CLASSIFICATIONS AND PHYLOGENIES
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Classification systems of Plants
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Hierarchy of Diversity
Domain
Kingdom
Phylum (plants) Division (animals)
Order
Family
Tribe
Genus
Species
Binomial Nomenclature
A system created to find order in diversity of organisms.
Systema Naturae
System that divided animals into SIX classes and plants into TWENTY FOUR classes
What are the six classes of Animals?
Quadrupedia
Aves (birds)
Amphibia (amphibians)
Pisces (fish)
Insecta (insects)
Vermes (worms)
How are plant Classes classified?
Class is determined by the number, fusion (free or fused) and length of stamens.
How are plant Orders classified?
Order is determined by the number of styles in each flower.
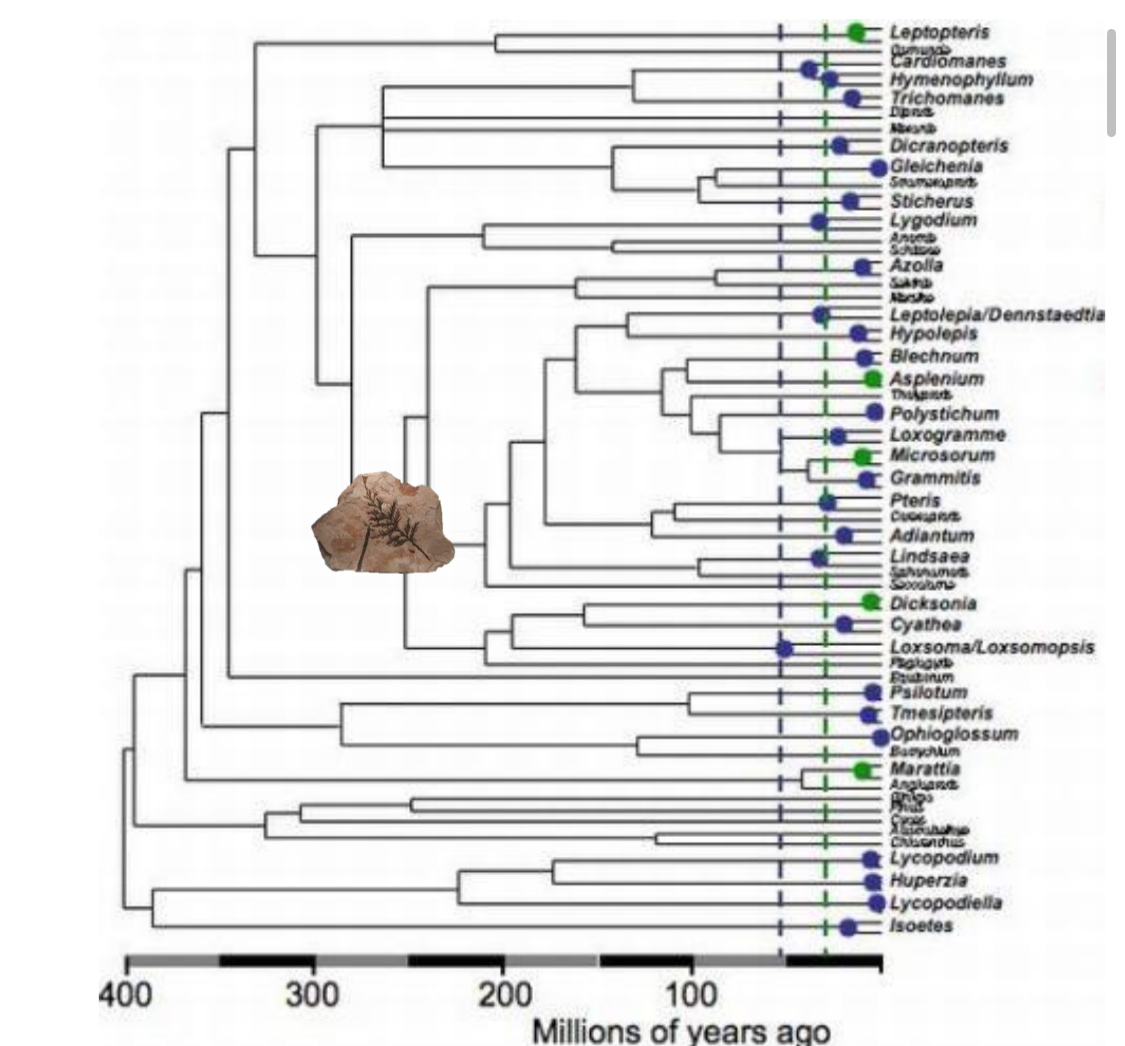
What is a Chronogram?
A cladogram with an added index of time.
What is Homology?
Similarity in form or function between lineages that are attributed to common ancestry
Types of Homology
Plesiomorphy: Is an ancestral trait that is shared by common ancestor of a group, but not all descendants.
Synamorphy: Trait shared by common ancestor of clade and all its descendants.
Autapamorphy: Unique trait of single terminal.
What is the difference between Primary Homology and Secondary Homology?
Primary Homology: Morphological characters hypothesized to be homologous prior to cladistic analysis.
Secondary Homology: Morphological characters defined as homologous as the result of cladistic analysis.
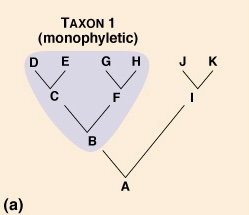
What does Monophyletic mean?
Taxon that includes the most recent common ancestor of a group of organisms, and all of its descendants.
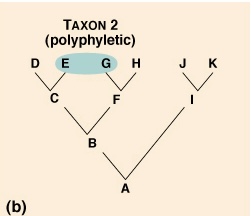
What does Polyphyletic mean?
Taxon that does not include the common ancestor of all members of the taxon.
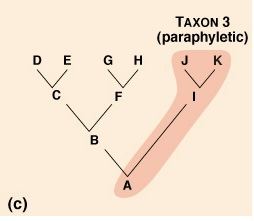
What does Paraphyletic mean?
Taxon that includes the most recent common ancestor, but not all of its descendants.
Don’t all share the same common ancestor in some cases as well.
What is Homoplasy?
Similarity in the form and function between lineages that are not attributed to common ancestry.
What is Ontogeny?
Development of an organism, from fertilization to adulthood.
What are the different types of Homoplasy?
Convergence: Production of identical characteristics by different ontogenies.
Parallelism: Production of apparently identical characteristics by the same ontogeny.
Reversion: Production of apparently identical plesiomorphic characteristics by the same ontogeny.