Electronics and Electrical Symbols
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
96 Terms

Electrical Wire
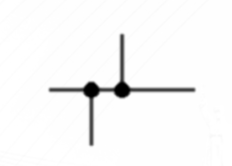
Connected Wires
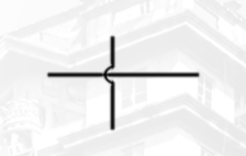
Not Connect Wires
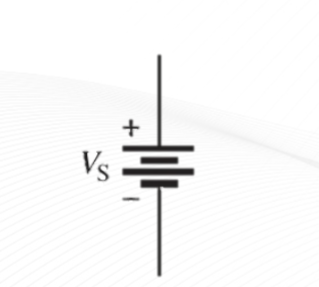
DC Voltage Source
Voltage, V
defined as energy per unit of charge.
Current, A
is the rate of flow of charge.
Resistance, Ω
is the opposition to current.
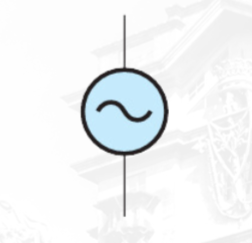
AC Voltage Source
Current Source
can provide a constant current in any load. Just as in the case of a voltage source, the ideal current source does not exist but can be approximated in practice.
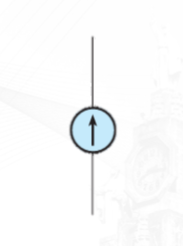
Current Source
Resistors
Components that are specifically designed to have a certain amount of resistance. The principal applications of resistors are to limit current, divide voltage, and, in certain cases, generate heat.
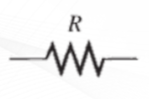
Resistor
Variable Resistors
are designed so that their resistance values can be changed easily.
Variable Resistance Sensors
Physical quantity alters the electrical resistance
Potentiometer
Used to divide voltage
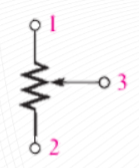
Potentiometer
Rheostat
Used to control current
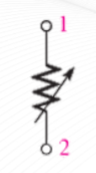
Rheostat
Thermistor
change resistance as a function of temperature

Thermistor
Photoconductive Cell
change resistance as a function of light
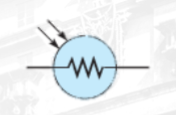
Photoconductive Cell
Strain Gauges
change resistance when a force is applied to them

Strain Gauges
Switches
Commonly used for controlling the opening or closing of circuits
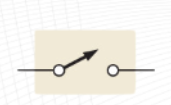
SPST
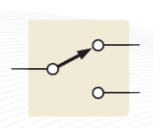
SPDT
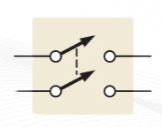
DPST
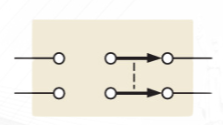
DPDT
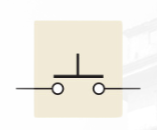
NOPB
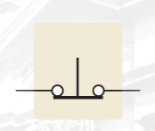
NCPB
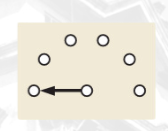
Single-pole rotary (6-position)
Single Pole Single Throw (SPST)
switch controls a single circuit
Single Pole Double Throw (SPDT)
switch has a single pole and two different switch output options.
Double-pole–single-throw (DPST)
switch permits simultaneous opening or closing of two sets of contacts.
Double-pole–double-throw (DPDT)
switch provides connection from one set of contacts to either of two other sets.
normally open push-button switch (NOPB)
the connection is made between two contacts when the button is depressed, and the connection is broken when the button is released
normally closed push-button switch (NCPB)
the connection between the two contacts is broken when the button is depressed.
rotary switch
a knob is turned to make a connection between one contact and any one of several others
Protective Devices
FUSES and CIRCUIT BREAKERS are placed in the current path and are used to deliberately create an open circuit when the current exceeds a specified number of amperes due to a malfunction or other abnormal condition in a circuit.

Fuse symbol
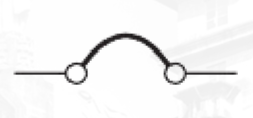
Circuit breaker symbol
Ground
The reference point in an electric circuit.
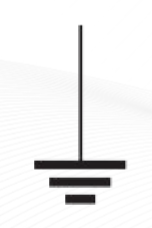
Reference Ground
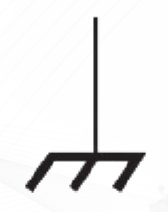
Chassis Ground

Alternate reference symbol
Capacitor
A passive electrical component that stores electrical charge and has the property of capacitance.
is an electrical device constructed of two parallel conductive plates separated by an insulating material called the dielectric.
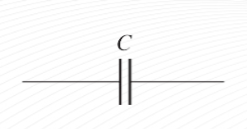
Basic Capacitor
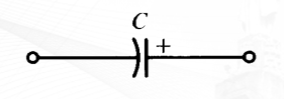
Electrolytic Capacitor

Variable Capacitor
Inductor
An inductor is a passive electrical component, formed by a coil of wire, that exhibits the property of inductance.
When a length of wire is formed into a coil, it becomes an inductor.
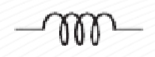
Fixed (Inductor)
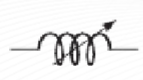
Variable (Inductor)
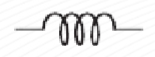
Air core
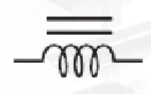
Iron core
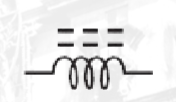
Ferrite core
Diode
A diode conducts current when it is forward-biased when the bias voltage exceeds the barrier potential. A diode prevents current when it is reverse biased at less than the breakdown voltage.
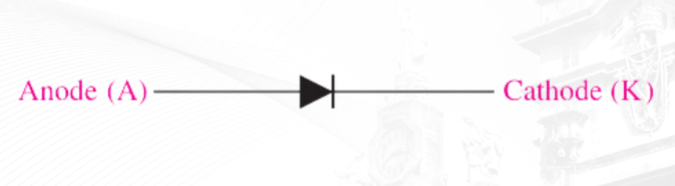
Diode
Zener Diode
is designed for operation in the reverse breakdown region.
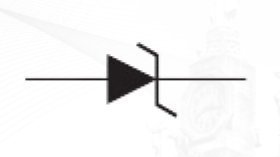
Zener Diode
Varactor Diode
A varactor is basically a reverse-biased pn junction diode that utilizes the inherent capacitance of the depletion region.
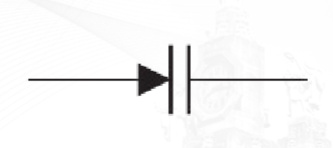
Varactor Diode
LED
is a semiconductor device that emits light when an electric current flows through it.
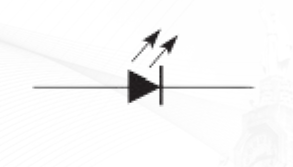
LED
Photodiode
A photodiode is a semiconductor device that convers photons (light) into electrical current.
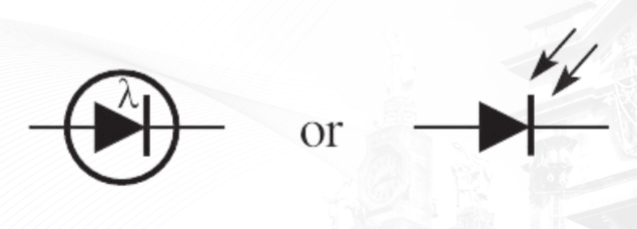
Photodiode
Tunnel Diode
is a very heavily doped p-n junction diode. In a Tunnel diode electric current decreases as the applied voltage increases, and at high voltage, it works as an ordinary p-n junction diode.
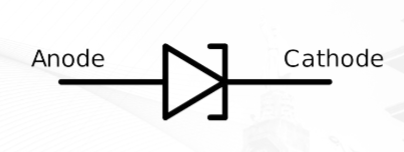
Tunnel Diode
Schottky Diode
is formed by the junction of a semiconductor with a metal, also known as hot-carrier diode.
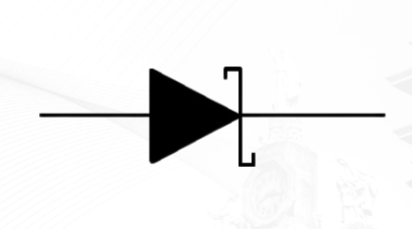
Schottky Diode
Transistors
is a semiconductor device that controls current between two terminals based on the current or voltage at a third terminal and is used for the amplification or switching of electrical signals.
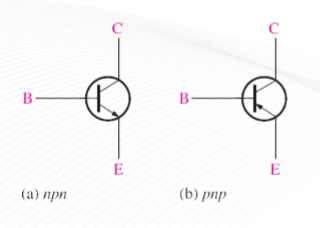
Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT)
(BJT) npn
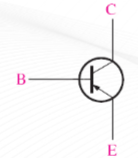
(BJT) pnp
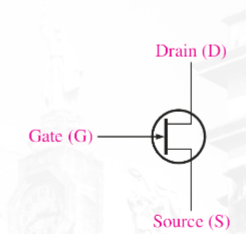
(JFET) n channel
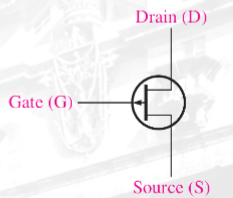
(JFET) p channel
Transistors
is a semiconductor device that controls current between two terminals based on the current or voltage at a third terminal and is used for the amplification or switching of electrical signals.
MOSFET
Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor
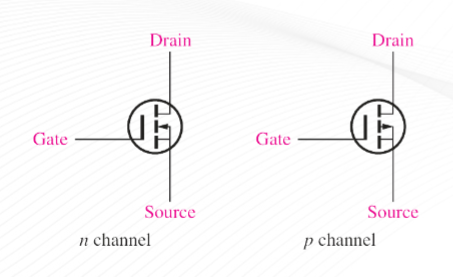
Enhancement MOSFET (E-MOSFET)
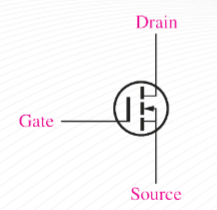
(E-MOSFET) n channel
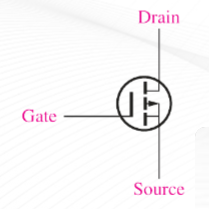
(E-MOSFET) p channel
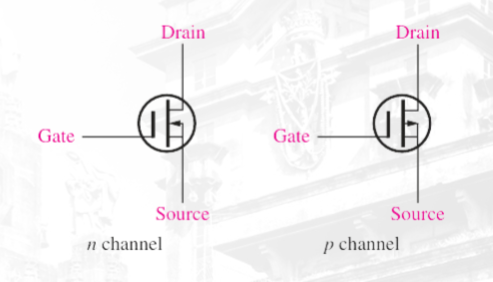
Depletion MOSFET (D-MOSFET)
(D-MOSFET) n channel
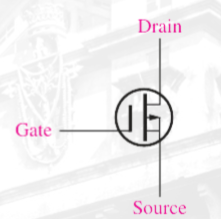
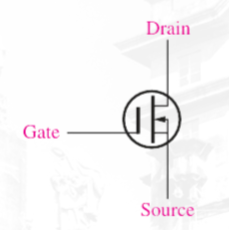
(D-MOSFET) p channel
Thysristors
The device acts as a switch and remains off until the forward voltage reaches a certain value; then it turns on and conducts. Conduction continues until the current is reduced below a specified value.
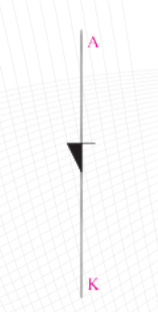
Shockley Diode
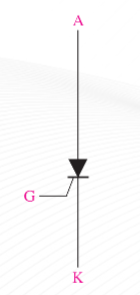
Silicon-Controlled Rectifier (SCR)
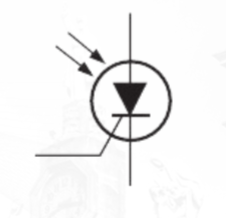
Light-Activated Silicon-Controlled Rectifier (LASCR)
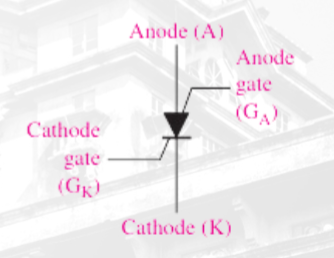
Silicon-Controlled Switch (SCS)
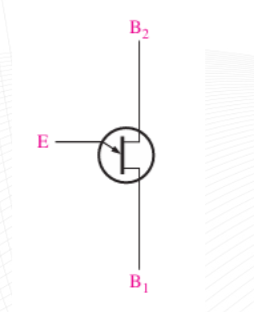
Unijunction Transistor (UJT)
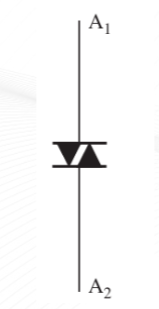
DIAC
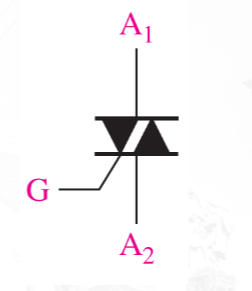
TRIAC
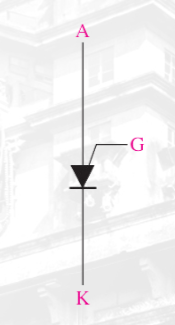
Programmable Unijunction Transistor (PUT)
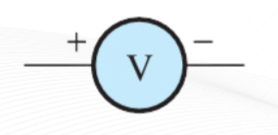
Voltmeter
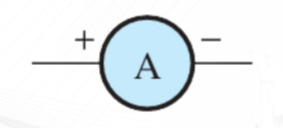
Ammeter
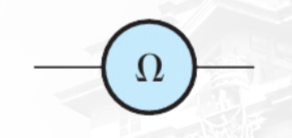
Ohmmeter