midterm 1 reaction reagents
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
reagents for nitration
HNO3, H2SO4
reagents and purpose for wolff kishner
NaOH, (NH2)2, heat ; purpose is to eliminate a carbonyl’s oxygen
how to bypass the drawbacks of FC alkylation
do FC acylation then wolff kishner to eliminate carbonyl’s oxygen
reagents for sulfonation
H2SO4, heat —> product has an added SO3H
reagents for iodination
I2, H2O2, H+
reagents to change NO2 to NH2
H2, Pd/C
reagents to change R group to carboxylic acid
H2CrO4
benzene to cyclohexane reagents
H2, Ni
reagents for wolff kishner (completely get rid of carbonyl’s oxygen)
(NH2)2, NaOH
reagents to change Br to R group (aka Suzuki rxn)
R-B-(OH)2, Pd, base
reagents to change NH2 to N≡N (before sandmeyer can occur)
NaNO2, HCl
what occurs when a benzene reacts with a diazonium ion
azo coupling occurs and an azo compound (-N=N- functional group in between the two benzene rings) is formed
reagents for ozonolysis (reduction)
1.) O3, -78C 2.)(CH3)2S (aka dimethylsulfide)
reagents to reduce acyl chloride into aldehyde
1.) LTBA 2.) H2O
reagents to reduce ester into aldehyde
1.) DIBAL, -78C 2.) H2O
reagent for secondary OH to ketone
H2CrO4
reagent for primary OH to carboxylic acid
H2CrO4
reagent for primary OH to aldehyde
PCC
reagents for primary alcohol to carboxylic acid
H2CrO4
reagents for aldehydes to primary alcohols and ketones to secondary alcohol (and C≡N to single bond)
H2, raney ni
reagent for acetal breakdown/reversing cyclic acetal into original cyclohexane-ketone structure)
an acid (eg. HCl, H3O+)
rank the reducing agents (via providing hydrides) for carbonyl derivatives from strongest to weakest
LAH (aka LiAlH4), NaBH4, DIBAL, LTBA (aka LiAlH(Ot-Bu)3)
what are the reversible nucleophiles learned so far
-CN, H2O, HOR
examples of irreversible nucleophiles learned
hydride ion (H-), carbanion (CH3-)
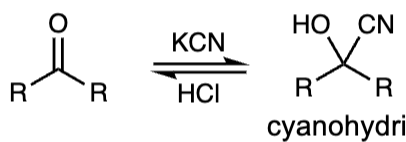
reagents to convert ketone to cyanohydrin
KCN, HCl
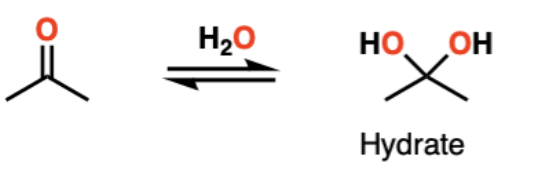
reagents to convert ketone into a hydrate
H2O (with either acid or base catalyst)
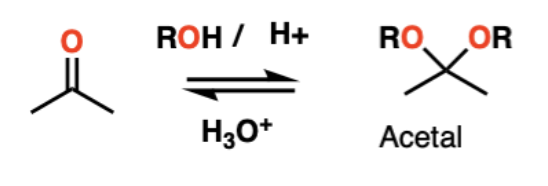
reagents to convert a ketone into an acetal
2 eq of HOR, H+ catalyst
reagents to make a grignard reagent
Mg0, EtO2, 35C
organolithium reagents (strongest of organometallic reagents; changes halogen substituent to Li)
R-Li
order of substituents for pre sandmeyer to end of sandmeyer
nitrate (with HNO3, H2SO4) then change to NH2 (via H2, Pd/C), change to diazonium salt (via NaNO2, HCl), then change to halide (via CuX)
reagents to change NH2 to diazonium salt
NaNO2, H-X
list hydrides from strongest to weakest with their uses
LiAlH₄ (LAH): reduces everything to alcohol
NaBH4: mild, reduces aldehydes and ketones to alcohols
DIBAL: reduces esters to aldehydes
LTBA: weak, reduces acyl chlorides to aldehydes
grignard reagents (middle strength of organometallics)
R-MgX
gilman reagents (weakest strength of organometallics; replaces halogen with R group)
R2CuLi
reagents for suzuki (couples R groups)
RB(OR2), L2Pd, base
key feature of generation of electrophile for bromination of benzene
generate FeBr5
key feature of generation of electrophile for nitration of benzene
make HNO3 have water LG to leave and generate +NO2
key feature of generation of electrophile for sulfonation of benzene
use to H2SO4 to generate H2O good LG to leave and generate +SO3H
key feature of generation of electrophile for FC acylation
Cl that never quits and generates acylium ion R+C(O)
key feature of generation of electrophile for FC alkylation
Cl that never quits and generates R+
rank organometallics from strongest to weakest
1.) organolithium (R-Li)
2.) grignard (R-Mg-X)
3.) organocuprates (R2CuLi)