cells and microscopy
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
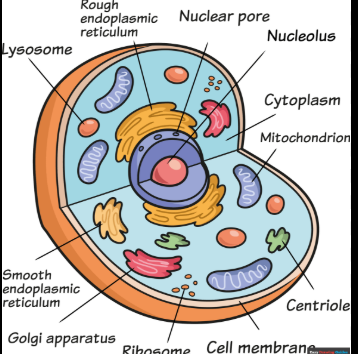
animal cells
cell organelles:
nucleus - contains genetic material (DNA) which controls the activities of the cell
cytoplasm - where most chemical reactions happen
mitochondria - respiration happens in the mitochondria that provides energy for the cell
cell membrane - creates barrier for the cell, controls what can flow in and out of the cell
ribosomes - found in the cytoplasm and make proteins. They ‘read’ dna and build proteins from that.
it is a eukaryote
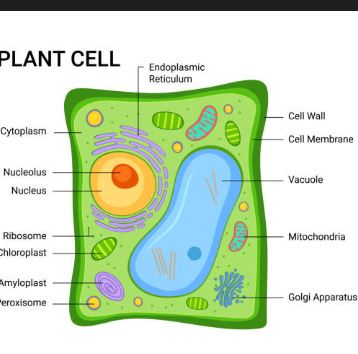
plant cell
they contain everything the animal cell card listed and more
cell organelles:
chloroplast - absorb light energy for photosynthesis. Only found in some plant cells
vacuole - filled with cell sap, keeps it turgid and suppourts the structure of the plant
cell wall - made of celllose, strengthens the plant cell, helps maintain shape
it is a eukaryote
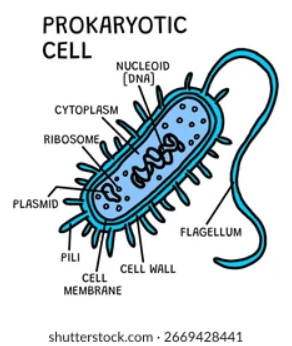
prokaryotes (bacteria)
they have no nucleus or mitochondria
prokaryote organelles:
cell membrane
cell wall
slime capsule - protects bacteria but not in every bacteria
loop of genetic material
plasmid - small circular dna
flagellum - allows movement only in some bacteria
ribosomes
prokaryotes and eukaryotes
cells can either be prokaryotic or eukaryotic.
eukaryotic cells are complex and include all animal and plant cells. Prokaryotic cells are smaller and simpler e.g. bacteria
eukaryotes are organisms made up of eukaryotic cells
a prokaryote is a prokaryotic cell (its a single celled organism)
both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells contain various cell parts called subcellular structures
exam question - compare a prokaryote and a eukaryote
Model Answer
Similarities: Both cell types possess a cell membrane, cytoplasm, ribosomes (for protein synthesis), and genetic material (DNA).
Differences - Genetic Material: Eukaryotic cells contain their DNA within a membrane-bound nucleus, whereas prokaryotic DNA is found free-floating in the cytoplasm in a region called the nucleoid. Additionally, prokaryotes often have small, circular DNA rings called plasmids, which are rarely found in eukaryotes.
Differences - Organelles: Eukaryotes contain membrane-bound organelles such as mitochondria and chloroplasts, which are absent in prokaryotic cells.
prepare a slide - human cheek cell
use a cotton bud to swab some cells off the inside of your cheek
smear it on a slide and put a couple drops of methylene blue
place a cover onto the methylene and place under microscope
required practical - preparing a slide to view onion cells
add a drop of water to clean the slide
cut up some onion and separate it out in layers. Use twezers to peel off some epidermal tissue from the bottom of one of the layers
using tweezers, place the epidermal tissue into the water on the slide
add a drop of iodine solution to stain/ highlight objects in a cell by adding colour to them
place a cover slip, tilt and lower so no air bubbles that might obstruct view of specimin
required practical - observing the onion cell specimin
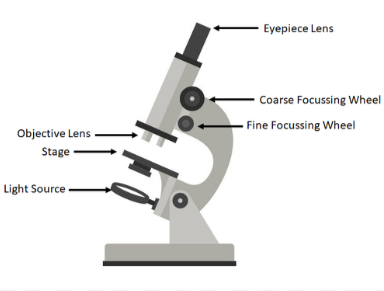
clip the slide onto the stage
select lowest powered objective lens (lowest magnification)
use coarse adjustment knob to move stage up and down to just below objective lens
look down eye piece. turn knob until in focus
adjust the focus with the fine adjustment knob until the image is roughly in focus
adjust more until you get a clear image of whats on the slide
if you need to see the slide with a greater magnification, swap to a higher powered objective lens and refocus.
required practical - drawing observations of onion cell
when drawing your specimin use a sharp pencil to draw clear unbroken lines, no colouring or shading, if you are drawing cells the subcellular structures should be drawn in proportion and if you are asked to draw a certain drawing it has to take up at least half of the space available. Also when labelling, use straight uncrossed lines and work out the magnification of the drawing.
specialsed cells defenition
a specialized cell is a cell that performs a specific function. Most cells in an organism are specialised
why do animals have specialised cells
Animals have specialized cells to efficiently perform specific, complex tasks necessary for survival, such as movement, oxygen transport, and nutrient digestion.
compare a specialsed and a generalised cell
Shape: Generalized cells are often depicted as simple, rounded, or irregular. Specialized cells have specific, often complex shapes (e.g., long, thin axons for nerve cells, biconcave shapes for red blood cells) to facilitate their function.
Organelle Abundance: Specialized cells alter organelle numbers to fit their role. For example, muscle cells contain high numbers of mitochondria for energy, while sperm cells have an acrosome for enzyme storage.
Unique Features: Specialized cells may possess unique structures, such as the contractile, striated fibers in muscle cells or the flagellum tail on a sperm cell.
Nucleus Presence: Some specialized cells, such as mature red blood cells in humans, lack a nucleus to maximize space for carrying oxygen, unlike a generalized cell which contains a nucleus.
muscle cells
musclec cells are specalized for contraction. The function of a muscle cell is to contract quickly. These cells so long (so they have space to contract) and contain lots of mitochondria to transfer the energy needed for contraction.
specialized cell - nerve cell
function - recives and sends messages from the body and back to the brain
adaptation - covered in fat to prevent electrical impulses
specialized cell - sperm cell
function - to carry the fathers genetic info (dna) when fertilizing the egg
adaptation - have long tail to swim fast to find the egg, lots of mitochondria in the cell to provide energy it needs to do this. It also carrys enzymes in its head to digest through the egg cell membrane
specialized cell - ciliated cell
function - stop lung damage and sweeps mucus and trapped dust and bacteria to be swallowed
adaptation - they line the air passages down to the lungs
specialized cell - egg cell
function - carrys the mothers dna and suppourts a growing embryo
adaptation - contains half the dna required to make a person
specialized cell - red blood cell
function - carrys oxygen from lungs to body
adaptation - large surface area with concave shape, has no nucleus to make room for more oxygen
specialized cell - palisade cell
function - to carry out photosynthesis
adaptation - packed with chloroplasts to absorb sunlight
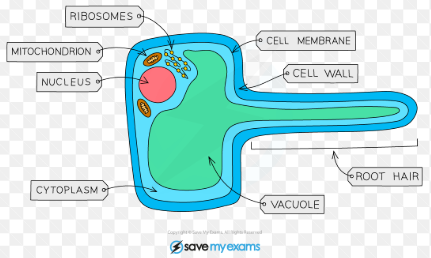
specialized cell - root hair cell
function - absorbs minerals and water from soil
adaptation - large surface area to absorb lots of water
a scientific drawing of a root hair cell observed using a light microscope
specialized cells - phloem and xylem
function - they are specialised for transporting substances. They form phloem and xylem tubes which transport water and food around plants. To form the tubes, the cells are long and joined end to end. Xylem cells are hollow in the centre and phloem cells have very few subcellular structures
adaptation - Xylem and phloem are vascular tissues with specialized adaptations for transport. Xylem (dead cells, lignin, no end walls) efficiently moves water upward via transpiration. Phloem (living cells, sieve plates, companion cells) facilitates bi-directional translocation of sucrose and amino acids. Both form organized bundles to provide structural support.
cell differentiation
differentiation is the process by which a cell changes to become specialised for its job. As cells change, they develop different sub-celullar structures and turn into different types of cells
most differentiation occurs as an organism develops. In most animal cells, the ability to differentiate is then lost after they become specialised however lots of plant cells dont lose this ablility. The cells that differentiate in mature animals are mainly used for repairing and replacing skin cells and blood cells
some cells are undifferentiated and they are called stem cells
resolution
the smallest distance you can see between two seperate points
light microscope
magnification - 300-2000 x larger
resolution - cant resolve distance smaller than 200nm (half of a visible light wave)
electron microscope
magnification - 2,000,000 x larger
resolution - as small as 0.2nm but 3d can only do 10nm
have to be kept in rooms with controlled temp, pressure and humidity
microscopesy conversions
cm →mm = x10
cm →um = x10,000
mm →um = x1000
um →nm = x1000
mm →cm = /10
um →cm = /10,000
um →mm = /1000
nm →um = /1000
parts of a microscope
magnification equation
magnification = image size / real size