Amino acids
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
structures/abbreviations+properties
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Glycine
Gly-G-Hydrophobic and usually resides in forbidden parts of protein structures e.g turns in structures
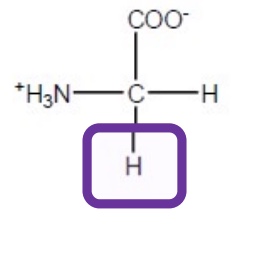
Alanine
Ala-A-hydrophobic
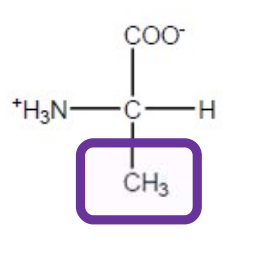
Valine
Val-V-hydrophobic and aliphatic i.e non polar,not charged and not aromatic
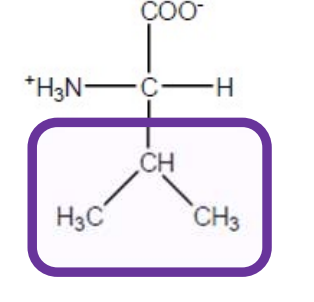
Isoleucine
Ile-I-hydrophobic and aliphatic
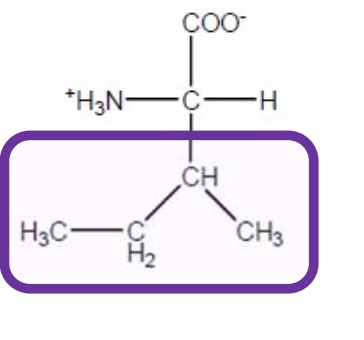
Leucine
Leu-L-hydrophobic and aliphatic
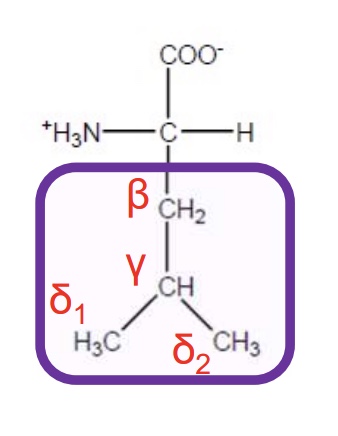
Methionine
Met-M-hydrophobic-starts protein chain and 1 of the 2 sulphur containing amino acids but S attached to a methyl group so limited role in function
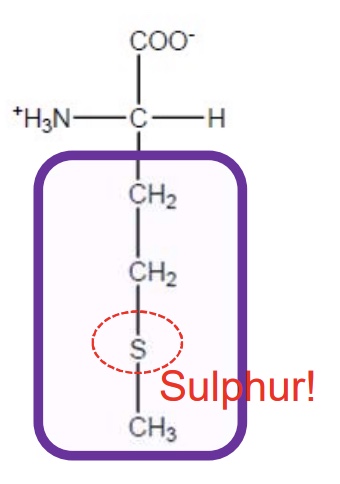
Serine
Ser-S-polar and uncharged-soluble in water and prefer to be on the surface of proteins
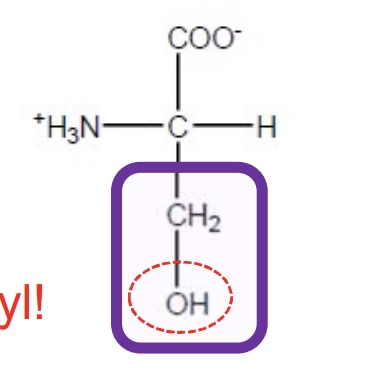
Threonine
Thr-T-polar and uncharged due to functional groups that can form hydrogen bonds
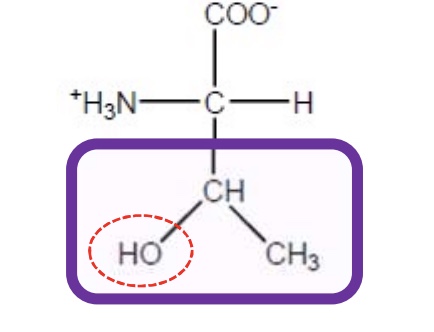
Asparagine
Asn-N-polar and uncharged
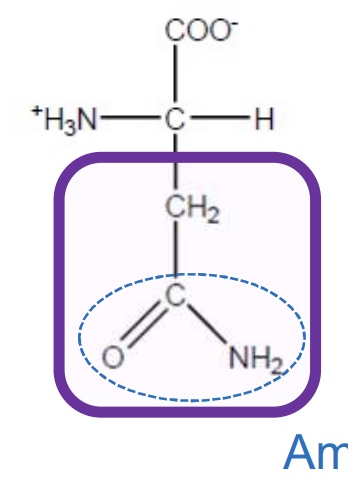
Glutamine
Gln-Q-hydrophobic and uncharged
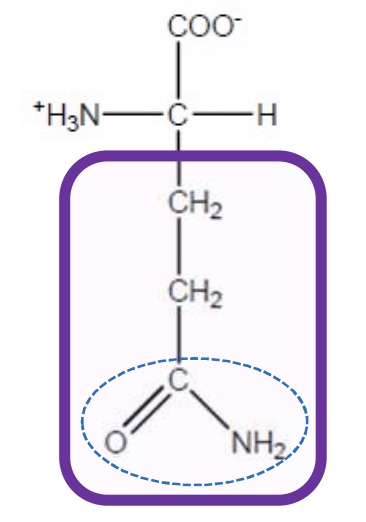
Aspartic Acid
Asp-D-polar and negatively charged
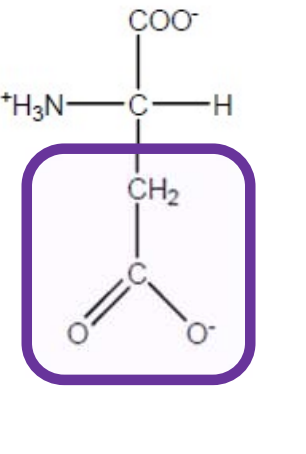
Glutamic Acid
Glu-E-polar and negatively charged - both are acidic due extra carboxyl
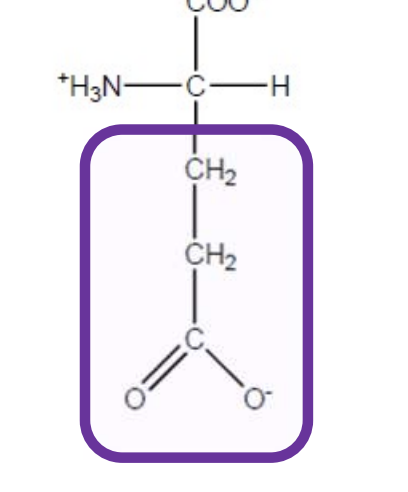
Histidine
His-H-imidazole group so polar,basic and positively charged. Fscilitates enzyme catalysed reactions by acting as a proton donor/acceptor due to pKa near physiological pH
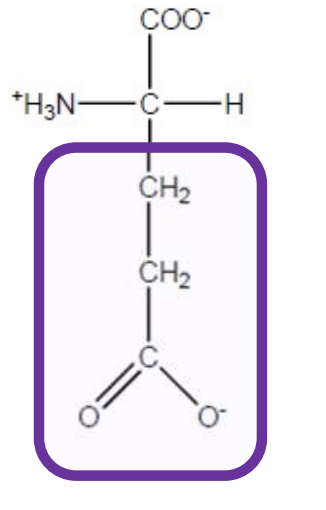
Lysine
Lys-K-polar,basic and positively charged due to amino group
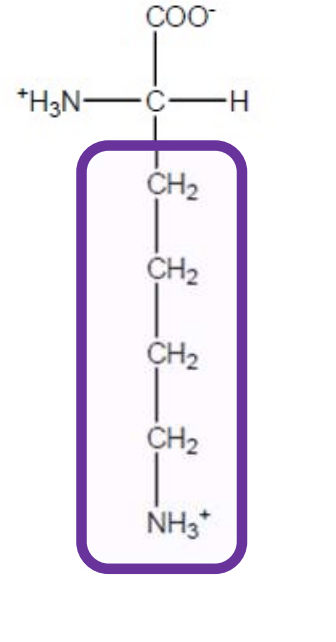
Arginine
Arg-R-polar and positively charged+basic due to guanidino group-all polar amino acids that are charged prefer to be on the surface of a protein and if deep in the protein can be used in salt bridges
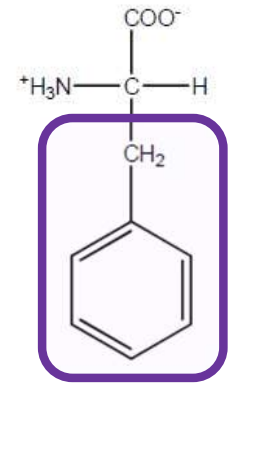
Phenylalanine
Phe-F-Aromatic and non polar
Tyrosine
Tyr-Y-Aromatic and non-polar but more polar than phenylalanine due to OH group
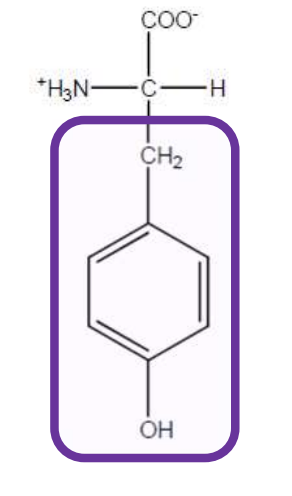
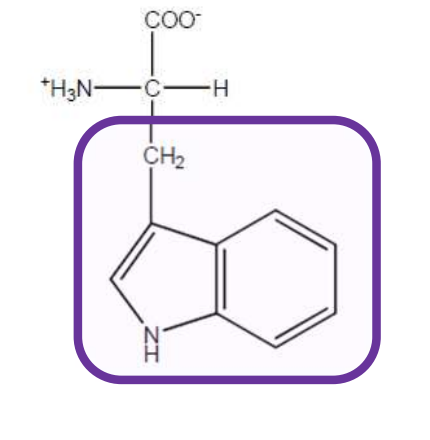
Tryptophan
Trp-W-Aromatic and non-polar but has indole ring and all aromatic amino acids can absorb ultraviolet light
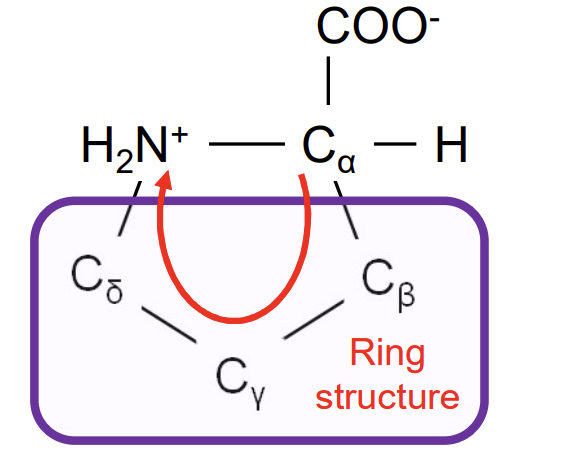
Proline
Pro-P-distinctive cyclical structure in a rigid conformation reducing flexibility-mostly forms trans peptide bonds , found in turns so mostly on protein surface
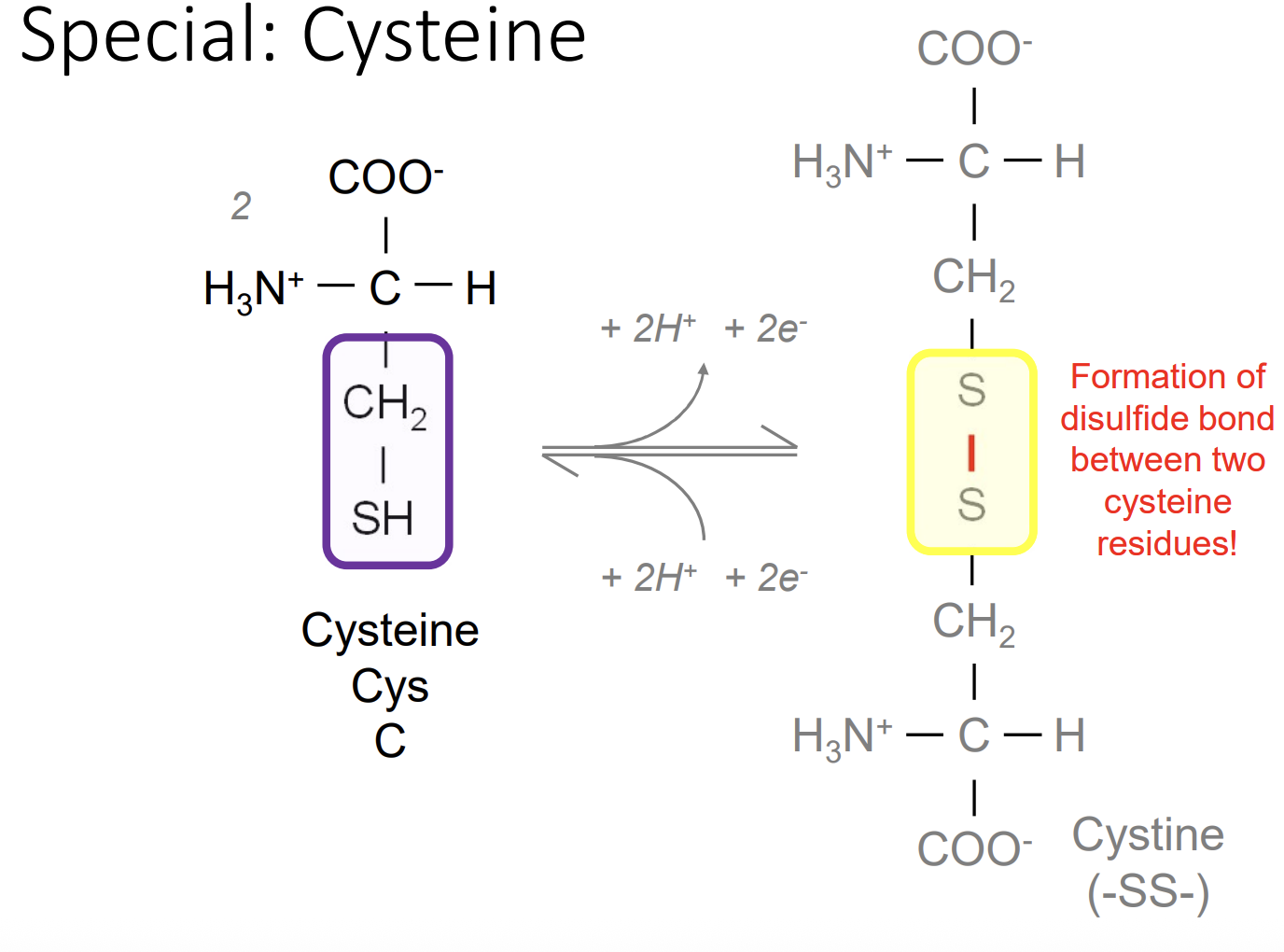
Cysteine
Cys-C-can form a dimeric amino acid using disulphide bridge which makes strongly hydrophobic residues and used to form covalent links between parts of a protein or between 2 different polypeptide chains
What are the different types of post-translational modifications?
phosphorylation,hydroxylation,acetylation,methylation,carboxylation,AMPylation,Glycosylation,lipidation,disulphide bond formation,SUMO-ylation,ubiquitylation,proteolysis and deamidation