BIOL1030 PROKARYOTIC CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
94 Terms
All organism are composed of cells
Cells come only from preexisting cells because cells are self-reproducing
Cells are the basic units of structure and function in organisms
CELL THEORY
Surface-Area-to-Volume Relationships
Requires that cells be small
Compound Light Microscope
Light is passed through the specimen.
Then it is focused by a series of glass lenses.
It forms an image on the human retina.
The maximum magnification is about 1,000×.
The compound light microscope resolves objects
separated by 0.2 µm, 500× better than the human
eye.
Magnification
The ratio between the size of an image and its actual size
Resolution
The minimum distance between two objects that allows them to be seen as two separate
Contrast
The difference in shading of an object compared to its background
Eukaryotic
Have nucleus and other membrane- bound organelles
Prokaryotic
Lack a membrane-bound nucleus
Two Domains of Prokaryotes
• Bacteria
• Archebacteria
Bacteria
• Cause diseases but are also environmentally important as decomposers.
• Can be useful in manufacturing products and drugs.
Archaea
• Live in extreme habitats.
• Spherical coccus.
• Rod-shaped bacillus.
• Spiral spirillum (if rigid) or spirochete (if flexible).
Three basic shapes of bacteria
Plasma membrane
Cell wall
Glycocalyx
Cell envelope includes
Plasma membrane
lipid bilayer with embedded and peripheral proteins
cell wall
maintains the shape of the cell and is strengthened by peptidoglycan
Glycocalyx
layer of polysaccharides on the outside of the cell wall
monococcus
single coccus
Diplococci
divide and remain in pairs.
Streptococci
divide on 1 plane to form chains
Tetrads
divide in 2 planes forming a square of 4 cocci
Sarcina
divide in 3 planes making cubic packet of 8 cocci
bacillus
rods
egg-shaped coccobacillus
oval-looking one bacillus
palisades
bacillus in a row
diplobacillus
2 bacillus
streptobacillus
linear bacillus
Vibrios
comma shaped bacteria
Spirilla
rigid spiral-shaped
Spirochetes
flexible spiral-shaped
Cytoplasm
Semifluid solution encased by the plasma membrane
Cytoplasm
Contains water, inorganic and organic molecules, and enzymes.
Nucleoid
A region that contains a single, circular DNA molecule
Plasmids
Small accessory rings of DNA
Ribosomes
Tiny structures in the cytoplasm that synthesize proteins
Flagella
provide mobility
Fimbriae
Small, bristle-like fibers that sprout from the cell surface
Conjugation pili
rigid, tubular structures used to pass DNA from cell to cell (singular pilus)
Cell membrane
A living boundary between the cell and the environment.
Phospholipids
Integrated proteins
Carbohydrates
What are the key components of the cell membrane?
Cell Membrane
In bacteria the _____________ synthesizes cell wall
components, helps in DNA replication, secretes
proteins, carries out respiration, captures energy (ATP)
Cell Wall
Structural boundary outside the cell membrane, gives cell its shape and prevents the cell from bursting under osmotic pressure.
Cell Wall
Made up of peptidoglycan (Murein), components are referred to as NAG and NAM, has peptide cross-links.
Cell Wall
Used to classify bacteria into Gram-positive and Gram- negative groups.
Simple stain
only one stain
Differential Stain
more than one stain
Crystal violet
Gram’s iodine
Acetone or Alcohol
Safranin
Gram stain
Primary stain: crystal violet
Stains both gram-positive&negative bacteria
Mordant: Gram’s iodine
Enters bacterial cell & forms iodine-crystal violet complexes
Decolorizer: Acetone/Alcohol
Gram positive remains purple
Gram negative cells becomes clear
Safranin
Gram positive remains purple
Gram negative cells becomes pink
Gram Positive bacteria
Have a thick layer of peptidoglycan in their cell walls
Gram Negative bacteria
Have a small amount of peptidoglycan, but have an outer membrane, much more complex cell wall.
Mycobacteria or Acid Fast Bacteria
Have barely any peptidoglycan but have a thick wall made up of lipids
Capsules
Well-organized layers made of polysaccharides
Slime layers
polysaccharide layers that are unorganized
Glycocalyx
Polysaccharide extension that aids in attachment to solid surfaces.
S-layers
geometric pattern made of protein that aid in protecting from ion and pH
fluctuations.
Capsules
Slime layers
Glycocalyx
S-layers
Components Outside the Cell Wall
Bacterial Cytoplasm
Makes up the largest part of the inside of the cell.
Made up of 4/5 water, and 1/5 dissolved substances including enzymes, proteins, carbohydrate, lipids and inorganic ions.
Many metabolic reactions will take place in the cytoplasm.
Intracytoplasmic Membranes
It is plasma membrane invaginations, created as a plasma membrane infoldings.
Observed in many photosynthetic bacteria
RIbosomes
Composed of rRNA, non-membrane bound organelles found
throughout the cytoplasm of bacteria.
Site of protein synthesis in the cell.
Ribosomes
Consist of a large subunit (50s )and a small subunit(20s).
Nucleid
The area in the cytoplasm
where the mostly DNA,
some RNA and
some proteins are located.
Plasmids
•carry genes that are not essential for survival -
nonessential cellular functions.
•can be exchanged between cells during a process
called conjugation which allows for genetic transfer.
•may give a selective advantage in some situations –
antibiotic resistance
Conjugation
the process by which one bacterium transfers genetic material to another through direct contact using sex pili
Flagella
Long, thin helical appendage used for mobility.
Atrichous
no flagella
Monotrichous
one flagella
amphitrichous
one flagella on both ends
cephalotrichous
mutiple flagellas on each sides
Peritrichous
Flagella is all around
Lophotrichous
Multiple flagellas in one end
Filament
Basal body
Hook
FLAGELLA ULTRASTRUCTURE PARTS
Filament
extends from cell surface to the tip.
Basal body
embedded in cell envelope.
Hook
short curved segment
Swimming
Flagellum rotates like a propeller
Swarming
Occurs on when cells move in unison across a moist
surfaces.
Spirochete Motility
Multiple flagella form axial fibril which winds around the
cell.
Flagella remain in inside the cell wall.
Corkscrew shape exhibits flexing and spinning
movements.
Twitching & Gliding Motility
Occurs on solid surface.
Does not involve flagella.
Chemotaxis
Movement toward a chemical attractant or away from a
chemical repellent.
Chemoreceptors
transmit signals throughout the
chemosensing system to signal movement
Pili (Pilus)
Tiny hollow projections that help the bacteria adhere
(stick) to surfaces
• NOT involved in movement
• found on Gram -ve bacteria only
Sex pili
Long, modified for transfer of genes between
cells in a process called conjugation.
Fimbriae
Short attachment pili. Pathogenicity.
Gram + & - bacteria.
Endospores
A resting stage
Allows bacteria to survive very harsh conditions
a way of survival when conditions are not favorable
Produces a dormant cell that can persist until nutrients are available and growth resumes
Capsule - Protection
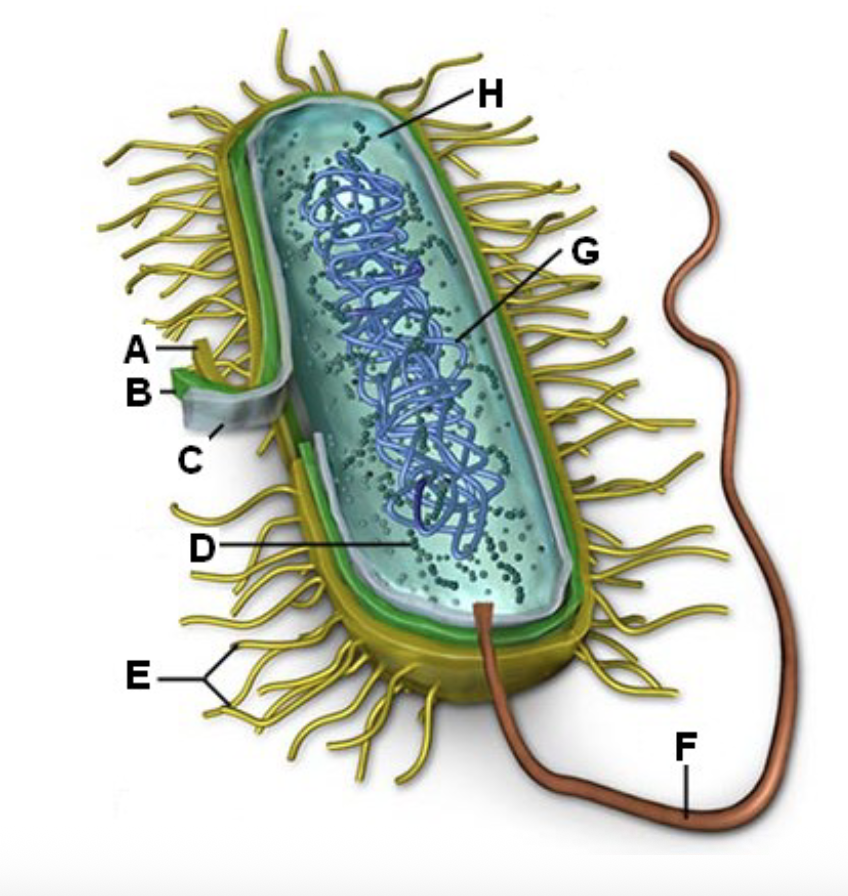
Identify letter A and the function
Cell Wall - Shape and prevents the cell from busting under osmotic pressure
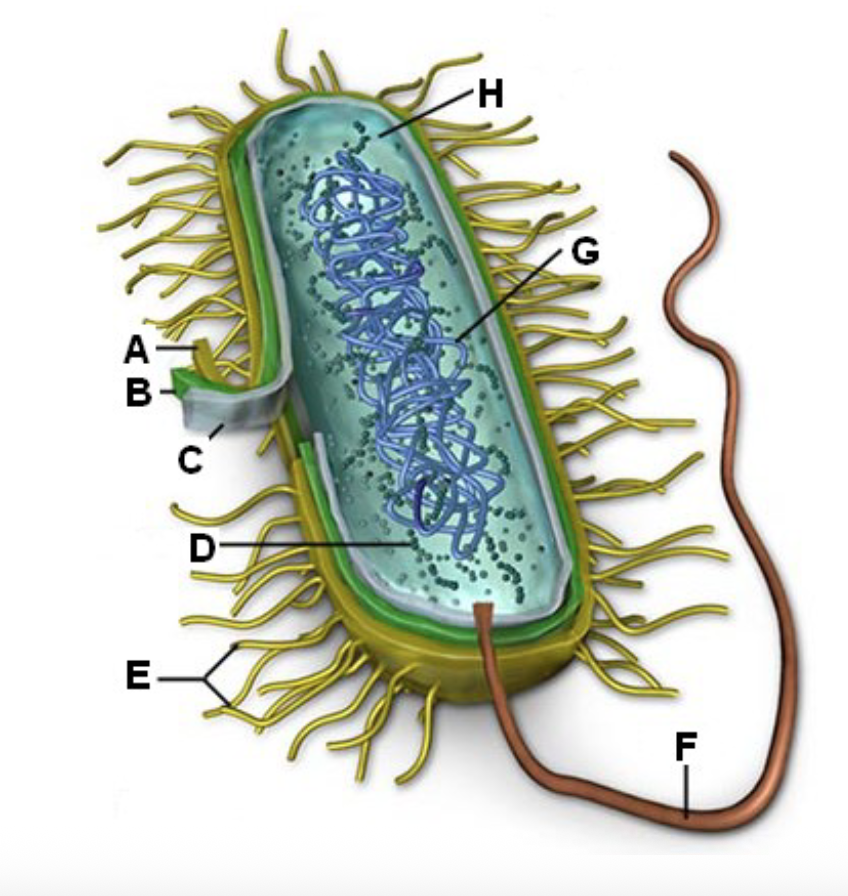
B?
Cell membrane - Controlling what enters and leaves the cell
In bacteria the cell membrane synthesizes cell wall
components, helps in DNA replication, secretes
proteins, carries out respiration, captures energy (ATP)
Cell transport
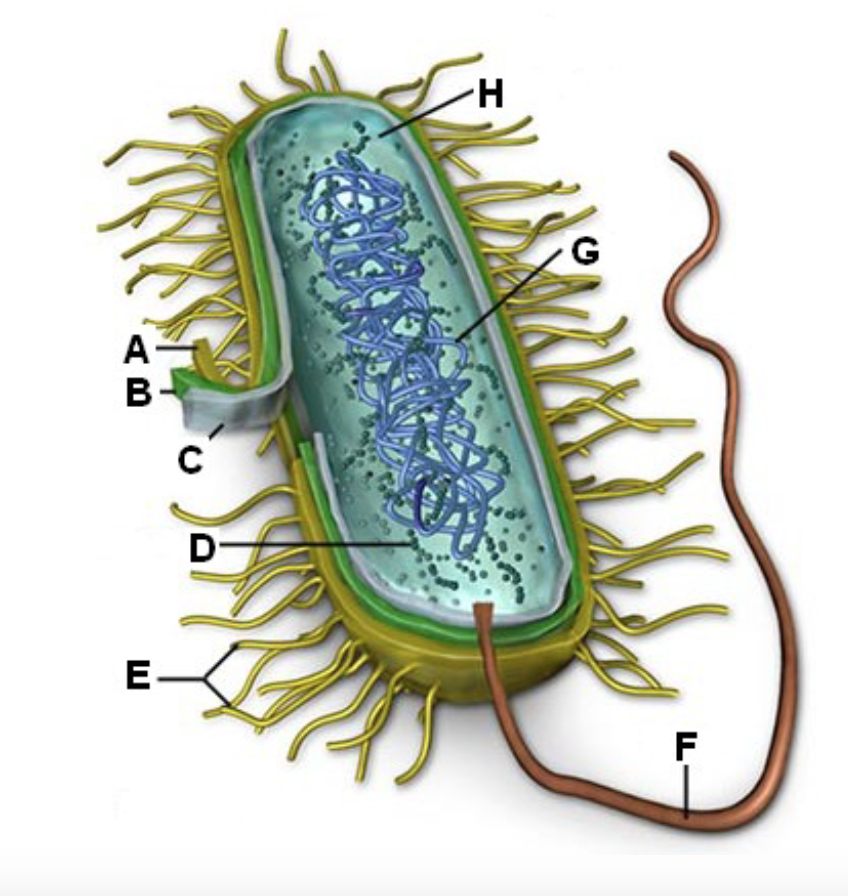
C?
Ribosome - Site of protein synthesis in the cell
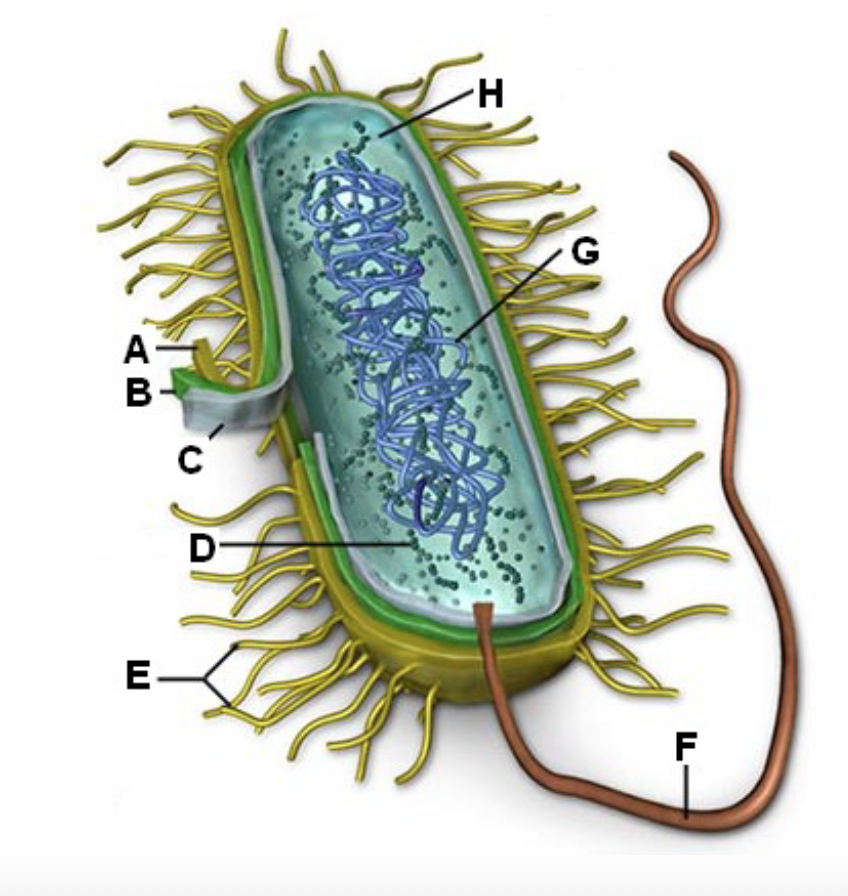
D?
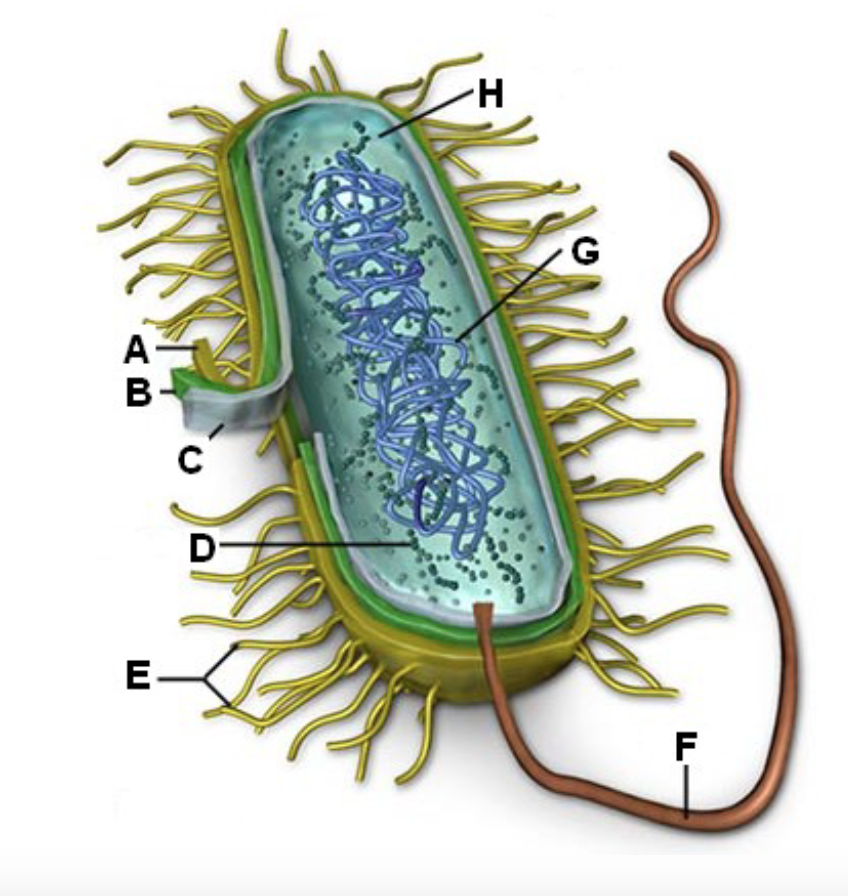
Fimbriae - Attachment
E?
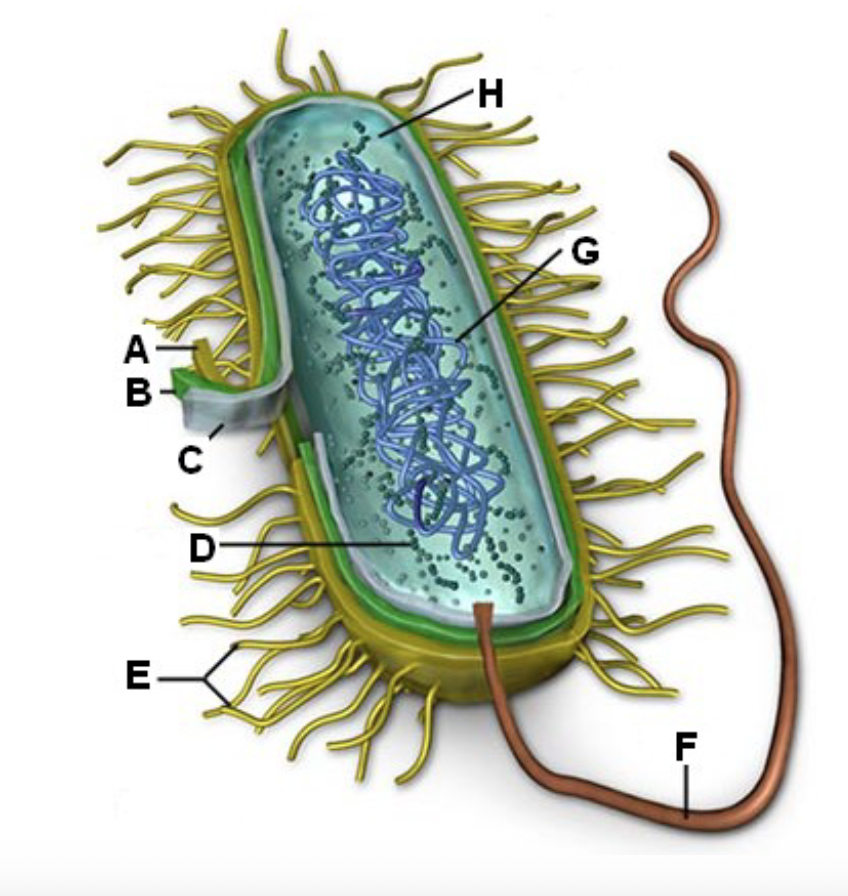
Flagella - mobility
F?
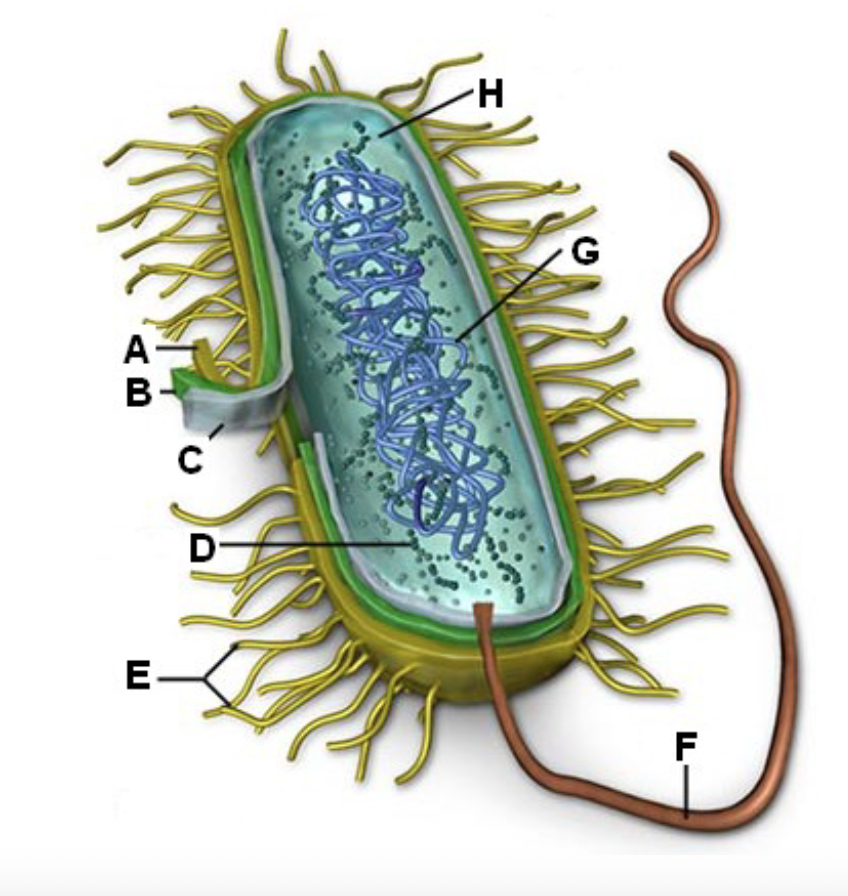
DNA/RNA - Genetic material
G?
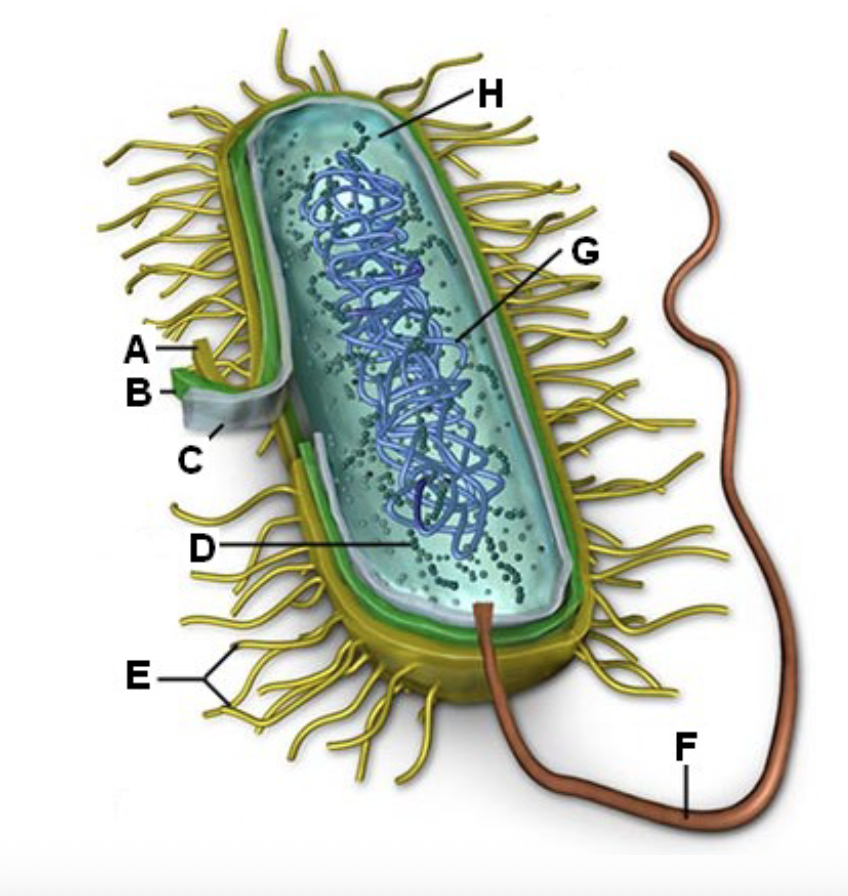
Cytoplasm - Many metabolic reactions will take place
H?