that is being monitored triggers a response that counteracts the initial fluctuation.
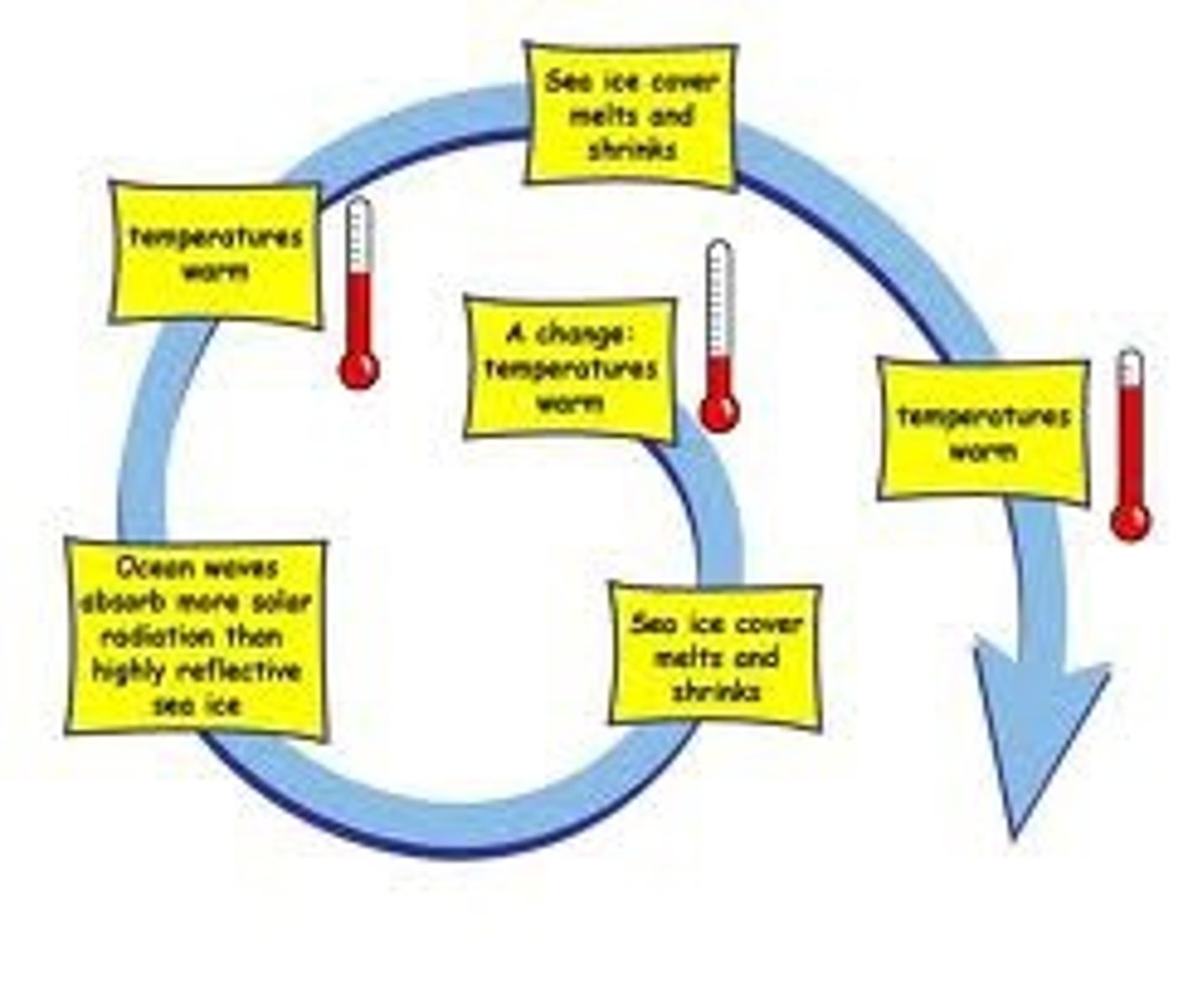
Positive feedback
A physiological control mechanism in which a change in some variable triggers mechanisms that amplify the change.
Cell Cycle
The regular sequence of growth and division that cells undergo
Interphase
Cell grows, performs its normal functions, and prepares for division; consists of G1, S, and G2 phases
G1 phase
The first gap, or growth phase, of the cell cycle, consisting of the portion of interphase before DNA synthesis begins.
S phase
The synthesis phase of the cell cycle; the portion of interphase during which DNA is replicated.
G2 phase
Stage of interphase in which cell duplicates its cytosol and organelles
G1 checkpoint
Checks to see if cell size is adequate; chromosomes replication is successfully completed and checks for DNA errors
G2 checkpoint
Assesses if DNA replication has occurred, go ahead signal triggers mitosis
Checkpoint
A control point in the cell cycle where stop and go-ahead signals can regulate the cycle.

M checkpoint
Checks for chromosomes attached to the spindle (just before anaphase)
Prophase
Chromosomes become visable, nuclear envelop dissolves, spindle forms
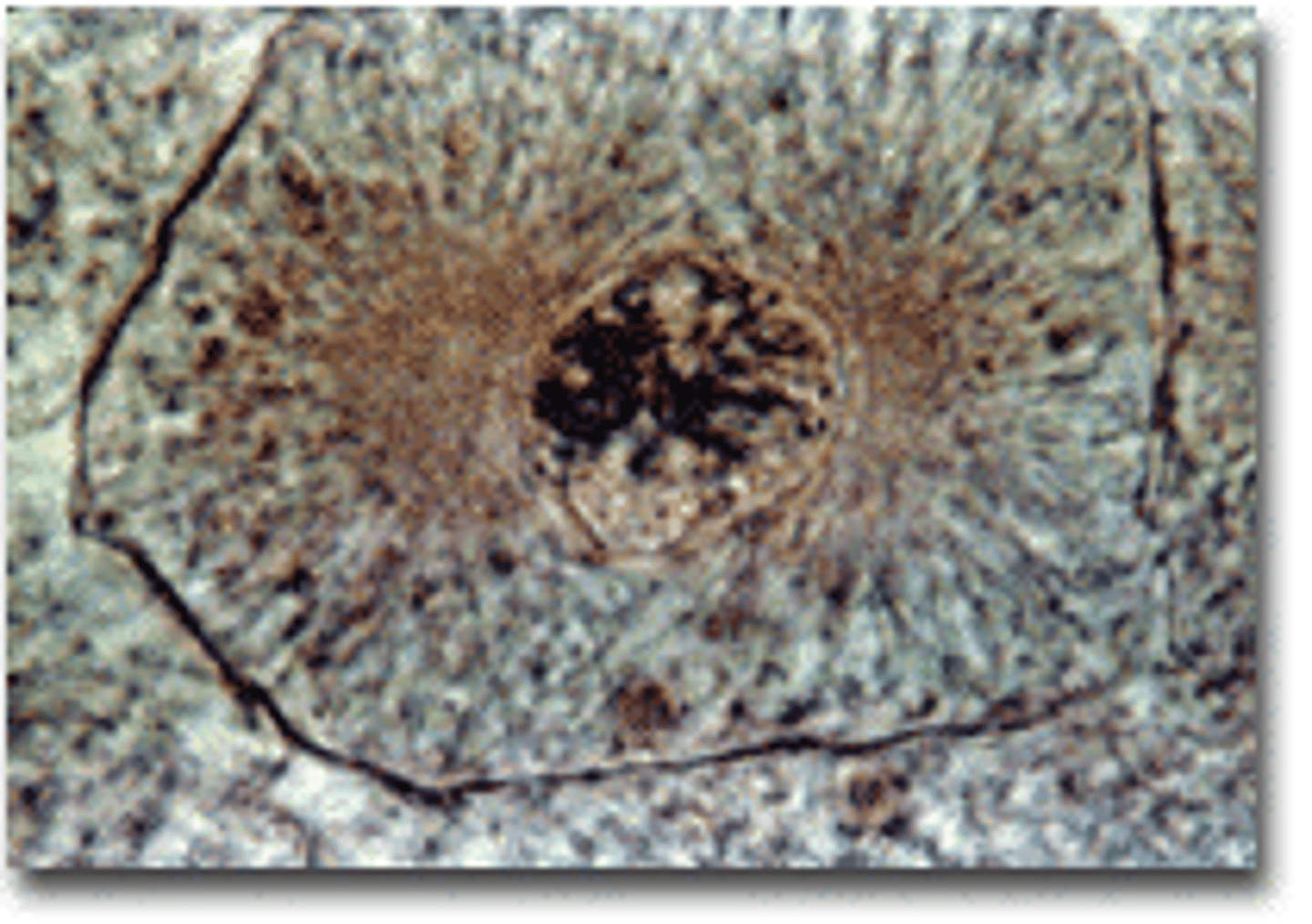
Metaphase
Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell
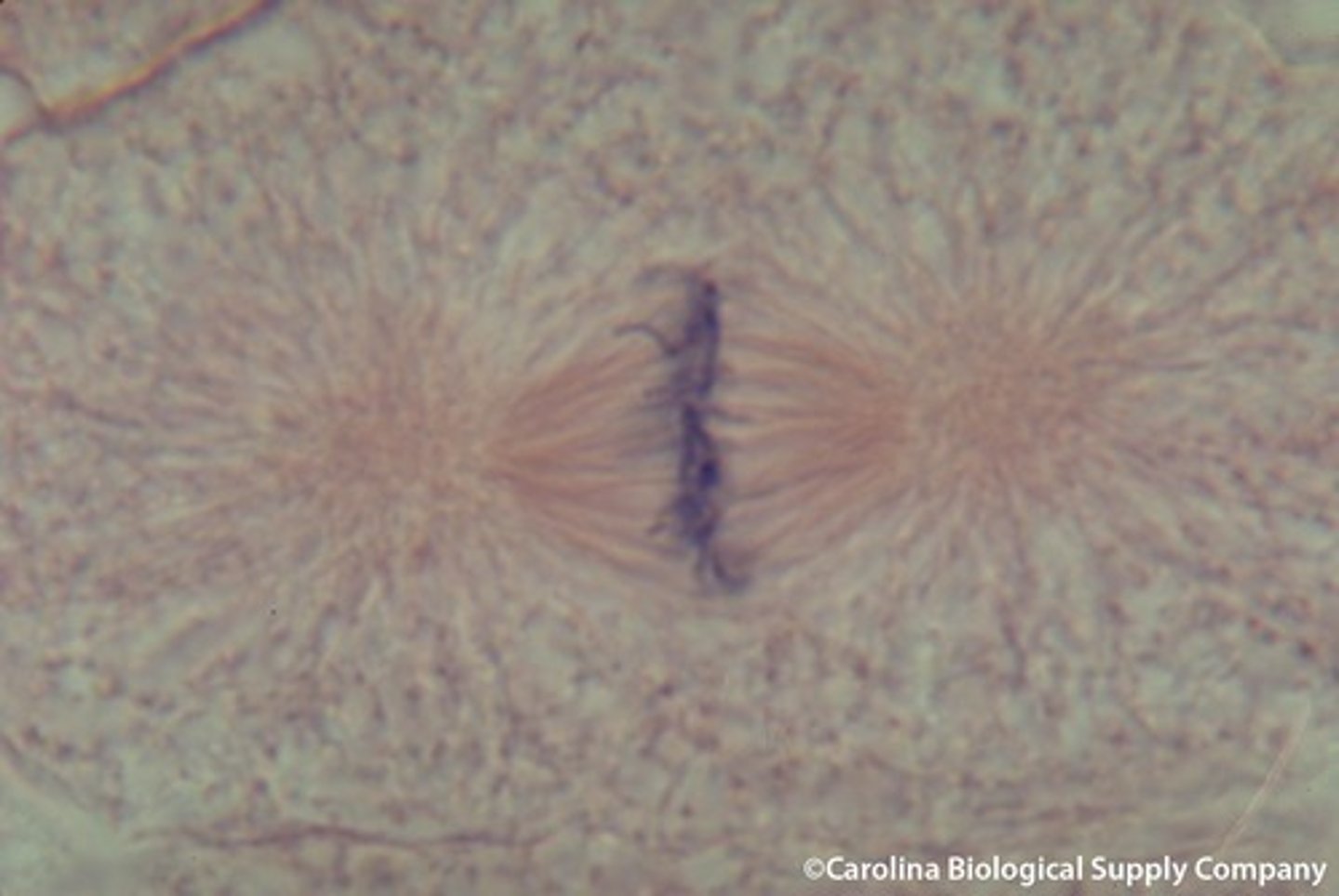
Anaphase
Phase of mitosis in which the chromosomes separate and move to opposite ends of the cell
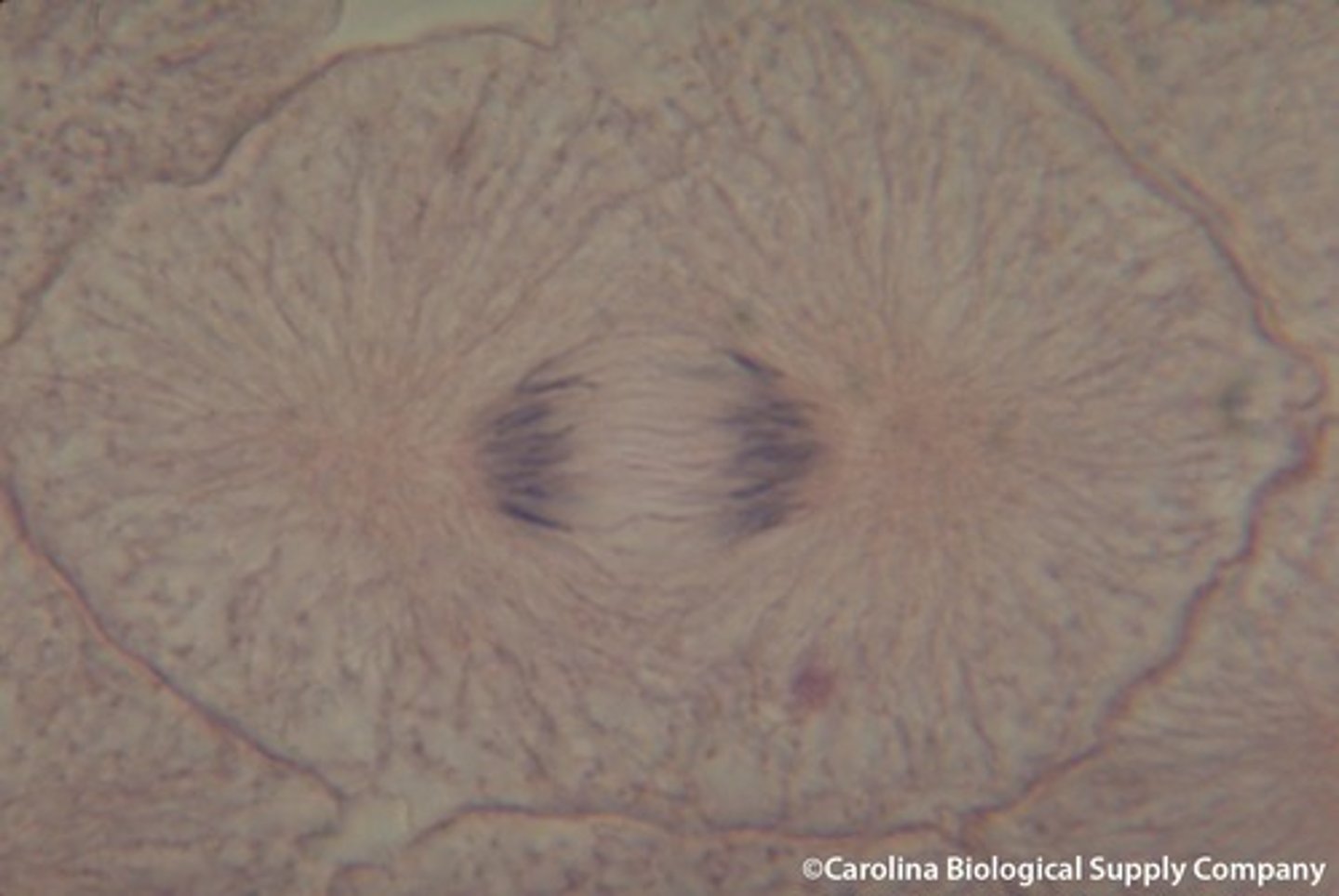
Telophase
phase of mitosis in which the distinct individual chromosomes begin to spread out into a tangle of chromatin
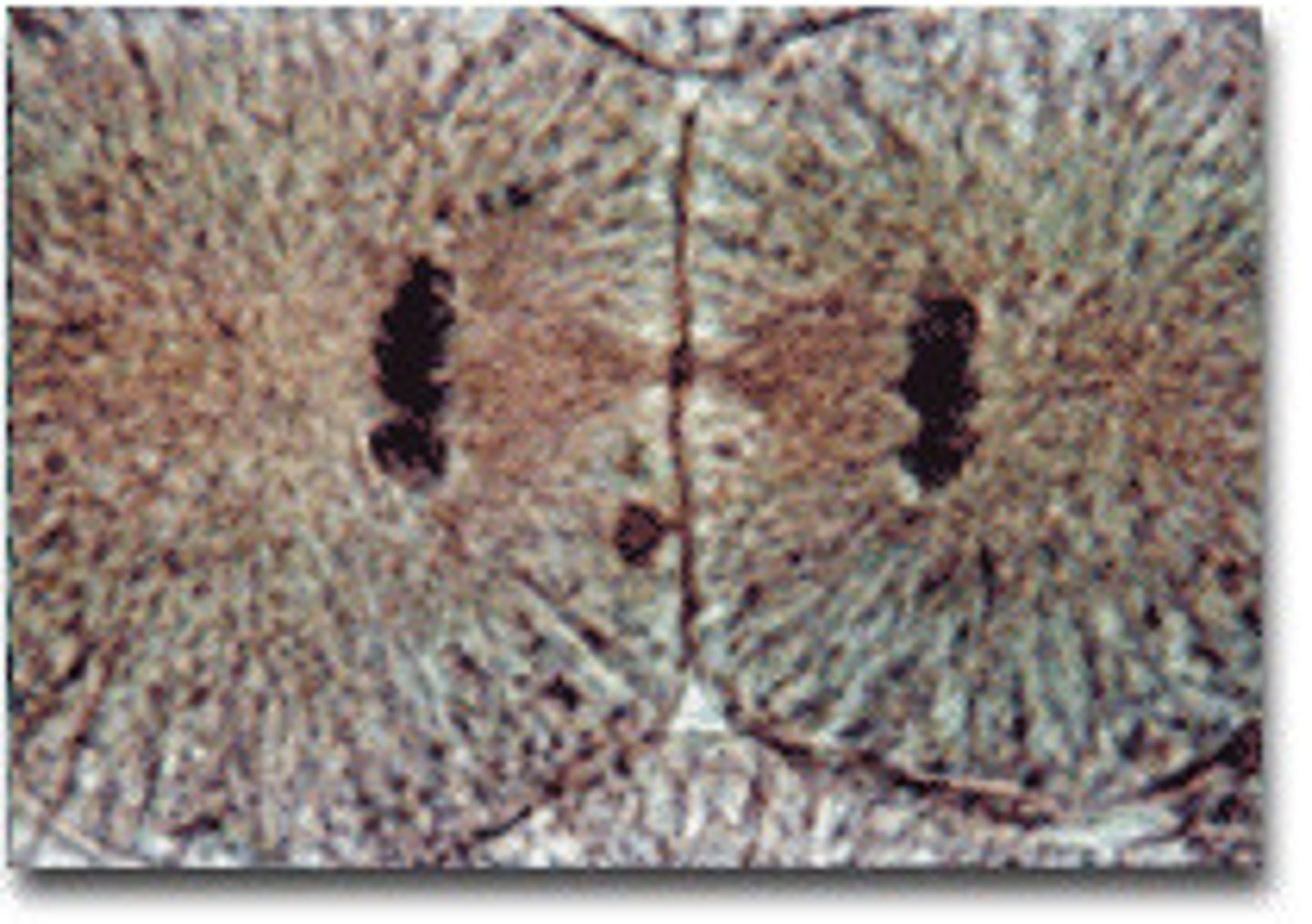
Cytokinesis
Division of the cytoplasm during cell division
Cleavage Furrow
The area of the cell membrane that pinches in and eventually separates the dividing cell
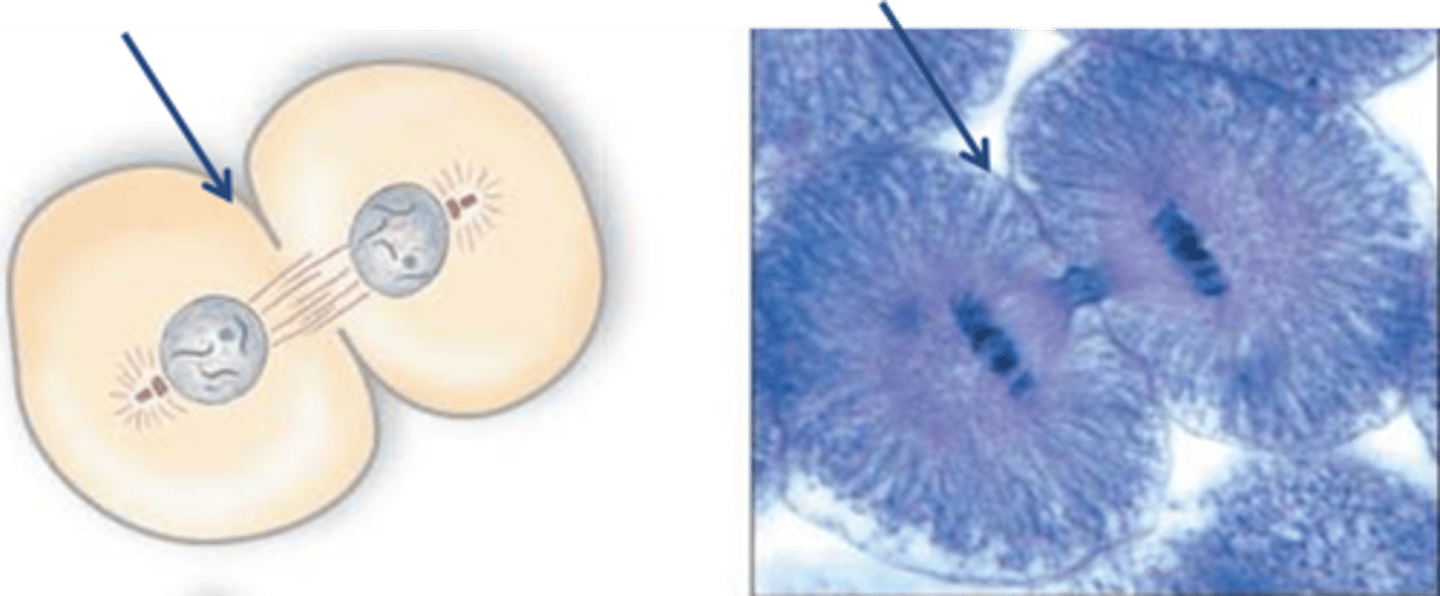
Cell Plate
In a plant cell, midline of dividing cells. Becomes the cell wall eventually.
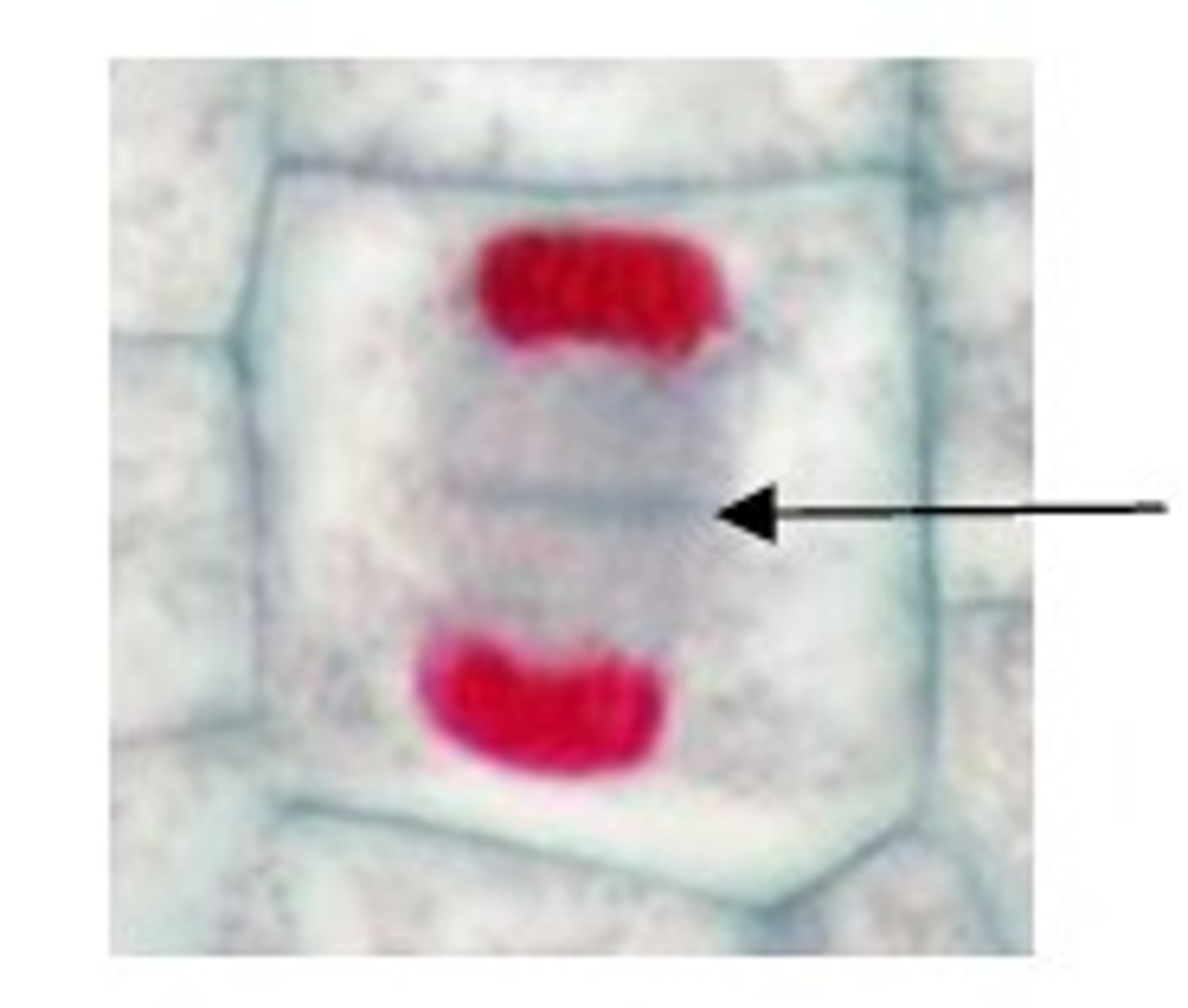
G0 phase
A nondividing state occupied by cells that have left the cell cycle, sometimes reversibly.
Cyclin
A cellular protein that occurs in a cyclically fluctuating concentration and that plays an important role in regulating the cell cycle.
Cyclin-dependent kinase (CDKs)
Enzyme to which cyclin binds during interphase and mitosis, triggering and controlling activities during the cell cycle
Cancer
Results from a variety of mutational events that cause some body cells to grow and divide uncontrollably, damaging the parts of the body around them.
CDK
Cyclin-dependent kinases. A protein kinase that is active only when attached to a particular cyclin. Activity rises and falls depending on the concentration of the cyclin partner.

Thymine
The nucleotide that hydrogen bonds with the nucleotide adenine in DNA.
Beta cells
Pancreatic cells that secrete insulin
Insulin
A protein hormone synthesized in the pancreas that regulates blood sugar levels by facilitating the uptake of glucose into tissues
Glucose transport protein (GLUT)
A type of protein molecule that works with insulin to facilitate glucose uptake by skeletal muscle fibers
Type 2 Diabetes
Diabetes of a form that develops especially in adults and most often obese individuals and that is characterized by high blood glucose resulting from impaired insulin utilization coupled with the body's inability to compensate with increased insulin production.
Growth Factor
A protein secreted by certain body cells that stimulates other cells to divide
Hormone
Chemical messengers, mostly those manufactured by the endocrine glands, that are produced in one tissue and affect another
Mitosis
Process that ensures the transfer of a complete genome from a parent cell to two genetically identical daughter cells.
Part of eukaryotic cell division during which the cell nucleus divides. Plays a role in growth, tissue repair, and asexual reproduction.
Mitotic cyclins
essential proteins that regulate the progression of the cell cycle, particularly during mitosis, by activating cyclin-dependent kinases (Cdks)
Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF)
a crucial protein that stimulates cell growth, proliferation, and differentiation, playing a significant role in various biological processes and therapeutic applications
Receptor Protein
A protein that binds to a specific signal molecule, enabling the cell to respond to the signal molecule
Dependent Variable
The outcome factor; the variable that may change in response to manipulations of the independent variable.
Independent Variable
The experimental factor that is manipulated; the variable whose effect is being studied.
% Change
((New value - old value)/old value) X 100