CMS III Final: Peds pt 1
1/407
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
408 Terms
define the gestational ages
- preterm = born before 37 weeks
- early term = 37 - 38+6
- full term = 39 - 40+6
- late term = 41 - 41+6
post term = born after 42 weeks
what does the fetal biophysical profile test for?
movement
tone
breathing
amniotic fluid volume
what does newborn screening test for?
Thyroid
Phenylketonuria (PKU)
Galactosemia
Sickle Cell disease
Cystic Fibrosis
what is the purpose of the prenatal visit during week 28?
glucose tolerance test, CBC, rhogam if needed
what is the purpose of the prenatal visit during 35-37 weeks?
Group B strep culture, if positive --> PCN prophylaxis
when is a baby considered 'term' age?
first day of 37th week
classify the following birth weight: 1200 grams
very low birth weight
low =<2500
very low = <1500
extremely low = <1000
what are the top 5 causes of infant mortality?
1. birth defects
2. preterm birth and low birth weight
3. maternal preg complications
4. SIDS
5. injuries
how does blood travel in the fetus?
ductus venosus → IVC → RA → foramen ovale → left heart
once a baby is born, how does circulation change?
increased paO2 → decreases pulm vascular resistance → allows more blood flow to pulm circulation
what causes higher blood flow to the lungs in the neonate?
closing of the ductus arteriosus
what is the PaO2 in a newborn at 1 hr and 24 hrs of life?
starting point = 20-30 mmHg
1 hr = 60 mmHg
24 hrs = 80-90 mmHg
what causes the ductus venosus to close?
clamping of the umbilical cord aka ligamentum venosus
what causes the foramen ovale to close at birth?
Increased pressure in the LA that excess RA pressure
what is the small ligament that attaches the aorta to the pulm artery?
ligamentum arteriosum (botallo's/harvey's ligament) → remnant of ductus arteriosus formed within 3 weeks after birth
what are the vascular components of the umbilical cord?
2 arteries and 1 veins
what can cross the placental barrier?
1. maternal steroid hormones (cortisol)
2. synthetic progestins (masculinize female fetuses)
3. thyroxine
4. viruses (TORCH)
5. drugs and drug metabolites
what is a pathologic cause of late pregnancy bleeding?
abruption → placental lining separated from the uterus prior to delivery
what is the term to describe when all/part of the placenta attaches abnormally to the myometrium?
accreta
what is the term to describe when chorionic villi invade the myometrium?
increta
what is the term to describe when chorionic villi invade through the myometrium to uterine serosa or adjacent organs?
percreta
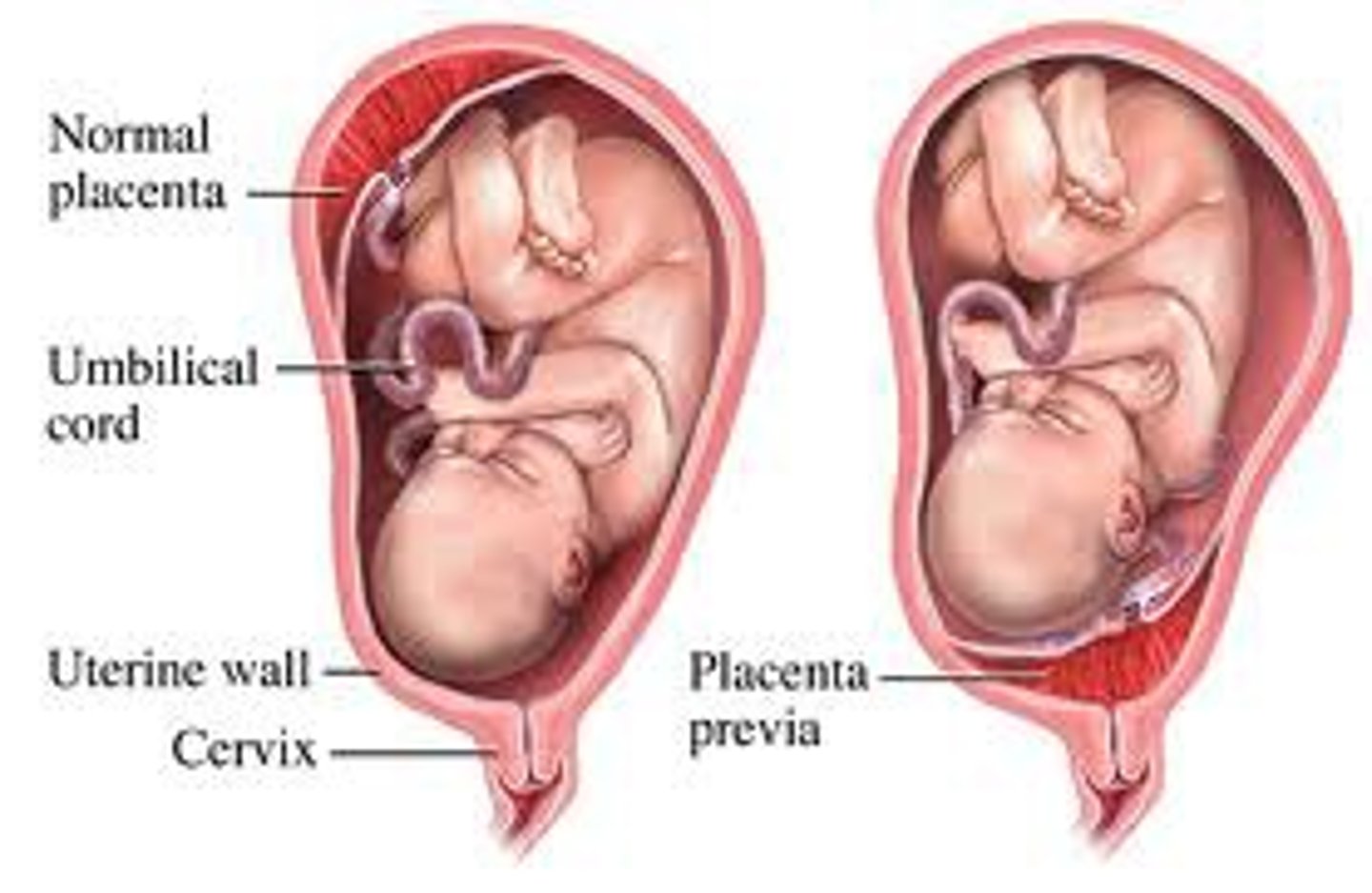
what is a cause of minimally painful bleeding after 20 weeks GA?
placenta previa → implantation in the lower uterine segment covering cervical os → prevents vaginal delivery!
what term describes when twins have 2 different types of RBCs, indicating that fusion of the two placentas was so intimate that RBCs were exchanged?
erythrocyte mosaicism
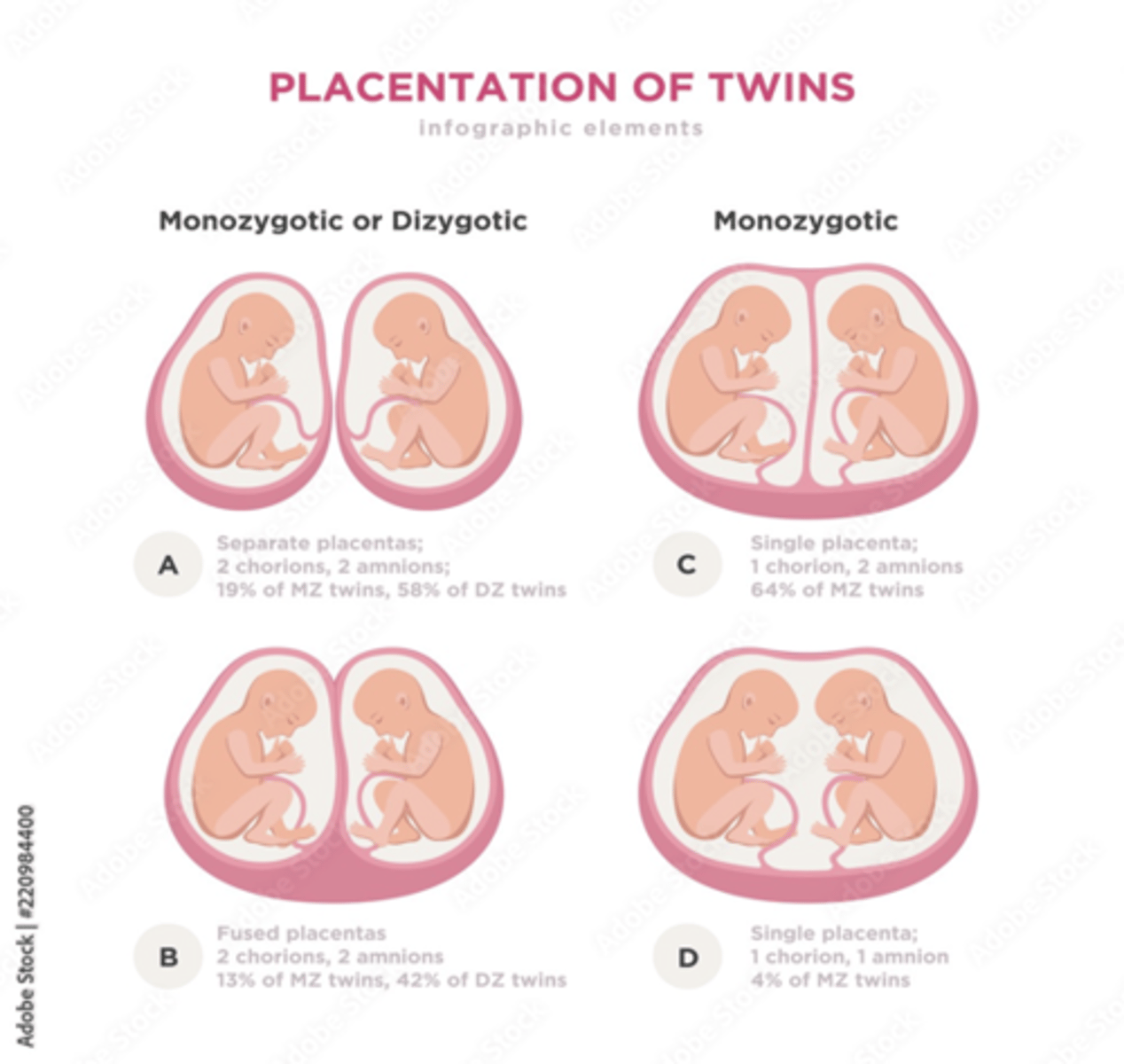
what are monochorionic twins?
Twins that share the same placenta.
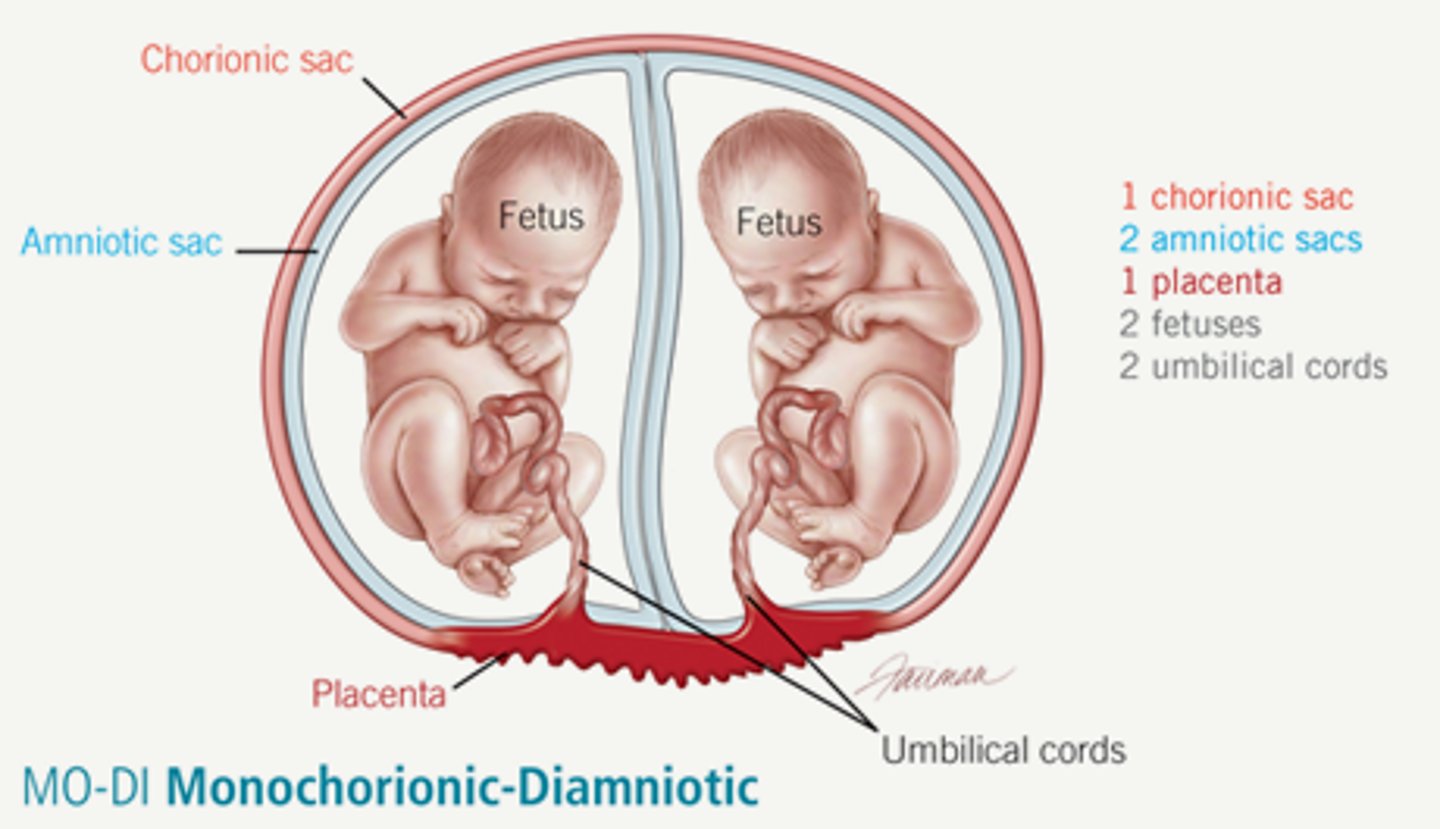
in monochorionic twins, circulatory systems have _______________ ____________ that results in vascular connections between the twins.
placental anastomoses
what is twin-twin transfusion syndrome?
Disproportionate blood flow to two fetuses. Donor twin transfers excess blood to recipient and has oligohydramnios and is smaller.
what occurs in the donor's sac during twin-twin transfusion syndrome?
oligohydramnios (dec. amniotic fluid for GA) → leads to stuck twin appearance
when is twin-twin transfusion screened for?
via US early-mid 2nd trimester
what is abnormal accumulation of fluid in at least 2 different fetal organ spaces?
fetal hydrops
what is the difference between symmetric and asymmetric intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR)?
symmetric = body is proportionately small → intrinsic causes (genetics, TORCH)
asymmetric = normal head/brain and small body → extrinsic causes (chronic hypoxia, undernourished, HTN)
what are the danger signs of preeclampsia?
HA
blurred vision
upper abd pain
when is a baby considered premature?
born before 37 weeks
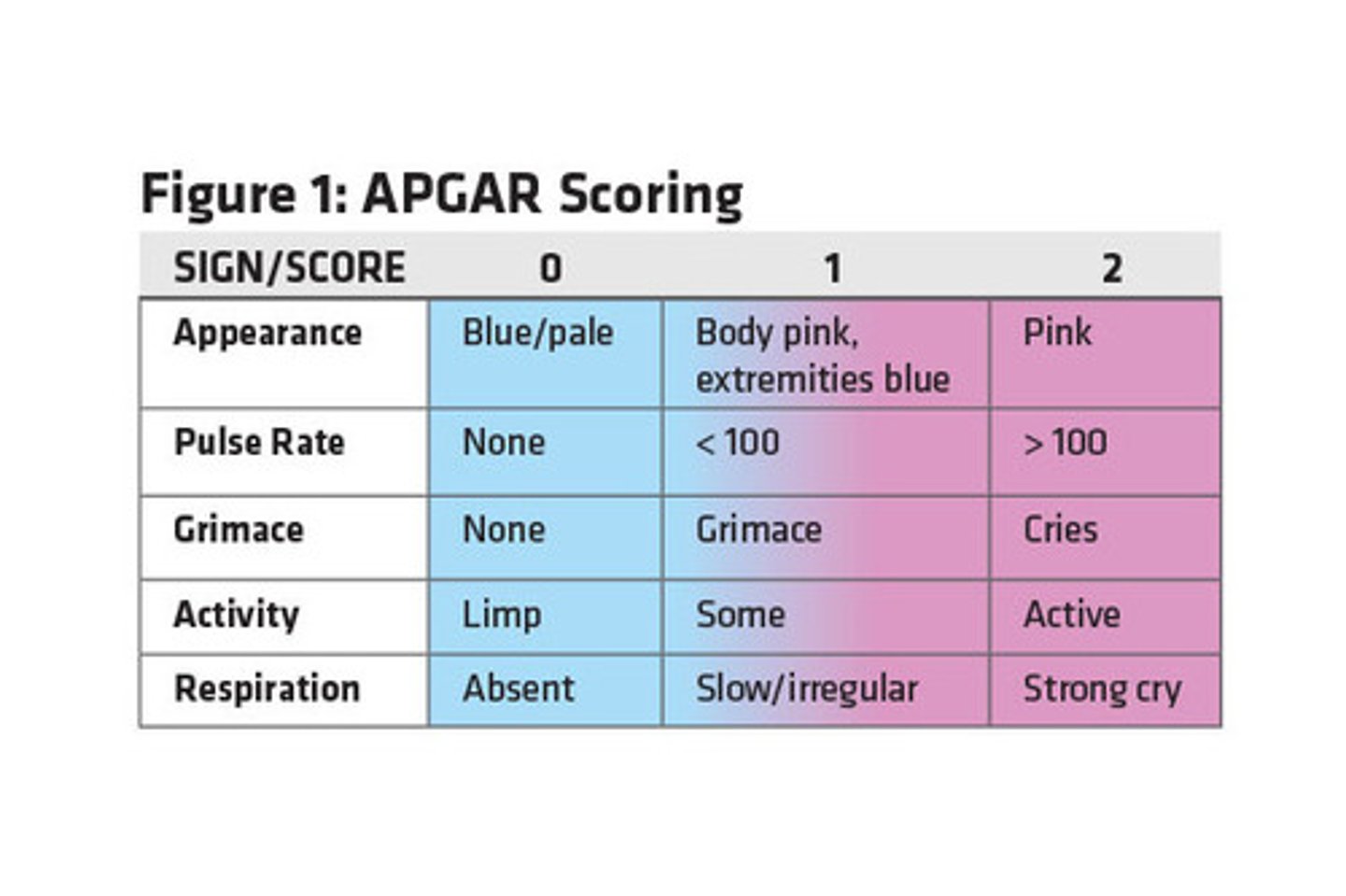
what is the APGAR criteria?
each criteria receives a score of 0, 1, or 2 @1 min and 5 min
Appearance
Pulse
Grimace
Activity
Respiration
what are the scores for APGAR?
>5 at 1 min + 8-10 at 5 min = smooth transition
<4 at 1 min = severe depression requiring immediate resuscitation
<7 at 5 min = high risk for CNS dysfunction or CV abnormality
what medications are part of newborn routine protocol?
1. eye prophylaxis → silver nitrate or erythro
2. vitamin k → prevent deficiency
3. hep B vax
what is the clinical presentation of Hyaline membrane disease (AKA neonatal RDS)?
tachypnea, grunting, increased work of breathing, cyanosis, nasal flaring within hours of delivery
what is seen on CXR in hyaline membrane disease?
air bronchograms and ground glass appearance**
what is the treatment and prevention for hyaline membrane disease?
tx = surfactant replacement within 30-60 mins
prevention = antenatal steroids administered between 24-34 wks
what are the complications of RDS?
chronic lung disease
PDA
intraventricular hemorrhage
what is the MC cause of resp distress in term infants?**
transient tachypnea of newborn → fetal lung fluid is retained → persistent postnatal pulm edema
what does persistent pulm HTN result in?
persistent R→L shunt of blood through fetal circulatory airways
what is the definitive dx of persistent pulm HTN?
echo
what is seen on CXR in meconium aspiration syndrome?
initially → streaky linear densities
w/ progression → hyperinflated lungs w flat diaphragm
severe → diffuse patchy densities with areas of expansion; patchy infiltrates, air leaks
central vs. obstructive apnea: inspiratory efforts are absent?
central → tx with gentle stimulation
central vs. obstructive apnea: inspiratory efforts persist but are ineffective?
obstructive → tx w/ clearance of airway secretions, avoid neck flexion
what drugs can be used to treat apnea?
methylxanthines → caffeine (pref), theophylline
what is seen on KUB in necrotizing enterocolitis?
pneumatosis intestinalis
***
what is described as bowel evisceration through the abd wall near the umbilicus that is NOT covered by membrane?
gastroschisis
what is described as bowel loop +/- organs midline through the umbilicus that is covered with membrane?
omphalocele → assoc. with chromosomal abnormality
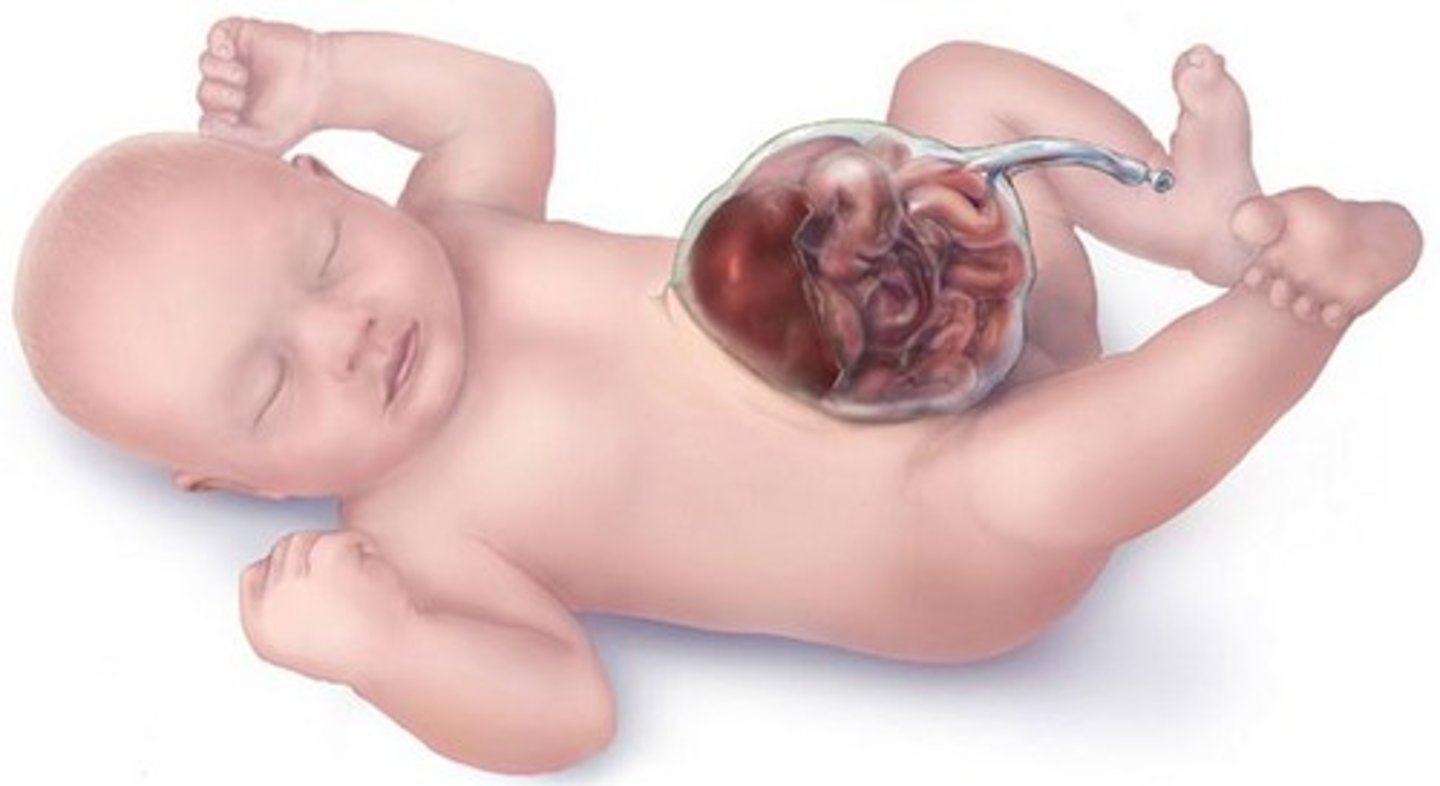
what is commonly seen in right congenital diaphragmatic hernia?
portion of liver and large bowel
left = small+large bowel and intraabd solid organs
what is a Bochdalek hernia?
posterolateral defect at foramen of bochdalek → MC on left
morgagni = anterior defect
if a newborn has resp distress, bowel sounds auscultated in thorax and barrel-shaped chest, what should you think of?
congenital diaphragmatic hernia
when cultured at 35-37 wks, if a pregnant woman has positive group B strep culture, how should she be treated?
treated at time of labor with penicillin/ampicillin
what is the neonatal tx for group B strep exposure?
pen G IV
what is the different between breast feeding jaundice and breast milk jaundice?
breast feeding = d/t inadequate milk intake
breast milk = d/t high concentration of enzyme that inhibits bilirubin excretion
when is neonatal jaundice always pathologic?
if occurs on day 1
what labs should be ordered if jaundice is present?
Blood type, Rh and Coombs test
Total and direct bilirubin
Hgb/Hct levels
Reticulocyte count
ABGs
LFTs
what test is used to assess the risk of developing severe hyperalbuminemia using total bilirubin?
Bhutani nomogram
what is a serious complication of neonatal jaundice?
kernicterus = extremely high bilirubin → lethargy, vomiting, irritability, poor feeding, high pitched cry
damages basal ganglia!
hypertonia → early
hypotonia → late
deaf → CN 8 damage
what is the leading cause of infant mortality between 1 month and 1 year of age in USA?
SIDS
what measures should be taken for prevention of SIDS in infants?
- prenatal care
- mothers avoid tobacco, alc, drug
- supine sleeping position
- cribs → no bumpers, +firm mattresses, no pillow or stuffed toys/blankets in crib
- avoid co-sleeping
- tummy time when awake
what does central cyanosis suggest?
congenital heart/pulm disease or sepsis
what is superficial edema/ecchymosis that cross the suture line and reconfigures within a week?
caput succedaneum
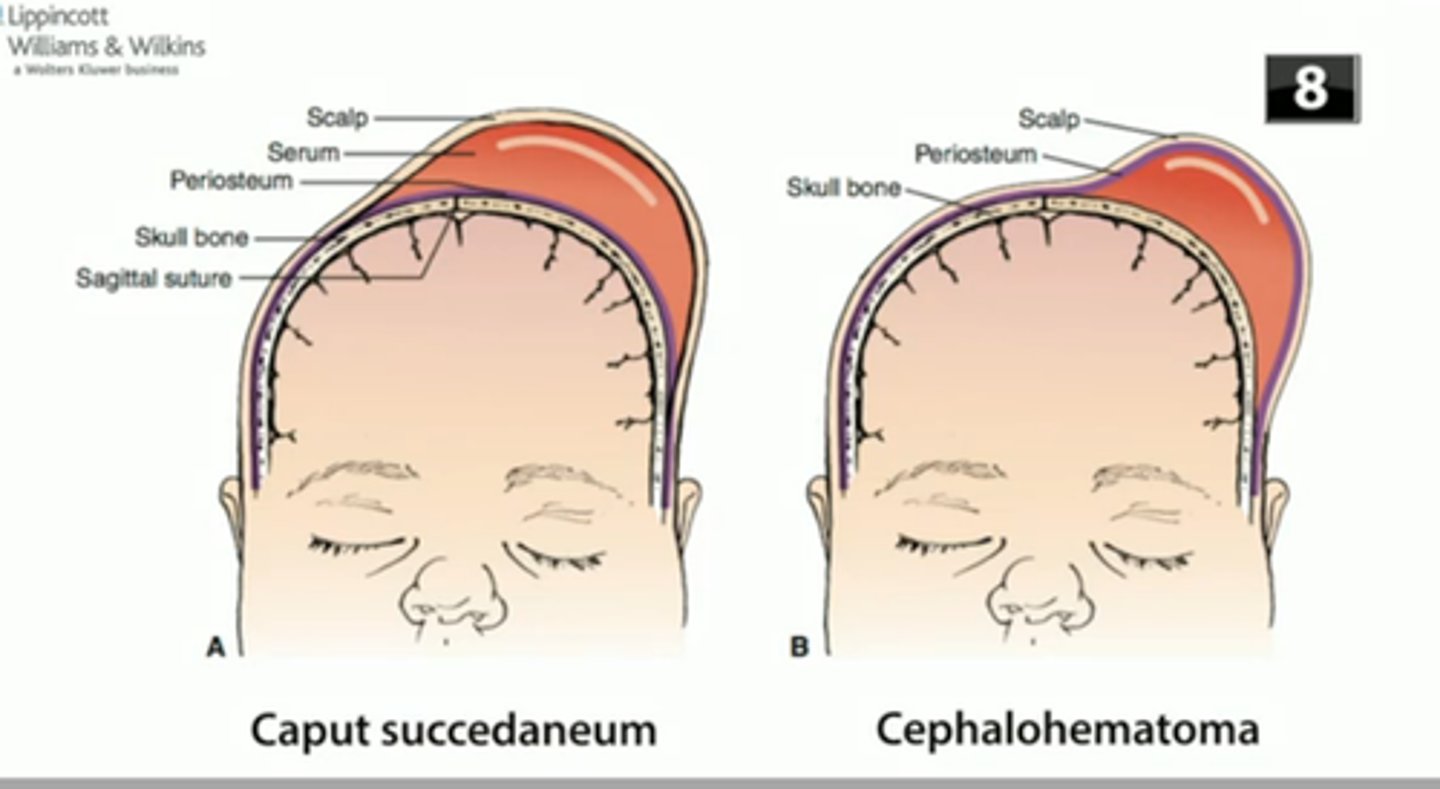
what is blood collection under the periosteum that does not cross the suture line?
cephalohematoma → takes several months to heal
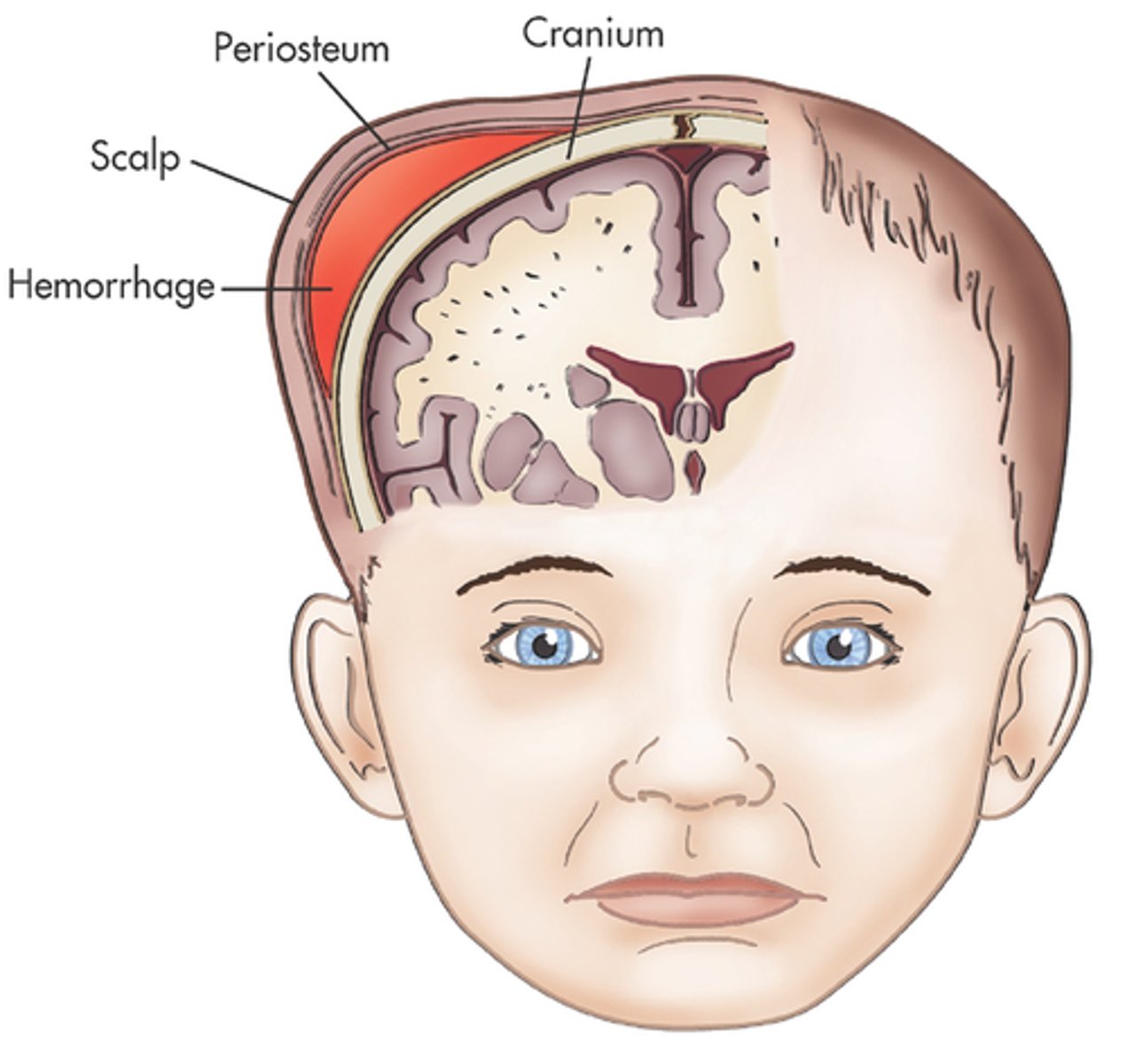
what is defined as dense CT between developing skull bones AKA soft spots?
fontanelles → anterior and posterior; allow for continued growth of brain and skull
what is craniosynostosis?
premature closure of cranial sutures →results in compensatory skull growth perpendicular to affected suture → inc. brain pressure → learning/developmental/vision, behavioral/self-esteem probs
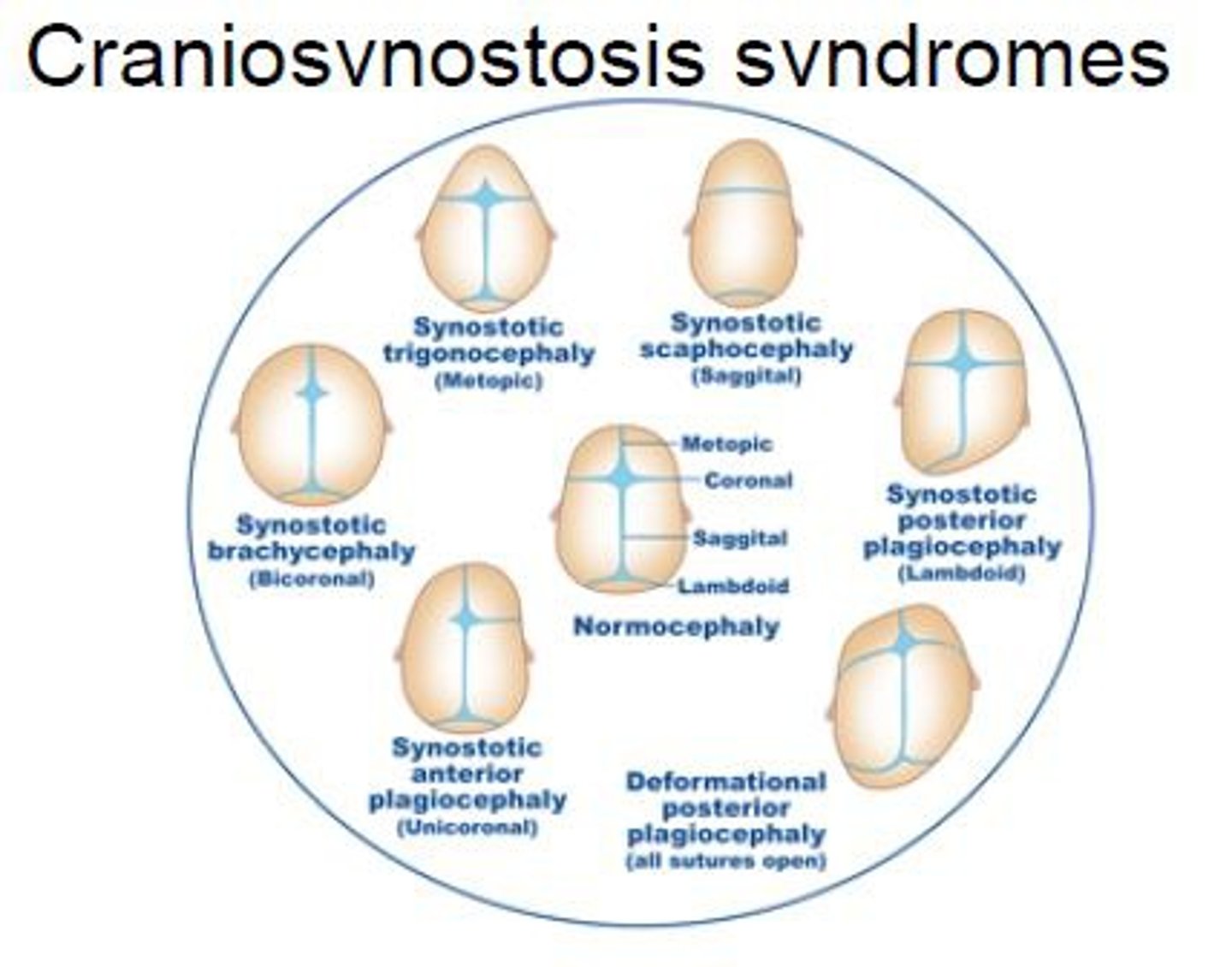
are the sutures closed in positional plagiocephaly?
NO! → due to supine position → reshape w/ helmet
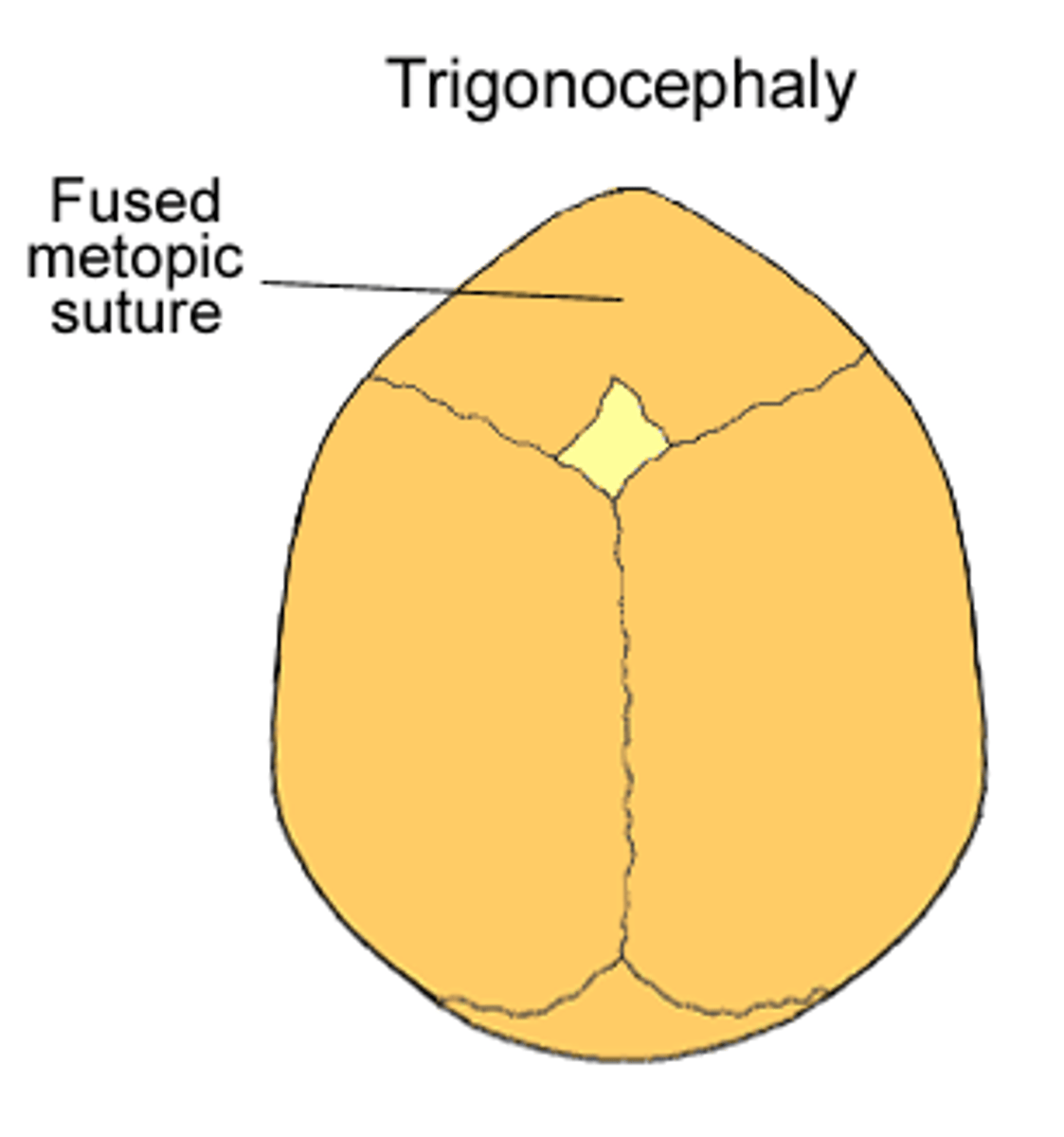
what is fusion of the metopic suture?
trigonocephaly
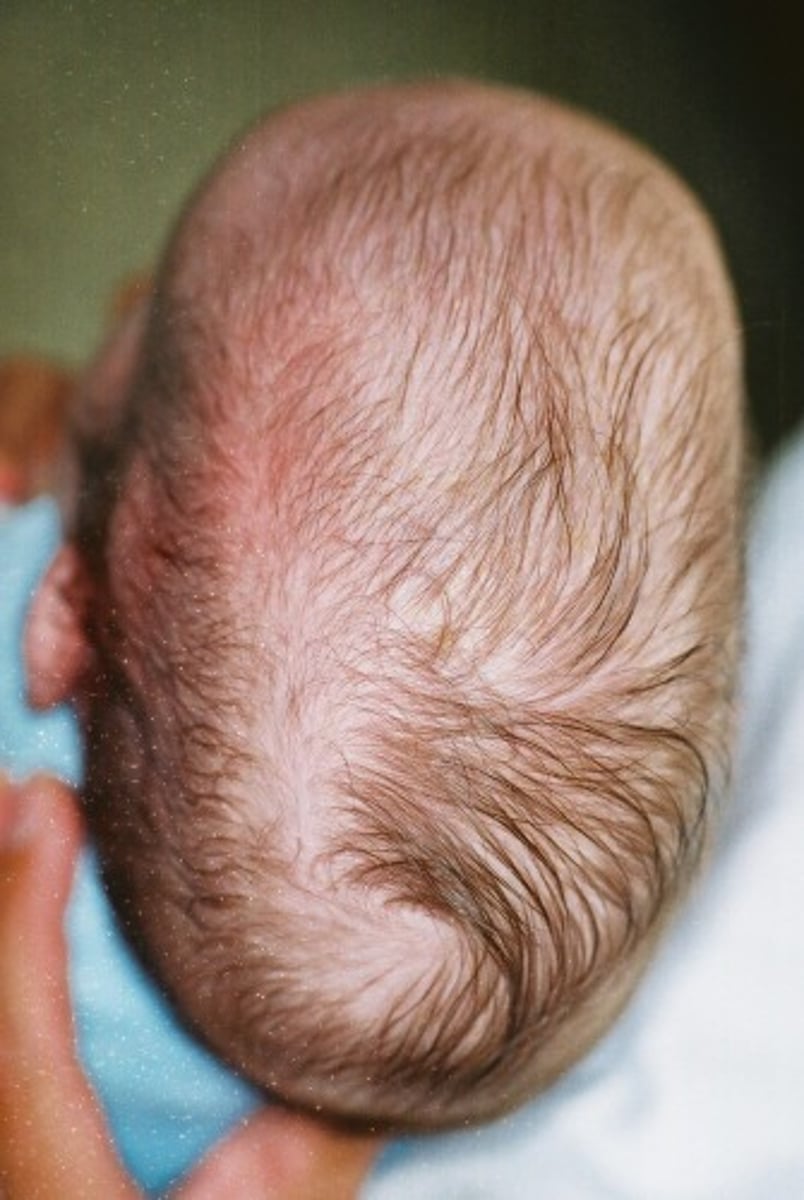
what is early fusion of the sagittal suture?
scaphocephaly → "hull" shaped skull
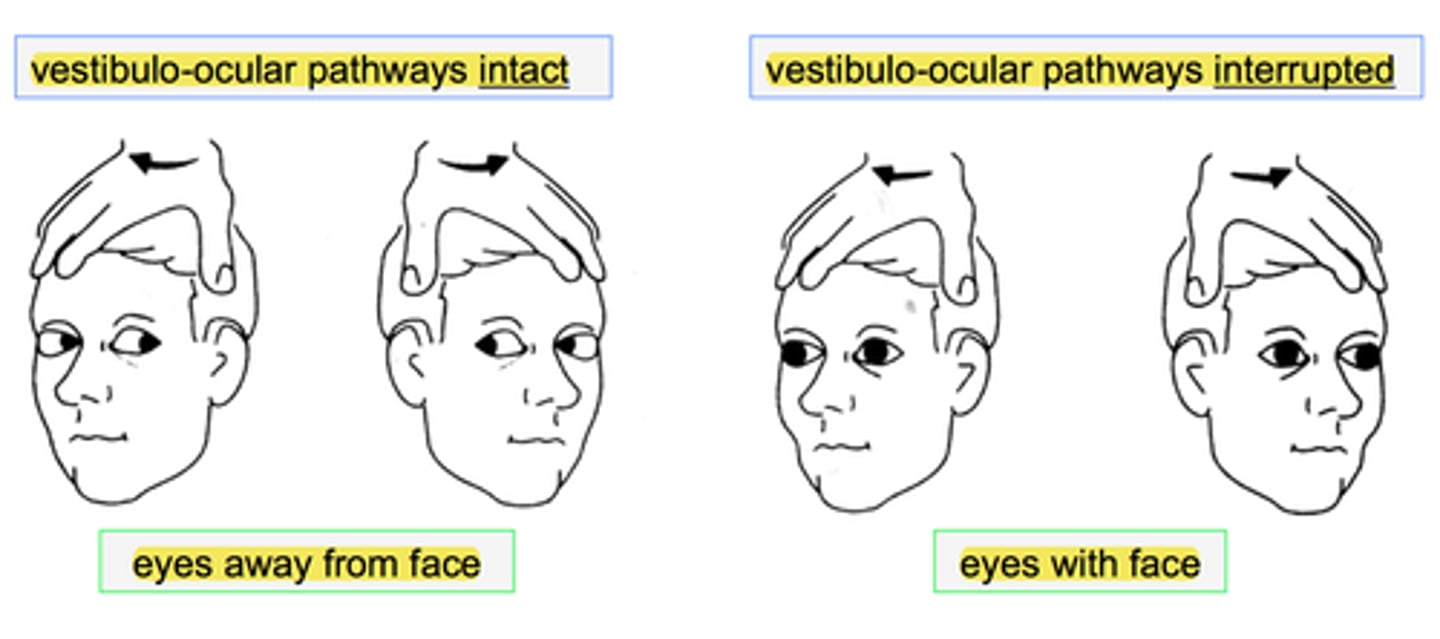
what is the doll's eye reflex?
infant's head is turned and eyes stay fixed with lag time before adjusting → present from birth to 3-4 months
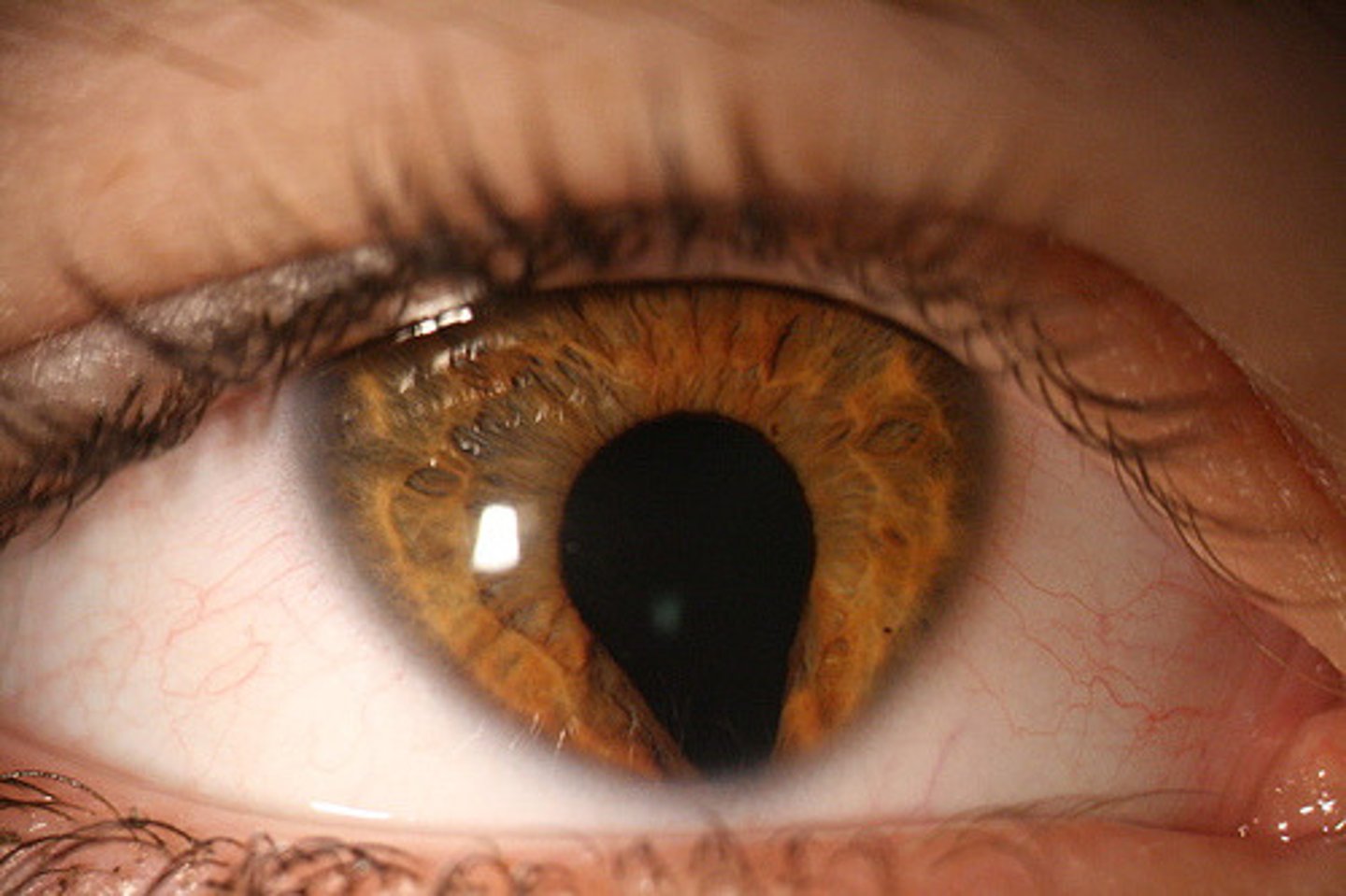
what eye abnormality is assoc. with CHARGE syndrome?
coloboma = absence/defect of ocular tissue
CHARGE:
Coloboma
Heart anomalies
Atresia of choanae
GU abnormalities
Ear anomalies
what is the tx for gonorrheal conjunctivitis in neonate?
rocephin
what is the tx for chlamydial conjunctivitis in neonate?
azithro
what is the tx for HSV conjunctivitis in the neonate?
trifluridine OR vidarabine PLUS acyclovir
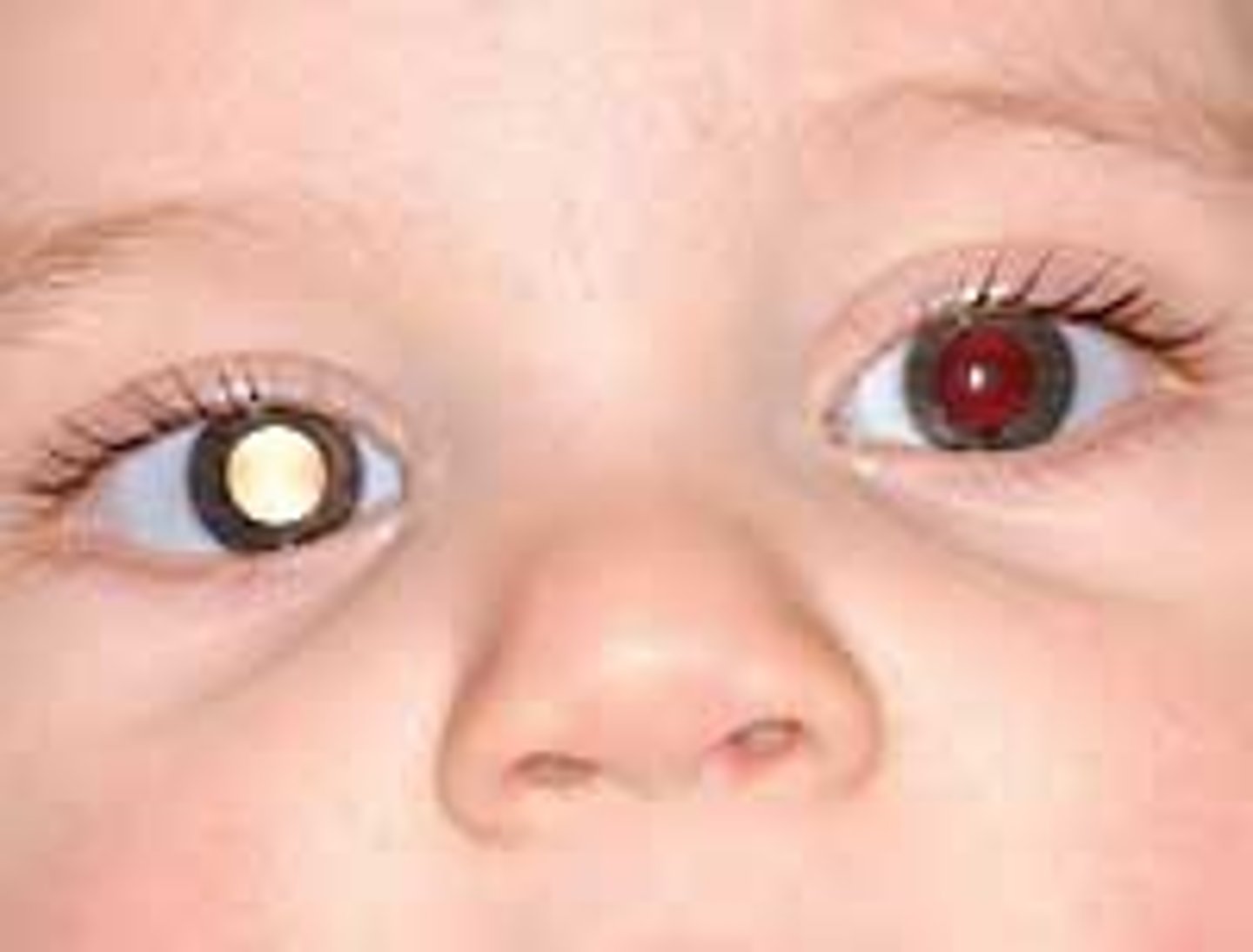
what should you suspect when no red reflex is present?
retinoblastoma --> 2/3 are unilateral
always eval siblings if + dx!
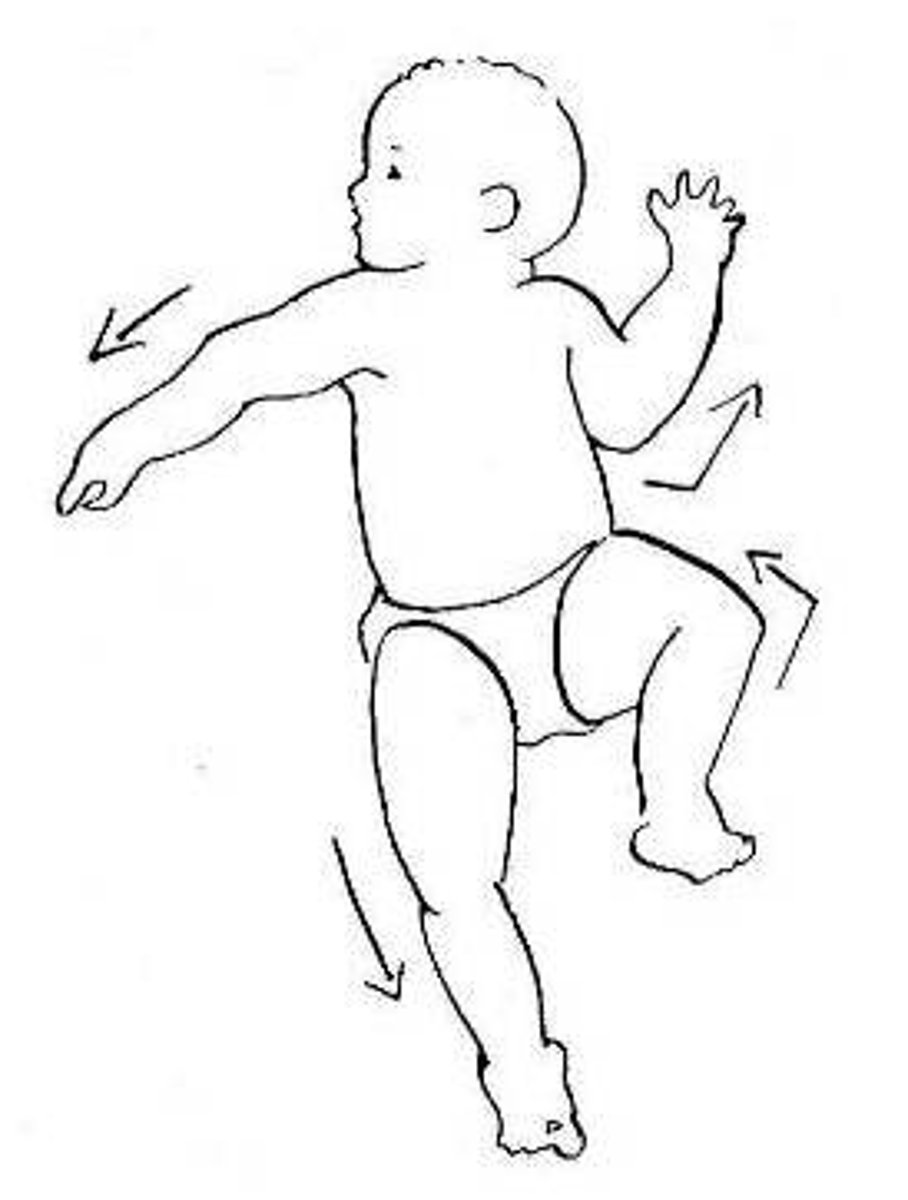
in which reflex do babies result in a "fencing position"?
asymmetric tonic neck reflex
**
what would you suspect if a neonate has weak pulses?
possible CoA or LV obstruction
what syndrome should you suspect with wideset nipples, excessive nuchal skin, and lymphedema?
turner's syndrome
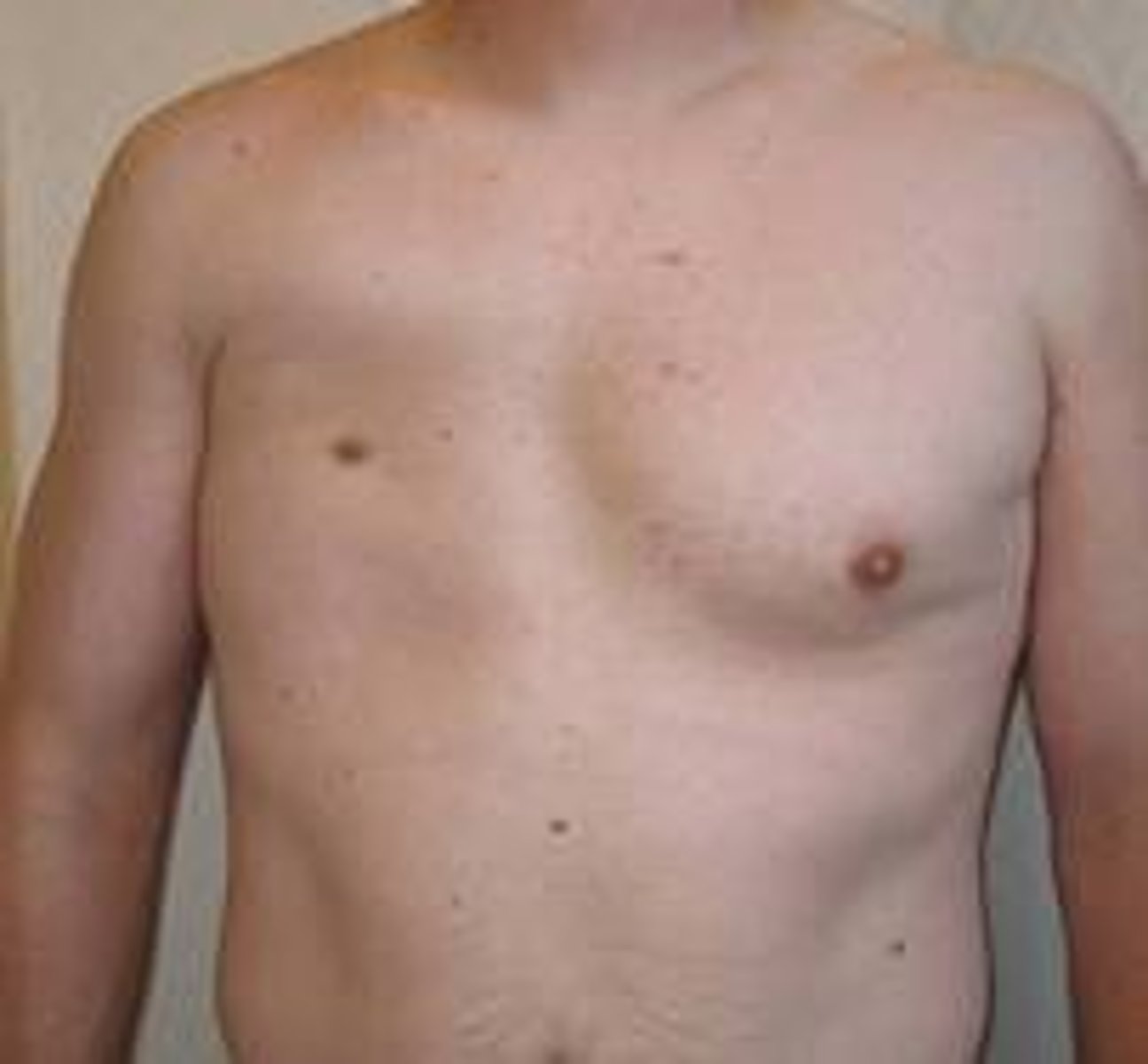
in which condition is there unilateral absence or hypoplasia of the pec major?
poland's syndrome
what is tachycardia in a neonate? bradycardia?
tachy = >160
brady = <100
what disease should you consider if the newborn is unable to pass stool?
hirschprung's disease
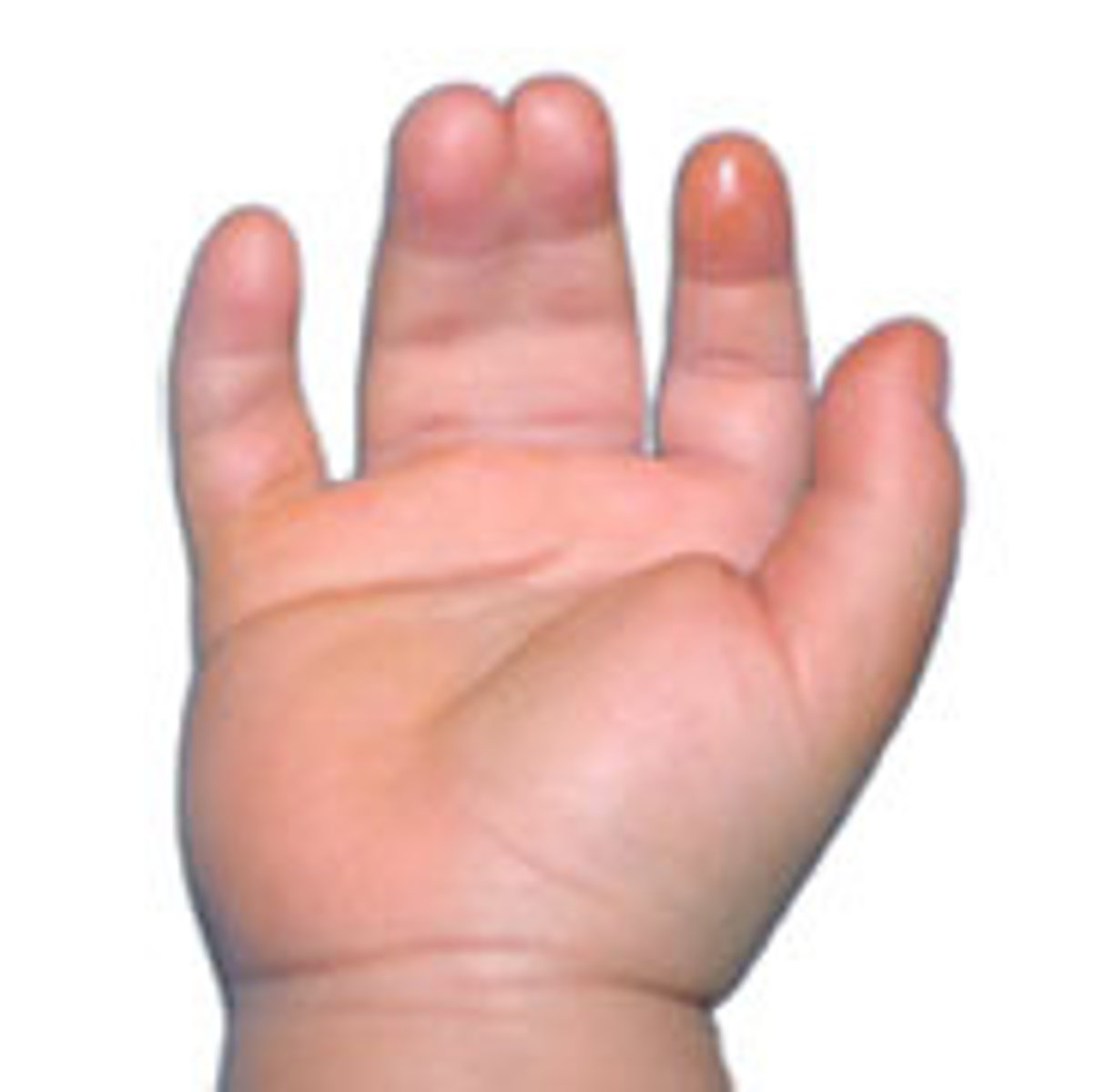
what is the approximation/fusion of 2+ digits by tissue?
syndactyly
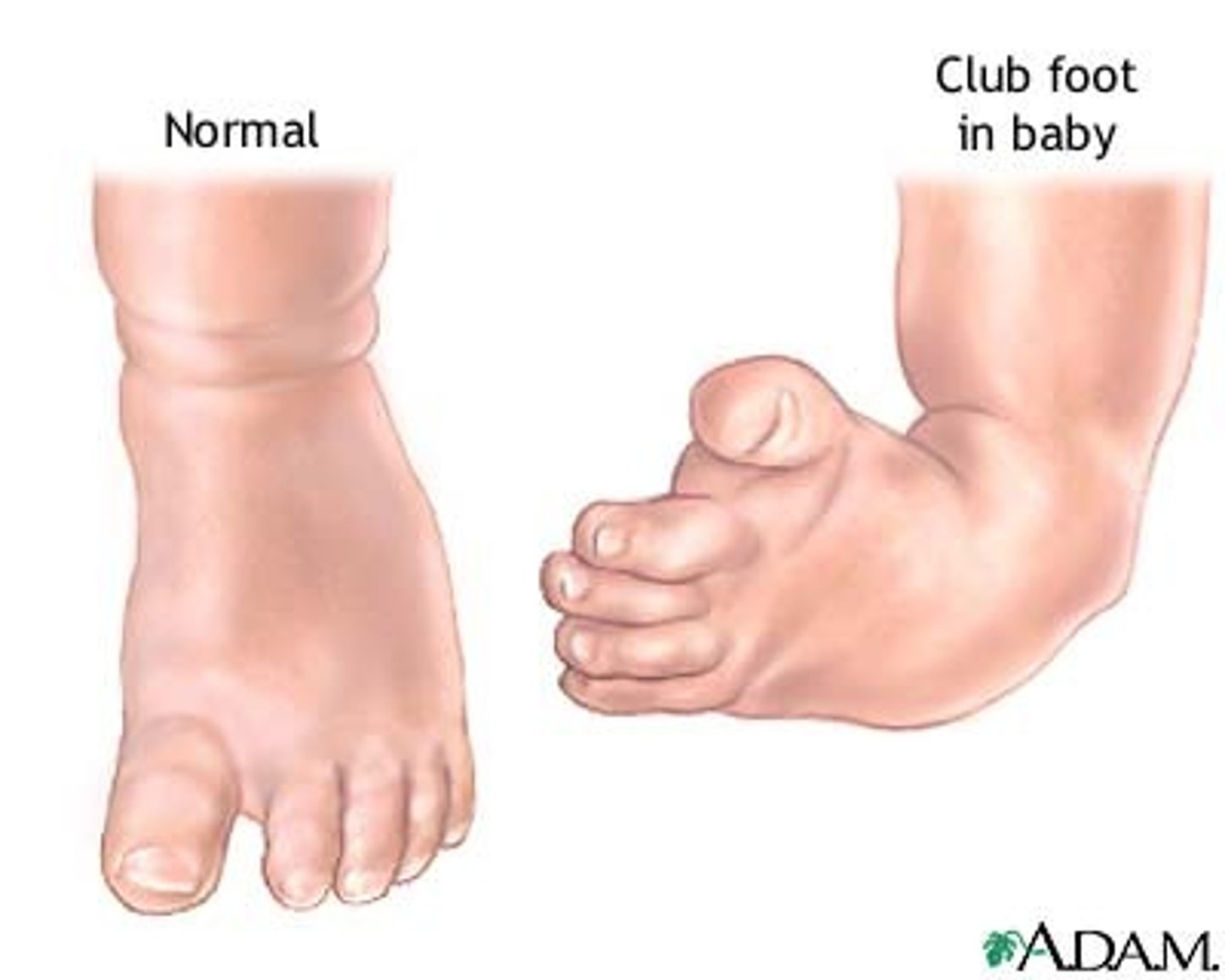
what diagnosis is characterized by forefoot adduction and inversion + plantar flexion of the entire foot?
clubfoot
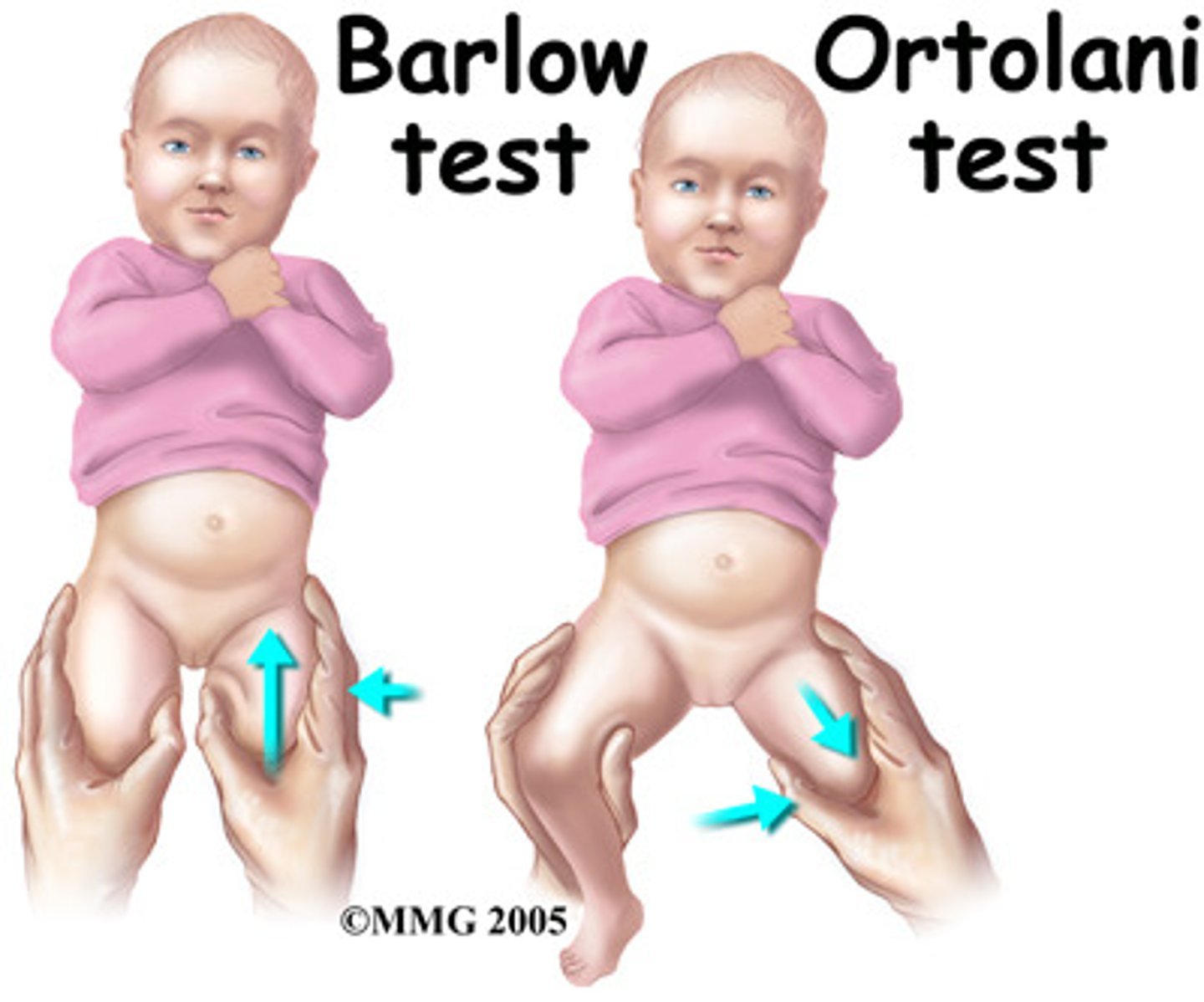
what are the RF for dip dysplasia?
breech in utero
fhx
female gender
what is the barlow maneuver?
posterior dislocation w ADduction
(think: barlow - back, ortolani - open)
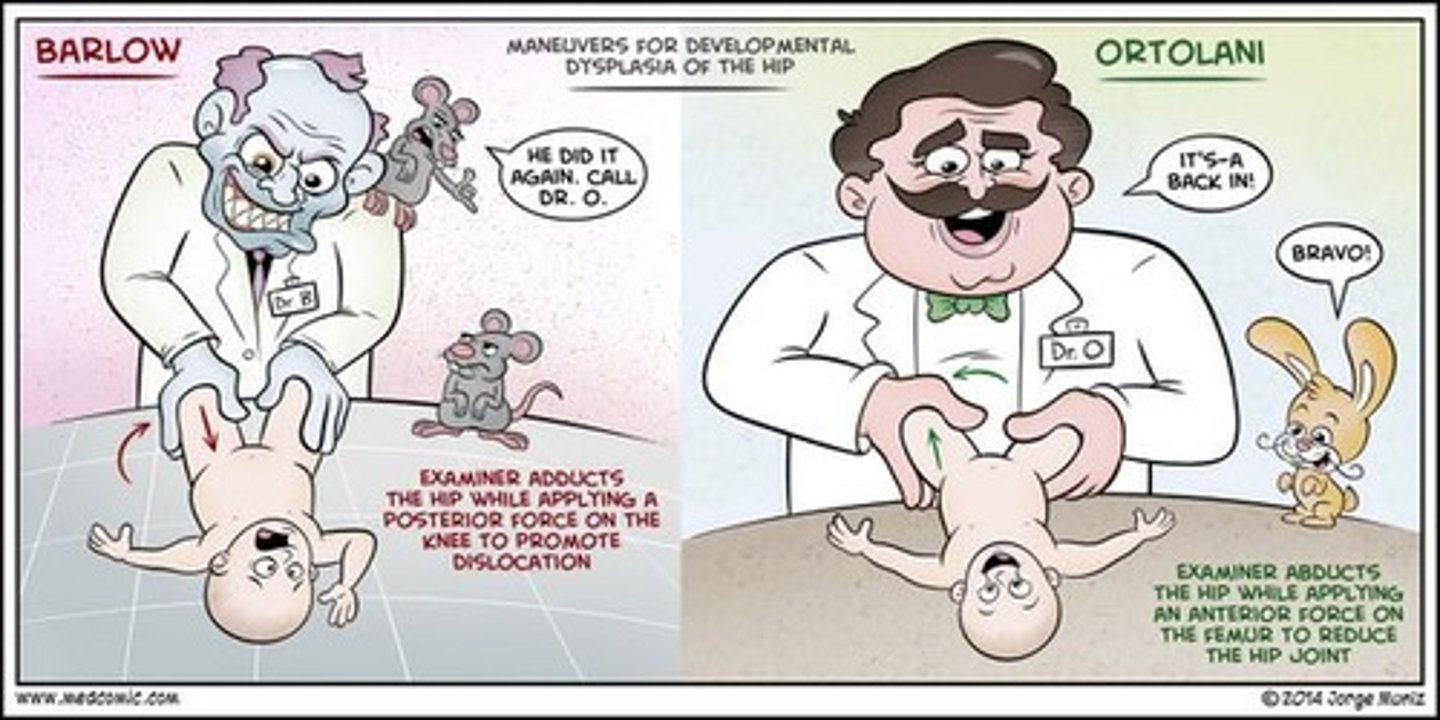

what is the ortolani maneuver?
anterior reduction w/ ABduction
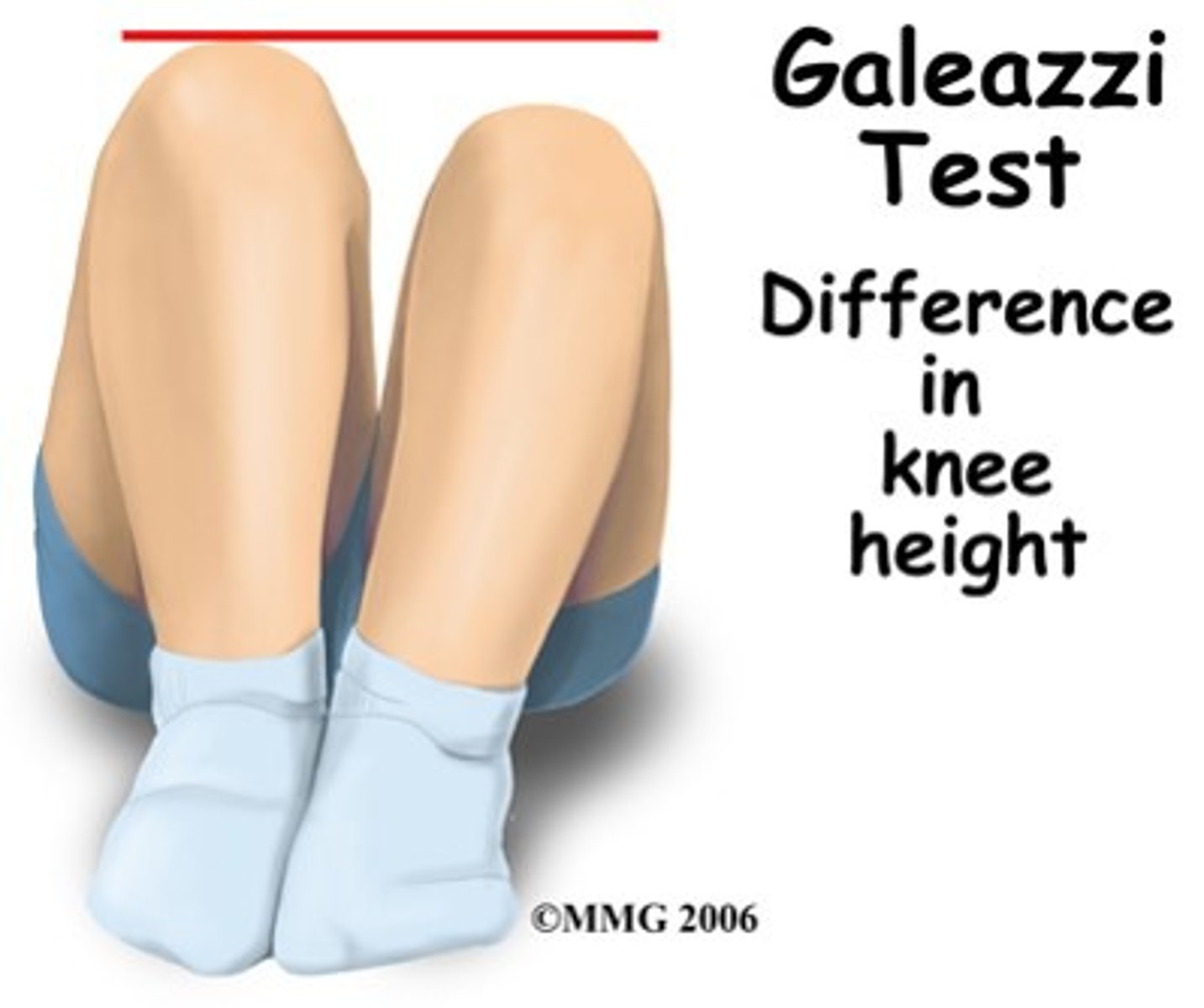
what is Galeazzi's sign?
when the pt is supine with knees flexed and dislocation can be seen if one knee is lower than the other
what is defined as cleft in the verterbral column with corresponding defect in the skin so the meninges and spinal cord are exposed?
myelomeningocele AKA open spina bifida (most serious)
what is a neural tube defect characterized by MSK weakness, gait deficit and urinary dysfunction?
spina bifida → 2 types: closed (occulta) vs. open
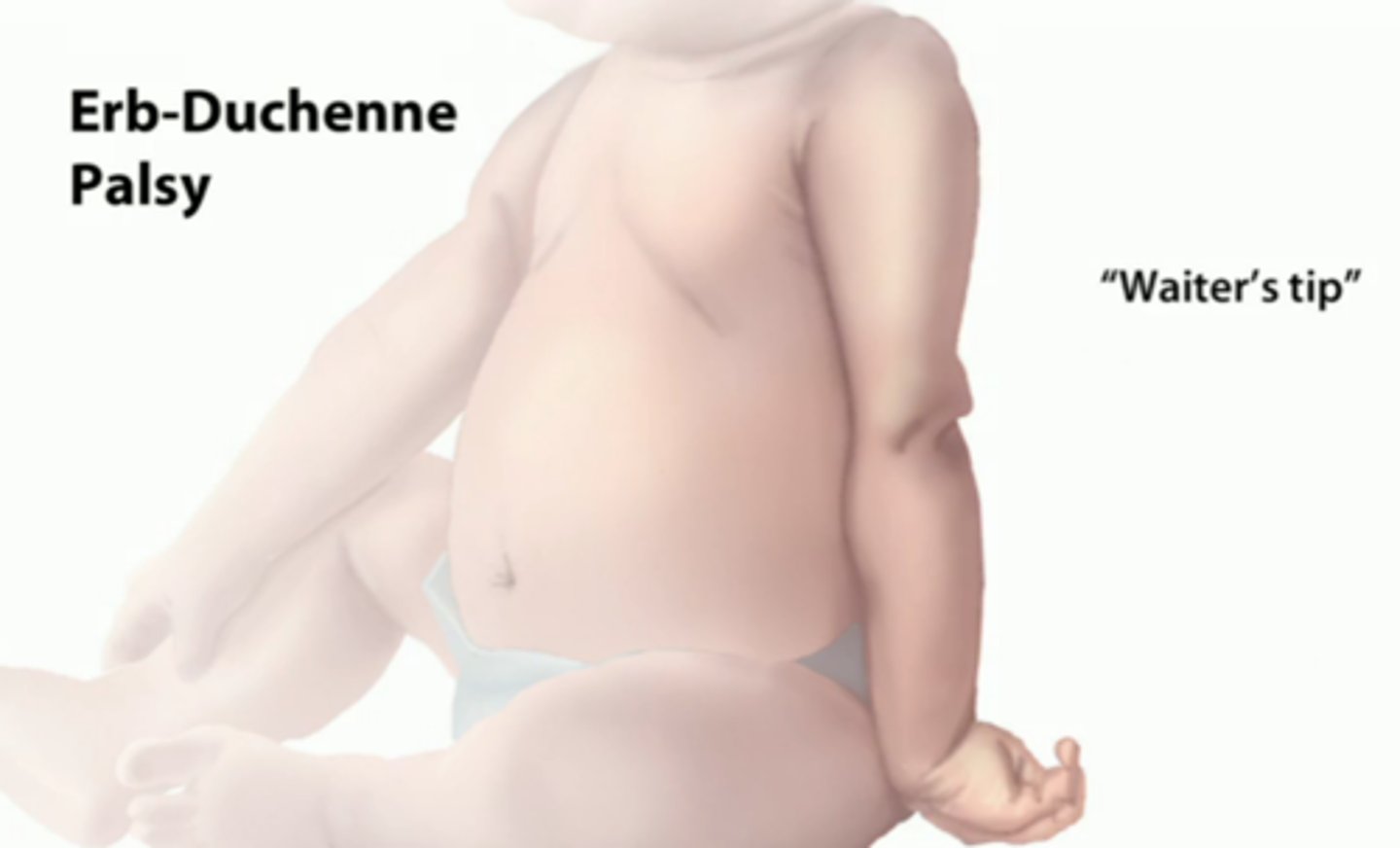
what the the most common cause of Erb Duchenne palsy?
shoulder dystocia during difficult birth
what does the "waiter's tip" sign signify and what nerves does it involve?
Erb duchenne palsy → adduction and internal rotation of shoulder w/ elbow extension and pronation of forearm, flexion of wrist, and intact grasp reflex → C5-C7
congenital nevi vs. nevus simplex: which lightens with age?
nevus simplex (macular stain) lightens with age
congenital nevi thickens with age
what is the mc vascular tumor of infancy?
hemangioma → common on face/neck
can involve liver, GI and lungs
when should you refer a baby with hemangioma to ENT?
if its in a beard distribution
if hemangiomas involve the liver, what should be suspected?
AV shunt that can cause CHF
what are large hemangiomas of the face associated with?
PHACE syndrome
Posterior fossa malformation
Hemangiomas
Arterial abnormalities
Cardiac abnormalities
Eye abnormalities
Sternal cleft
what are white papules caused by retention of keratin/sebaceous material commonly found on nose and cheeks?
milia
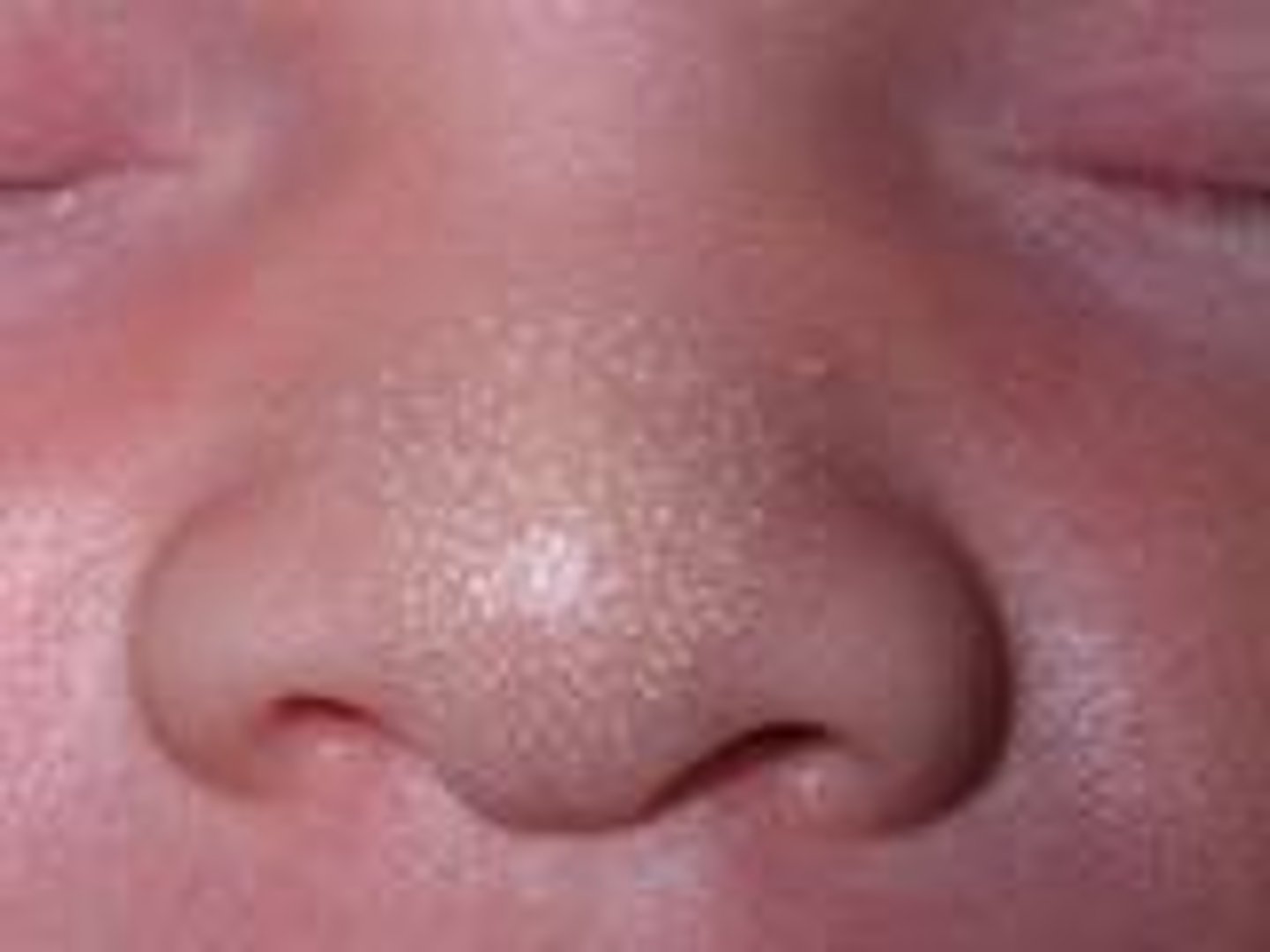
what is the different between epstein pearls and bohn nodules?
both types of gingival inclusion cysts
epstein pearl = on palate
bohn nodule = on vestibular or lingual surface of alveolar ridge
what syndrome are port wine stains assoc. with?
Surge Weber syndrome → port wine stain + leptomeningeal angioma involving brain and eye → seizures, glaucoma, intellectual disability, hemiplegia
what is seen on urine test in neuroblastoma?
increased catecholamines