Benign and Malignant Uterine Pathology
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
What are some indications for an ultrasound examination of the uterus?
Uterine enlargement, pelvic pain, irregular or postmenopausal bleeding, palpable pelvic mass, amenorrhea or dysmenorrhea, and infertility.
Also called an epithelial inclusion cyst, it forms in response to inflammation of an endocervical gland and is found in the cervix.
Nabothian cyst
How do Nabothian cysts appear on ultrasound?
Anechoic with enhanced sound transmission in the cervix.
what size range are nabothian cyst?
3mm-3cm
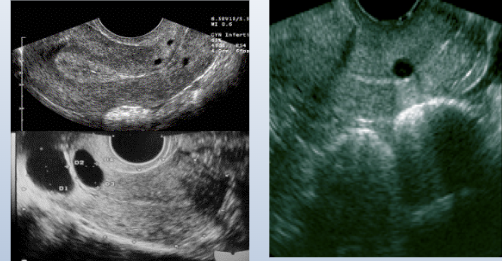
what do these images show?
nabothian cyst
In whom are cervical polyps more common?
Multigravidas and patients in their 40s and 50s.
What is the most common benign cervical neoplasm?
Cervical polyps.
How might cervical polyps appear on ultrasound?
Small echogenic areas in the cervix.
What is a common clinical presentation of cervical polyps?
Irregular bleeding - asymptomatic - chronic inflammation
cervical polyps may be?
pedunculated, projecting out of the cervix, broad-based and may or may not app in us
what arises from hyperplastic protrusion of epithelium of Endo cervix?
benign conditions
what benign condition occurs in cx 3-8% of the time?
cervical myoma (fibroid)
what is another name for cervical myoma?
fibroid
what may cervical myoma (fibroid) cause?
dyspareunia (sexual act pain), dysuria, cervical obstruction, prolapse, bleeding, obstructed labor
how may the cx appear with a cervical myoma?
bulky, distorted, enlarged
what are some treatment for a cervical myoma?
resection, hysterectomy if warranted
what may be pedunculated and prolapsed into the vaginal canal?
myoma
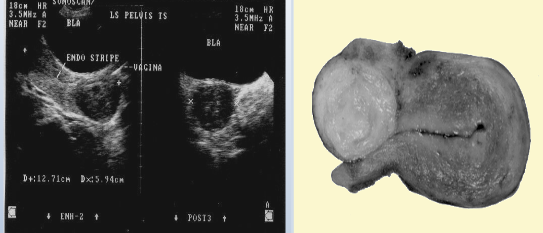
what does this image show?
cervical myoma
What are potential causes of cervical stenosis?
Radiation therapy, previous cone biopsy, postmenopausal cervical atrophy, chronic infection, laser or cryosurgery, or cervical carcinoma.
what may occur with postmenopausal patients with cervical stenosis?
asymptomatic, produce distended fluid-filled ut, accumulation of hydrometra; pyometra; hematometra
what may occur with premenopausal patients with cervical stenosis?
abn bleeding, oligomenorrhea, amenorrhea, cramping, dysmenorrhea, infertility
List risk factors for cervical carcinoma.
Early sexual encounters, multiple sexual partners, infection by STD or a partner with an STD, human papilloma virus (HPV), or exposure to DES.
What is the most common type of cervical carcinoma?
Squamous cell carcinoma.
what is via lymphatic system of pelvis?
metastases
Describe Stage 1 of cervical carcinoma
Confined to the cervix, 80-90% survival rate, five year
Describe Stage 2 of cervical carcinoma
Spread to the vagina, upper cervix, and parametrium.
Describe Stage 3 of cervical carcinoma
Spread to the lower portion of the vagina and to the pelvic wall.
Describe Stage 4 of cervical carcinoma
Extends beyond the true pelvis, bladder and/or rectal involvement, metastases (mets) to distant organs (lung, bone, and liver).
List some signs and symptoms of cervical carcinoma.
Abnormal Pap smear(1st sign), vaginal discharge, intermittent bleeding (especially after intercourse).
List some signs and symptoms of more advanced stages of cervical carcinoma.
bladder irritability, back pain, and ureteral obstruction (always in advanced cases).
what ages is cervical cancer most commonly diagnosed?
25-45yrs
what is the most common cause of death in cervical carcinoma?
uremia
what condition involves abnormally high levels of waste products in the blood, occurs when the kidneys no longer filter properly, in the final stage of chronic kidney disease?
uremia
Symptoms include fatigue, nausea, loss of appetite, a metallic taste in the mouth, and mental confusion. Treatment includes dialysis or a kidney transplant.
uremia
List some treatment options that are dependant on the stage of cervical carcinoma.
Cone biopsy (younger women), radical hysterectomy (older), radiation therapy, and if mets then chemotherapy.
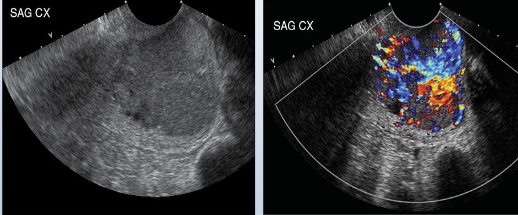
what does this image show?
cervical carcinoma, enlarged, hypoechoic, decrease transmission, increase vascularity
what may be some differential diagnoses for cervical carcinoma?
leiomyoma in cx, endometrial carcinoma inv cx, endometrial polyps prolapsed in vag
What is translabial or transperineal sonography useful for?
Useful when transvaginal US is contraindicated, 5-7.5 MHZ
What are some uses for Sonohysterography?
delineates Endo cav, evaluation of endometrial polyps,fibriods,and endometrial hyperplasia
25-30ml of sterile saline in endometrial cavity?
sonohysterography
What condition can follow prolonged endogenous and exogenous estrogenic stimulation?
Endometrial Hyperplasia
what may be a precursor of endometrial cancer?
endometrial hyperplasia
what are sono findings of endometrial hyperplasia?
ab thickening of endometrium
what do majority of women with postmenopausal bleeding experience?
endometrial atrophy
what is the measurement of an atrophic endometrium on a transvaginal sonography?
thin, <5mm
If postmenopausal patient has irregular bleeding and thickened endometrium, may warrant?
sonohysterography procedure and/or endometrial biopsy
what develops from unopposed estrogen stimulation?
hyperplasia
how much will a Endo in a premenopausal women with hyperplasia measure?
< 14mm (double nl)
when is the optimal time period for this assessment in women still having menses?
day 6-10, after bleeding, before endo is stimulated again
in asym
What are some potential sonographic findings that may indicate endometritis?
Endometrium appears prominent, irregular, or both, with a small amount of endometrial fluid and pus may be demonstrated in cul-de-sac as echogenic particles or debris.
in postmenopausal women that are asymptomatic what is the upper limit of normal measurement of en
In what patients is Asherman's Syndrome found?
Women with posttraumatic or postsurgical histories
What is the most common gynecologic malignancy in North America?
Endometrial Carcinoma
List risk factors for endometrial carcinoma.
Obesity, diabetes, high blood pressure, short in height, Jewish, African American women, age (postmenopausal), or estrogen use after menopause.
What are some signs and symptoms of Endometrial Carcinoma?
Bleeding or discharge after menopause and pain
What are some sonographic findings of Endometrial Carcinoma?
Thickened endometrium, prominent endometrial complex and enlarged uterus with irregular areas of low-level echoes.
What are some components in treating Endometrial Carcinoma?
Complete hysterectomy with bilateral oophorectomy, lymphadenectomy, pre or post operative radiation therapy and chemotherapy.
What effects does Tamoxifen have on the endometrium?
May lead to development of polyps, endometrial cancer, myoma growth
What is adenomyosis?
Endometrial glands and stroma grow into the myometrium
What is the ultrasound appearance of adenomyosis?
Enlarged uterus of normal or decreased echogenicity
What are some sonographic findings of adenomyosis?
Diffuse uterine enlargement, thickening of posterior myometrium, indistinct border between endometrium and myometrium, and myometrial cysts
What is a leiomyoma?
Benign muscle tumors of the uterus.
In relation to the uterine wall, how can leiomyomas be classified?
Intramural, subserosal, submucosal, or pedunculated.
What happens to Fibroids after menopause?
Fibroids tend to shrink
What are the most common causes of Uterine Calcifications?
Myomas
What are some sonographic findings that show Arteriovenous Malformations?
Serpiginous, anechoic structures seen within the pelvis and may be florid-colored mosaic pattern with apparent flow reversals and areas of color aliasing