Electric Potential and Capacitance
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Electric Potential
Work done by an external force in bringing a unit positive charge from infinity to a point
Potential due to a Point Charge
V=Kq/r
Potential Due To An Electric Dipole
(derivation)
V=Kpcosθ/r²
Potential Due To A System Of Charges
V=V₁+V₂+V₃…+Vₙ
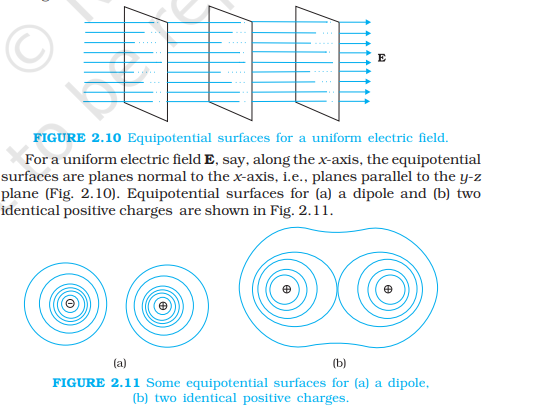
Equipotential Surfaces
An equipotential surface is a surface with a constant value of potential at all points on the surface
For any charge configuration, equipotential surface through a point is normal to the electric field at that point
Potential Energy Of A System Of Charges
Two charges,
U = Kq₁q₂/r
Three charges,
U = K[ q₁q₂/r₁₂ + q₂q₃/r₂₃ +q₁q₃/r₁₃ ]
Potential Energy In An External Field
Single charge:
W=qv
System of two charges:
W = q(V2-V1)
A dipole:
U = -pEcosØ
Relation between E and V
E = -dV/dr
Electrostatics of Conductors
- Inside a conductor, the electrostatic field is zero since, in the static situation, the free charges distribute themselves in such a way that the electric field cancels out everywhere inside the conductor.
- At the surface of a charged conductor, electrostatic field must be normal to the surface at every point, E=σ/εₒ (n-cap)
- Under static conditions, all the charges in a conductor lie on the surface
- The potential inside a conductor which is charged is non-zero and it equals to potential on the surface
- Inside a cavity, electric field is zero and it is protected from external electric field. This is known as electrostatic shielding
Dielectrics
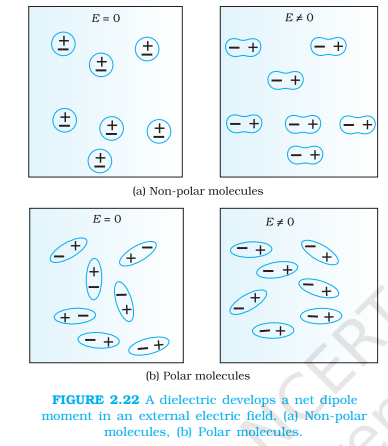
Non-conducting materials that have bound charges
In the presence of an external electric field, charges slightly shift from their average equilibrium positions
Polarised by applied electric field
Types of dielectric: polar and non polar
Types of Dielectrics
Polar Molecule
+ve and -ve charge centre don’t coincide
permanent dipole movement
H₂O, HCl
Non-Polar Molecule
+ve and -ve charge centre coincides
induced dipole moment
H₂, CO₂
image: E=0: No external field applied, E ≠0: External field is applied
Effect of dielectric
See table in cw
Polarisation
Dipole moment per unit volume
P = ε₀χE
Capacitance
C = Q/V F (Farad)
Parallel Plate Capacitor
Two parallel plates separated by a distance d
(derivation)
E = σ/ε₀
V = σd/ε₀
c = ε₀A/d
Effect of Full Dielectric on Capacitance in Parallel Plate Capacitor
c = ε₀A/d * K
Effect of Partial Dielectric on Capacitance in Parallel Plate Capacitor
c = ε₀A/d-t+(t/k)

Spherical Capacitor
c = 4πε₀R
Combination of Capacitors
Series:
1/cₛ = 1/c₁ + 1/c₂ +1/c₃
For n identical capacitors: cₛ = c/n
Parallel:
cₚ = c₁ + c₂ +c₃
For n identical capacitors: cₚ = c x n
Energy Stored in Capacitor
Work done to move charge from battery to capacitor will be stored as potential energy
U = ½ Q²/C
U = ½ CV²
U = ½ QV
Energy Density
Energy Stored/Volume
U = ½ ε₀E²