Working Memory
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Types of memory
Short-term memory
Sensory processing
Working memory
Application of ‘attention to short-term memory
Hold a series of facts or actions for a few minutes to complete a task
Very limited capactiy (4-7 ‘chunks’)
Long-term memory
Turn short/working memory into ‘permanent’
Huge capacity
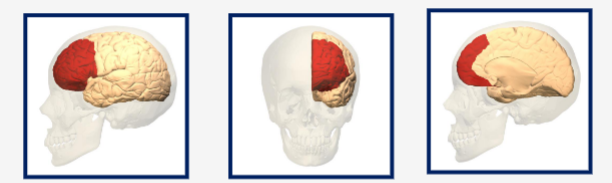
What structure is represented by this image?
Prefrontal cortex
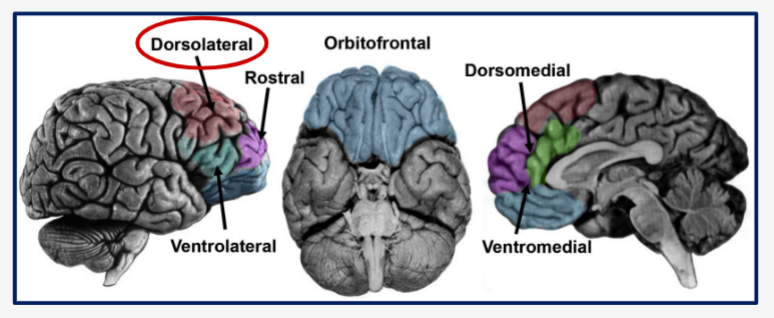
Subdivisions of the PFC
Dorsolateral
Rostral
Ventrolateral
Orbitofrontal
Dorsomedial
Ventromedial
Dorsolateral prefrontal cortex
Brodmann Areas 9+46
Monitoring and manipulation of working memory content
Susceptible to Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)
Role of dorsolateral prefrontal cortex
Abstract reasoning
Top-down regulation of attention
Projects to hippocampus
encoding long term memory
recalling memory to replayMany many other regions involved in working memory
Testing Cognitive Function
Wechsler Memory Scale
Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale
Cambridge Neuropsychological test automated battery
All include multiple tasks, measuring multiple cognitive functions, including working memory
Cognitive Tests
Standardised - allows comparisons
Reliable - taking the same test twice gives the same result
Valid? Does the test measure what it claims to?
Link from test results to anatomy/neuroscience?
Working memory functions and tests
Maintenance
Retaining information
Digit span forward task
Spatial span forward task
Monitoring
Attending to info
N-Back task
Manipulation
Working with information
Letter-number sequencing task
Digit span forward task
Verbal/auditory maintenance
Administrator recites a series of numbers - 1 per second, monotone delivery
Subject asked to repeat those numbers
Length of series increased with each trial
Task ends when participant fails twice at a specific length
length = score
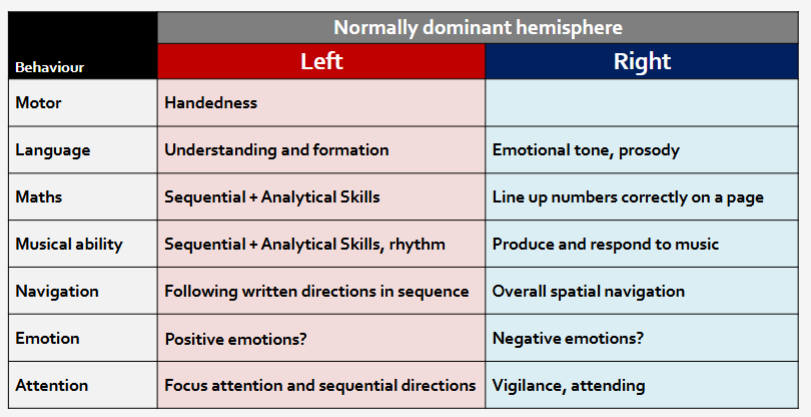
Dominance/laterality
Brains composed of two identical hemispheres
Mirror images
Some functions thought to arise largely in one hemisphere
Not the same hemisphere in everyone
Different hemispheres dominant for different behaviours
Lots of variance
N-Back task
Remembering backwards
A series of digits are presented, one at a time (about 15-50 in total)
Answer ‘yes’ if a digit appeared ‘n’ back
‘N’ is the number of digits back you have to remember
The higher the ‘n’ the harder the task
Stimuli can be varied to test different sub-types of working memory
Letters/words (verbal and auditory)
Sound (auditory)
Shapes (spatial)
Smells (olfactory)
Letter-number sequencing task
Administrator reads out a string of words and letters
Participant must first say the number in ascending order and then letters in alphabetical order
Cut-off when cannot reproduce a certain string length 3 times
Manipulation of verbal working memory
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)
Restless, impulsive, difficulty concentrating (age inappropriate)
- 7% worldwide
Multiple subtypes (hyperactive/impulsive/combines, child/adult
Problems with response inhibition
The ability to ‘resist internal or external interferences to achieve goal directed behaviours’ (Barkley 1997)
Challenges with Working Memory
Visuospatial more than verbal
Improves with age
Improved by methylphenidate
Response inhibition causes, or is it cause by working memory problems?
Neurobiology poorly understood
Train your working memory
Multiple meta-analytic studies show that working memory training does not improve intelligence etc.
Short-term effects
Do not really transfer across WM tasks
Do not transfer to other cognitive abilities - or academic performance
Many studies poorly designed/controlled
Schema
Learned content can be retrieved as one chunk
The more is learned, the bigger the ‘chunk’ - but it still one chunk
Is a simple example of how expertise develops
Examples - area codes, times tables
Neural Efficiency
Learning results in reduced brain activity
Seen in working memory and attention areas
Less processing power required to achieve complete same cognitive task
IQ may reflect baseline differences in neural efficiency
Controversial - technology may not be sensitive enough