Intro Unit 5
1/130
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
131 Terms
Why are patient interviews necessary
-To establish patient rapport between the clinician and patient
-To obtain info essential for making diagnosis
-To help monitor changes in the patient's symptoms and response to therapy
Patient Interview techniques
-Introduce yourself in social space (4-12 feet)
-Interview in personal space (2-4 feet)
-Eye contact
-No leading questions; neutral questions
COPD
persistent respiratory symptoms and airflow limitation due to airway and alveolar abnormalities
usually characterized by significant exposure to noxious particles or gases
COPD symptoms
-shortness of breath
-chronic cough & persistent dyspnea
-wheezing & chest tightness
-sputum
asthma
characterized by chronic airway inflammation
Asthma symptoms
-wheezing
-shortness of breath
-chest tightness
-cough
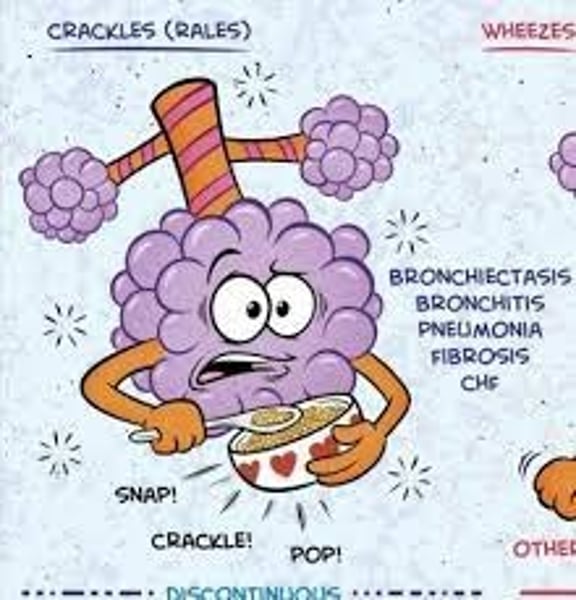
Discontinuous adventitious lung sounds
intermittent crackling
Bubbling sounds of short duration
chronic stridor
Laryngomalacia
vocal fremitus is increased with...
pneumonia and atelectasis
Which diseases mentioned in class are obstructive
COPD
Asthma
CF
how do we diagnose COPD?
spirometry
COPD risk factors
-host factors
-tobacco
-occupation
-indoor/outdoor pollution
Why does asthma make it hard to breathe?
-bronchoconstriction
-airway wall thickening
-increased mucus
what is the most frequent finding during a PE for patients with asthma
wheezing on auscultation (esp on forced expiration)
Cystic Fibrosis
imbalance of ions such as sodium, chloride, bicarbonate into and out of the cell --> leads to thick, viscous secretions
chronic inflammation --> lung damage that leads to irreversible bronchiectasis & respiratory failure
CF PE Findings
-recurrent cough
-increase in the AP diameter of chest due to progressive air tapping
-thick, sticky mucus
-hemoptysis
-wheezing
-salty sweat
-failure to thrive
Interstitial Lung Disease
Disease outside of the lung in the interstitial space. Causes fibrosis.
Interstitial lung diseases causes ___________________ which decreases lung compliance
fibrosis
makes lungs stiff
Patients with interstitial lung diseases complain about...
-dyspnea
-increased WOB
-shallow breathing
-gasping
What clinical findings do we see in Pneumonia
pleuritic chest pain (sharp pain that increases w deep breathing)
vocal fremitus
unilateral reduction in chest expansion
decreased resonance
electrolyte disorders
How do Neuromuscular Diseases effect breathing
the muscles of breathing are not receiving the proper signals to initiate mechanics of breathing
Dyspnea
sensation of breathing discomfort by patient (subjective feeling)
Orthopnea
dyspnea that is triggered when the patient assumes the reclining position
Orthopnea is common in patients with
CHF
mitral valve disease
superior vena cava syndrome
Platypnea:
dyspnea triggered by assuming the upright position
Orthodeoxia
O2 desaturation on assuming upright position
What accompanies platypnea
Orthodeoxia
What is the most common, nonspecific symptom observed in patients with pulmonary disease
cough
what causes a cough
cough receptors in airways are stimulated by inflammation, mucus, foreign material, noxious gases
A chronic cough lasts for _______ weeks or more
8
Characteristics of a Cough
Dry or Loose
Productive or nonproductive
Acute or chronic
if sputum has pulls cells it is said to be _______________
purulent sputum
if the sputum is foul smelling, it is called
fetid sputum
mucoid sputum
translucent, white, or gray sputum
phlegm
mucus from the tracheobronchial tree not contaminated by oral secretion
hemoptysis
coughing up blood or bloody sputum
Massive hemoptysis is more than _______ml/24 hours.
300
What causes Massive Hemoptysis
Bronchiectasis
Lung abscess
Acute/chronic TB
nonmassive hemoptysis
Common causes include: infection of airway, tuberculosis, trauma, & pulmonary embolism
normal lung sounds
audible vibrations primarily generated by turbulent airflow in the larger airways
low frequency sounds
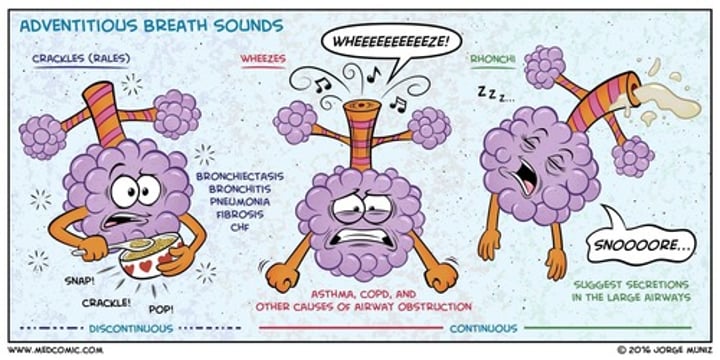
Abnormal lung sounds
wheezing, crackles and silent chest
adventitious lung sounds
What are the 2 types of adventitious lung sounds
Discontinuous
Continuous
continuous adventitious lung sounds
Wheezes
wheezing heard in the upper airway is also known as
stridor
a breath sound is considered abnormal if heard over.....
peripheral lung regions
a breath sound is diminished when...
when sound intensity @ site of generation is reduced due to shallow/ slow breathing
or
when sound transmission through lung or chest wall is decreased (COPD/asthma)
which lung sound is most consistent with airway obstruction
wheezing
Monophonic wheezing
indicates one airway is affected
Polyphonic wheezing
indicates many airways are involved
stridor
strained, high-pitched sound heard on inspiration caused by obstruction in the pharynx or larynx
what are the 4 types of stridor
chronic
acute
inspiratory
expiratory
acute stridor
croup
inspiratory stridor
narrowing above glottis
expiratory stridor
narrowing of lower trachea
which lung sound is identified if airflow moves secretions or fluid in airways
coarse crackles
which lung sound is caused by the sudden opening of small airways in lung deep breathing
fine crackles
Pulm fibrosis and atelectasis
what provides the first clue to AEs to treatments
vital signs
which vital signs are taken frequently
body temp
pulse rate
RR
BP
what is the normal body temp
98.6 F or 37 C
hyperthermia/hyperpyrexia
increased temp
hypothermia
decreased body temperature
where do we measure body temp
mouth
axilla
ear
rectum
which measurement of body temp is the most accurate
rectum
where do we typically palpate to find Pulse Rate
radial artery
normal adult pulse rate
60-100 bpm
Tachycardia
HR > 100 bpm
Bradycardia
HR
Pulses paradoxus
a significant decrease in pulse strength during spontaneous inspiration (>10 mmHg)
which type of patients would we see pulses paradoxus
-acute obstructive pulmonary disease
-asthma attack
pulsus alternans
alternating strong and weak pulses
which type of patients would we see pulses alternans
left side heart failure
not related to respiratory disease
resting adult RR
12-18 breaths/min
Tachypnea
RR > 20 breaths per min
exertion, fever, hypoxemia, hypercarbia, metabolic acidosis, anxiety
bradypnea
RR
systolic pressure
peak force exerted in the major arteries during contraction of the left ventricle
normal systolic blood pressure
90-140 mmHg
120 is ideal
Diastolic pressure
the force in the major arteries remaining after relaxation of the ventricles
normal diastolic blood pressure
60-90 mm Hg
80 is ideal
Pulse pressure
systolic pressure - diastolic pressure
normal pulse pressure range
30-40 mm Hg
Hypertension
BP persistently >140/90
Hypotension
SBP
BP shock
inadequate delivery of O2 and nutrients to the vital organs relative to their metabolic demand
SBP
how do we treat BP shock
fluids
blood products
vasoactive drugs
levels of consciousness
confusion
delirious
lethargic
obtunded
stuporous
comatose
(box 16.6)
2 types of chest pain
pleuritic and nonpleuritic
which type of chestpain is located laterally or posteriorly. it results in sharp pain and increases with deep breathing
pleuritic chest pain
pneumonia& pulm. embolism
which type of chest pain is located in the center of the chest and may radiate to shoulder or arm. it is not affected by breathing
nonpleuritic chest pain
angina, gastroesophageal reflux
Angina
chest pain
List several indicators to assess a patient's overall (general) appearance.
- level of consciousness
-facial expression
-level of anxiety/ distress
-body positioning
-personal hygiene
what affects level of consciousness
poor cerebral blood flow
Nasal flaring is often seen in infants with _________ _______________
respiratory distress (increase WOB)
jugular venous distension (JVD)
a notable prominence of the jugular vein when the patient is seated at a 45 degree angle
what is the most common cause for JVD
patients with CHF and cor pulmonale
barrel chest
abnormal rounded chest cavity
increased AP diameter
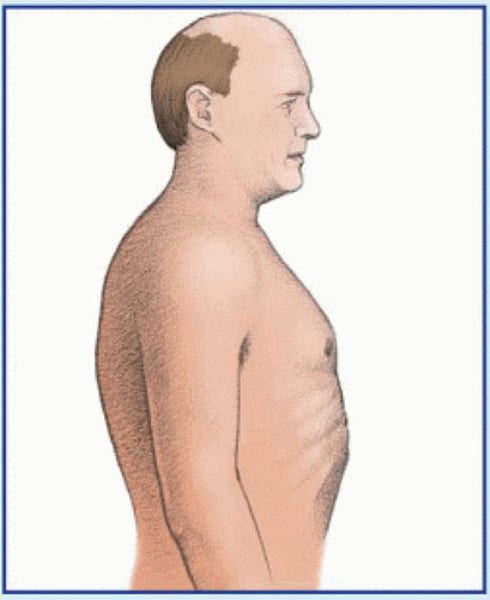
barrel chest is associated with
emphysema
pectus carinatum
abnormal protrusion of sternum
(breastbone pushed out)
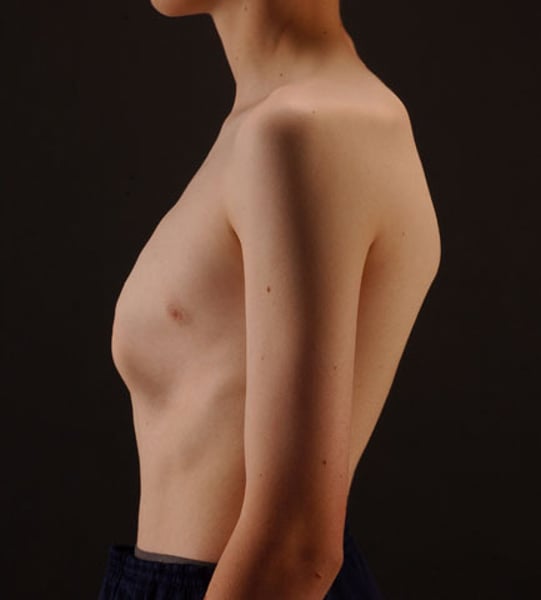
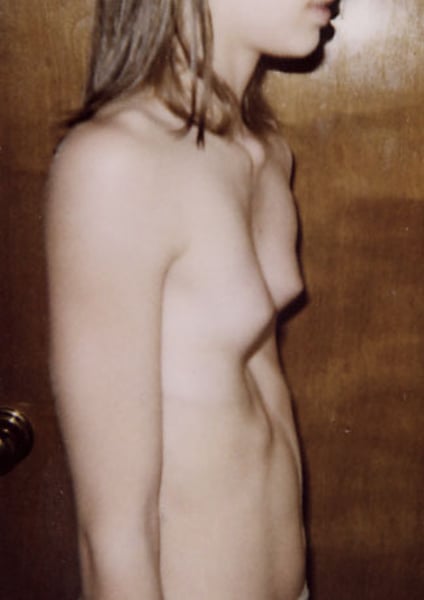
pectus excavatum
Depression of part or entire sternum, which can produce a restrictive lung defect
(breastbone pushed in)

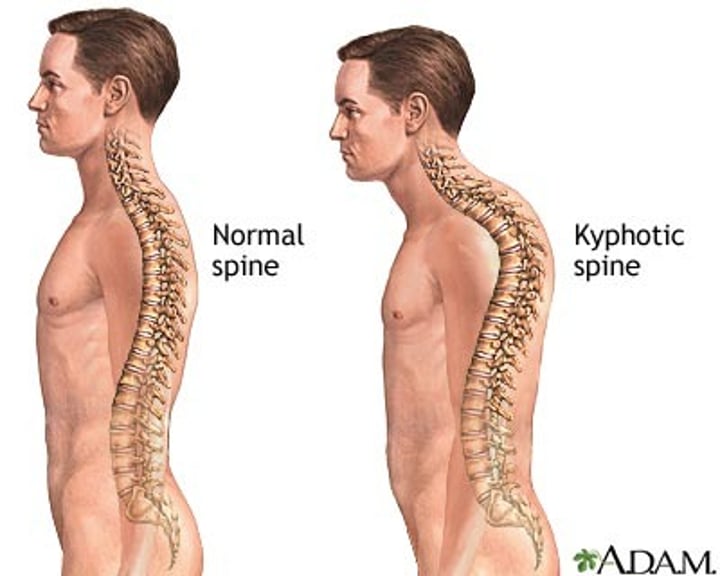
kyphosis
spinal deformity in which the spine has an abnormal AP curvature
"hunchback"
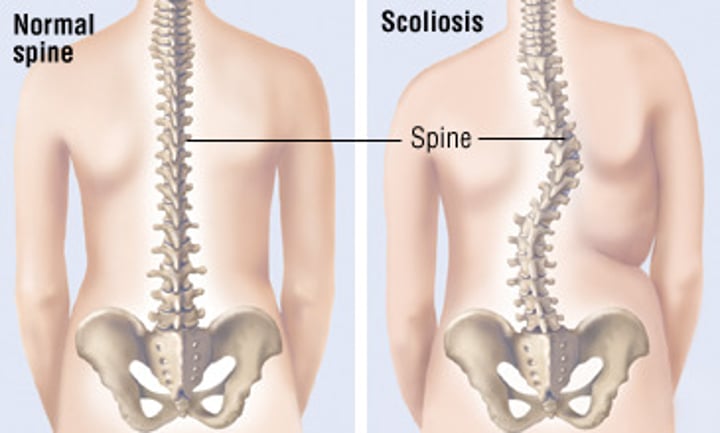
scoliosis
spinal deformity in which the spine has a lateral curvature