General Chemistry 1 Exam 2 Review
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
What is the formula for internal energy?
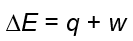
What is the formula for enthalpy?
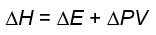
What is the formula for work?
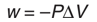
What is the formula for the amount of heat that is lost or gained?
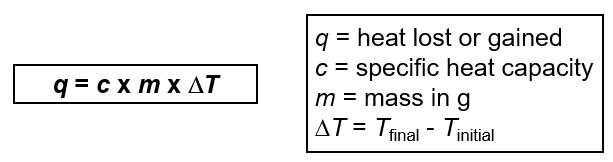
What is the formula for kinetic energy?

Open system vs. Closed system vs. Isolated system
Open systems exchange matter and energy, closed systems exchange just energy, and isolated systems exchange neither.
How does the energy of a system relate to that of the calrimeter?
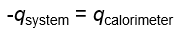
What is a state function?
Functions that do not depend on the path taken to reach a specific value (e.g., temperature, enthalpy, energy).
What is a path function?
Functions that do depend on the path from two values (e.g., heat, work).
What is Hess’s Law?
The overall enthalpy is equal to the sum of the enthalpies of the individual steps.
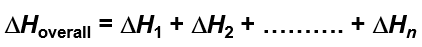
What is the standard enthalpy of formation?
The change in enthalpy during the formation of 1 mole of the substance from its elements (in standard states).
How many moles of product should be formed when balancing equations?
1 mole (may be fractional exponents).
What is the standard enthalpy of formation for decomposition?
ΔH°f < 0
What is the formula for relating wavelength, frequency, and energy?
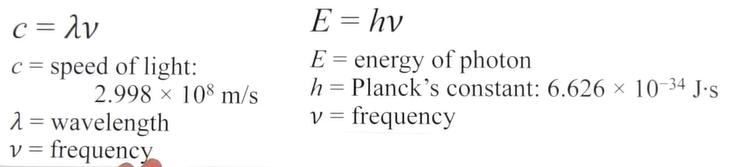
How does subshell relate to angular momentum?

What is Heisenberg’s Uncertainty Principle?
There is inherent uncertainty in measuring a variable of a particle.
What are degenerate orbitals?
Orbitals that have the same energy level.
What is Pauli’s Exclusion Principle?
No two electrons in the same atom can have the same four quantum numbers.
Orbitals can only hold up to 2 electrons.
What is nuclear charge (Z)?
The total charge in the nucleus of all the protons.
How does shielding affect Z?
Shielding reduces Z to Zeff.
What is the effective nuclear charge (Zeff)?
The nuclear charge an electron actually experiences.
How does the energy level/shell relate to the energy sublevel/subshell?
Energy level/shell = energy sublevel/subshell
What is the Aufbau Principle?
Electrons fill lower-energy sublevels first.
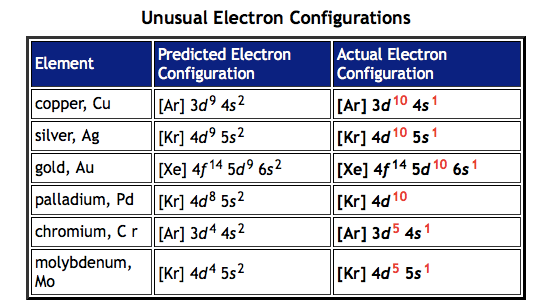
What are exceptions to electron configuration rules?
What periods have dips in ionization energy (IE), and why?
Periods 2A and 3A because they have single electron that is easier to remove.
What is electron affinity (EA)?
The energy change that occurs when 1 mole of electrons is added to 1 mole of gaseous atoms or ions (low EA = cations, high EA = anions, becomes more negative across a period.
What is metallic character and its trend?
A metal’s level of reactivity that increases down a group.
What is the trend of ionic (metal), covalent (nonmetal), and amphoteric (metal or metalloid) oxides?
Oxides become more basic down a group and more acidic across a period.
How do you solve for kinetic energy of photons?
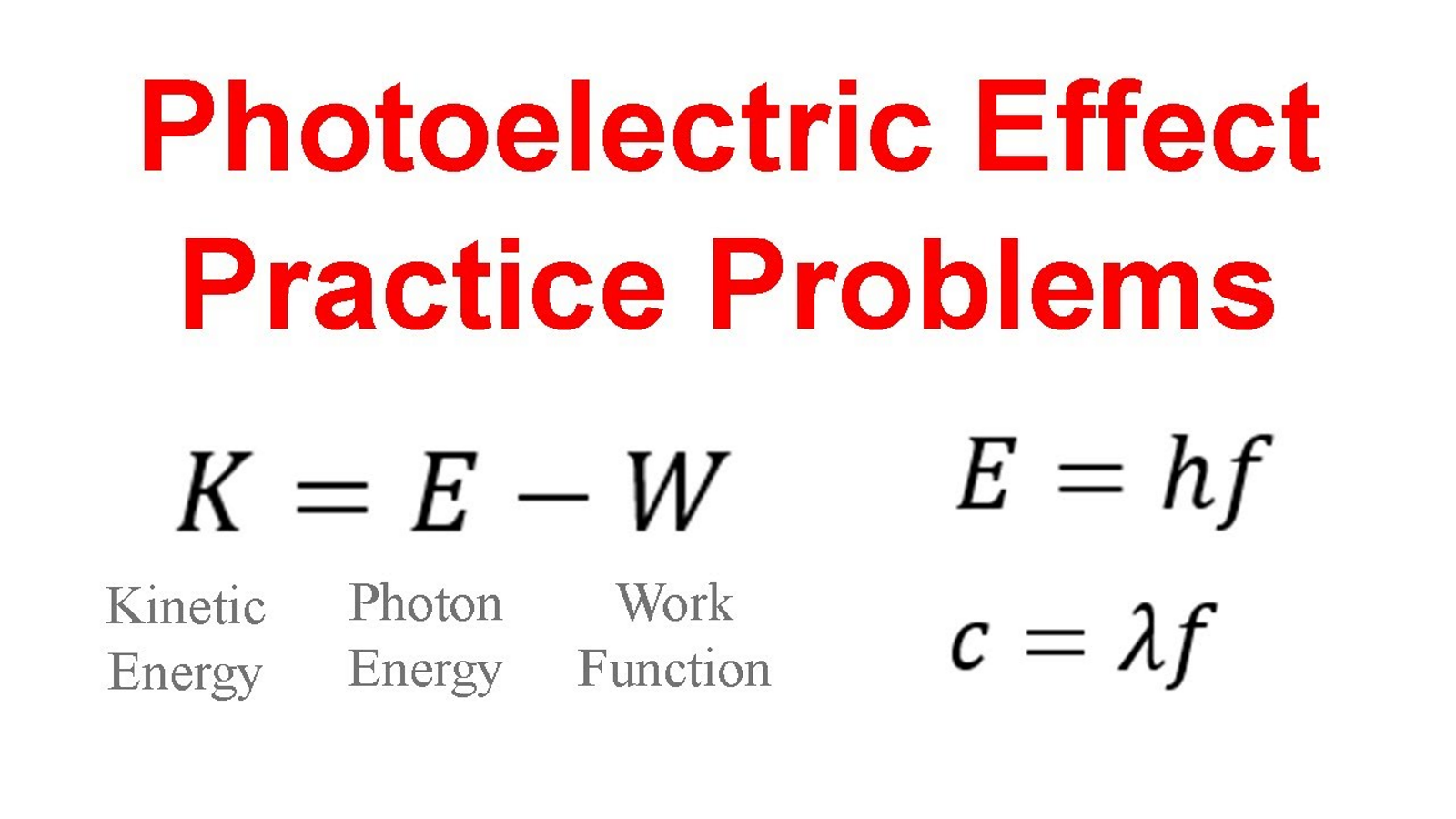
How do you find the maximum amount of electrons that can be ejected?
ϕ=hf−K, where ϕ is the work function and K is the kinetic energy of the electron.

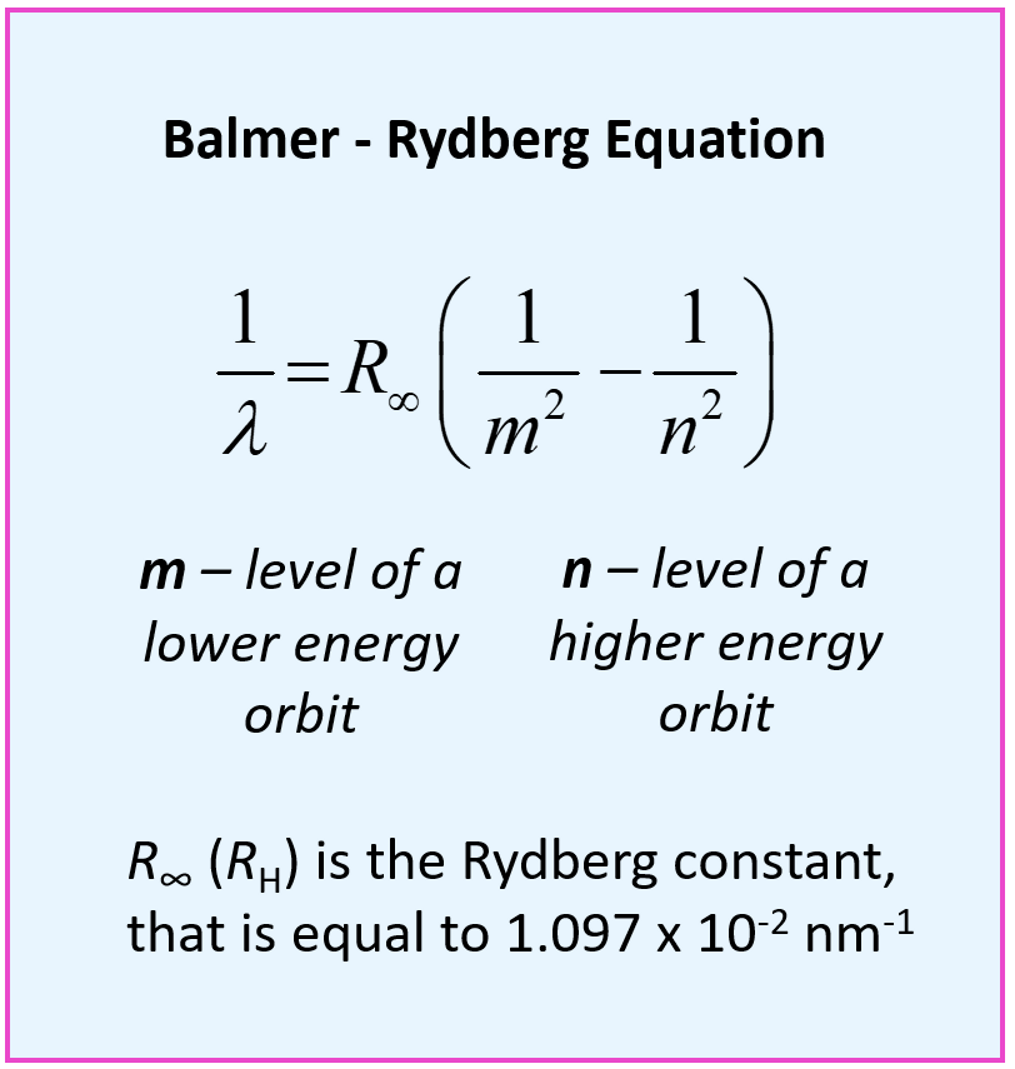
What is the Balmer Rydberg Equation?
How do you find the amount of orbitals?
2l + 1
How does the energy of the reaction relate to that of the solution?
-qreaction = qsolution
How does the energy of metal relate to that of the water?
-qmetal = qwater
What are the units of enthalpy?
-q/n → kJ/mol
What happens to atomic radius across a period and why?
It decreases because Zeff increases, which increases attraction.
What is bond order (BO)?
The number of electron pairs being shared.
What is bond energy (BE)?
The energy needed to overcome a bond’s attraction.
What is bond length (BL)?
The distance between two bonded nuclei.
What is the trend of BE and BL?
BL increases down a group while BE decreases.
How do you find the standard enthalpy change?

How do you find oxidation number?

How do you find Zeff?
Zeff = Z - S (atomic number - core electrons).
What do elements with half-filled p or fulfilled s orbitals do?
They jump in front of the elements to their right for IE.
How do you find lattice energy?
|product of charges| (excluding stoichiometric coefficients)
What is the enthalpy of formation equal to?
Enthalpies of sublimation + Bond energy + Ionization energies + Electron affinities + Lattice energy.
What does EA tell you?
Which elements are more likely to gain an electron (absorb = doesn’t want much, released = wants it).