Scientific Method
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Scientific Method
A series of steps that scientists use to answer questions and solve problems

Problem
Always in form of a question; the question we are trying to answer by doing the experiment. Requires research.

Hypothesis
An educated statement that is testable. It can be written in a "IF....,then" statement.

Data and Results
A summary of the data you have collected (graphs, tables, charts, photos, etc.); all your observations from the experiment

Conclusion
The answer to your question; a summary of what you have learned from an experiment; support or refute the hypothesis.

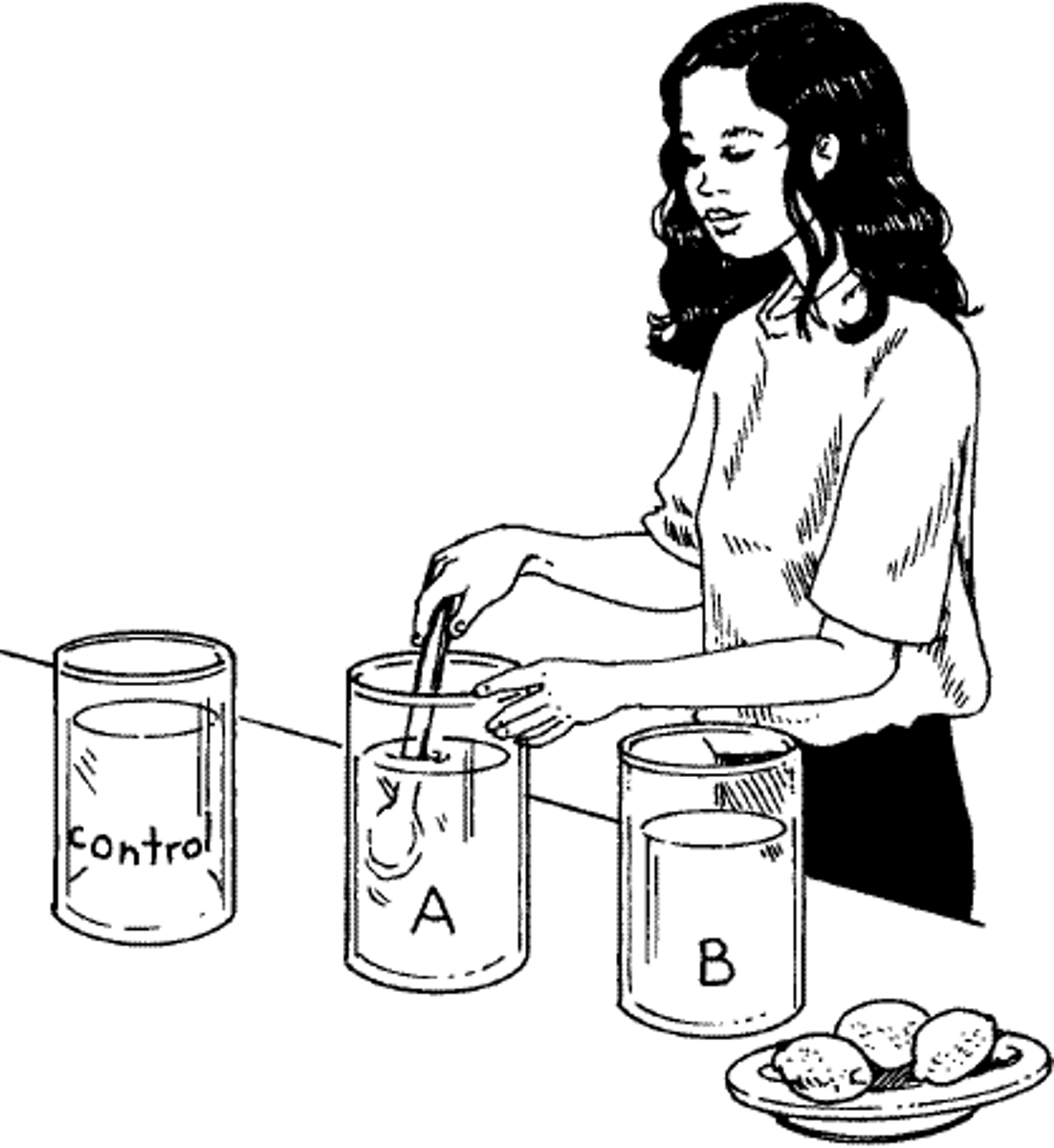
Control Group
All conditions are kept normal; used as a COMPARISON. The groupd that doesn't receive the treatment or I.V.

Independent Variable (I.V.)
Factor in an experiment that a scientist purposely changes; the cause. It is what you are testing or manipulating.

Dependent Variable (D.V.)
The factor that changes (measured) as a result of the experiment; the effect. It is what you are measuring.
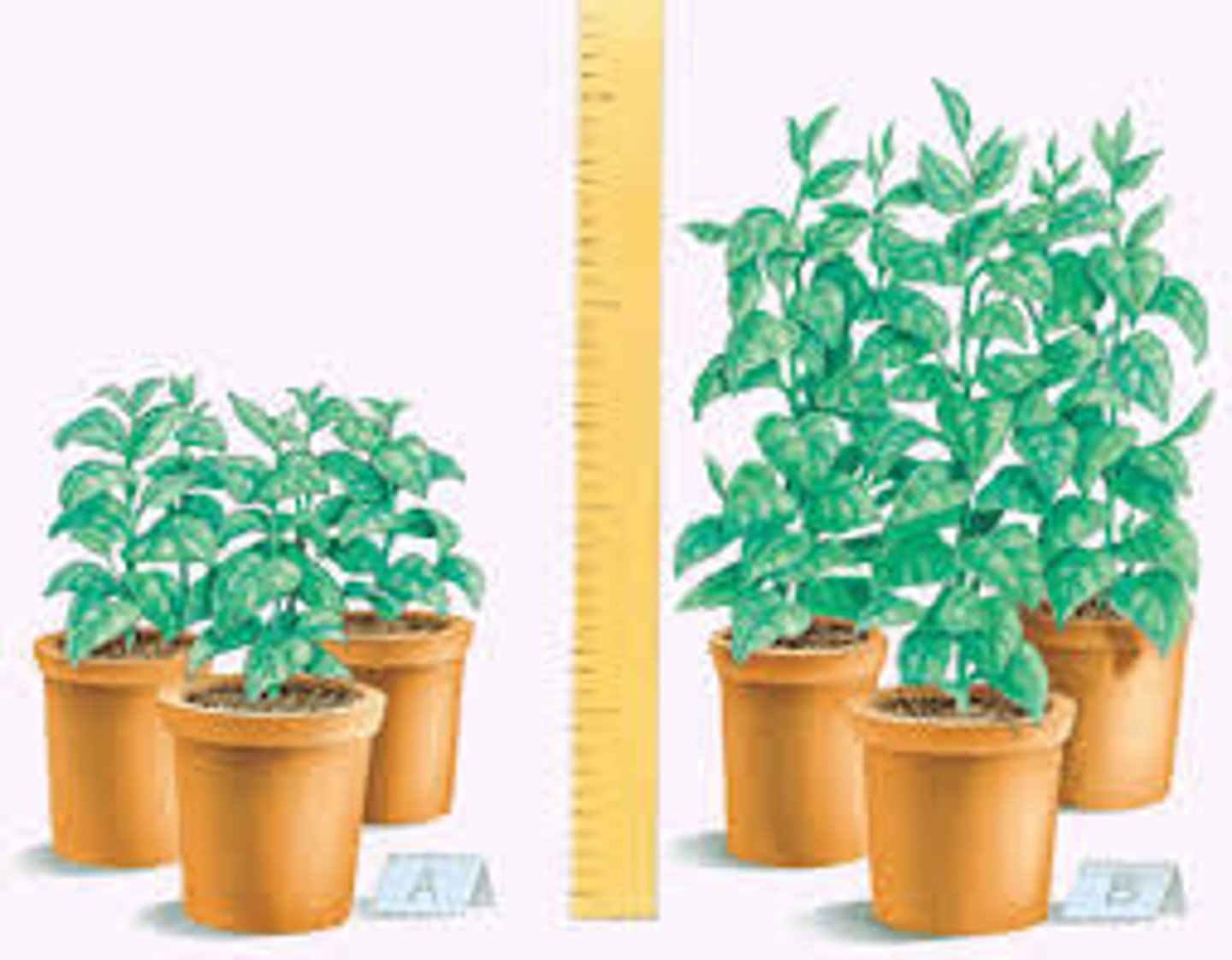

Experiments
Test your hypothesis. You may need to do this step more than once to see if the results are the same each time.
choose materials and lab equipment.

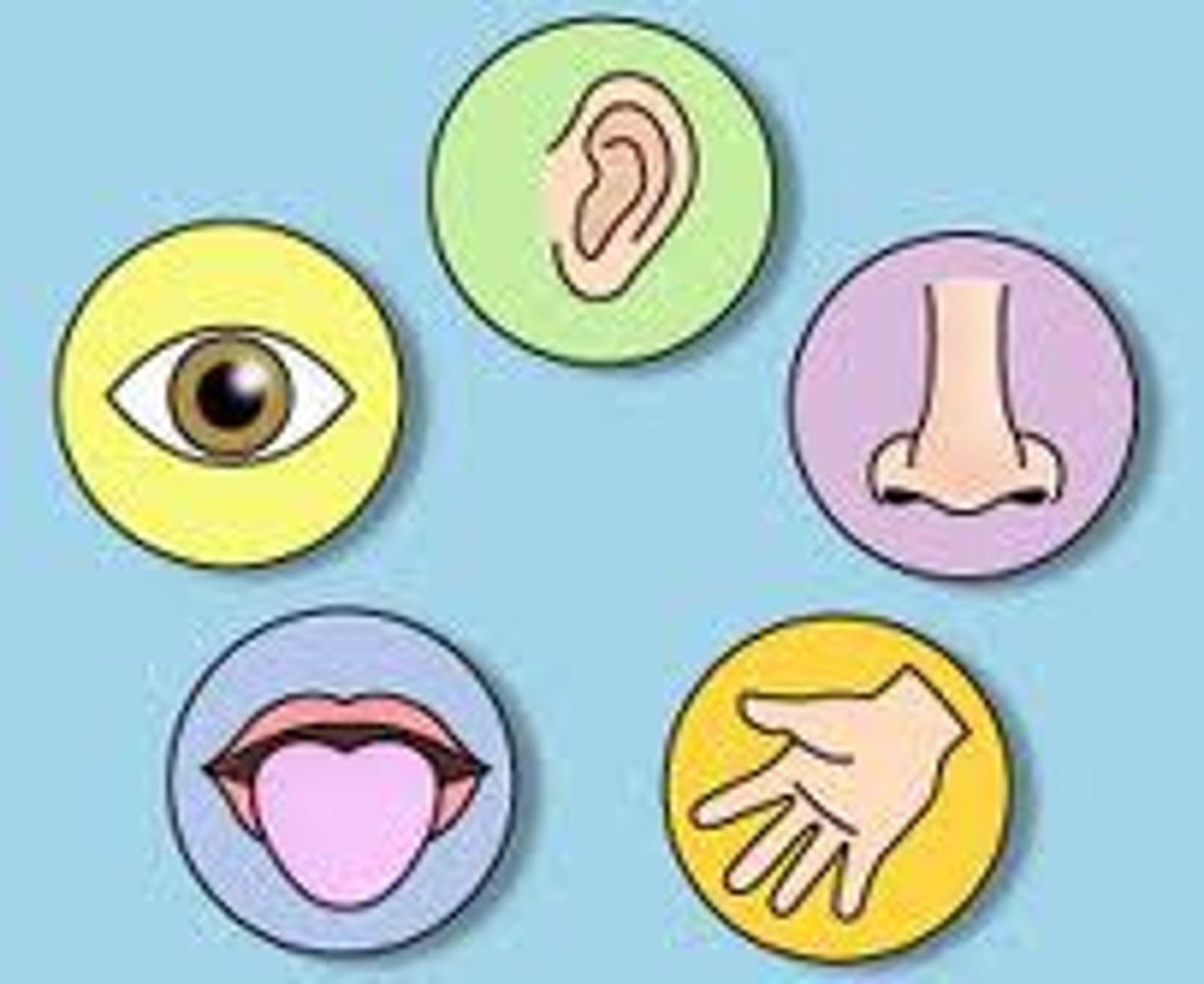
Observation
Information obtained through the five senses.
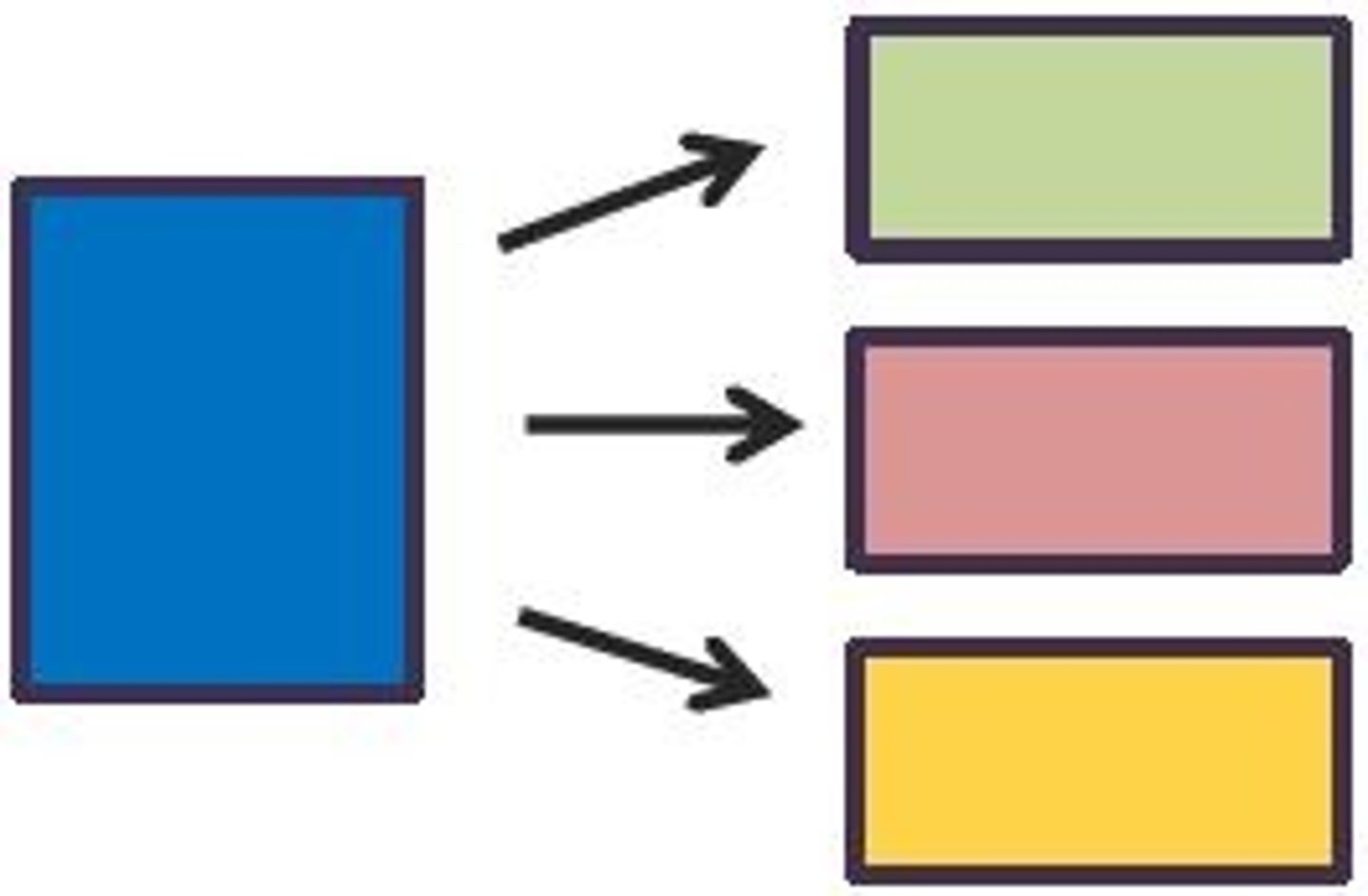
Cause and Effect
The reason something happens and the result of it happening.
Inference
A conclusion reached on the basis of evidence and reasoning

Validity
Factually sound or accepted.

Reliability
Consistently correct.

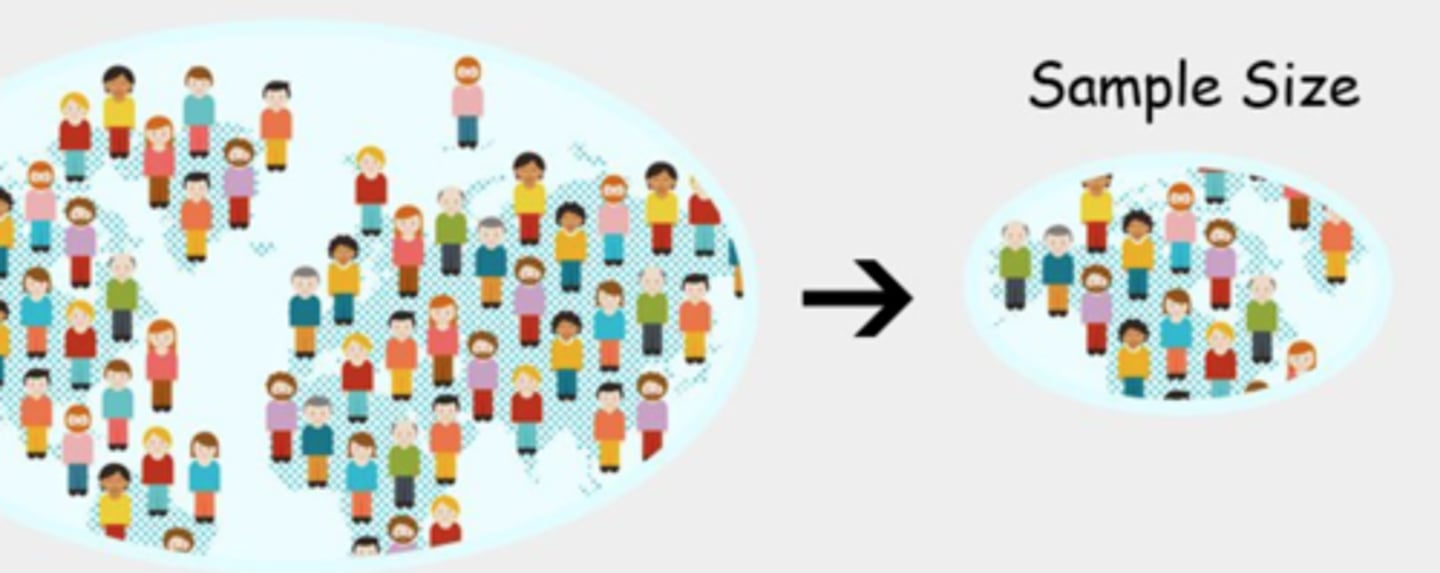
Sample size
The number of subjects used in an experiment or study. Generally, the larger the better.
Test subject
The object of study or observation in an experiment

Repeating an experiment to see if the same results are obtained
A way to increase the validity of an experiment.

Increasing the number of test subjects.
A way to increase the validity of an experiment.
Have other scientist check your experiment and results.
A way to increase the validity of an experiment.
refute
disprove
