IB Biology - Chemistry of Life
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Where did cells first originate?
Cells first evolved in bodies of water
Water is a medium where most life process occur
What is water a medium of?
solvent
reactions
transport of substances
temperature regulator
protection (brain, spinal cord, joints)
absorption of nutrients
excretion of waste
Polarity
When a molecule has both a partially negative (δ−) and positive charge (𝛿+)
What are a consequent of the polar bonds within water molecules
Hydrogen bonds
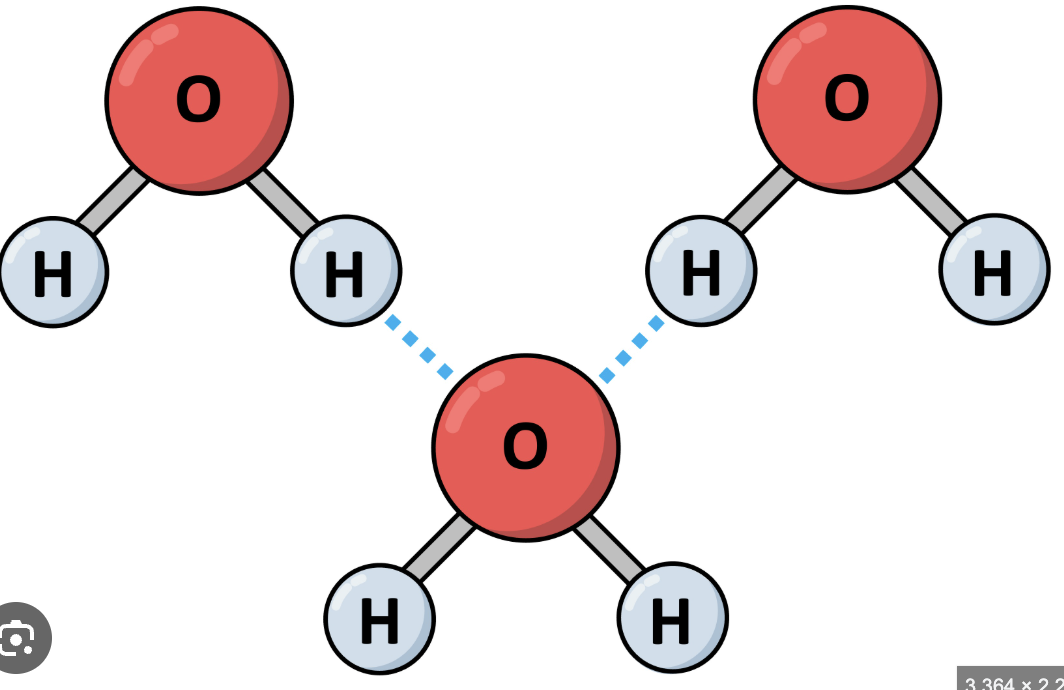
Causes of the polarity of covalent bonding in water molecules
Due to the unequal sharing of bonded electrons
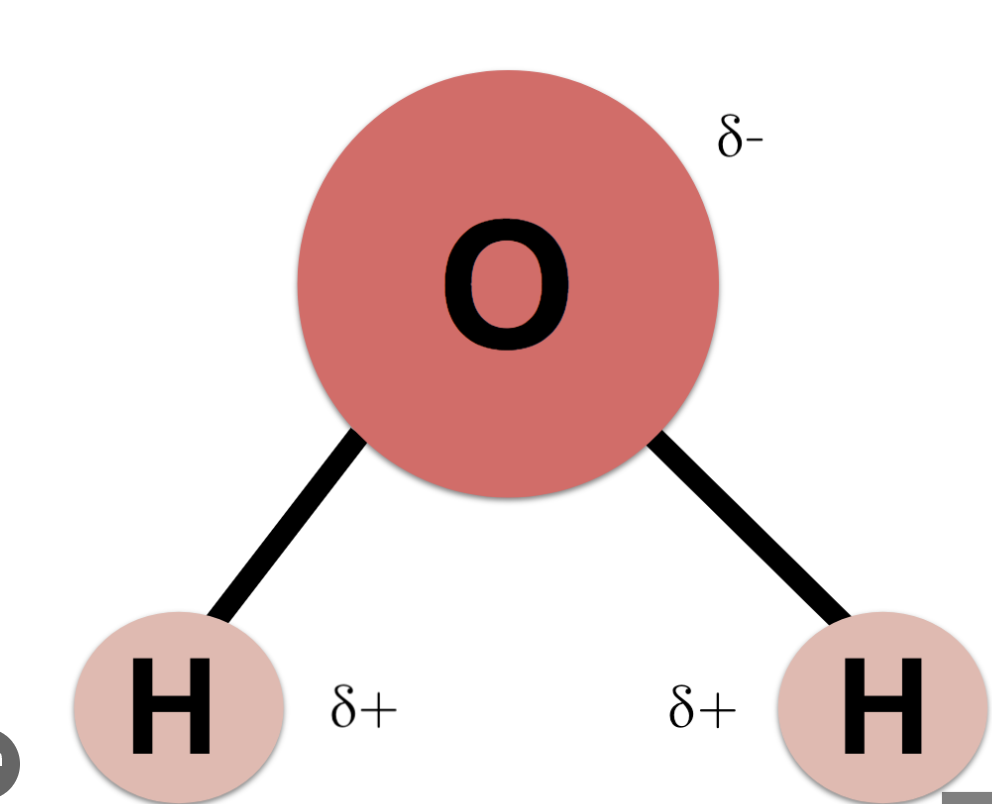
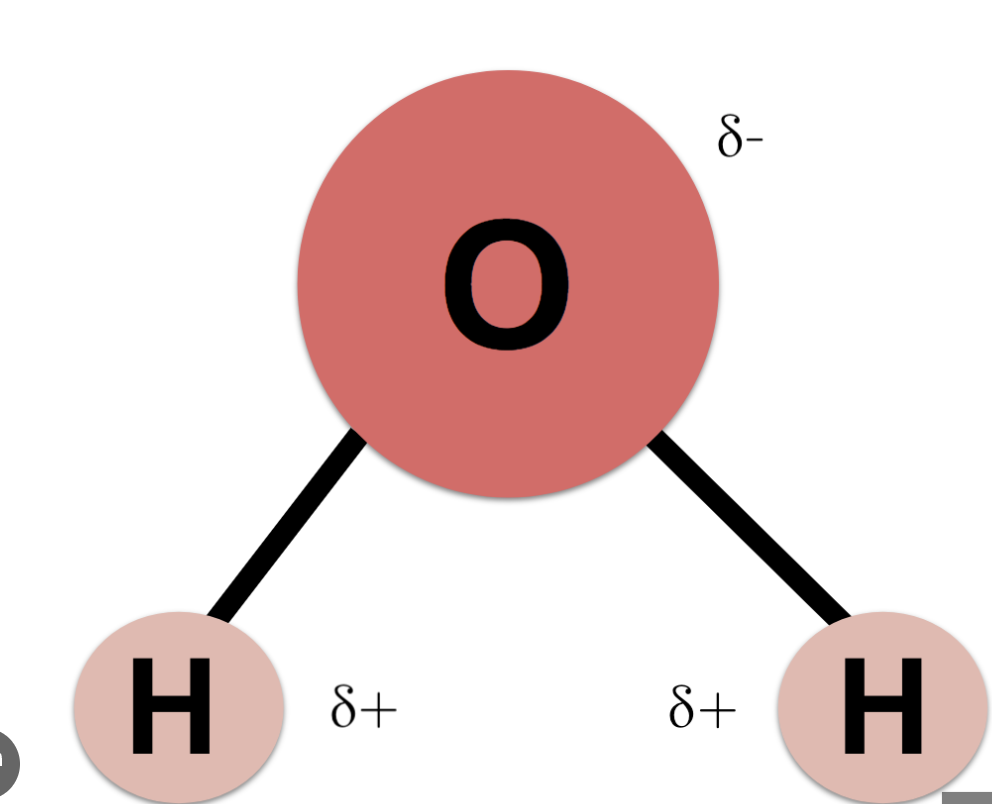
1 O atom (partially negative) covalently bonds with 2 H atoms (partially positive)
Dipolar nature
TREAT THIS THE SAME AS POLAR, DIPOLAR = 2 OPPO. POLES
Polarity due to excess electrons surrounding O atom (not the usual excess of electrons due to ionic bonding) → hydrogen bonds (weak bonds) form between different water molecules → cause specific properties of water
Cohesion
binding together of molecules of the same substance due to H bonds (same molecules sticking together)
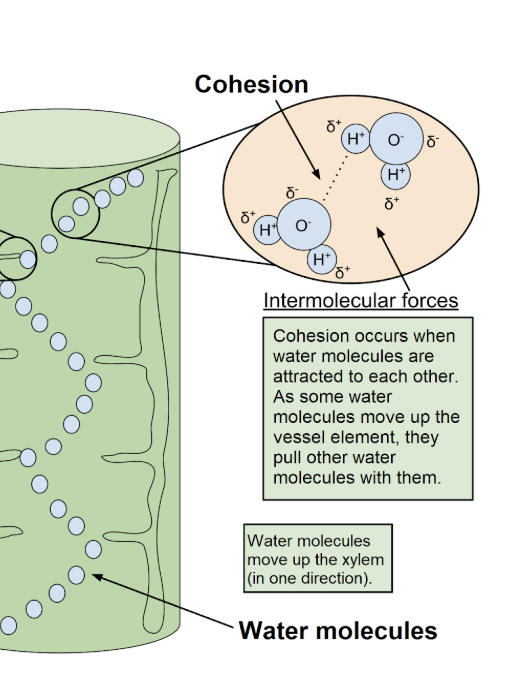
Movement of water in the xylem vessels
(against gravity) by water molecules “pulling each other up”
Surface tension
creates a specific habitat on the border between water + air (elastic - like) → due to strong cohesive forces from H - bonds between molecules
Adhesion
H bonds form between water + other polar molecules (water sticking to other compounds)
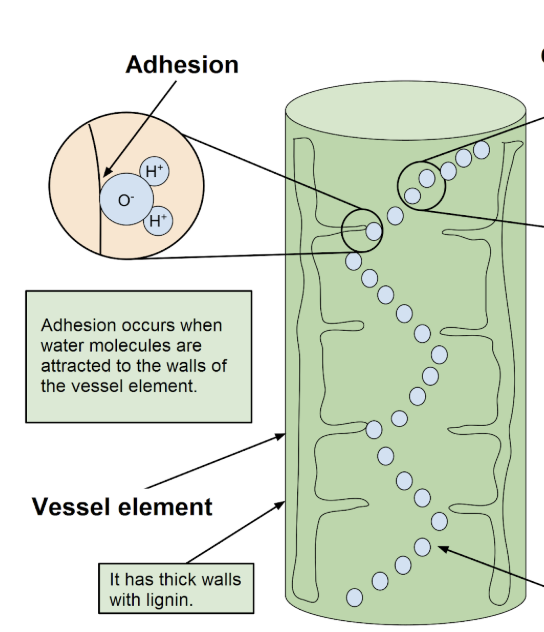
Adhesion enables
Movement of water in xylem (against gravity) by water molecules adhering to polar cellulose molecules in cell walls
Adhesion enables
Movement of water molecules between soil particles by adhering to polar organic matter in the soil → spreading due to plants’ uptake of water through roots
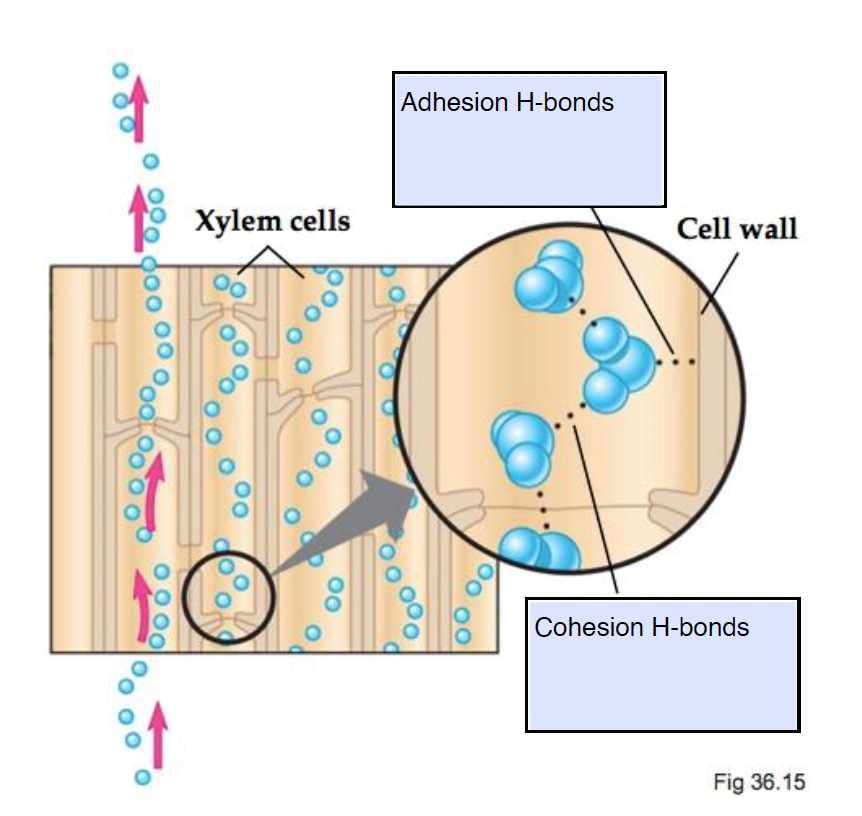
BOTH adhesion and cohesion contribute to capillary action
Role of solvent properties of water
medium for metabolism
for transport in plants + animals
A wide variety of hydrophilic molecules dissolve in water → most enzymes catalyse reactions in aqueous solutions
Functions of some molecules in cells depends on them being hydrophobic + insoluble
Solvent property
Because of polarity, water molecules dissolve a number of other polar molecules
HYDROPHILIC (water-loving) SUBSTANCES = soluble in water
chemically attracted to water: polar charged or substances that water adheres to (glucose, cellulose, sodium chloride)
Hydrophilic substances
extremely important for transport of nutrients + wastes
most metabolic enzymatic reactions happen in a watery environment
HYDROPHOBIC (“water-fearing”) SUBSTANCES = insoluble in water
nonpolar (uncharged) particles that can not be attracted to water (acetone, oils, fats)
Hydrophobic substance
extremely important that some substances remain hydrophobic → e.g. some lipid-based hormones, efficient energy storage as fats, transport of fatty substances in blood via “lipoprotein complexes” → vesicle-like structures hydrophilic on the outside but hydrophobic on the inside
DON’T ASSUME that hydrophilic + soluble are together
CAN ASSUME hydrophobic + insoluble
Transport of glucose in blood

Transport of amino acids in blood

Transport of cholesterol + other lipids in blood

Transport of sodium chloride in blood

Transport of oxygen in blood

Physical Properties of water: water anomaly (thermal)
most substances increase in density as their temperature decreases until they reach a solid state → water is densest at 4°C rather than 0°C → ice is less dense than water, so it floats on the surface → enables survival of aquatic plants + animals
Physical Properties of water: HBP (thermal)
high because of high heat of vaporization → boiling point is the max temp. in which substance is still liquid
Physical Properties of water: high latent heat of vaporization (thermal)
high amount of heat (energy) required for a water molecule to break H bonds (set free from the liquid) → become a water vapor molecule
evaporation has a cooling effect (sweating) on organisms → e.g. humans
very large span of liquid water availability on Earth (0-100C)
Physical Properties of water: high specific heat capacity (thermal)
water can absorb or lose significant energy without major temperature changes → provides stable thermal conditions for aquatic environments
Physical Properties of water: thermal conductivity (thermal)
water conducts heat much more effectively than air → means aquatic animals lose body heat more rapidly
material's ability to conduct heat → water has a much higher thermal conductivity than air, so aquatic animals are more likely to lose heat to the environment → must be adapted to reduce heat loss
Physical Properties of water: buoyancy (DOESNT MEAN THAT IT FLOATS ON WATER)
upwards force exerted by a fluid on an object immersed in it → liquid water is a denser fluid than air, providing greater buoyancy for aquatic animals → allows them to float or swim more easily
helps many aquatic animals conserve energy → allows them to stay afloat without expending a lot of effort
Aquatic mammals have a layer of blubber that provides buoyancy → helps them float on the surface of the water (also provides thermal insulation)
Physical Properties of water: viscosity
measure of a fluid’s resistance to flow → the higher the viscosity, the more difficult it is for animals to move through the fluid
Water has a higher viscosity than air, so most aquatic animals have various hydrodynamic shapes → streamlined body shape which allows them to smoothly move through water
Ringed seal - buoyancy

Ringed seal - viscosity

Ringed seal - thermal conductivity

Ringed seal - high specific heat capacity

Black throated loons - buoyancy
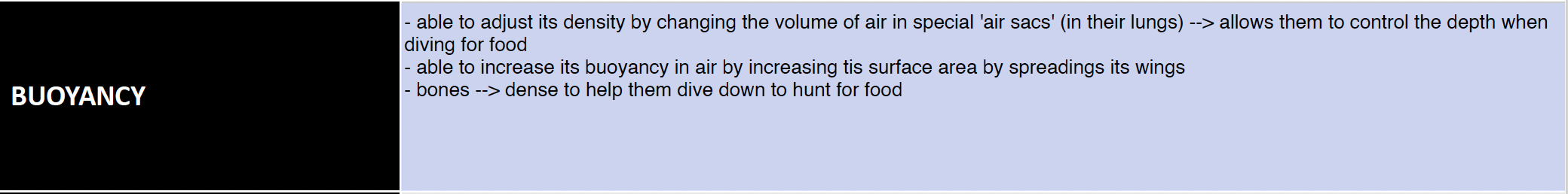
Black throated loons - viscosity

Black throated loons - thermal conductivity

Black throated loons - high specific heat capacity

Why was there no water on “proto-Earth”?

How did Earth gain its water?

How did Earth retain its water?

What is required for life to exist? - Liquid water
acts as a solvent → enables chemical reactions
What is required for life to exist?
Source of energy
What is required for life to exist? - essential chemical elements
Carbon
Hydrogen
Nitrogen
Oxygen
Phosphorus
Sulfur
What is required for life to exist? - stable environment
Habitable zone around a star = zone in which liquid water can form and remain = the Goldilocks zone