4- coral reefs
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
coral
- phylum cnidaria
- related to jellies and anemones
types of corals
- soft corals
- hard corals
soft corals
do not secrete calcium carbonate
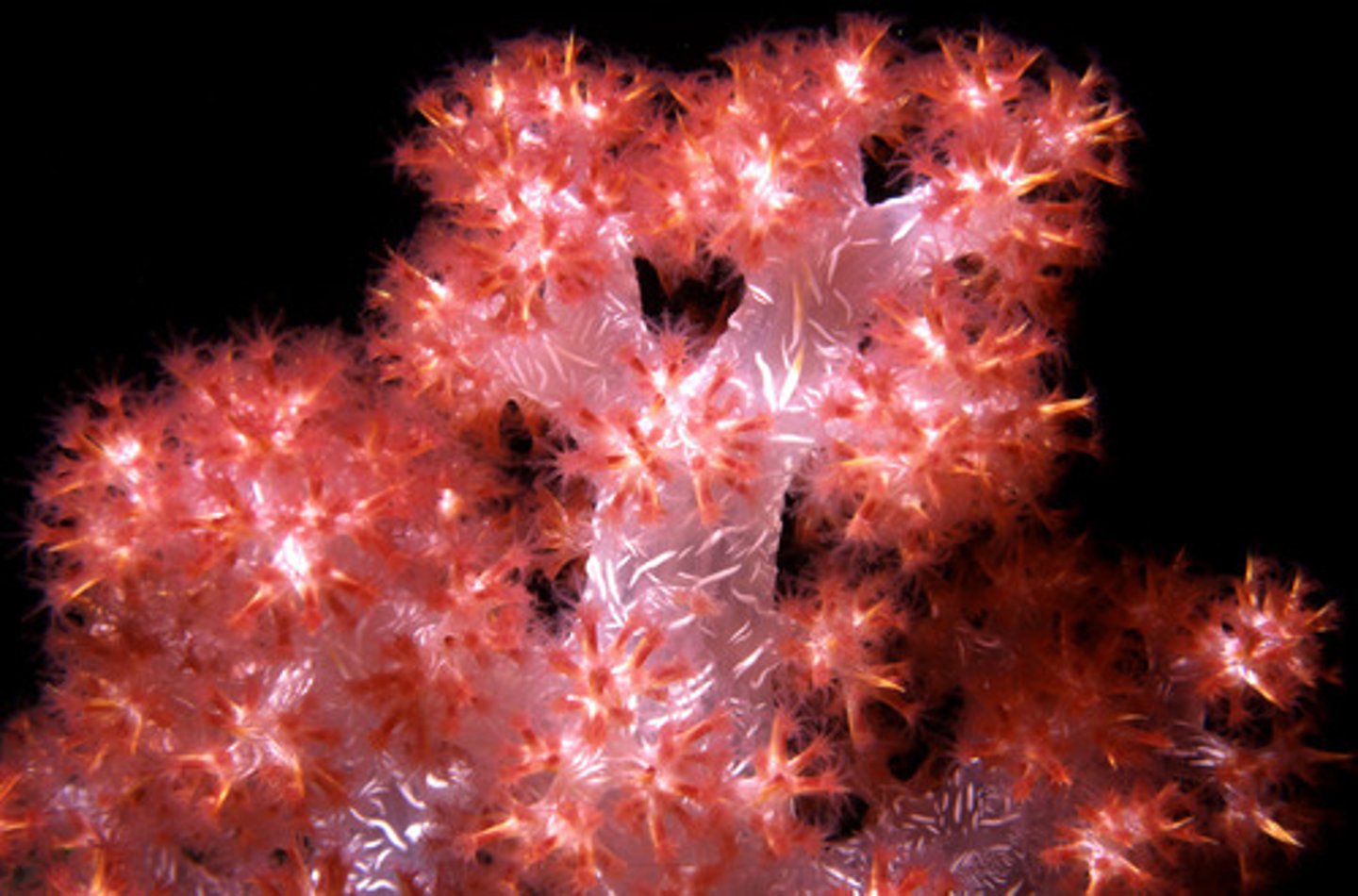
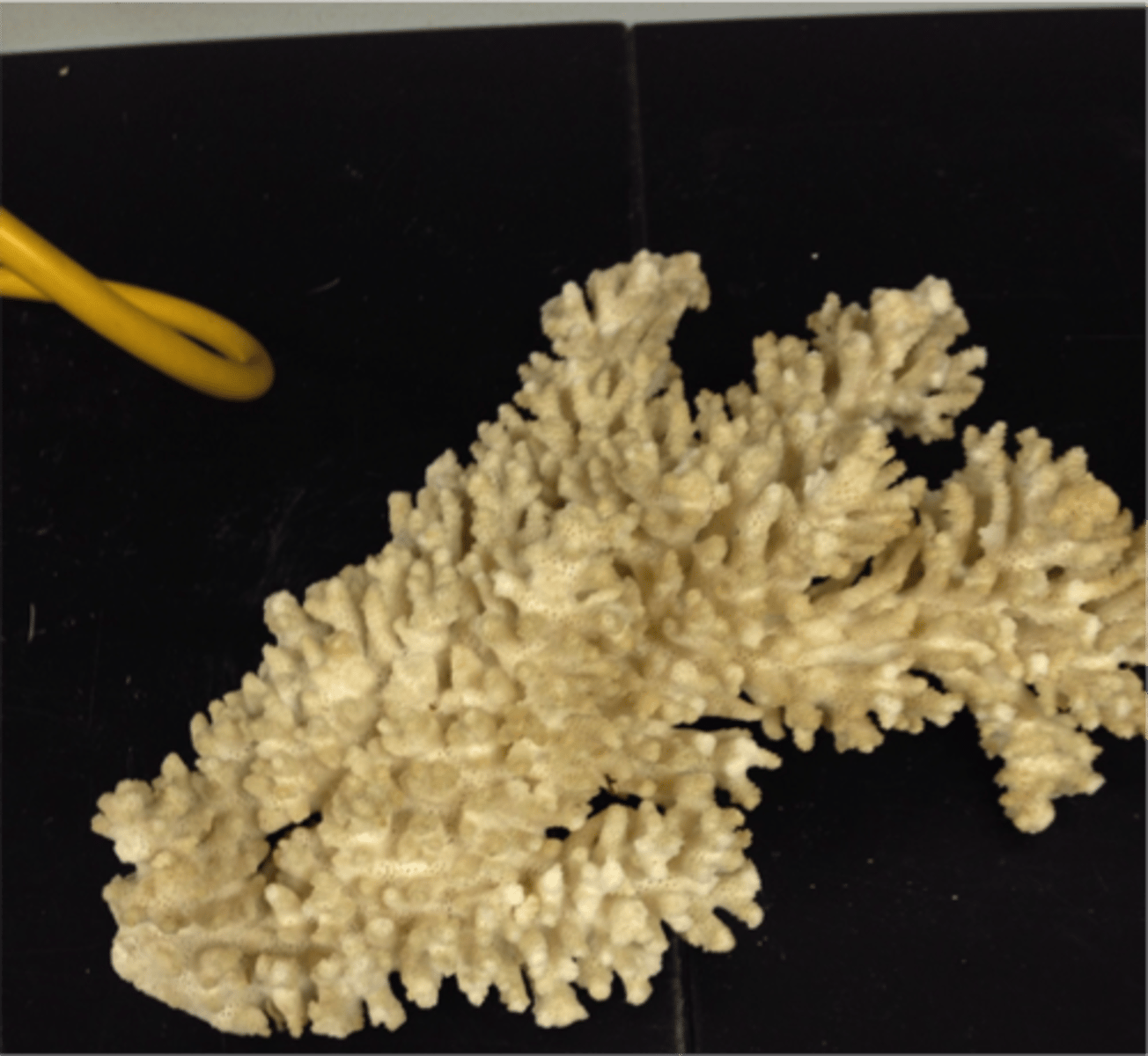
hard corals
- secrete calcium carbonate skeletons
- hermatypic= reef building corals
- ahermatypic= non reef building corals
zooxanthellae
- obligate symbionts
- single-celleed, dinoflagellate, photosynthetic algae
- live intracellularly in the endodermal tissues of scleractinian corals
- give coral its color
- asexual reproduction = transfer of zooxanthellae
- sexual reproduction = acquisition of zooxanthellae from environment
- responsible for 80% of photosynthesis which corals use as energy
coral-algal mutualism
symbiodinium spp= endosymbiotic dinoflagellates
polyp structure
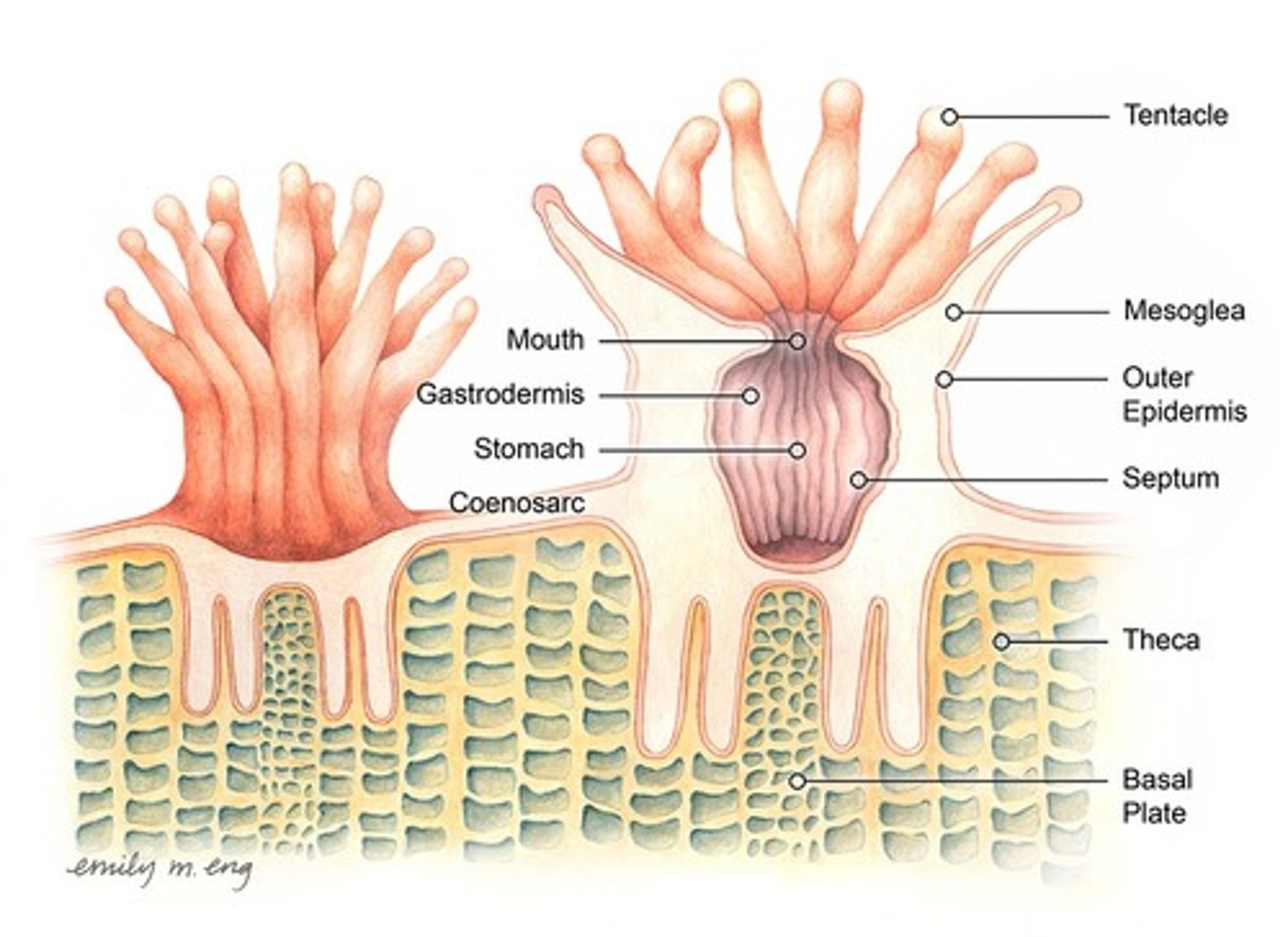
polyp feeding
- capture plankton with nematocysts
- digest in gastrovascular cavity
- polyps will emerge at night to feed
coral skeleton
- reef building corals form CaCO3 skeletons
- massive corals grow ~1 cm/yr
- branching corals grow ~10 cm/yr
meroplankton
Species of zooplankton that spend only part of their lives as members of the plankton community
coral spawning
- timed with rising spring temps and lunar cycle
- species have coordinated release of gametes
- some species have male and female corals
- some release sperm+egg packets
- increases chance of fertilization success
conditions required for corals
- hard substrate
- sunlight
- clear water and low sedimentation
- warm temperature
- constant salinity
hard substrate
- coral larvae need hard substrate to attach
- can be rocks, dead coral, coraline algae
- hard substrate environment= competition for space= attack and defense
competition for space
- some will digest competitors
- others will grow over or out grow neighbors
- some have sweeper tentacles (longer, more densely packed with nematocysts, used in aggressive and defenseive actions)
hermatypic corals need high sunlight
since zooxanthellae are photosynthetic they are light limited
clear water
- corals need clear water
- tropical waters very nutrient poor= less plankton= clear water
low sedimentation
- land run off brings sediment
- sediment can smother corals
- scleractinian corals generate mucous (protect against UV rays)
- immportance of mangroves: mangroves accrete sediment
influence of sedimentation and runoff
corals off mainland
- subject to more freshwater input and land runoff
- increased sedimentation (smothers corals)
- eutrophication (allows algae to out compete)
- as population increases, runoff increases and corals decrease
corals off oceanic islands
- often get more pristine coral reefs
- less populated by humans, but tourist areas can have a big impact
- less freshwater input and land runoff
temperature
- corals thrive in water temperature 18-29 C (64-84)
- 18C: rate of calcium carbonate deposition less than rate of erosion
- 29C: coral bleaching and death (isolated high even won't immediately cause bleaching)
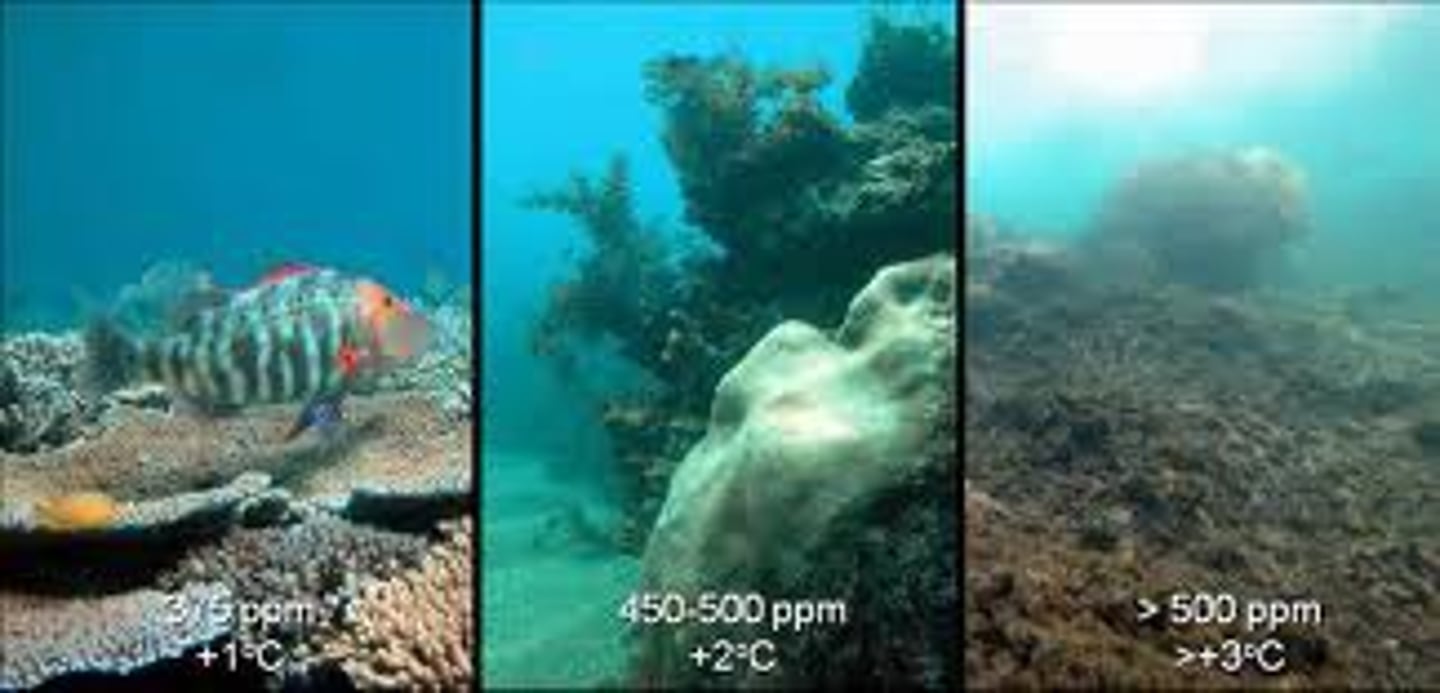
coral bleaching
- loss of symbiotic zooxanthellae
- response to thermal stress
- zooxanthellae are ejected
- are not dead but only get about 15% of their nutrition
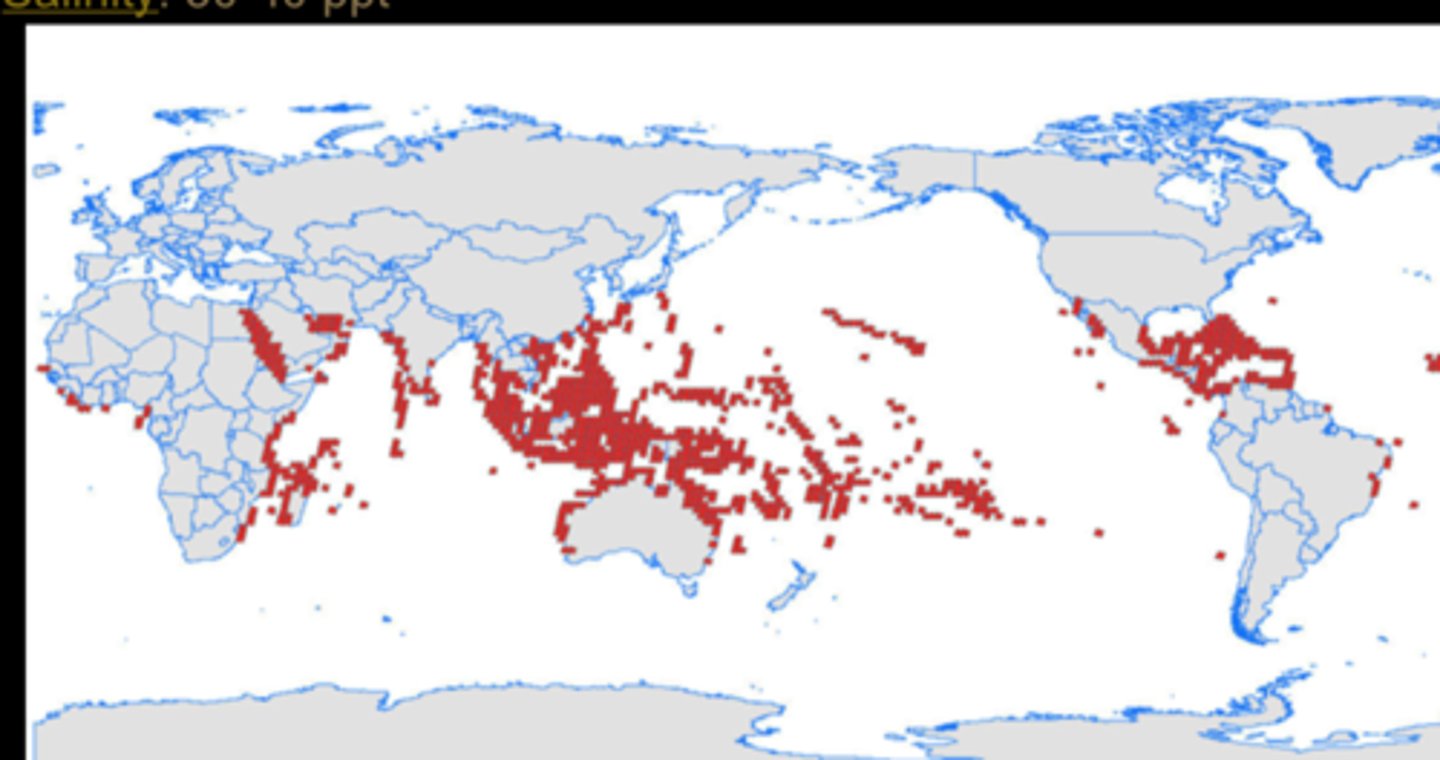
global distribution of coral reefs
30-30 range
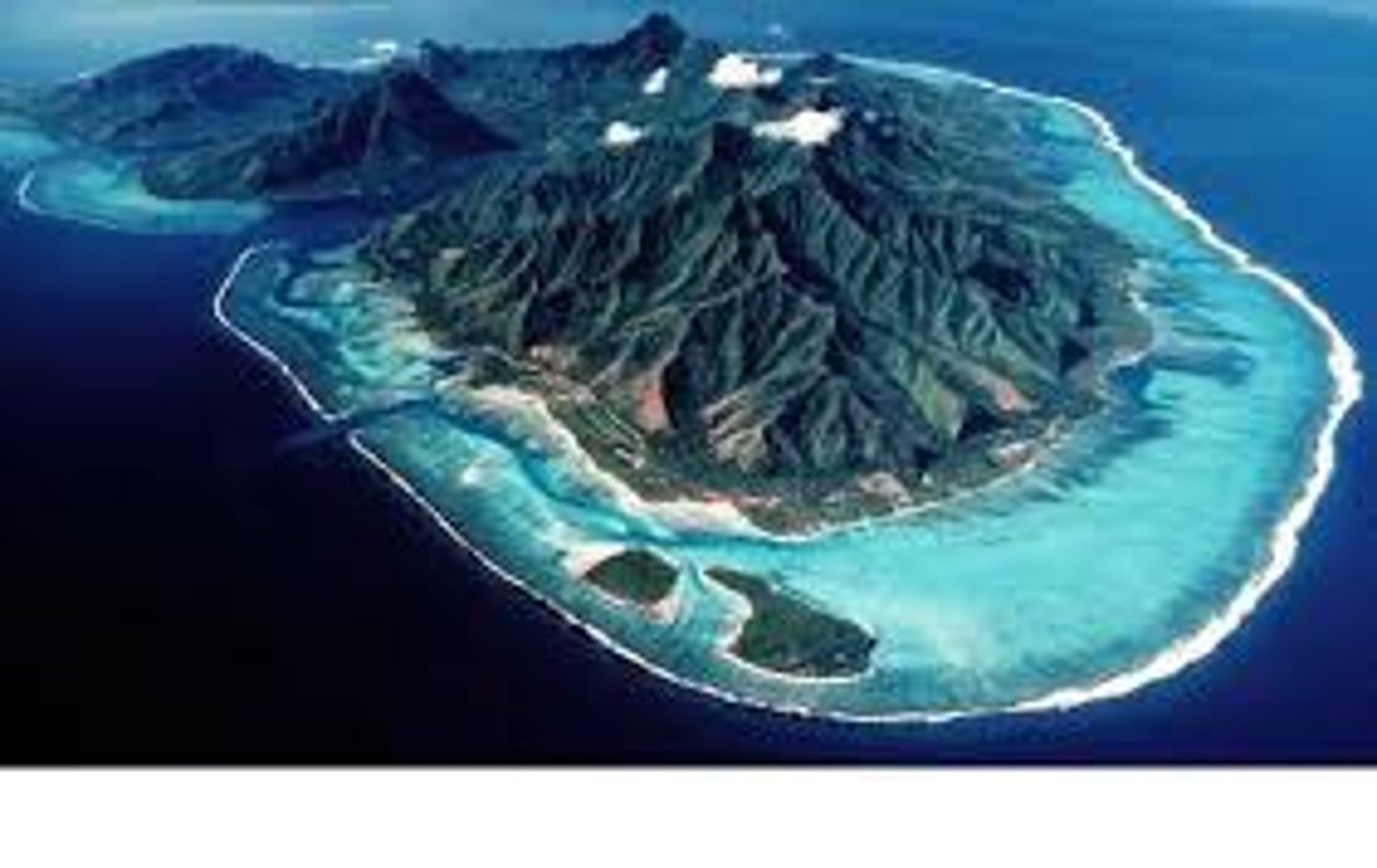
fringing reef
a coral reef that lies close to the shore

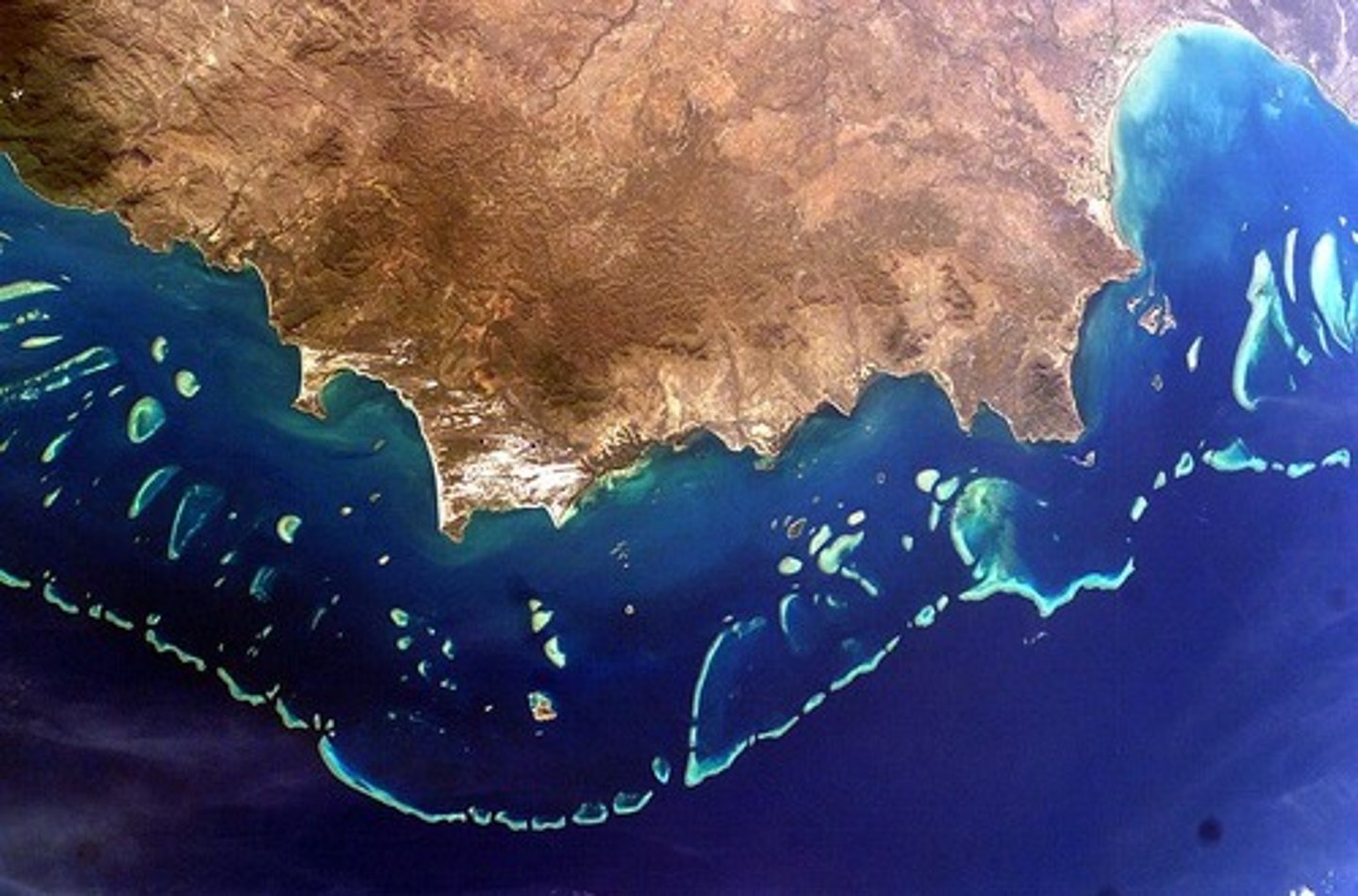
barrier reef
forms a barrier between the open ocean and the island

atoll
no longer have an island, land has subsided already and the coral can establish on the rocky substrate
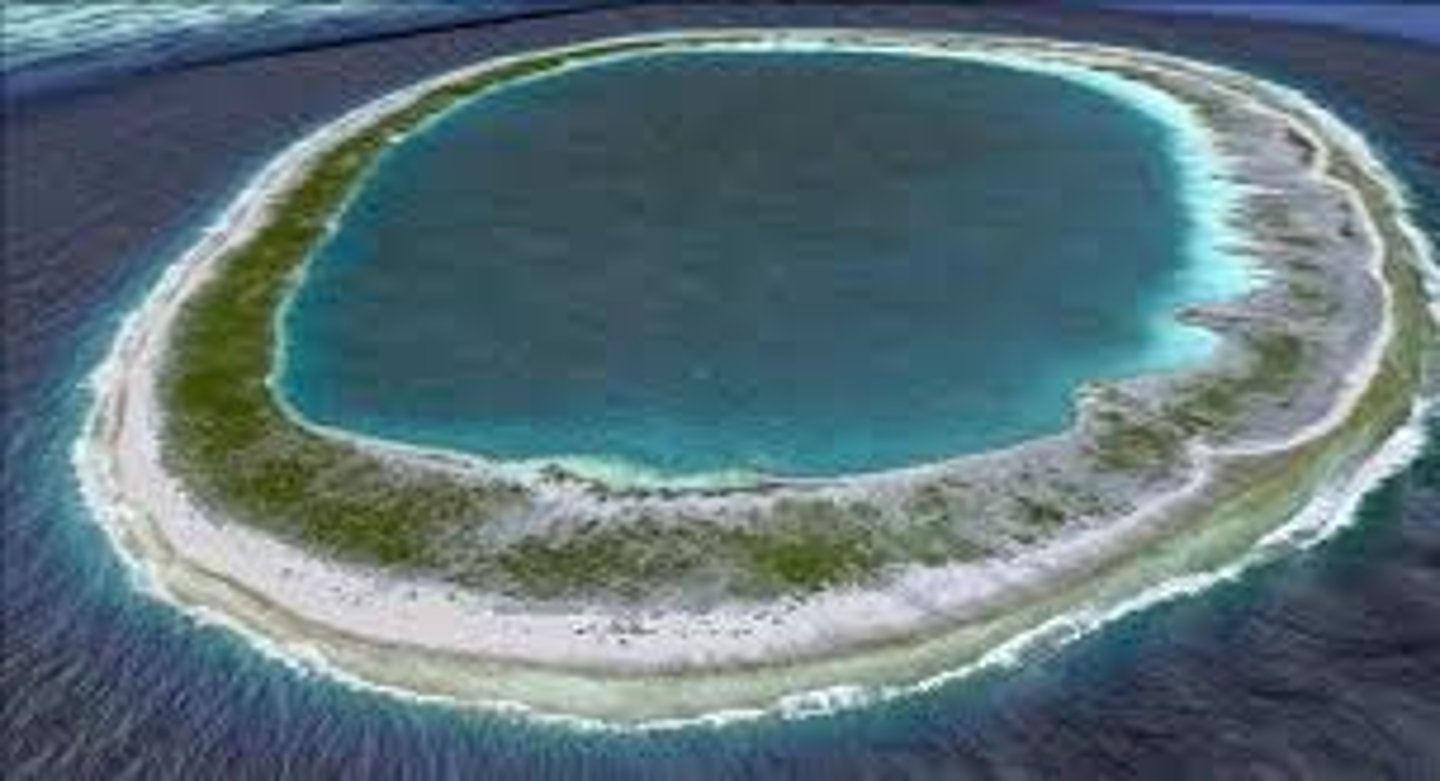

atoll formation
proposed by Darwin
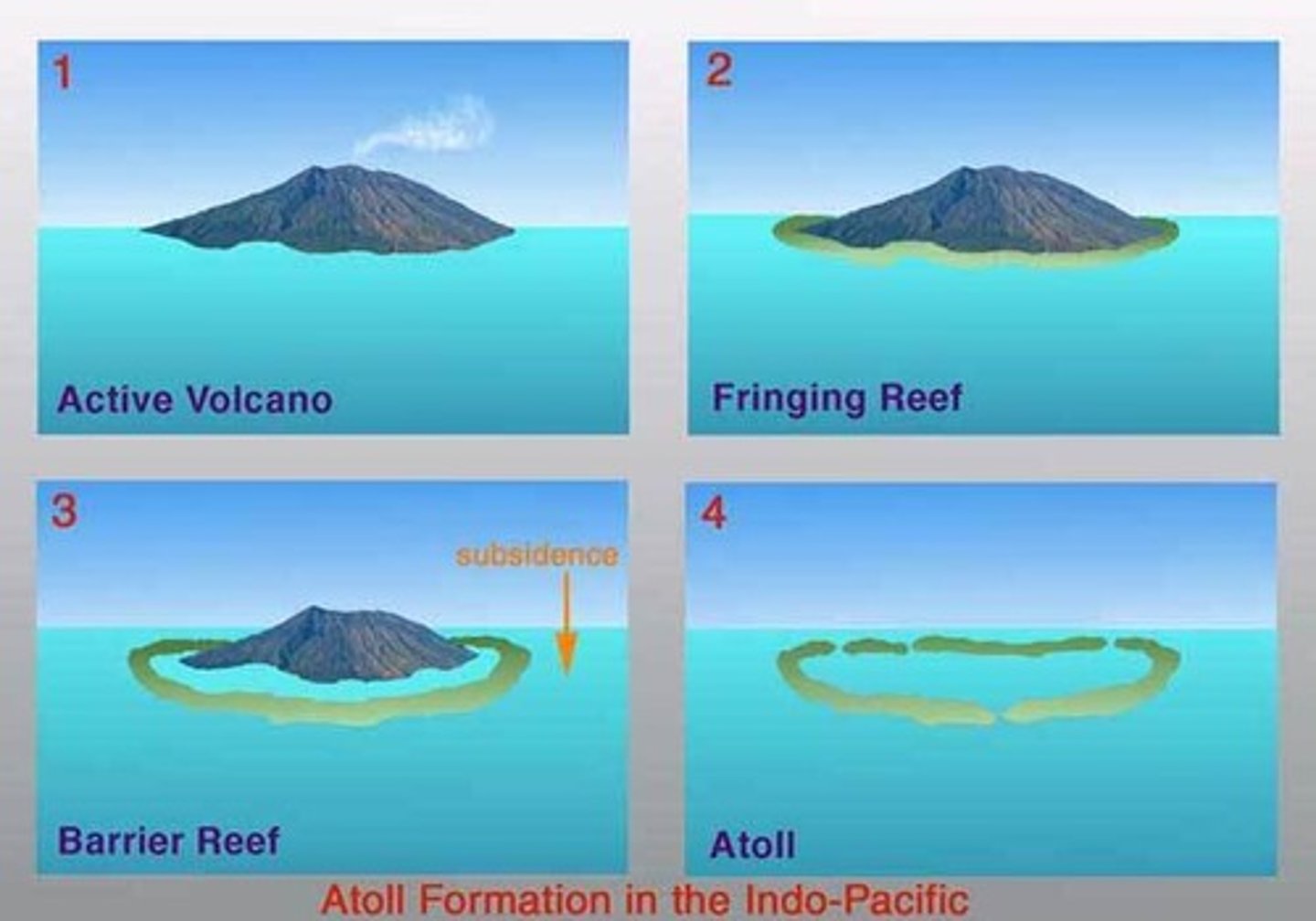
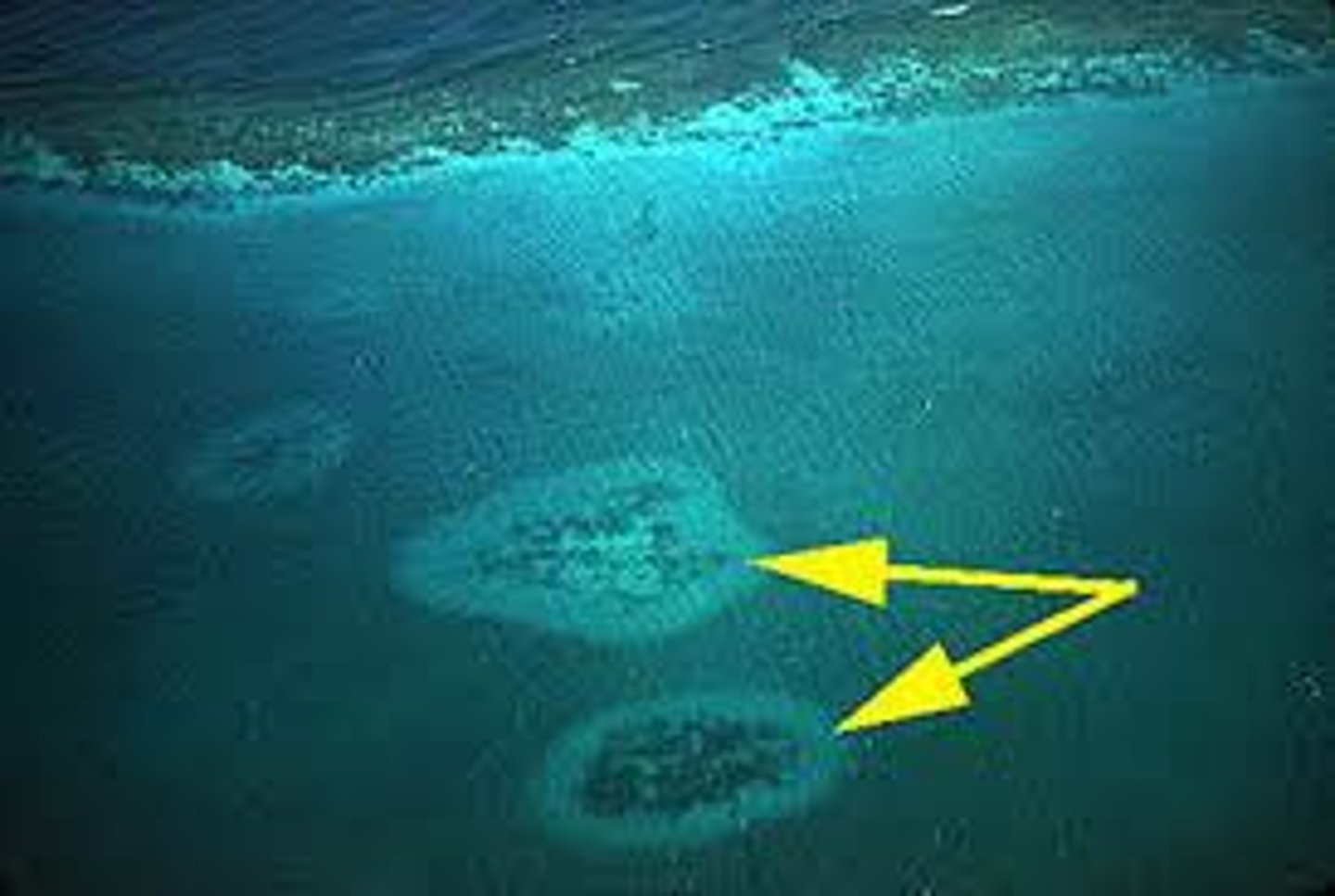
patch reef
in between the land and the barrier reef, show up here and there

zonation of coral reefs
- drop-off zone
- fore reef zone
- reef flat zone
- back reef zone
- shore zone
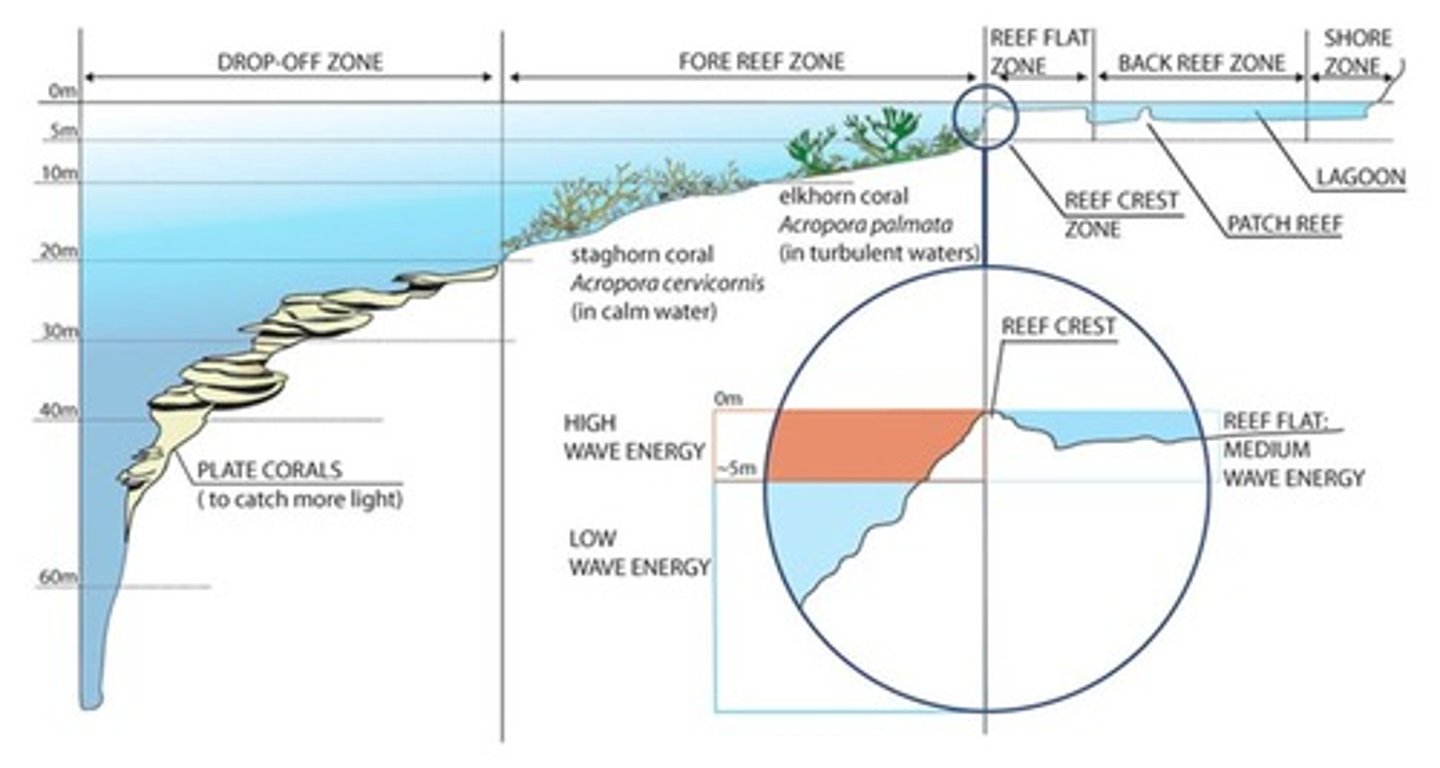
drop-off zone
- plate coral found here (catch more light)
- strong variation in light, exposure to strong currents
fore reef zone
- high wave energy
- branching corals do well in high wave energy because the fragmentation benefits their growth
back reef
has high variation in salinity, temp, and exposure
reef crest
has high wave energy, scouring
competition on reefs corals vs. algae
- algae grows faster and is a better competitor
- herbivores and low nutrients keep algae in check
mutualism on the reef
- closely coevolved species
- crabs live in corals and fight off predators
- both species receive protection
- many vertebrate and invertebrate species burrow into coral or live on and around its branches
- ex. clownfish and sea anemones
abiotic factors in the reef
- hurricanes
- wave action
biotic factors in the reef
bioerosion
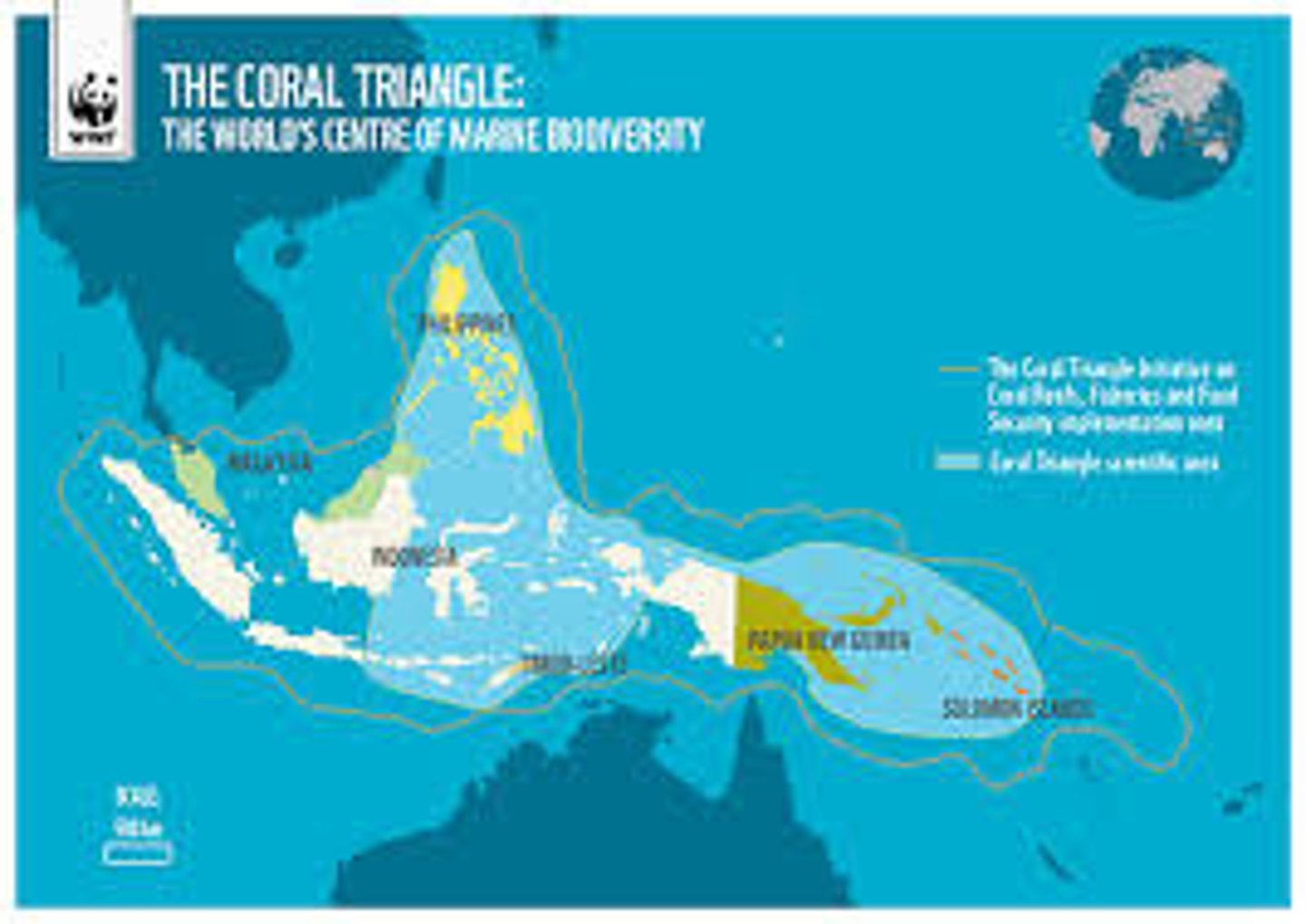
coral triangle
biodiversity hotspot (especially for zooxanthellae)
threats to corals
- climate change: bleaching and ocean acidification
- acanthaster (sea stars)
- trawling
- coral disease
- eutrophication
bleaching
- stress causes coral to expel zooxanthellae
- physiological stress caused by: high temperature, toxins, reduced salinity, microbial infections, reduced temperature
ocean acidification
decreasing pH of ocean waters due to absorption of excess atmospheric CO2 from the burning of fossil fuels

acanthaster: crown of thorns sea star
- eats coral
- recent outbreaks
- decreased predation on larvae
- eutrophication
- simultaneous settling of many larvae
trawling
- trawl nets drag across the ocean floor and tear up coral
- corals cannot recover fast enough
- lots of bycatch
coral disease
- white band disease
- black band disease
- white plague
eutrophication
- land runoff puts nutrients into ocean
- as nutrients increase, algae increases, water clarity decreases, and corals decrease
- Algal blooms can block out sunlight
phase-shift
coral to macroalgal domination