PPQs ETC
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
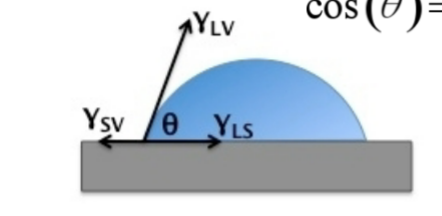
Sketch a droplet of water on a surface and label all the surface tensions
What 3 inputs are needed to specify a molecule in ADF
Structure, Charge and Multiplicity
What 3 specifications are needed for an ADF calculation
Basis set (TZP etc), the functional (b3lyp etc) and the type of calculation (geometry etc)
How would you modify an ADF input to calculate different species of a molecule
Change the charge and multiplicity (e.g. for mono-anionic change 00 to -1 1 (unrestricted) or -1 0 (restricted))`
State the importance of mapping 1-1 between ground state density and external potential
The external potential along with the total number of electrons which is obtained from the density fully specifies the system Hamiltonian
Surface area and volume of a sphere
A=4pi r², V=4/3pi r³
Surface area and volume of a cylinder
A=2pirL+2pi r² , V=pi r² L
Outline the idea behind Kohn sham approach to DFT
You want to calculate the total energy as a function of the density but the kinetic energy is hard to formulate. The Kohn Sham approach consists of constructing the density from a non-interacting Slater orbital evolving in an effective potential in such a way that the density is the same as that of the real system, then the kinetic energy term is taken, everything unknown is included in the exchange-correlation funcitonal and the variational principle is used to minimize the energy
Why is it harder to characterise transition metal complexes with KS DFT compared to other compounds
At higher values of the density gradient in transition metals, the GGA functionals diverge from one another, while at lower values (which are more common for closed shell organic systems) the exchange enhancement factor takes on similar values regardless of the formulation of the functional used
How would you characterise Jahn-Teller distortion using KS DFT
Within the fractional occupation scheme, the 2E state can be optimised in D3 symmetry, employing a convenient XC functional and a large enough basis set. Then you can optimise the states of lower symmetry and allow you to estimate the Jahn-Teller stabilisation energy and describing the structural variation
Could there be any complications with the Jahn-Teller calculations
No because the target states are within the same spin state manifolds
Explain whether the surface becomes more hydrophobic or hydrophilic when the metal-water surface tension increases
Using Youngs equation:

by increasing the LS surface tension, theta gets larger, therefore the material becomes more hydrophobic
Calculate the chiral angle of a CNT

Given the length of C-C bond, calculate the diameter of a CNT

Why do quantum dots have enhanced quantum efficiency in their fluorescence compared to bulk
Pauli exclusion principle, because their size is small, their momentum is large so the transitions between density of states has less restriction on momentum conservation, allowing larger quantum efficiency in electron transitions and relaxations
What 2 major contributions to the quantum dot band gap energy and what causes them + size dependency
Quantum confinement energy originating from the reduced size and is inversely proportional to x² and increases band gap energy.
Coulomb energy originating from the reduced size and inversely proportional to x and reduces band gap energy
How does root growth and tip growth for CNT occur and what does it affect
root growth occurs when the catalyst stays on the substrate and forms carbon species near the substrate and is caused by a stronger attractive interaction between the catalyst and substrate. Tip of CNT is clean no metal. Tip growth occurs when the catalyst is lifted up and stays on the tip of CNT and is due to weak interaction between the catalyst and substrate. Tip contains metal
What vapor pressure and viscosity level is preferred for nanofibers and which for nanocups and why
for nanofibres, low vapor pressure and high viscosity as nanofibres need a lower internal pressure to stop the solvent leaving pores as it evaporates and viscosity to hold together better during electrospinning
For nanocups, opposite
HF energy

KS energy
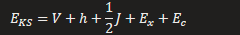
Discuss the idea of system/property/method triumvirate in DFT methdology
You need appropriate method which is selected based on the specific system and desired properties
How does a Boron centre act as a charge traffic node
It has an unoccupied pz orbital which allows it to sumultaneously accomodate and donate charge density by both resonance and induction (can recieve and donate electrons through sigma and pi orbitals, allowing for dynamic control of electron delocalization in ring system) the core of a boron bonded with 2 carbons to form a triangle can host pi electron delocalisation
How can you switch on and off aromaticity in Boroirene systems
the unoccupied pz orbital allows the borene to interact with the pi system of a double bond and a lone pair at the same time. Depending on which interaction dominates shifts the aromaticity. More Boryl groups/lone pair donation means aromaticity on
Quaternization blocking lone pair donation reduces aromaticity
Discuss the possible applications of reverse-back donation in transition metal complexes
Reverse-back donation involves electron donation from ligands to metal centers, affecting the reactivity and stability of transition metal complexes and is used in designing catalysts and understanding bonding interactions.
Explain Spin crossover phenomena
Spin-Crossover refers to the reversible transition between high spin and low spin states in certain metal complexes, influenced by external factors like temp and pressure, affecting structure and magnetic properties
(iron bypyradine) why is the curvature of the totally symmetrical breathing mode larger for excited quintet states than the singlet states
Anti-bonding eg* orbitals are populated in the high spin states, the Fe-N bonds are weakened thus making the force constants of the high spin excited states smaller hence the curvature
(iron bypyradine) What causes the relaxation from high spin to low spin and make an expression for the relaxation constant
Caused by tunneling.

Explain why hybrid functionals can prove useful when characterising spin crossover systems
due to the compact d space of spin crossover transition metals, it is important to manage self-interaction error and the inherent multireference character which XC functionals that incorporate exact exchange can deal with
Sketch and describe the structure of a TiO2 based dye sensitised solar cell and explain how the photoexcited electron-hole pairs are formed and how charges are moved in and out of the cell
(transparent electrode with tio2 balls attached to it with dye on them, then Iodine cycle then other electrode) Photo excited electrons and holes are formed on the dyd molecules after light is absorbed, these electrons are transferred to the conduction band of tio2 and are collected by the electrode and carried out of the cell. used electrons are returned to the other electrode and reduce I3- to 3I-, within the cell the I- travel from the other electrode to the dye molecules and are oxidised with the holes I- to I3-
Why is water not used as a solvent in dye sensitised solar cells
The redox potential of water is too low and the redox produces H2 and O2 gases which will cause the electrolyte to leak
When making TiO2 nanotubes, describe the cathode half cell reaction and explain the function of low concentrations of water and NH4F
2H2O+2e→H2+2OH-
The NH4F is used to dissolve the TiO2 to form the porous structure while H2O offers oxygen to oxidise the Ti
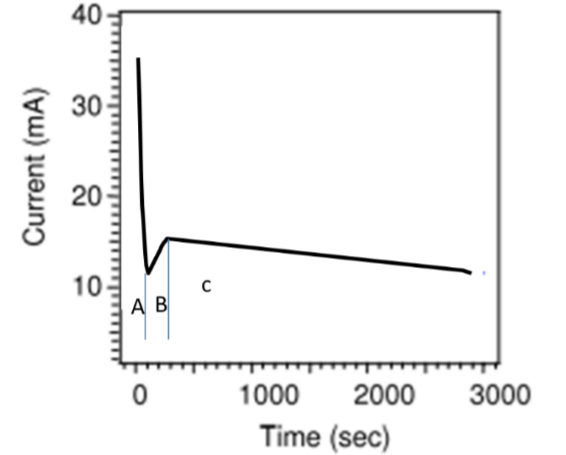
Label 3 stages on a anodisation current curve and explain what happens at each
At A, the current decreases rapidly due to the build up of the oxide
At B, the electric potential becomes stronger at the surface and attracts the F- ions which causes the dissolving of the TiO2 and the formation of the porous structure
At C the equilibrium between the oxidation and dissolution is equal. As the nanotubes get longer, the current density decreases