Concept 5.4: Proteins include a diversity of structures, resulting in a wide range of functions
1/17
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
Proteins
Biological molecules that account for more than 50% of the dry mass of most cells, serving in a variety of functions
Contain one or more polypeptides
Functions result from their structure of polypeptides twosted, foiled, and coiled to bind to other molecules

Enzymatic proteins
Proteins that selectively accelerate chemical reactions
Digestive enzymes catalyze the hydrolysis of bonds in food molecules
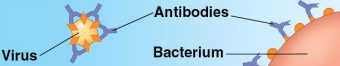
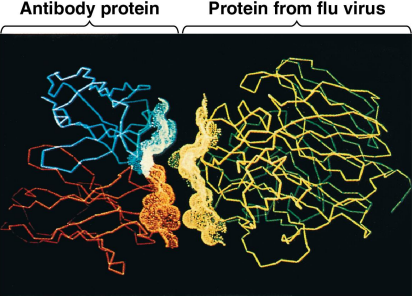
Defensive proteins
Proteins that protect against disease
Antibodies activate and help destroy virsues and bacteria
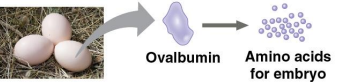
Storage proteins
Proteins that store amino acids
Casein in milk is the major source of amino acids for baby mammals
Plants have storage proteins in their seeds
Ovalbumin is the protein of egg white, used as an amino acid source for the developing embryo
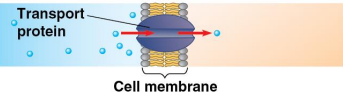
Transport proteins
Proteins that transport substances
Hemoglobin is the iron-containing protein of vertebrate blood, transporting oxygen from the lungs to other parts of the body
Transport proteins exist in cell membranes for molecular passage
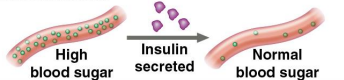
Hormonal proteins
Proteins that coordinate an organism’s activities
Insulin (a hormone secreted by the pancreas) causes glucose uptake in cells, regulating blood sugar concentration
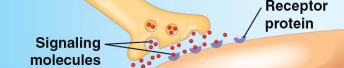
Receptor proteins
Proteins that aid cellular responses to chemical stimuli
Receptors in nerve cell membranes detect signaling molecules released by other nerve cells
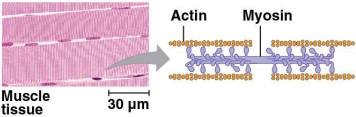
Contractile proteins (motor proteins)
Proteins that function in movement
Motor proteins aid the movement of cilia and flagella
Actin and myosin proteins are responsible for the contraction of muscles
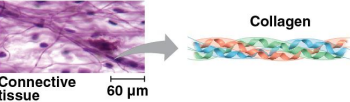
Structural proteins
Proteins that support cellular structures
Keratin is the protein of hair, horns, feathers, and other skin appendages
Insects and spiders use silk fibers to make their cocoons and webs
Collagen and elastin proteins provide a fibrous framework in animal connective tissues
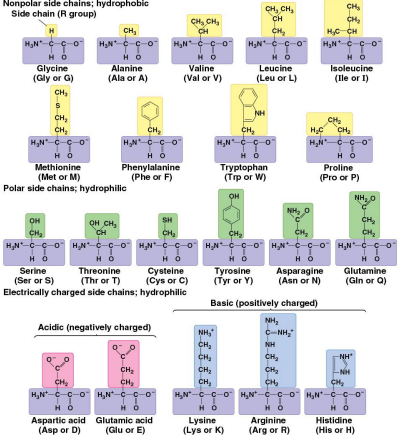
Amino acids
Organic molecules with amino and carboxyl groups that serve as the monomers in proteins
Have differing properties due to differing side chains called R groups
Polypeptides
Unbranched polymers built from amino acids joined by peptide bonds
Peptide bonds
Bonds that join amino acids in polypeptides
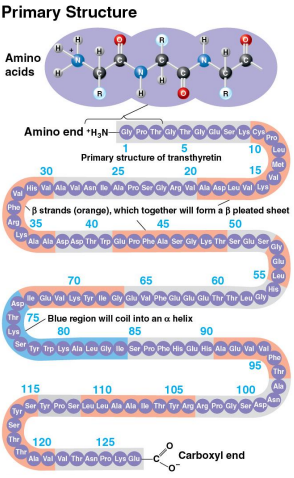
Primary structure
A protein’s first structure defined by its unique sequence of amino acids
Like the order of letters in a long word
Determined by inherited genetic information
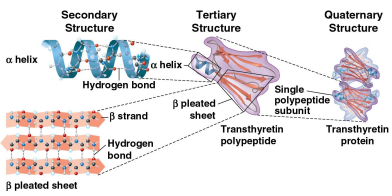
Secondary structure
A protein’s second structure defined by its coils and folds in its polypeptide chains
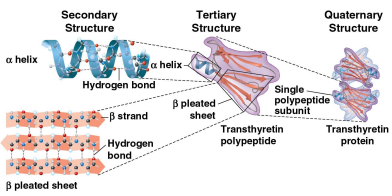
Tertiary structure
A protein’s third structure defined by its interactions among various side chains (R groups)
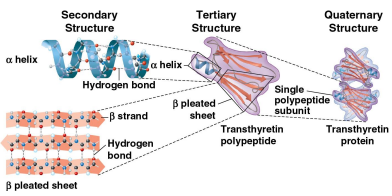
Quaternary structure
A protein’s fourth and final structure when a protein consists of multiple polypeptide chains to form one macromolecule
Collagen consists of three polypeptides like a rope
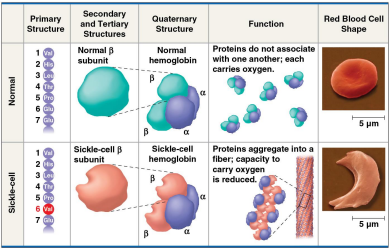
Sickle-cell disease
An inherited blood disorder that results from a single amino acid substitution in the protein hemoglobin, causing an abnormal sickle shape in the red blood cell
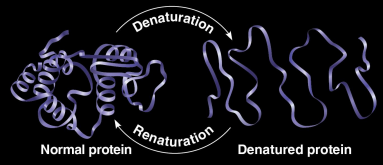
Denaturation
The loss of a protein’s native structure caused by physical or chemical conditions
pH, salt concentration, and temperature are some factors
Extremely high fevers can be fatal because of this