Divisions of the Nervous System
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
Peripheral Nervous System
Includes cranial nerves arising from the brain, somatic fibers connecting to the skin and skeletal muscles, autonomic fibers connecting to viscera, and spinal nerves arising from the spinal cord.
Sensory Nerves
Conduct impulses into the brain or spinal cord.
Motor Nerves
Conduct impulses to muscles or glands.
Mixed Nerves
Contain both sensory nerve fibers and motor nerve fibers; most nerves.
General somatic efferent fibers
Carry motor impulses from CNS to skeletal muscles.
General somatic afferent fibers
Carry sensory impulses to CNS from skin and skeletal muscles.
General visceral efferent fibers
Carry motor impulses from CNS to smooth muscles and glands.
General visceral afferent fibers
Carry sensory impulses to CNS from blood vessels and internal organs.
Special somatic efferent fibers
Carry motor impulses from brain to muscles used in chewing, swallowing, speaking, and forming facial expressions.
Special visceral afferent fibers
Carry sensory impulses to brain from olfactory and taste receptors.
Special somatic afferent fibers
Carry sensory impulses to brain from receptors of sight, hearing, and equilibrium.
Cranial Nerve I
Olfactory (I) - sensory fibers transmit impulses associated with smell.
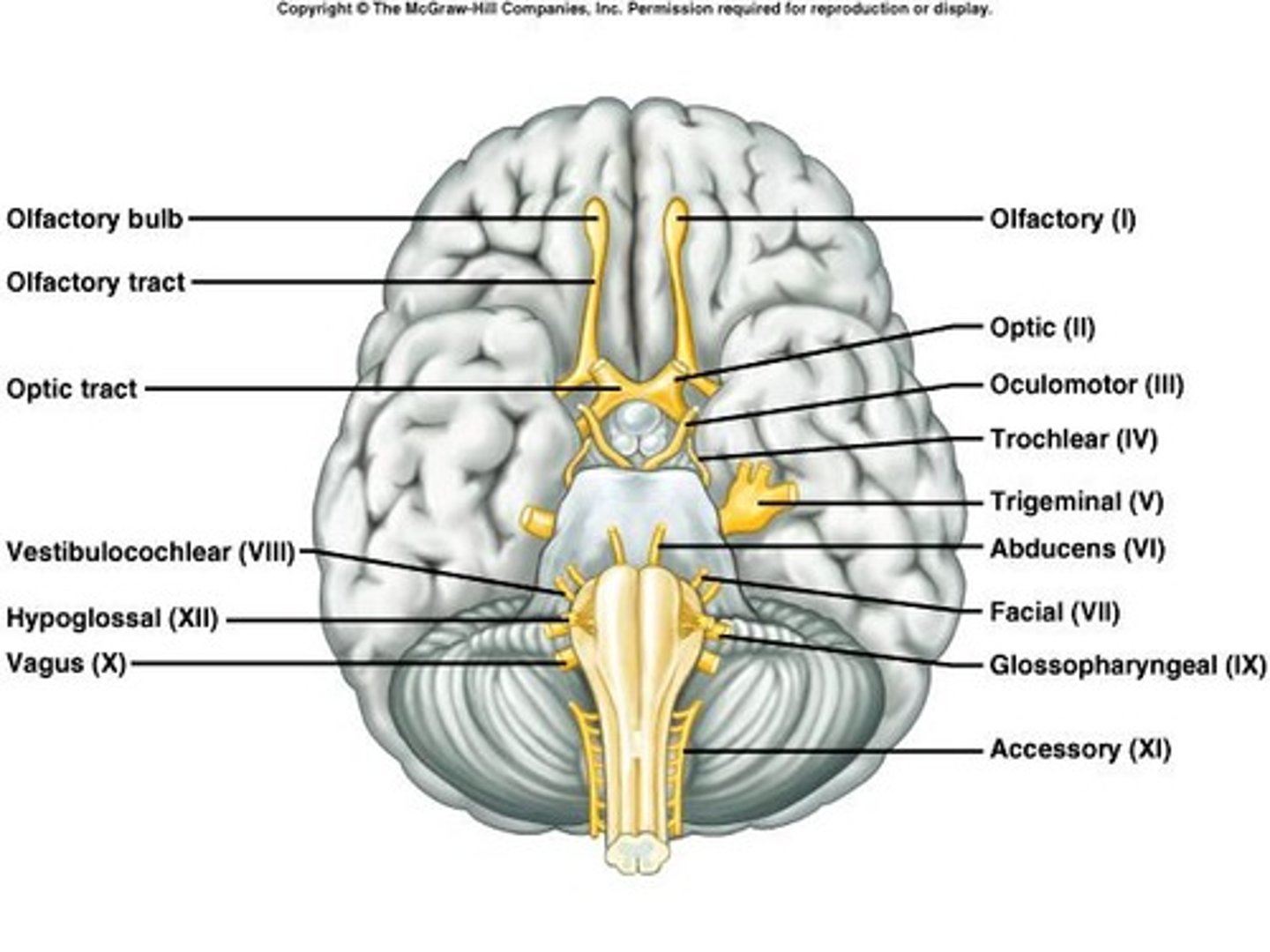
Cranial Nerve II
Optic (II) - sensory fibers transmit impulses associated with vision.
Cranial Nerve III
Oculomotor (III) - primarily motor; motor impulses to muscles that raise eyelids, move the eyes, focus lens, adjust light entering eye.
Cranial Nerve IV
(Trochlear) Cranial Nerve IV is primarily a motor nerve that facilitates movement of the eyes, specifically controlling the muscles that move the eyes downward and medially.
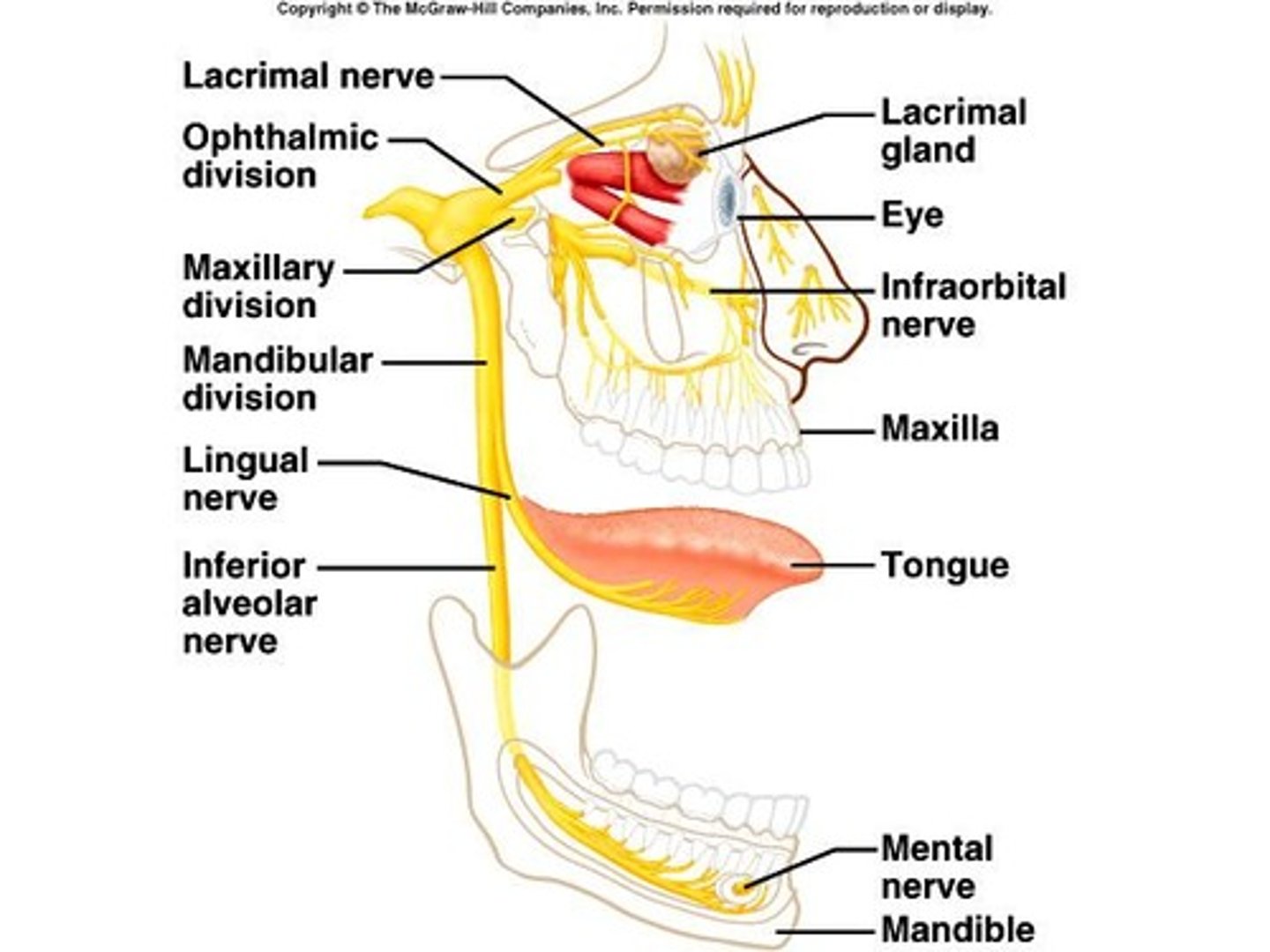
Cranial Nerve V
Trigeminal (V) - mixed; sensory from surface of eyes, tear glands, scalp, forehead, upper eyelids, and motor to muscles of mastication.
Cranial Nerve VI
Abducens (VI) - primarily motor; motor impulses to muscles that move the eyes.
Cranial Nerve VII
Facial (VII) - mixed; sensory from taste receptors, motor to muscles of facial expression.
Cranial Nerve VIII
Vestibulocochlear (VIII) - sensory; vestibular branch from equilibrium receptors of ear.
Cranial Nerve IX
Glossopharyngeal (IX) - mixed; sensory from pharynx, tonsils, tongue, and motor to salivary glands.
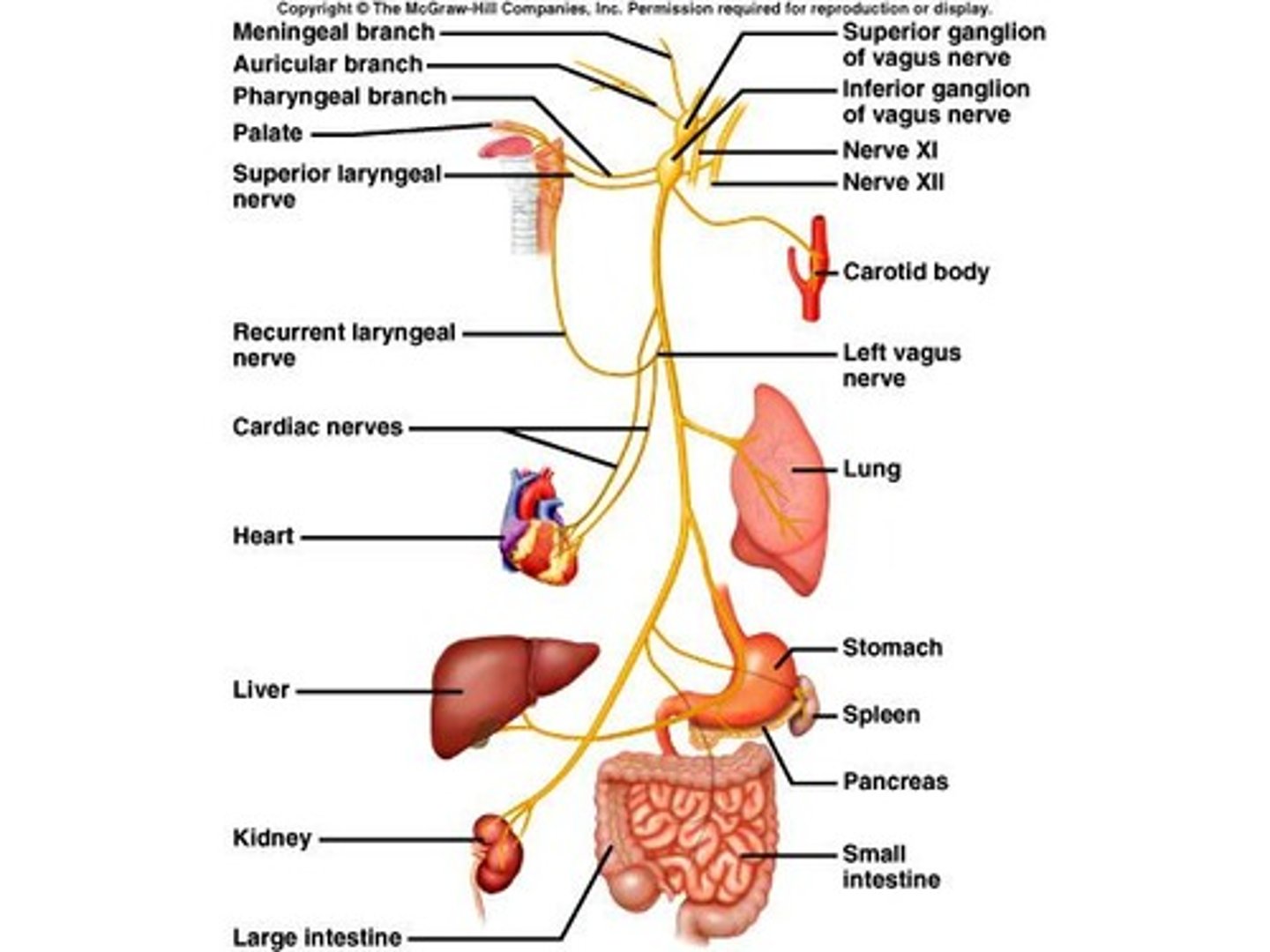
Cranial Nerve X
Vagus (X) - mixed; somatic motor to muscles of speech and swallowing, autonomic motor to viscera of thorax and abdomen.
Cranial Nerve XI
Accessory (XI) - primarily motor; motor to muscles of soft palate, pharynx, and larynx.
Cranial Nerve XII
Hypoglossal (XII) - primarily motor; motor to muscles of the tongue.
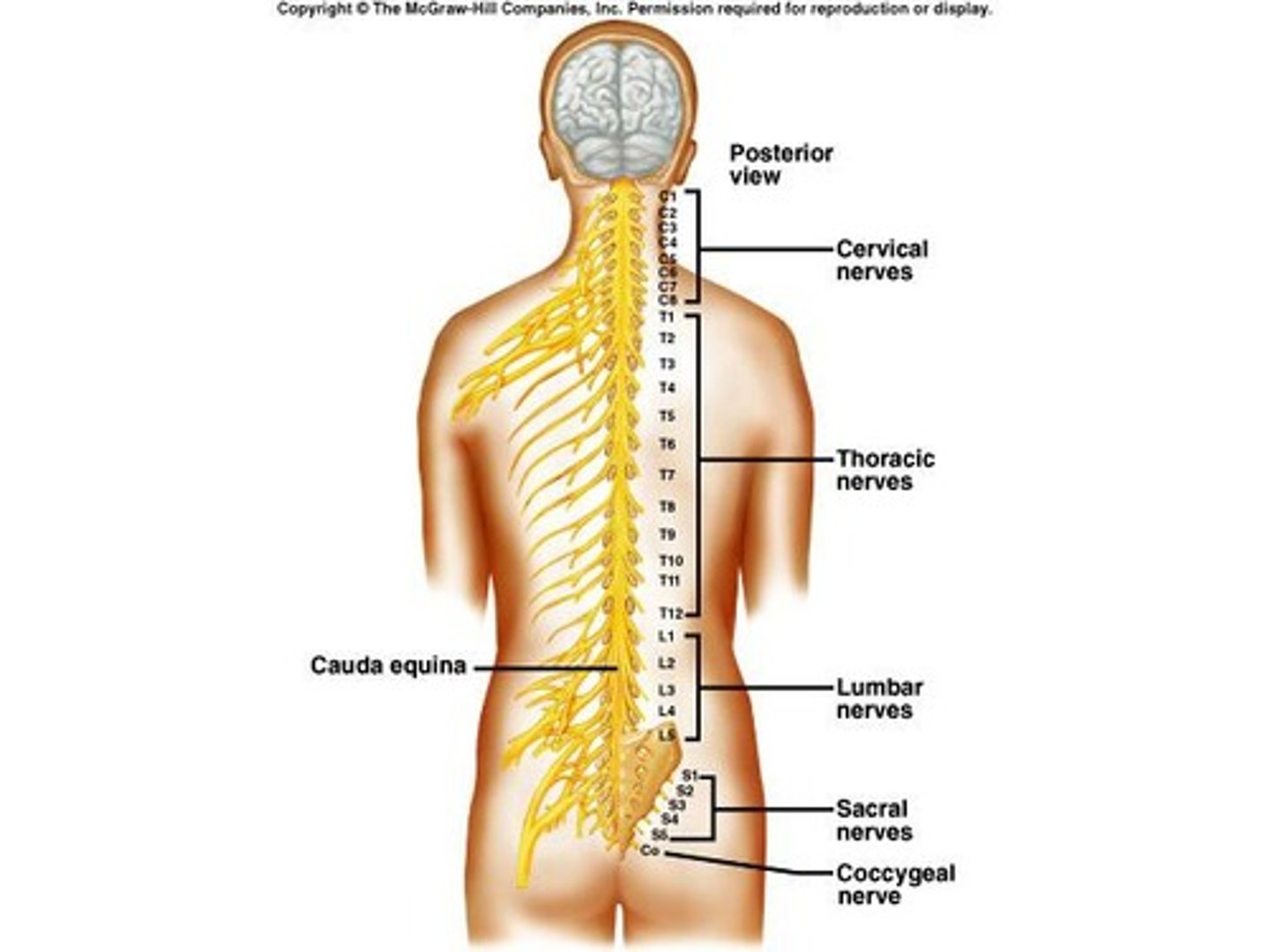
Spinal Nerves
31 pairs including 8 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, 5 sacral, and 1 coccygeal.
Dorsal root
Posterior or sensory root; axons of sensory neurons in the dorsal root ganglion.
Dorsal root ganglion
Cell bodies of sensory neurons whose axons conduct impulses inward from peripheral body parts.
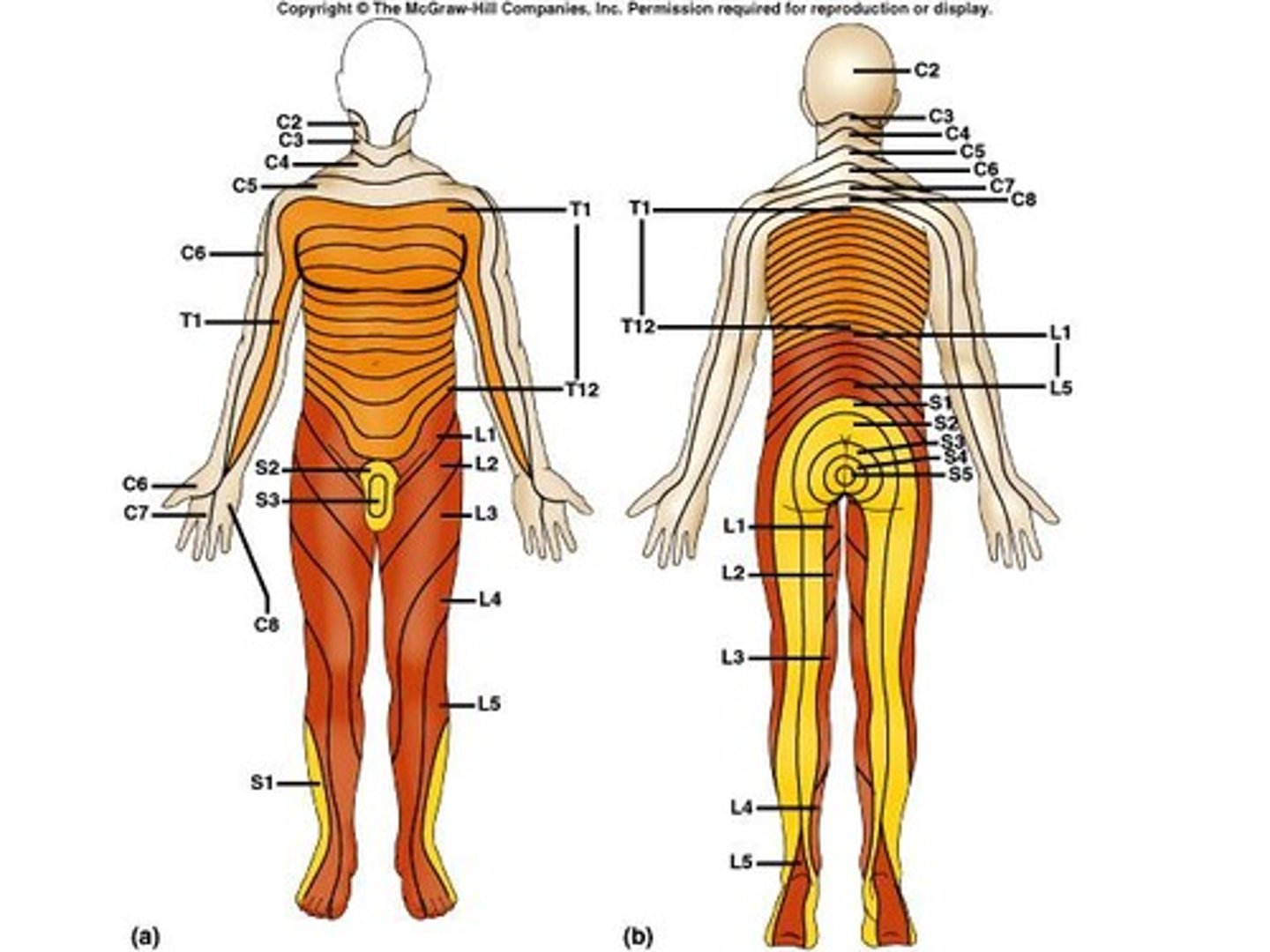
Dermatome
An area of skin that the sensory nerve fibers of a particular spinal nerve innervate.
Ventral root
Anterior or motor root.
Ventral root
axons of motor neurons whose cell bodies are in spinal cord
Spinal nerve
union of ventral root and dorsal root
Cervical Plexuses
Nerve plexus - complex networks formed by anterior branches of spinal nerves; fibers of various spinal nerves are sorted and recombined
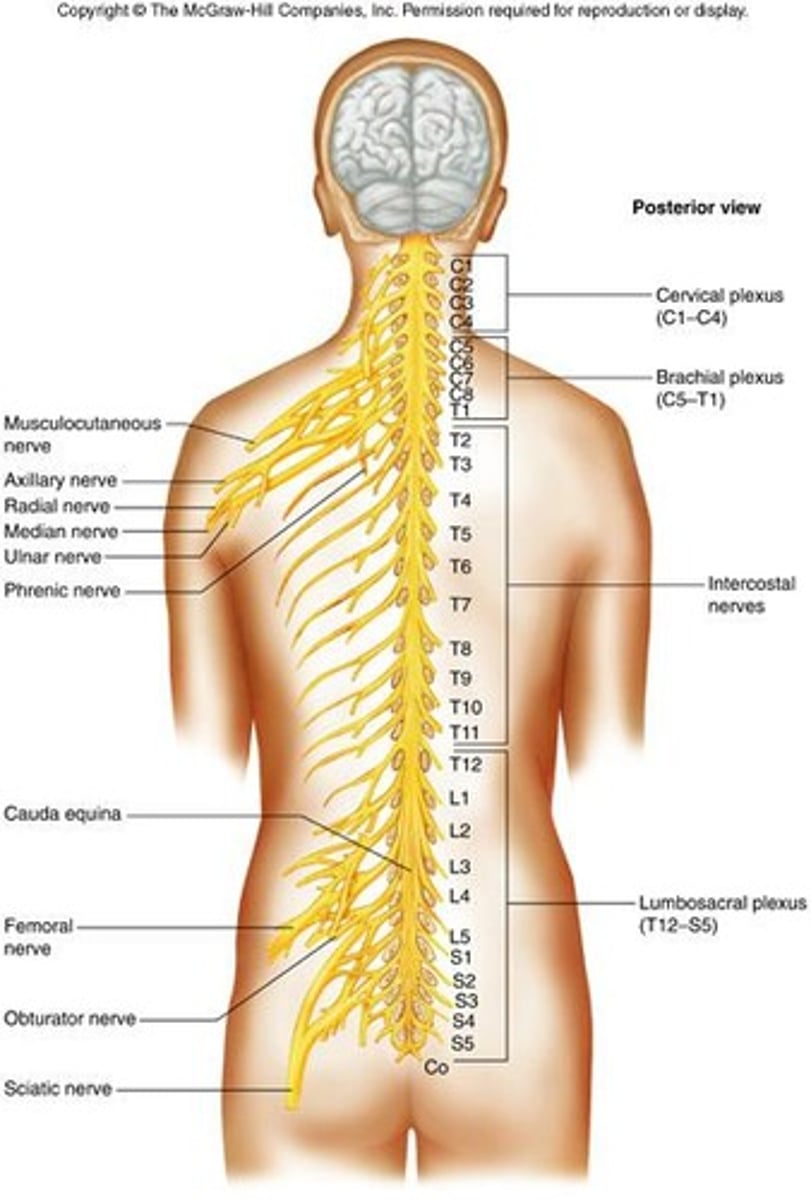
Cervical Plexus
formed by anterior branches of C1-C4; lies deep in the neck; supply muscles and skin of the neck
C3 - C5
contribute to phrenic nerves
Brachial Plexuses
C5-T1; Lies deep within shoulders
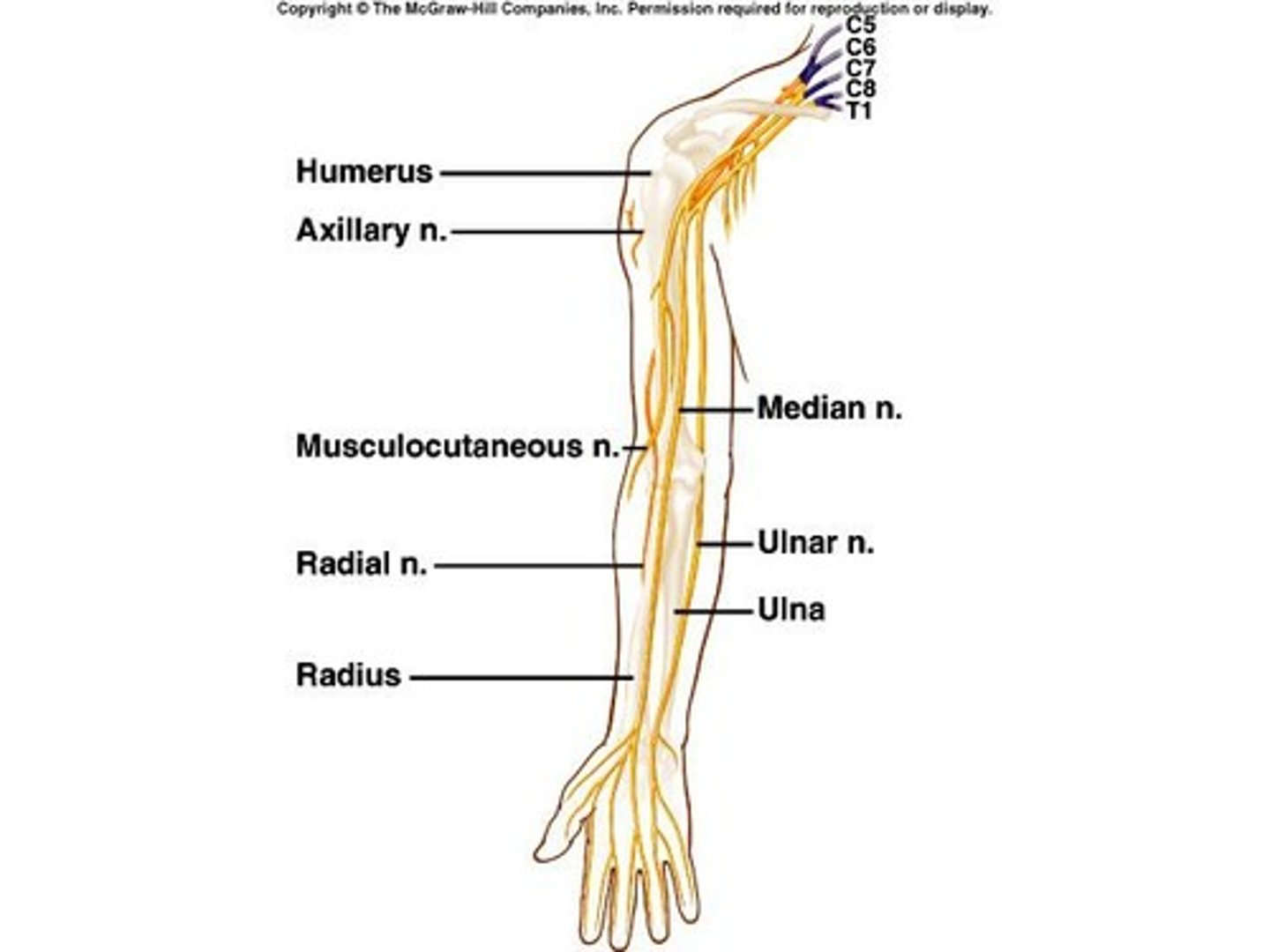
Musculocutaneous nerves
supply muscles of anterior arms and skin of forearms
Ulnar and Median nerves
supply muscles of forearms and hands; supply skin of hands
Radial nerves
supply posterior muscles of arms and skin of forearms and hands
Axillary nerves
supply muscles and skin of anterior, lateral, and posterior arms
Lumbosacral Plexuses
T12 - S5; Extend from lumbar region into pelvic cavity
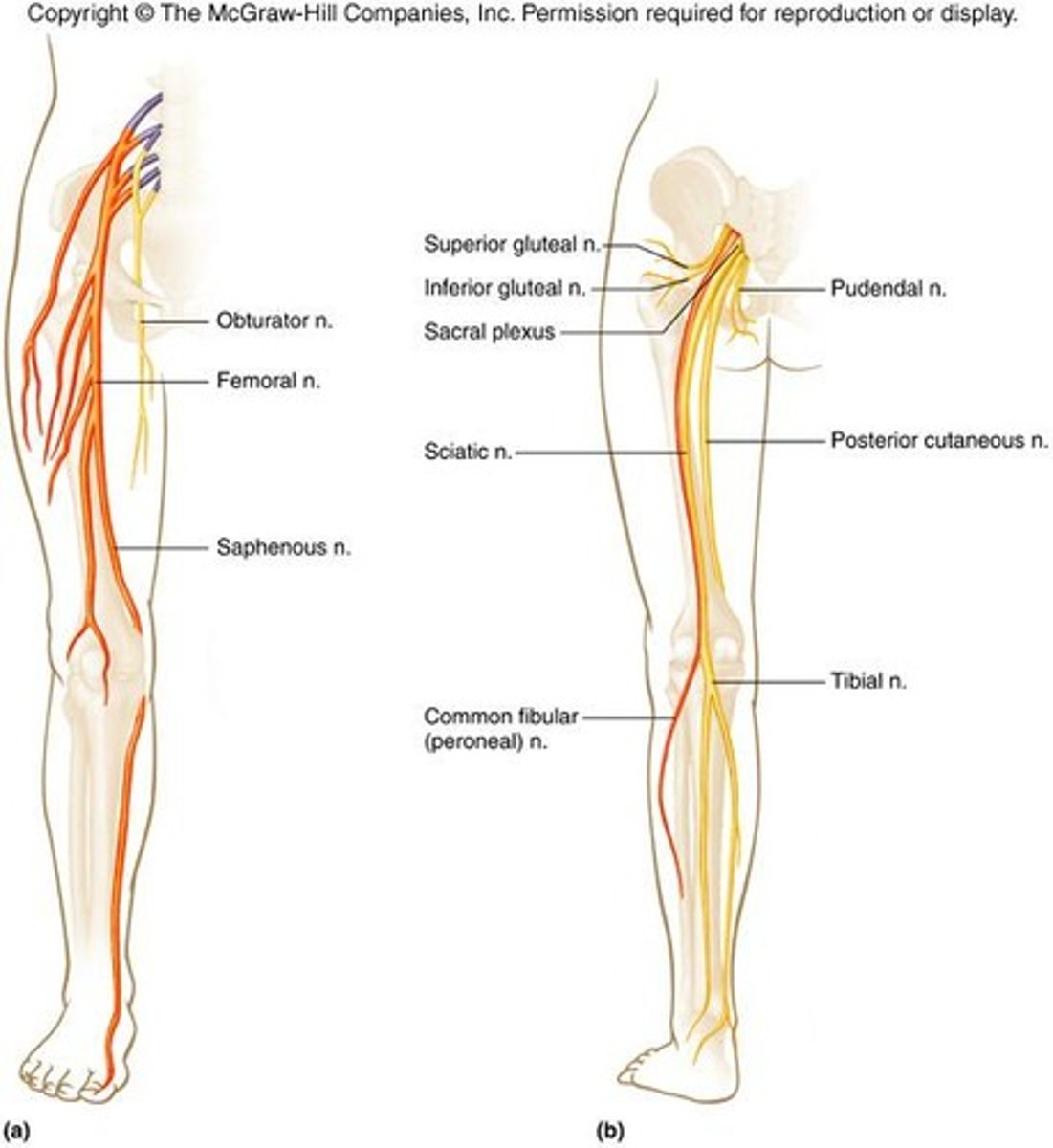
Obturator nerves
supply motor impulses to adductors of thighs
Femoral nerves
supply motor impulses to muscles of anterior thigh and sensory impulses from skin of thighs and legs
Sciatic nerves
supply muscles and skin of thighs, legs, and feet
Autonomic Nervous System
Functions without conscious effort; Controls visceral activities; Regulates smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands
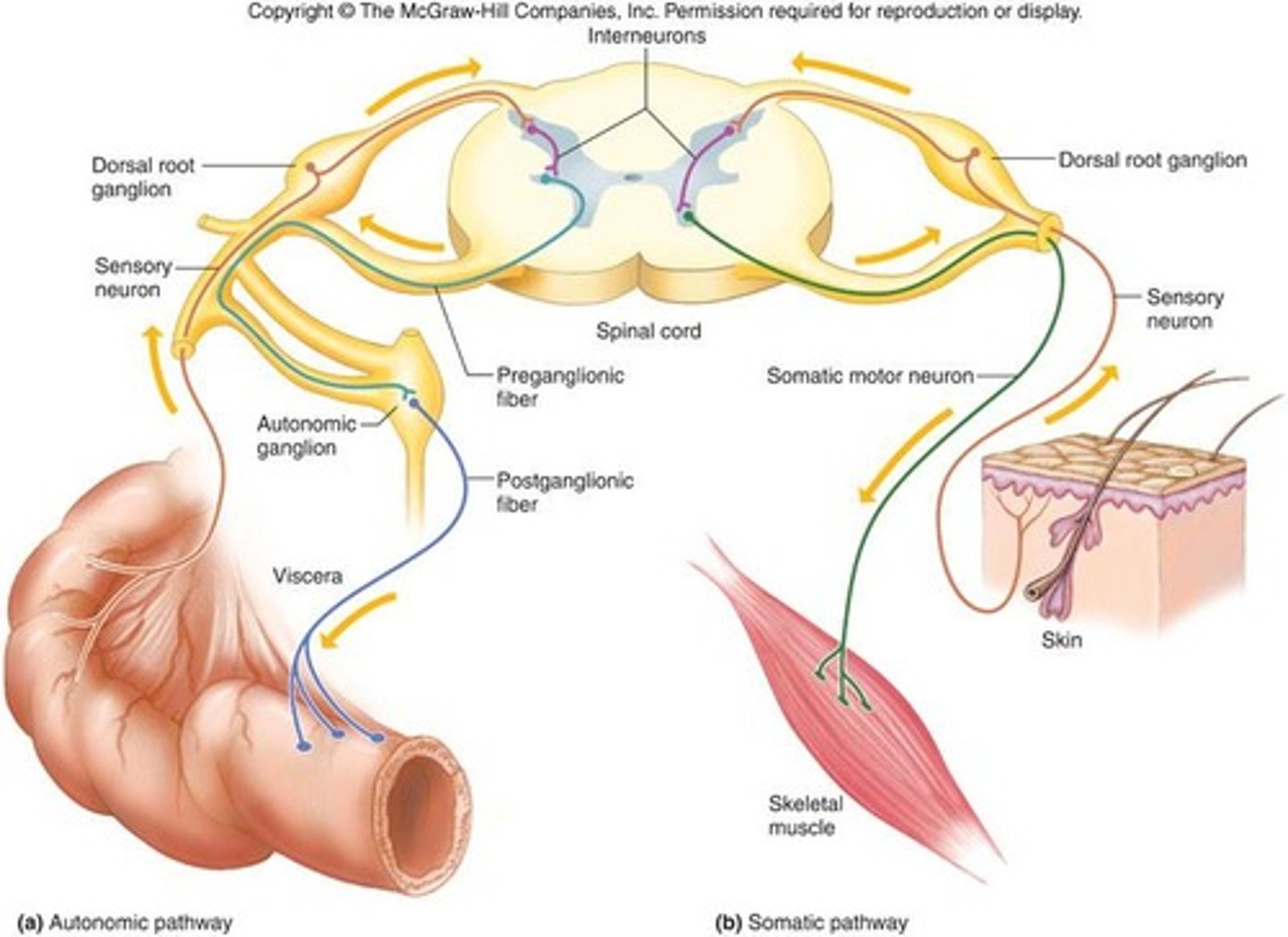
Efferent fibers
typically lead to ganglia outside CNS
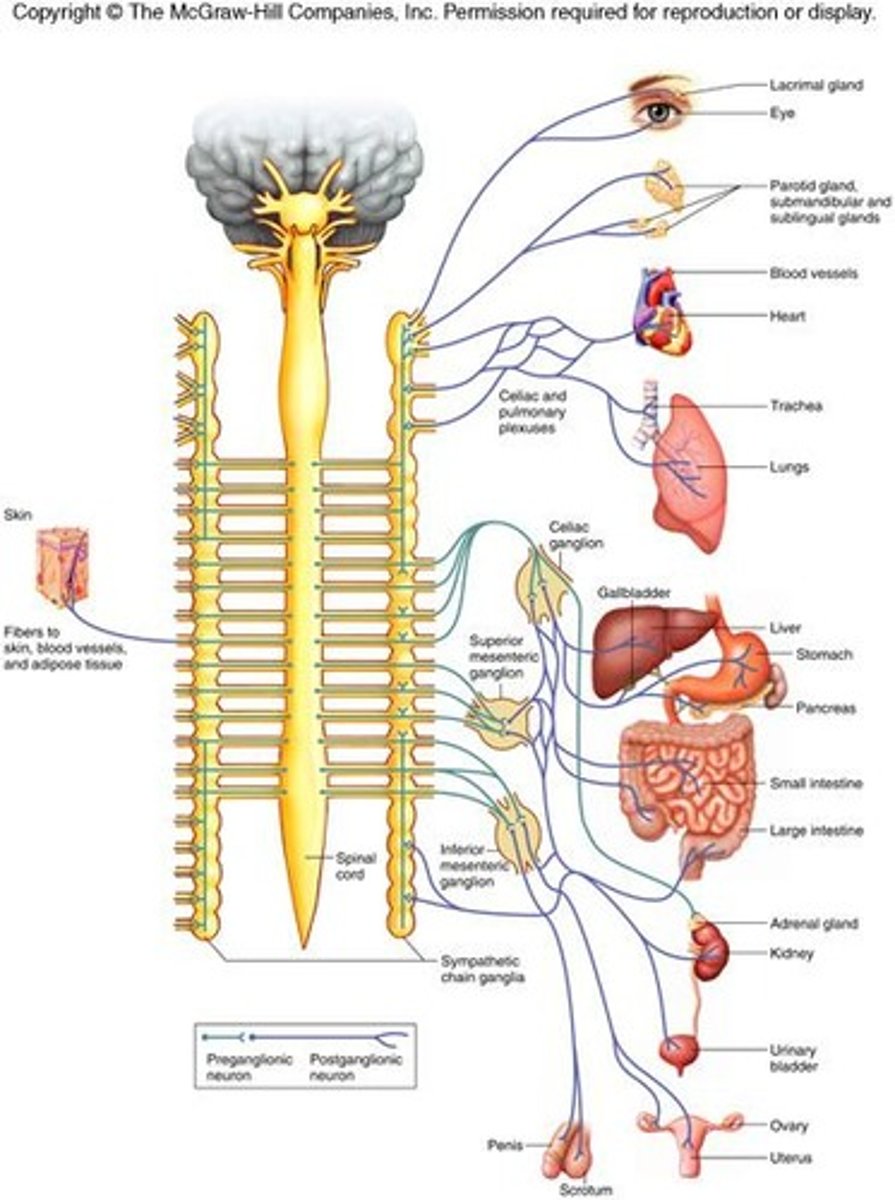
Sympathetic Division
thoracolumbar division - location of preganglionic neurons
Preganglionic fibers
leave spinal nerves through white rami and enter paravertebral ganglia
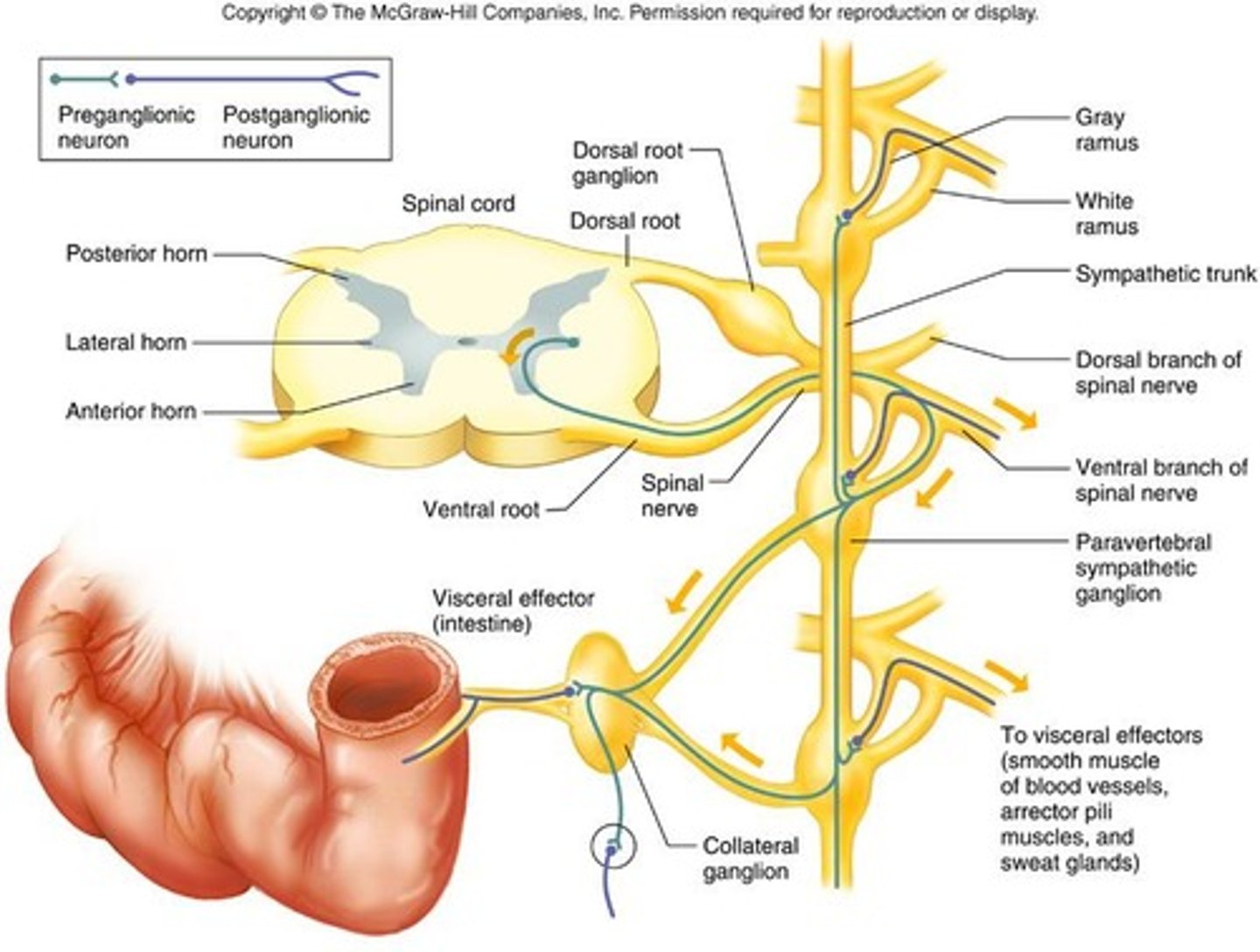
Sympathetic trunk
made up of paravertebral ganglia and fibers that connect them
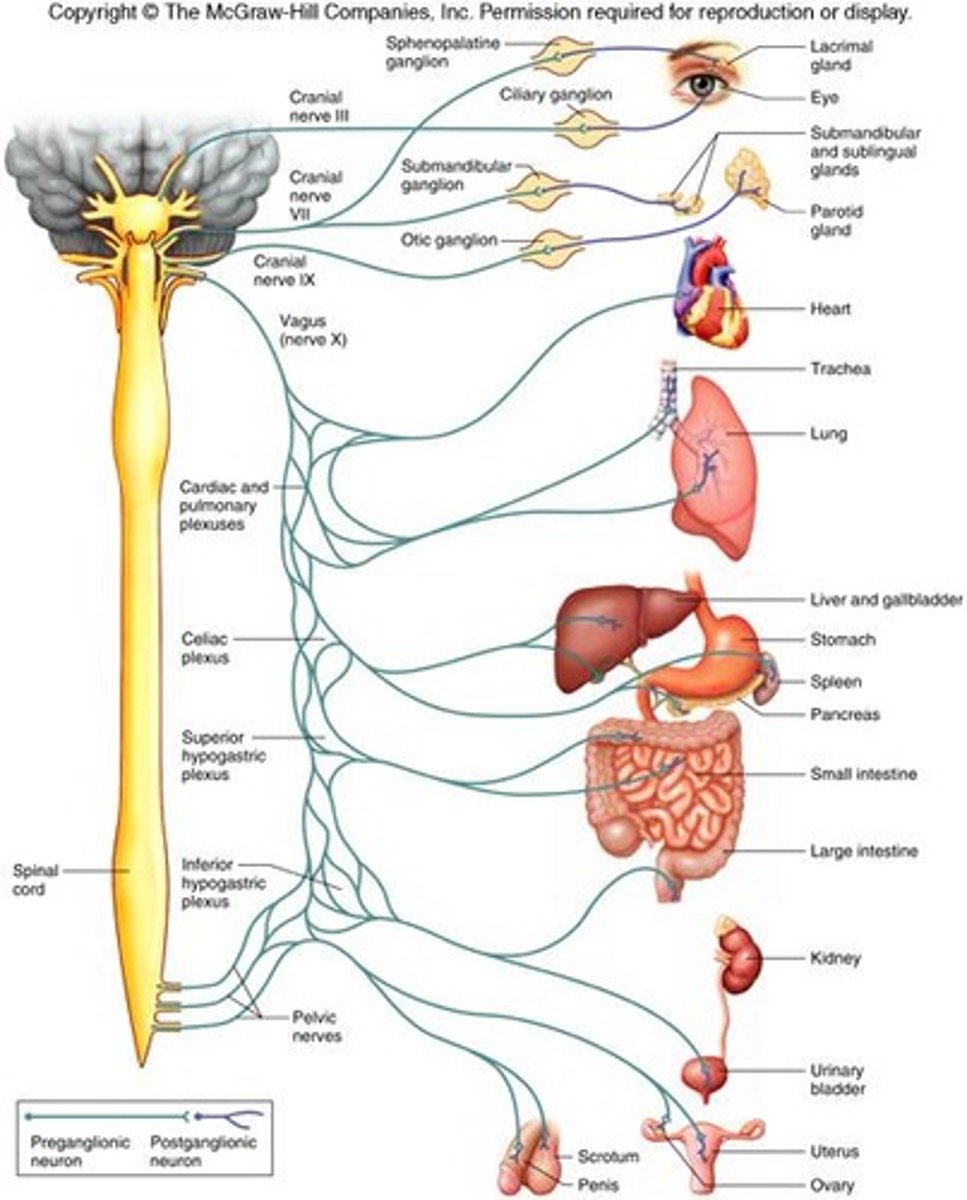
Postganglionic fibers
extend from sympathetic ganglia to visceral organs
Parasympathetic Division
craniosacral division - location of preganglionic neurons
Terminal ganglia
Ganglia are near or within various organs
Cholinergic Fibers
release acetylcholine; include preganglionic sympathetic and parasympathetic fibers and postganglionic parasympathetic fibers
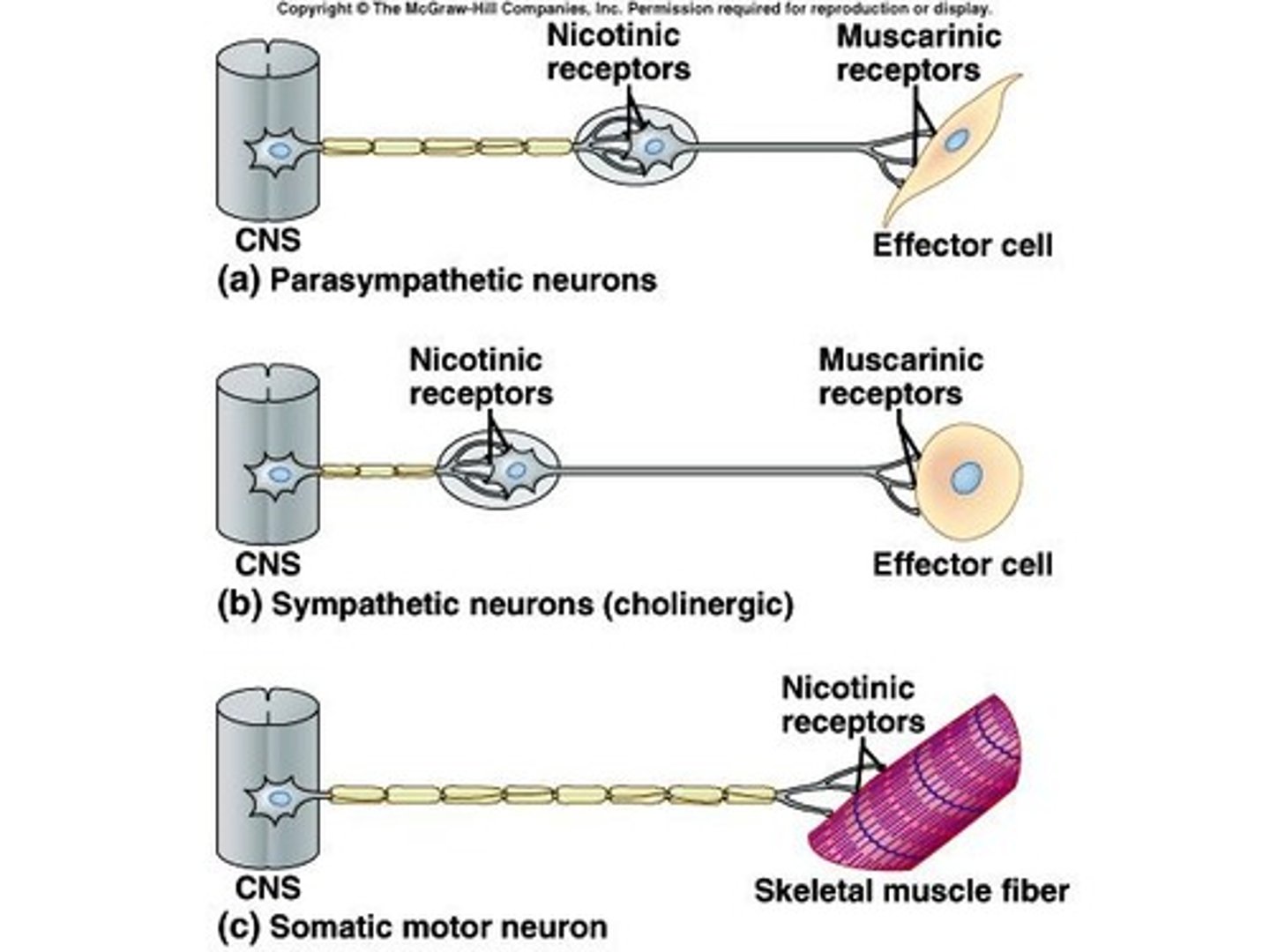
Adrenergic Fibers
release norepinephrine; most postganglionic sympathetic fibers
Cholinergic receptors
bind to acetylcholine; include Muscarinic (excitatory, slow) and Nicotinic (excitatory, rapid)
Adrenergic Receptors
bind to epinephrine and norepinephrine; Alpha and Beta both elicit different responses on various effectors
Control of Autonomic Activity
Controlled largely by CNS; Medulla oblongata regulates cardiac, vasomotor and respiratory activities; Hypothalamus regulates visceral functions
Life-Span Changes
Brain cells begin to die before birth; Over average lifetime, brain shrinks 10%; Most cell death occurs in temporal lobes
Aging Effects
By age 90, frontal cortex has lost half its neurons; Number of dendritic branches decreases; Decreased levels of neurotransmitters; Fading memory; Slowed responses and reflexes; Increased risk of falling; Changes in sleep patterns that result in fewer sleeping hours