Electricity
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Circuits + Domestic electricity
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
fixed resistor
A resistor restricts or limits the flow of electrical current. A fixed resistor has a resistance that does not change.
variable resistor
Moving the position of the slider on this resistor, changes the resistance. A variable resistor is used in some dimmer switches and volume controls.
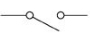
switch (open)

switch (closed)
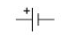
cell
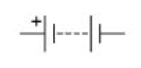
battery
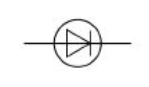
diode
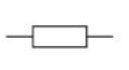
resistor
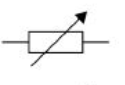
variable resistor
LED
lamp
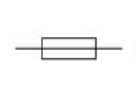
fuse
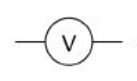
voltmeter
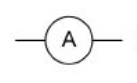
ammeter
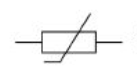
thermistor
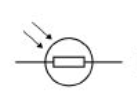
LDR
Voltmeter
measures potential difference
always connected ‘across’ a component (known as parallel)
Ammeter
measures current
always connected ‘in line’ with a component (known as series)
What is current
rate of flow of electric charge.
current flows from
+ to -
current is
conserved - it has the same value everywhere in a single closed loop
current going into a junction = current going out of a junction
current through a component
depends on the resistance of the component and the p.d across the component
• More resistance = less current
• More p.d = more current
the current through a fixed resistor at constant temperature
is directly proportional to p.d across it
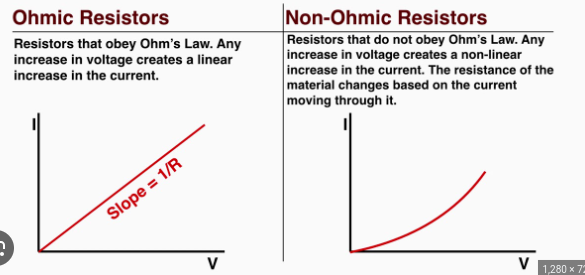
the difference between ohmic and non-ohmic reistors
Ohmic - obey ohms law
Non-Ohmic- do not obey ohms law
ohmic resistor
fixed resistance (at a constant temp)
current is directly proportional to pd
resistance of a filament lamp
increases as current and temp increase
diodes
only let current flow in one direction
because the resistance is so high in the reverse direction
resistance of a thermistor
decreases as temperature rises and this can be used in a thermostat
resistance of an LDR
decreases as it gets brighter and this can be used to automatically switch on lights
when components are connected in series:
• there is the same current through each component
• the total potential difference of the power supply is shared between the components
• the total resistance of two components is the sum of the resistance of each component.
when components are connected in parallel
the potential difference across each component is the same
the total current through the whole circuit is the sum of the currents through the separate components
the total resistance of two resistors is less than the resistance of the smallest individual resistor
adding resistors in series
increases resistance because the current is the same in every single component in the circuit, so the more resistors we add, the harder it is for current to flow.
adding resistors in parralell
decreases resistance because because there are more paths for the current to pass through.
What is pd
the difference in the amount of energy that charge carriers have between two points in a circuit
Alternative current
The electrons are constantly changing their direction of movement, the flow of charge is alternating
Direct Current
one-directional flow of electric charge
Energy is transferred by
circuit components
Power is the
rate of energy transfer
Step-up transformers
Increase pd (voltage)
Current goes down
Power lines have a
low current (avoid energy loss) and high voltage (dangerous)
For a circuit to work we need
we need a source of potential difference and a closed circuit in order for electrical charge to flow
that UK mains electricity
frequency of 50Hz and about 230V
Alternating vs Direct Potential Differences
In DC, the electrons flow steadily in a single direction, or "forward." In AC, electrons keep switching directions, sometimes going "forward" and then going "backward."
most appliances connect to the mains using
a three-core cable
earth wire
-green and yellow
-doesn’t normally carry a current
-safety wire: stops appliance becoming live
-only carries a current if there is a fault in the circuit
-pd = 0V
live wire
-brown
-electricity flows through this wire
-carries alternating pd at 230V from the mains
-starts off the flow of current through the circuit
neutral wire
-blue
-electricity flows out through this wire
-neutral wire completes the circuit
-0V
why is mains electricity dangerous?
the live wire is dangerous even if a switch is open and it is dangerous to provide a connection between the live wire and earth
a powerful device
transfers more energy per second and will have a larger p.d across it or a larger current through it
energy transfers in electrical appliences
-Every electrical appliance in the home is designed to transfer energy from one store to another.
energy transfer in a torch
the energy stored in the battery is used to heat up the filament of the bulb.
Work is done
when a charge flows in a circuit and energy is transferred
that the longer a device is used
the more energy will be transferred and the more powerful a device is the more energy will be transferred
The National grid
a system of cables and transformers that link power stations to consumers
step-up transformers
increase p.d for efficient transmission in power lines
increasing p.d reduces the current, so less energy is wasted as heat
step-down transformers
reduce the p.d to a much lower value for safe domestic use