3 Infections of Central Nervous System
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
True or False: Once symptoms of CNS infections are recognized, it will take up to 2 months before need for treatment becomes urgent
False ==> CNS infections are extremely dangerous (significant morbidity & mortality) & there is very little time to act upon recognition of symptoms
True or False: The brain is protected by five layers of tissue
True ==> skin --> skull --> meninges (dura mater --> arachnoid--> pia mater)--> brain
Describe how the CNS is protected against infections.
-physical barriers to infection --> skin, skull, meninges
-blood-brain barrier (BBB) --> tight junctions bwtn endothelial cells of vasculature in brain
-blood-cerospinal fluid barrier (choroid plexus) --> tight junctions bwtn epithelial cells that make up the CSF vessels
-immunosurveillance --> presence of glial cells, infiltrating dendritic cells, marcophages, T cells (in subarachnoid space)
blood-cerospinal fluid barrier (choroid plexus)
barrier that protects the CNS from infection via tight junctions bwtn epithelial cells that make up the CSF vessels
blood-brain barrier (BBB)
barrier that protects the CNS from the infection via tight junctions bwtn endothelial cells of vasculature in brain
True or False: Immune cells surveillance the CNS to protect against infections
True
-glial cells, infiltrating dendritic cells, & macrophages
- T cells w/in subarachnoid
Routes of CNS Infection
-direct trauma to CNS --> direct inoculation of pathogenic microbes into the CNS
-neural route --> migration thru the peripheral nerves or olfactory nerves
-hematogenous route --> from blood stream into CNS via crossing the BBB or via the CSF by crossing choroid plexus
What are the 3 types of CNS diseases due to infection?
-encephalitis = inflammation of the brain
-meningitis = inflammation of meninges
-myelitis = inflammation of the spinal cord
encephalitis
inflammation of the brain
*symptoms
-fever
-altered mental status
-headache
-weakness in certain areas of the body
-confusion
meningitis
inflammation of the meninges
*Symptoms
-altered mental status
-stiff neck
-high fever
-headache
myelitis
inflammation of the spinal cord
What are the general symptoms of prion disease?
-cognitive changes
-lack of coordination
-progressive dementia
Important CSF Parameters in Diagnosing CNS Infections
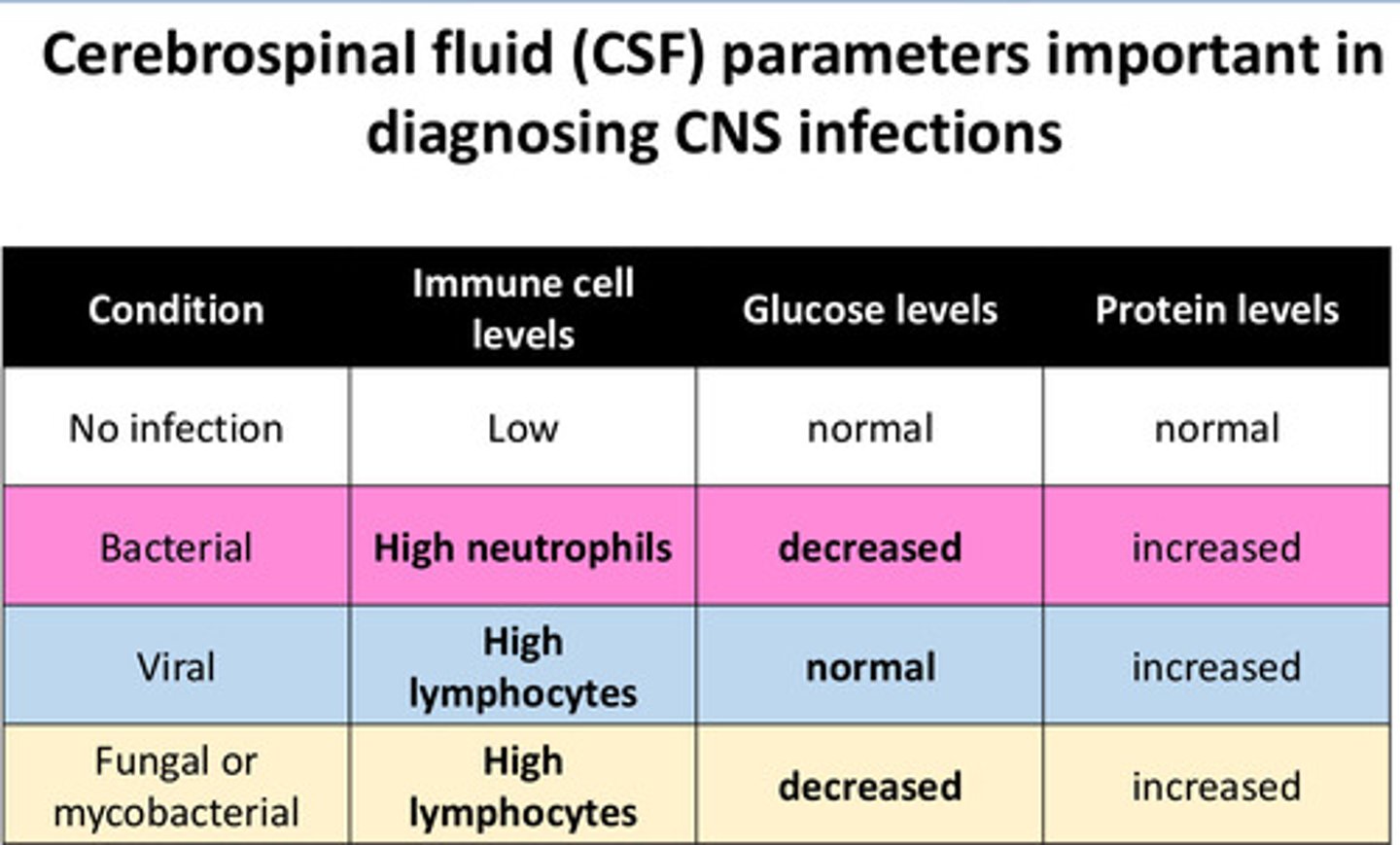
What parameters will the CSF have when the CNS has a bacterial infection?
-high neutrophils
-decreased glucose
-increased protein levels
What parameters does the CSF have under normal conditions?
-low immune cells
-normal glucose levels
-normal protein levels
What parameters does the CSF have when the CNS has a viral infection?
-high lymphocytes
-normal glucose levels
-increased protein levels
What parameters does the CSF have when the CNS has a fungal or mycobacterial infection?
-high lymphocytes
-decreased glucose levels
-increased protein levels
True or False: All CNS infections result in increased protein levels w/in the CSF
True
True or False: All CNS infections result in increased lymphocyte levels w/in the CSF
False ==> lymphocytes only increased in CSF in viral, fungal, & mycobacterial CNS infections; bacterial CNS infections have increased neutrophils in CSF
How are the glucose levels in CSF altered during bacterial CNS infection?
decreased
How are the glucose levels in CSF altered during viral CNS infection?
glucose levels are not altered; glucose levels are normal
How are the glucose levels in CSF altered during fungal or mycobacterial CNS infections?
decreased
True or False: Bacteremia can precede some CNS infections
True
True or False: The concentration of glucose in the CSF is decreased during both viral & bacterial meningitis
False==> glucose levels normal during viral CNS infections (decreased in bacterial CNS infections)
What are some common bacteria that infect the CNS?
- S. pneumoniae
-N. meningitidis
-H. influenzae
-L. monocytogenes
Streptococcus pneumoniae
gram positive coccus that colonizes the nasopharynx
*can infect the CNS
Haemophilus influenzae
gram negative coccobacillus that colonizes the nasopharynx
*can infect the CNS
Listeria monocytogenes
gram positive bacillus acquired from contaminated food
*can infect CNS
Neisseria meningitidis
gram negative diploccous that infects the CNS to cause meningitis (has 6 different serogroups)
-encounter --> close person-to-person contact (kissing or respiratory droplets) or own microbiota (commensal that colonizes the nasopharynx)
-entry --> respiratory or oral route via group settings (ex: coleges)
-endemic in sub-sharan Africa (meningitis belt) & Saudi Arabia --> travelers at risk
Describe why the incidence of meningitis due to N. meningitidis is increased in 6-24 mo. olds & college students.
-6-24 mo. olds ==> the age where IgG levels that the baby received from mother drops & their own immune system isn't fully fxnal/strong yet = increased susceptibility to N. menin
-college students ==> living & closely interacting with many different people at a time
How does N. meningitidis spread to the CNS?
spread to blood stream --> bacteremia --> crosses the blood brain barrier
Describe disease due to N. meningitidis
-initial symptoms --> fever, headache, neck stiffness, aversion to bright light
-damage
> sepsis (growth of N.menin in blood)
> meningitis
>petechiae = hemorrhagic rash--> spotted fever
>purpura fulminans = necrosis & damage to blood vessels
-outcomes --> very rapid progression
> can be fatal w/in hrs
> w/o antibiotic, brain damage can take place w/ 50% fatality
purpura fulminans
necrosis & damage to blood vessels
*can happen due to meningitis from N. menin infection
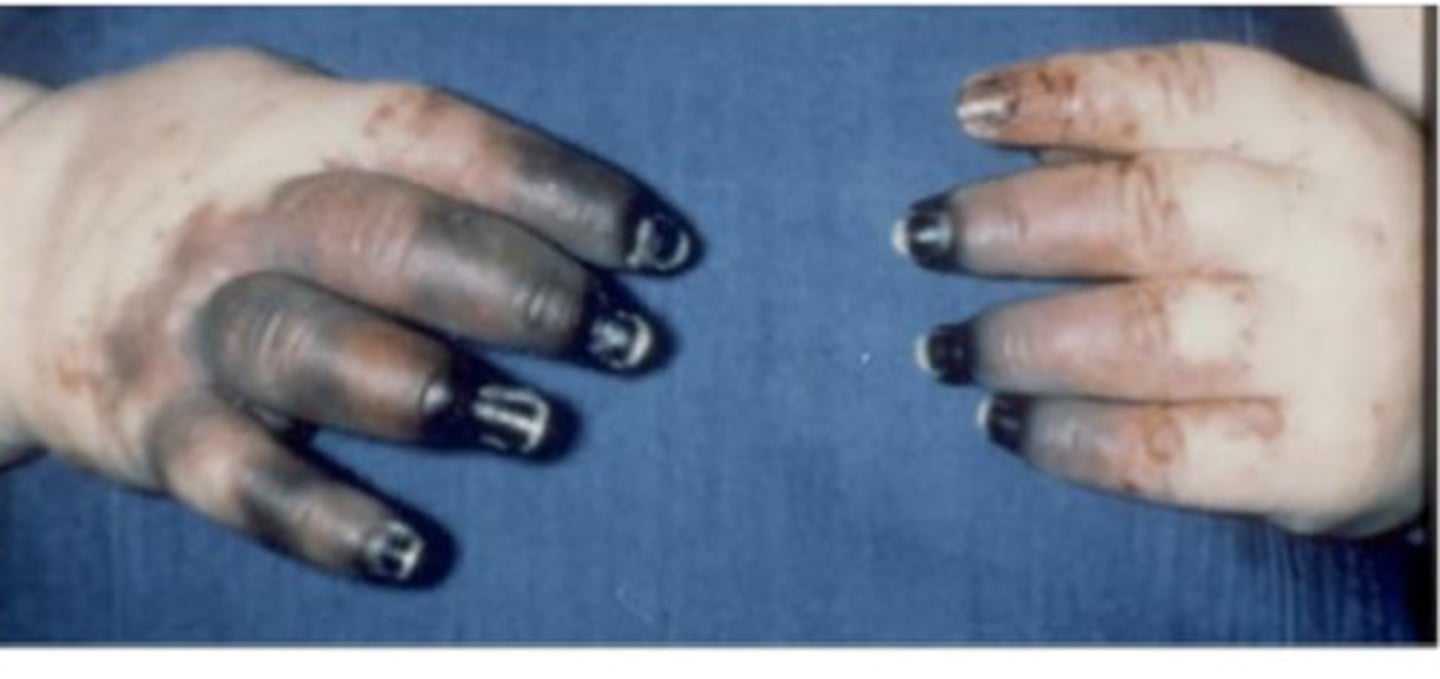
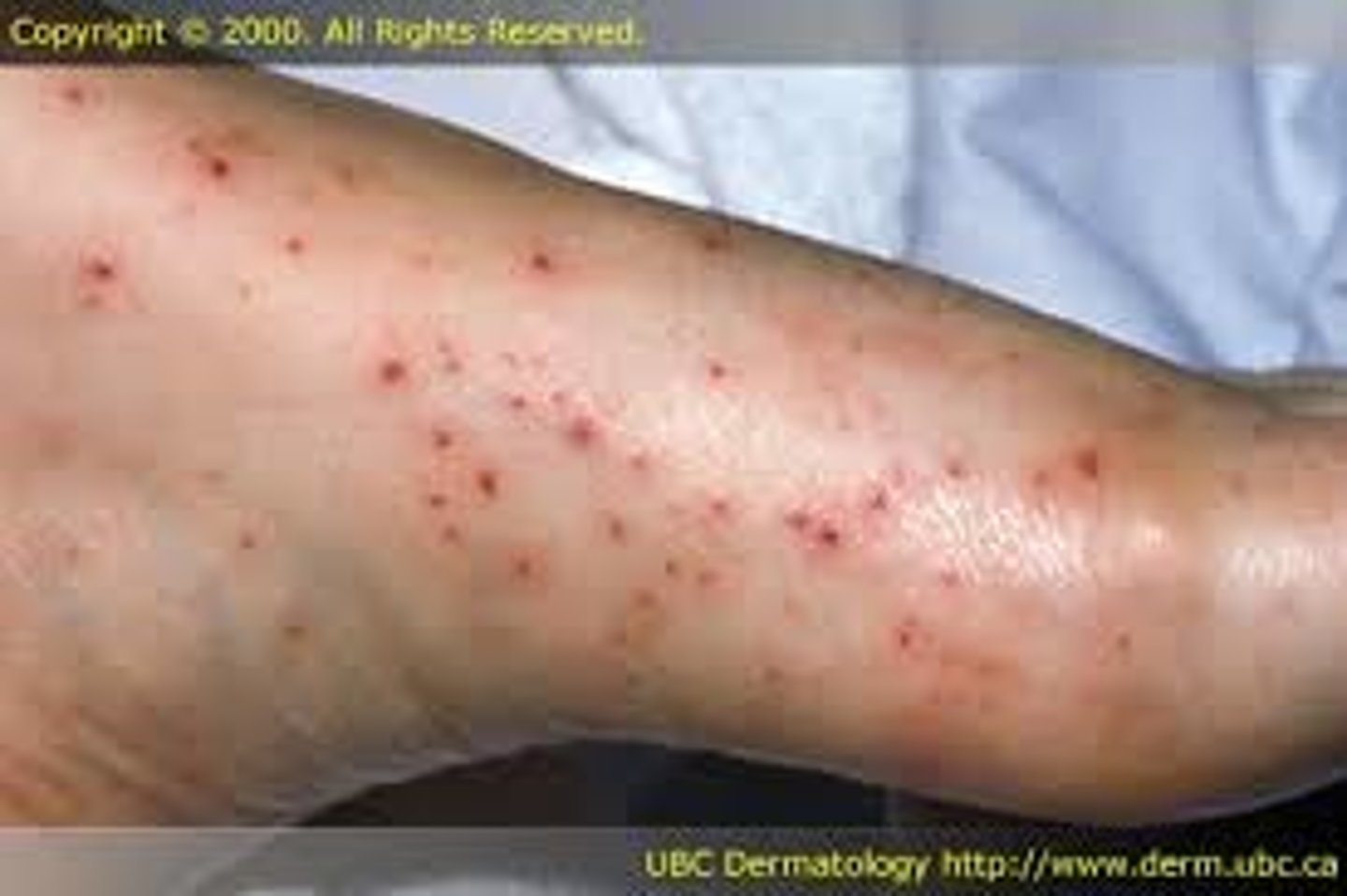
petechiae
hemorrhagic rash spotted fever observed during meningitis due to N. meningitidis infection
N. meningitidis virulence factors
-capsule --> makes it anti-phagocytic
-pili--> attachment to host cells
-phase & antigenic variation --> avoid the immune system
-lipooligosaccharide (LOS) --> inflammatory endotoxin
Pili Phase Variation
the high frequency reversible on/off switching of pilus production
*N. meningitidis has this virulence factor
What are the vaccines available against N. meningitidis?
-MenACWY --> vaccine for 11-12 yo or for travelers to endemic areas
-MenB --> 16-18yo (pre-college)
True or False: All 6 serogroups of N. meningitidis are capable of causing meningitis in equal proportions
False ==> 3 serogroups cause most meningococcal diseases
What are some neurotropic viruses that can potentially infect the CNS?
-herpes simplex viruses
-varicella -zoster virus
-cytomegalovirus
What are some respiratory viruses that can potentially infect the CNS?
-measles
-influenza
-SARS-CoV-2
True or False: Rabies virus can potentially infect the CNS?
True
Arboviruses
viruses transmitted by vectors
*some can infect the CNS
-west nile virus
-yellow fever virus
-zika virus
-eastern equine encephalitis virus
What kind of viruses can potentially infect the CNS?
-neutropic --> infects nerves
>herpes simplex viruses
>varicella-zoster virus
>cytomegalovirus
-respiratory
>measles
>influenza
>SARS-CoV-2
-rabies
-arboviruses
>west nile virus
>yellow fever virus
>zika virus
>eastern equine encephalitis virus
Eastern Equine Encephalitis Virus (EEEV)
Arbovirus transmitted by mosquitos, ticks, or other arthropods that can infect the CNS
-multiplication --> replication in mesenchymal lineage tissues (fibroblasts, osteoblasts, myocytes, etc)
-invades CNS via hematogenous route (blood stream)
-4-10 day incubation period
-often asymptomatic, but sometimes develop febrile (fever) illness or neurologic disease
>30% mortality
> mild to severe mental & physical impairment in survivors
*diagnosed via patient history (where they traveled & clinical features) & testing CSF for anti-EEEV IgM & viral RNA genomes
Describe Oral & CNS infections with Herpes Simplex Virus
-transmitted in saliva & other bodily fluids
-oral infection ==> infects mucosal epithelial cells of the oral region = primary mucosal infection = gingivostomatitis (inflammation of the gums & oral epi)
-CNS infection ==> spreads to local sensory neurons--> travels along the fiber to craniospinal ganglia (trigeminal nerve ganglion) --> CNS (rare to travel to CNS)
Herpes Simplex Encephalitis (HSE)
most severe complication of herpes simplex virus ==> seizures, fever, headaches, language impairment, mental status change
-diagnosed via testing CSF--> PCR for HSV DNA, increased lymphocyte count, MRI (hemorrhagic necrosis of temporal lobes)
-most common viral encephalitis
-most treatable viral encephalitis
>intravenous acyclovir = anti-viral used to Tx; given based on suspicion --> reduces mortality 20-30% but 3% never recover normal fxn
True or False: Hemorrhagic necrosis of temporal lobes are characteristic of CNS infection with Eastern Equine Encephalitis
False ==> characteristic of Herpes Simplex Encephalitis
intravenous acyclovir
efficient & safe anti-viral used to treat herpes simplex encephalitis
-administered to patients upon suspicion of having HSE
-reduces mortality to 20-30% but less than 3% recover normal function
What is the only CNS virus that can be treated with anti-virals?
herpes simplex virus
Describe the epidemiology of prion diseases in humans
-sporadiac mutations --> Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease (CJD)
-genetic (hereditary) --> all make different mutations to the same gene
>CJD
>fatal familial insomnia (FFI)
>Gerstmann-Straussler-Scheinker (GSS)
-aquired via infection or inoculation
>Kuru
>Variant vCJD
prion diseases
group of rare, fatal brain disorders which occur in humans & some animals
-difficulty walking & changes in gait
-rapidly developing dementia
-confusion
-hallucinations
-difficulty speaking
Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease (CJD)
prion disease that manifests clinically via cognitive changes like failing memory, behavioral changes, lack of coordination, progressive dementia, & fatality
-diagnosis
>electroencephalography (EEG)
>CSF tests --> elevated 14-3-3 & tau proteins (these are always released from damaged brain tissue)
>MRI for disrupted brain tissue
>brain biopsy or autopsy for definitive diagnosis
-No Tx available, just palliative care
True or False: 14-3-3 & tau proteins are definitively diagnostic for CJD prion disease
False==> these proteins are just signs of brain tissue damage (released when brain tissue becomes damaged)
prion protein (PrP)
shape-shifting proteins found in the brain w/ unclear function
*exists in 2 forms
-Prpc = non-pathogenic cellular form
-Prpsc = the pathogenic form--> converts Prpc into pathogenic form & forms amyloid fibers in a chain reaction
How do prions cause disease?
Prpsc (pathogenic form of prion) forms amyloid fibers --> very stable & resistant to heat, irradiation, & many chemicals --> fiber accumulation--> sponge-like lesions --> disruption of brain structure & function
How are aquired prion's encountered?
-inoculation via contaminated surgical tools (direct route)
-ingestion via consumption of brain tissue or meat contaminated with brain tissue (unknown how it gets from the gut to the brain)
ex: -Kuru ==> canabalistic ppl in new guinea
-variant CJD ==> mad cow disease that led to emergence in humans
True or False: You can ingest prions and not develop symptoms on prion infection until 20 years later.
True==> prion infections have a very long incubation time
True or False: Prion diseases can only result from ingestion of food contaminated with pathogenic (disease-causing) prion proteins
False ==> also contracted iatrogenically via contaminated surgical tools, sporadic mutations, or hereditary diseases