Lecture 5 - Social cognition and learning
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
What is social cognition?
Social cognition refers to the ability to understand other individuals in relation to oneself. It involves recognizing social cues—such as gaze direction—and interpreting what they reveal about another individual’s mental state or intentions.
What is the theory of mind (ToM)?
Theory of mind is the ability to imagine what another individual knows, sees, or intends. It involves being aware of others’ attention and understanding that they have separate mental states.
Example: A dog fetching a ball behind a glass wall instead of a wooden one demonstrates an understanding that the human can see through glass but not wood.
What is intentionality in social cognition?
Intentionality is the understanding that others act with purpose and intention. Recognizing intentional behavior allows individuals to interpret and predict others’ actions.
Example: Dogs may interpret human pointing or reaching gestures as intentional cues about an object or goal.
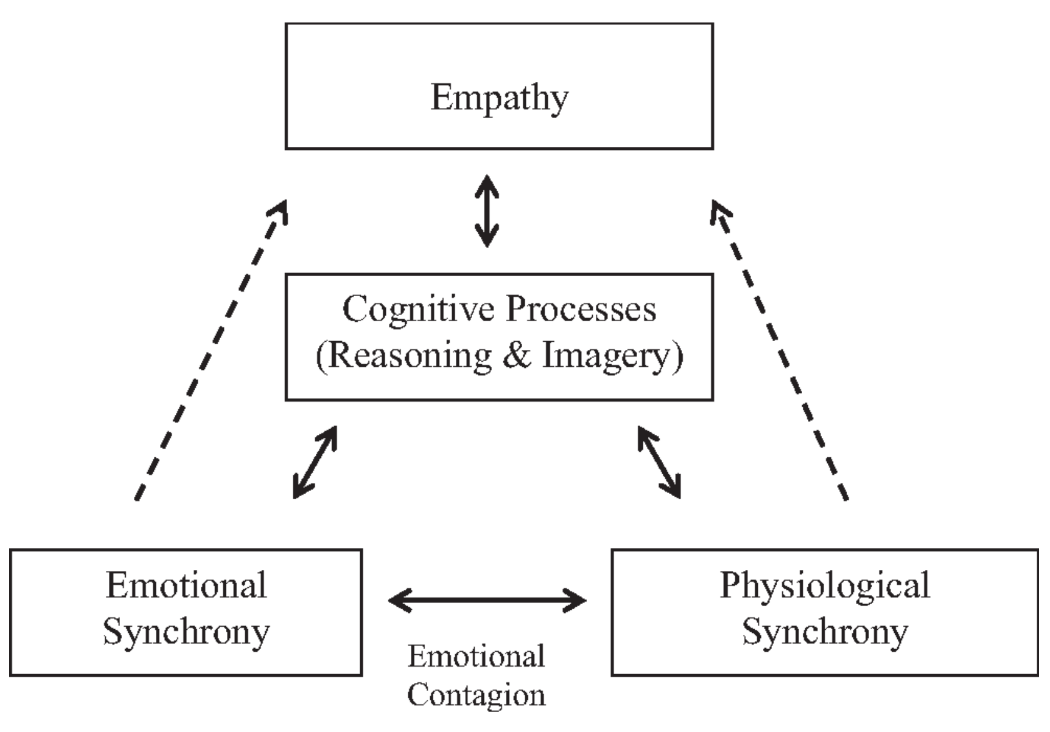
What is empathy and emotional contagion?
Emotional contagion is when one individual mirrors another’s emotional state, leading to emotional synchrony. Empathy builds on this by allowing one to understand why another feels a certain way, taking their perspective.
Example: A dog becoming stressed when its owner is anxious illustrates emotional contagion; comforting the owner would reflect empathy.
What are the levels of social cognition?
1⃣ Motor mimicry & emotional contagion – automatic emotional or behavioral mirroring.
2⃣ Empathic concern & consolation – showing concern or offering comfort to others.
3⃣ Perspective taking & targeted helping – understanding another’s viewpoint and providing goal-directed assistance.
Example: Rats open a cage door to free a trapped companion when distress calls are heard.
What is the social significance of yawning in dogs?
Yawning is a socially contagious behavior. Dogs are especially sensitive to the yawns of familiar humans, suggesting emotional attunement and social empathy.
What is social learning?
Social learning refers to acquiring new behaviors or information by observing others, rather than through direct experience. It allows individuals to adapt efficiently by using social information
What is allelomimetic (social facilitation) behavior?
Allelomimetic behavior involves automatically copying the actions of others without conscious thought. It’s an instinctive form of social learning.
Example: One sheep starts grazing, and others in the flock follow immediately.
What are local and stimulus enhancement?
Local enhancement: An individual becomes attracted to a location after seeing another individual act there.
Stimulus enhancement: An individual becomes interested in a particular object after observing another interact with it.
These mechanisms direct attention and increase learning opportunities.
What is imitation and how does it differ from emulation?
Imitation: Copying another’s specific actions to achieve a goal.
Example: A dog pulls a lever with its nose after seeing a demonstrator do the same.*Emulation: Achieving the same outcome using different actions.
Example: A dog pulls the lever with its paw after seeing another use its nose.*
What is over-imitation and when does it occur?
Over-imitation is when an individual copies even irrelevant actions in a demonstration. It is more common when there is strong attachment or trust toward the instructor—seen in both dogs and children.
What are mirror neurons and why are they important?
Mirror neurons are brain cells that activate both when performing an action and when observing the same action performed by others. They are thought to underlie imitation, empathy, and behaviors like contagious yawning. Evidence suggests dogs may also possess mirror neuron-like systems.
How can social learning lead to culture?
When socially learned behaviors are transmitted across generations, they form culture. This leads to group-specific traditions or behavioral variants.
Example: Different chimpanzee populations use unique tools or techniques passed down through learning.
What did Duranton et al. (2017) discover about behavioral synchrony?
Duranton et al. (2017) found that dogs and humans exhibit behavioral synchronization—for instance, dogs tend to move, rest, or change activity in coordination with their owners. This synchronization reflects social attunement and mutual responsiveness rather than simple conditioning.
How does oxytocin mediate attachment and emotional contagion?
Oxytocin strengthens social bonds by promoting trust, attachment, and emotional synchrony. In both humans and dogs, oxytocin release occurs during positive social contact, reinforcing empathy and mutual calming—thus functioning as a neurobiological bridge for emotional contagion.
What did Whiten (2021) propose about animal culture?
Whiten (2021) defines culture as “all that is learned from others and transmitted repeatedly, forming traditions inherited by successive generations.” This emphasizes that social learning can lead to cultural diversity within species, such as group-specific tool use or communication patterns.
How might social learning contribute to species survival?
By allowing individuals to learn from others instead of through trial and error, social learning increases efficiency, reduces risk, and promotes adaptability. When passed across generations, these learned behaviors enhance group cohesion and long-term survival.