Monohybrid Crosses
1/3
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
4 Terms
What is the result of a monohybrid cross where there is a dominant and recessive allele for the same characteristic
two heterozygous individuals will produce offspring with a phenotypic ratio of 3 dominant:1 recessive
What is a monohybrid backcross (test cross)
method used in genetics to determine if an individual is homozygous or heterozygous for a dominant characteristic
eg tall pea plant could be homozygous dominant (TT) or heterozygous dominant (Tt)
backcross is a ‘cross’ between an individual with the dominant phenotype but unknown genotype and a known ‘recessive’ genotype
recessive phenotype has known genotype because only one allele combination can produce it
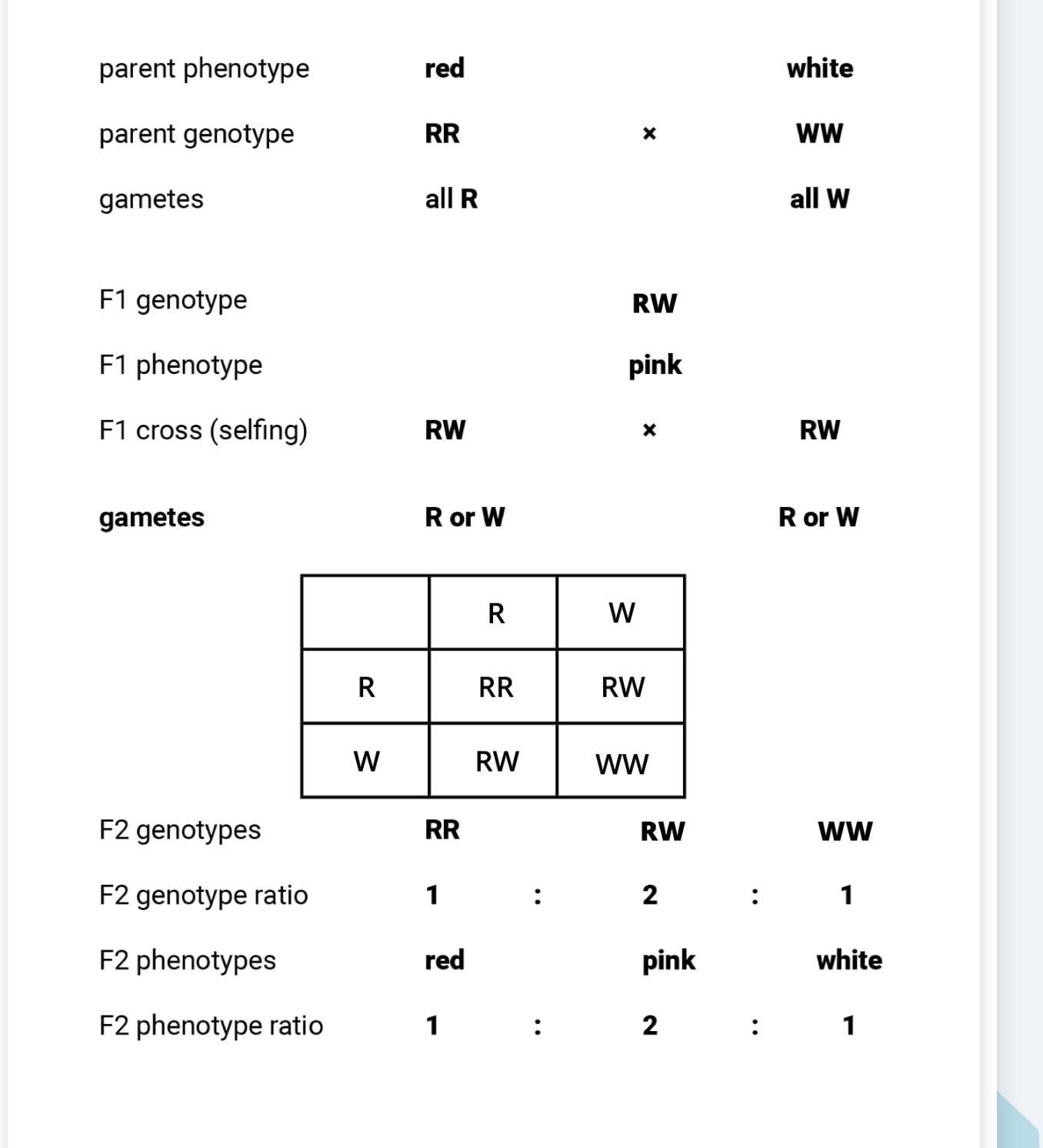
What is co-dominant inheritance
sone characteristics controlled by genes with alleles that aren’t completely dominant or recessive
eg:
alleles that express themselves equally in phenotype
heterozygote generally shows a phenotype intermediate between those of the two homozygotes
What is sex linked inheritance
inheritance of genes found on sex chromosomes
non-sex chromosomes known as autosomes
men XY women XX
Y chromosome shorter than X so some genes only present on X chromosome
In male, recessive alleles carried on X chromosome will be expressed in phenotype as are unpaired so no dominant allele present
called sex-linkage
male carrying sex-linked allele on X chromosome can’t pass it on to sons as they must receive Y chromosome to become male (they would get the X from mum Y from dad)
Daughters of male with sex-linked allele on X chromosome must receive the recessive allele from him
Females that are heterozygous for sex-linked recessive traits are known as carriers so have 50% chance of passing recessive allele to sons