Biology 1 Honors - Chapter 6+7 Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Test Study Guide
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
89 Terms
phosphorolation
transfer of third phosphate group from ATP -> makes burst of energy ATP turns to ADP

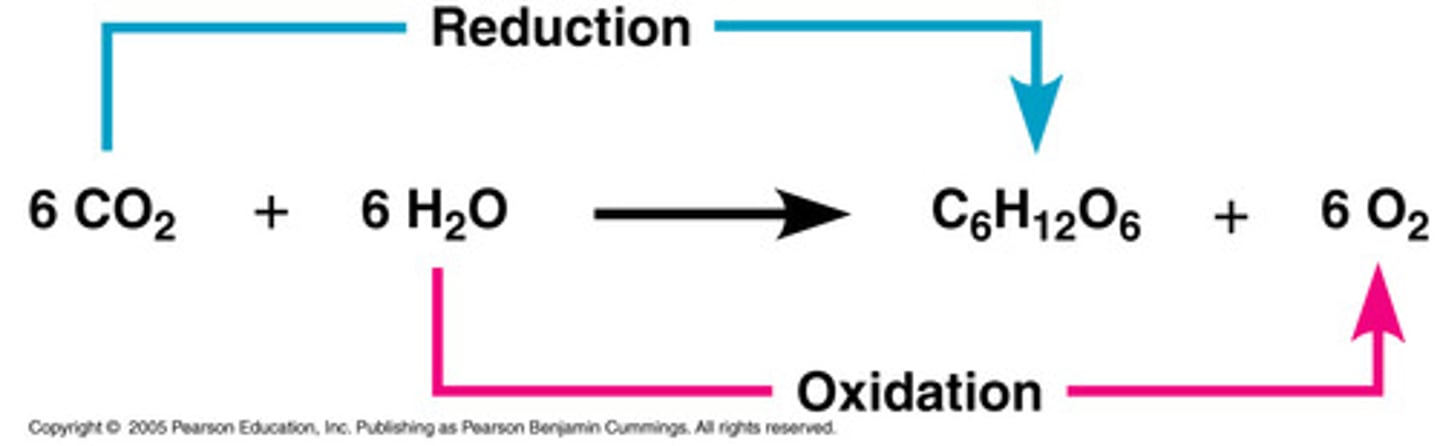
In photosynthesis, _________ is oxidized and _________ is reduced.
water, CO2
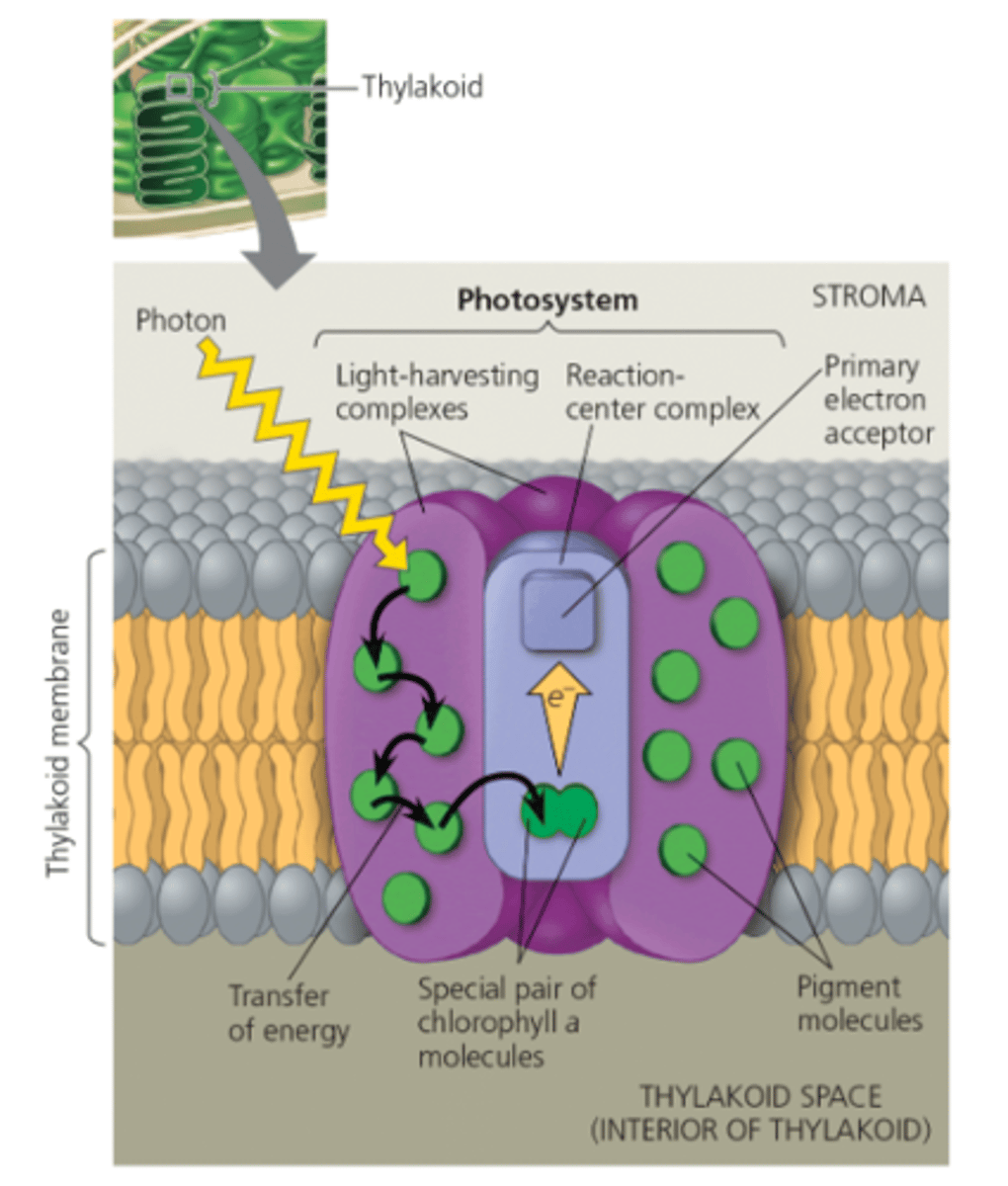
which of the following are produced by reactions that take place in the thylakoids and consumed by reactions in the stroma?
ATP and NADPH
When light strikes chlorophyll molecules in the reaction-center complex, they lose electrons, which are ultimately replaced by
splitting water.
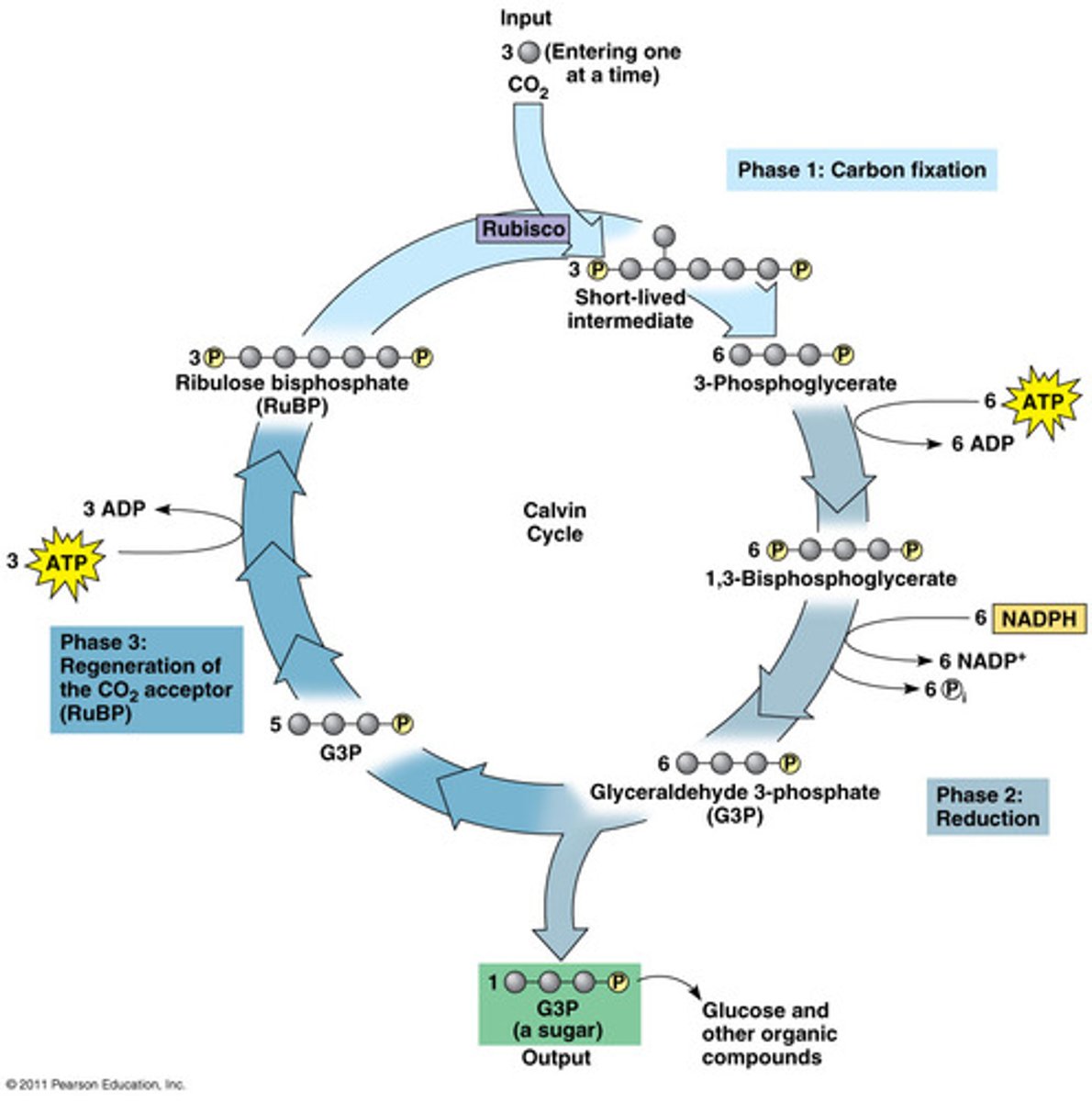
The reactions of the Calvin cycle are not directly dependent on light, but they usually do not occur at night. Why?
The Calvin cycle depends on products of the light reactions.
Which of the following does not occur during the Calvin cycle?
release of oxygen
Why is it difficult for C3 plants to carry out photosynthesis in very hot, dry environments such as deserts?
The closing of stomata keeps CO2 from entering and O2 from leaving the plant.
Bloom's level: Remembering/Understanding 7.1 Which of the following are photoautotrophs?
kelp, a large sea alga
The light reactions of photosynthesis yield __________. The Calvin cycle produces __________.
O2, ATP, NADPH; sugar, ADP, NADP+
In the light reactions, __________ and an __________ transform __________ energy into __________ energy of ATP and NADPH
two photosystems; electron transport chain; light; chemical
What is the final electron acceptor in the light reactions of photosynthesis?
NADP+
Two separate processes occur in the light reactions of photosynthesis. In one, __________ is generated as the result of an electric transport chain. In the other, the high concentration of __________ in the thylakoid space drives the synthesis of __________.
NADPH; H+; ATP
Plants remove __________ from the atmosphere and return __________ to the atmosphere. The other product(s) of photosynthesis is (are) ________
carbon dioxide; oxygen; sugars
How does photosynthesis contribute to climate change? In what way is it a solution to climate change?
Fossil fuels produce CO2 when burned. Plants remove CO2 from the atmosphere in photosynthesis.
Chloroplasts are located in __________ cells. Each such cell contains __________ chloroplasts. Chlorophyll molecules are located on membranes of the __________.
mesophyll; 30-40; thylakoids
Stomata
Small openings on the underside of a leaf through which oxygen and carbon dioxide can move
mesophyll
the tissue in the interior of the leaf
Stroma
cytoplasm of a chloroplast
Granum
stack of thylakoids
Thylakoid
saclike photosynthetic membranes found in chloroplasts
In glycolysis, ATP molecules are produced by _____.
substrate-level phosphorylation
Which of these is NOT a product of glycolysis?
FADH2
In glycolysis, what starts the process of glucose breakdown?
ATP
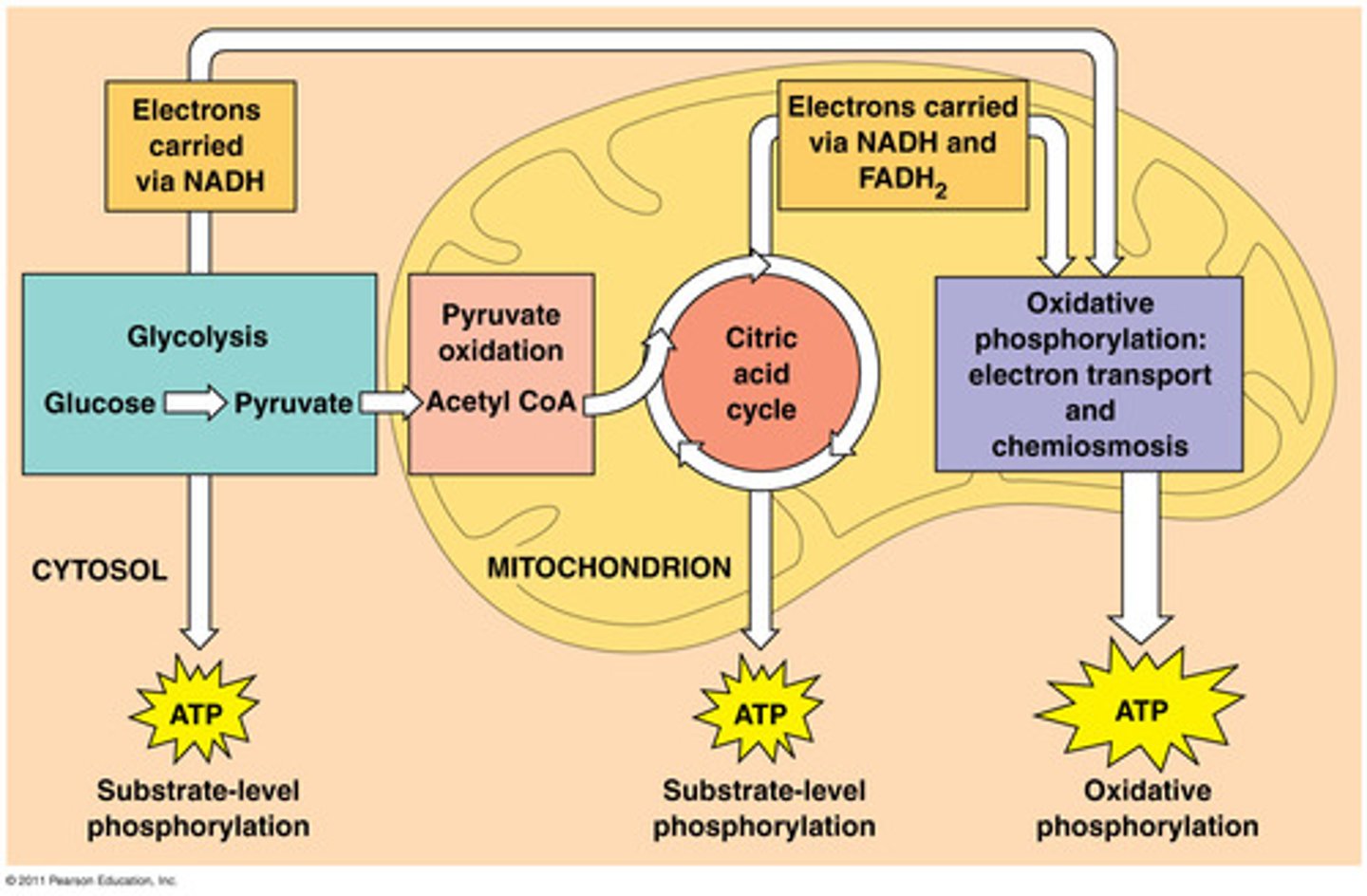
What is the net gain of ATP from glycolysis?
2 ATP
For each glucose that enters glycolysis, _____ NADH enter the electron transport chain.
10
In cellular respiration, most ATP molecules are produced by _____.
Oxidative Phosphorylation
The proximate (immediate) source of energy for oxidative phosphorylation is _____.
kinetic energy that is released as hydrogen ions diffuse down their concentration gradient
During chemiosmosis
ATP is synthesized when H+ ions move through a channel in ATP synthase.
What is the final acceptor in the electron transport chain?
oxygen
Given the relatively modest number of calories burned by anything but the most vigorous of activities, how can people consume over 2,000 kilocalories a day yet maintain a healthy body weight?
Most of the energy consumed in food is spent maintaining the body's functions over the course of a day, so a healthy amount of daily exercise would require only a modest increase in the number of kilocalories consumed to maintain a healthy weight
In cellular respiration, glucose __________ electrons, whereas __________ electrons.
loses, o2 gains
In muscle cells, fermentation produces _____.
lactate and NAD+
Sunlight is essential for the varied life on Earth because it provides __________.
the energy necessary to power the rearrangement of chemical bonds in H2O and CO2
Which of the following is the role of cellular respiration?
to harvest energy from organic molecules
A person's basal metabolic rate (BMR) is equal to about __________.
1,300-1,500 Calories/day

A molecule that functions as the electron donor in a redox reaction __________.
loses electrons and becomes oxidized
In cellular respiration, glucose __________ electrons and oxygen __________ electrons.
loses, gains
Oxidative phosphorylation could not occur without glycolysis and the citric acid cycle because __________.
these two stages supply the electrons needed for the electron transport chain.
Which of the following statements about glycolysis is correct?
Glycolysis requires ATP to make ATP.
Glycolysis begins with __________ and ends with __________.
one molecule of glucose, two molecules of pyruvate
At what point in cellular respiration is the first molecule of CO2 produced?
in the reaction that creates acetyl CoA (coenzyme A) from pyruvate
What "powers" ATP synthase, allowing it to catalyze the conversion of ADP to ATP in the presence of phosphate?
the flow of H+ ions down their concentration gradient.
Fat is the most efficient fuel molecule because __________.
with their numerous hydrogen atoms, fats provide an abundant source of high-energy electrons
Let's look at the big picture here: Fueled by the ATP generated during cellular respiration, the intermediates of glycolysis and the citric acid cycle, such as pyruvate and acetyl CoA, are siphoned off and used to __________.
build proteins, fats, and carbohydrates
A biochemist wanted to study how various substances were used in cellular respiration. In one experiment, she allowed a mouse to breathe air containing O2 "labeled" by a particular isotope. In the mouse, the labeled oxygen first showed up in
H2O.
In glycolysis, ______ is oxidized and ______ is reduced
glucose, NAD+
Most of the Co2 from cellular respiration is released during...
citric acid cycle/krebs cycle
Which of the following is the most immediate source of energy for making most of the ATP in your cells?
the movement of H+ across a membrane down its concentration gradient
Which of the following is a distinction between cellular respiration and fermentation?
NADH is oxidized by passing electrons to the electron transport chain in respiration only.
The poison cyanide binds to an electron carrier within the electron transport chain and blocks the movement of electrons. When this happens, glycolysis and the citric acid cycle soon grind to a halt as well. Why do you think these other two stages of cellular respiration stop? (Explain your answer.)
They run out of NAD+ and FAD.
In the citric acid cycle, an enzyme oxidizes malate to oxaloacetate, with the production of NADH and the release of H+. You are studying this reaction using a suspension of bean cell mitochondria and a blue dye that loses its color as it takes up H+. You set up reaction mixtures with mitochondria, dye, and three different concentrations of malate (0.1 mg/L, 0.2 mg/L, and 0.3 mg/L). Which of the following graphs represents the results you would expect, and why?
The mixtures all start out the same, and then the ones with more malate (reactant) decolorize faster.
Which of the following statements regarding the reduction of CO2 to sugar during photosynthesis is true?
Electrons (with accompanying hydrogen ions) are added to CO2 during photosynthesis.
A redox reaction involves the transfer of
an electron
Which statement best describes the transfer of energy and matter in photosynthesis?
Energy in sunlight is transformed into chemical energy when electrons move to a more excited state.
What is the photosynthesis equation?
6 CO2 + 6 H2O → C6H12O6 + 6 O2
Where does the Calvin cycle occur
stroma
The light reactions of photosynthesis involve __________.
reduction of NADP+
What provides the electrons for light reactions
water
Sunlight is a type of ________ energy.
electromagnetic
The primary function of light absorption by photosystems I and II is to produce __________.
energized electrons
Why do chlorophyll turn red in the presence of UV light?
fluorescence
What is the chemical equation for the Cellular respiration
C6+H12+O6(glucose) + 6O2 -----> 6 CO2 + 6 H2O (water) + ATP (energy)

What does it mean for reaction to be light-independent? Give an example
Light is not required, Calvin cycle is an example
What does it mean for a reaction to be light dependent? Give an example
Light is required. An example is the light reaction in photosynthesis.
What are the two main events in photosynthesis?
Light-dependent reaction and the Calvin Cycle
What are the reactants and products of the light dependent reaction?
reactants- Light energy, H2O, NADP+
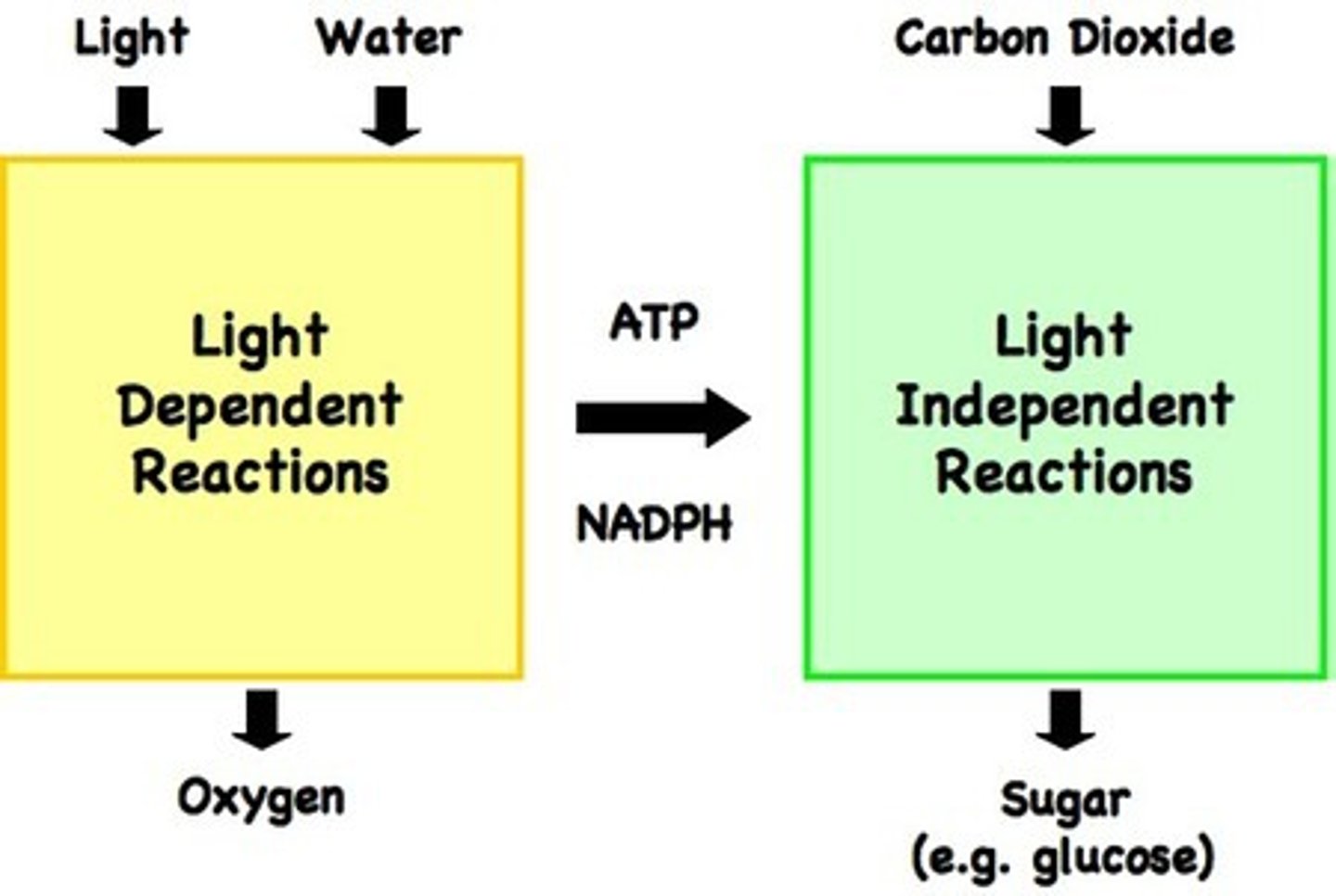
What are the reactants and products of the Calvin Cycle?
CO2, NADPH, ATP
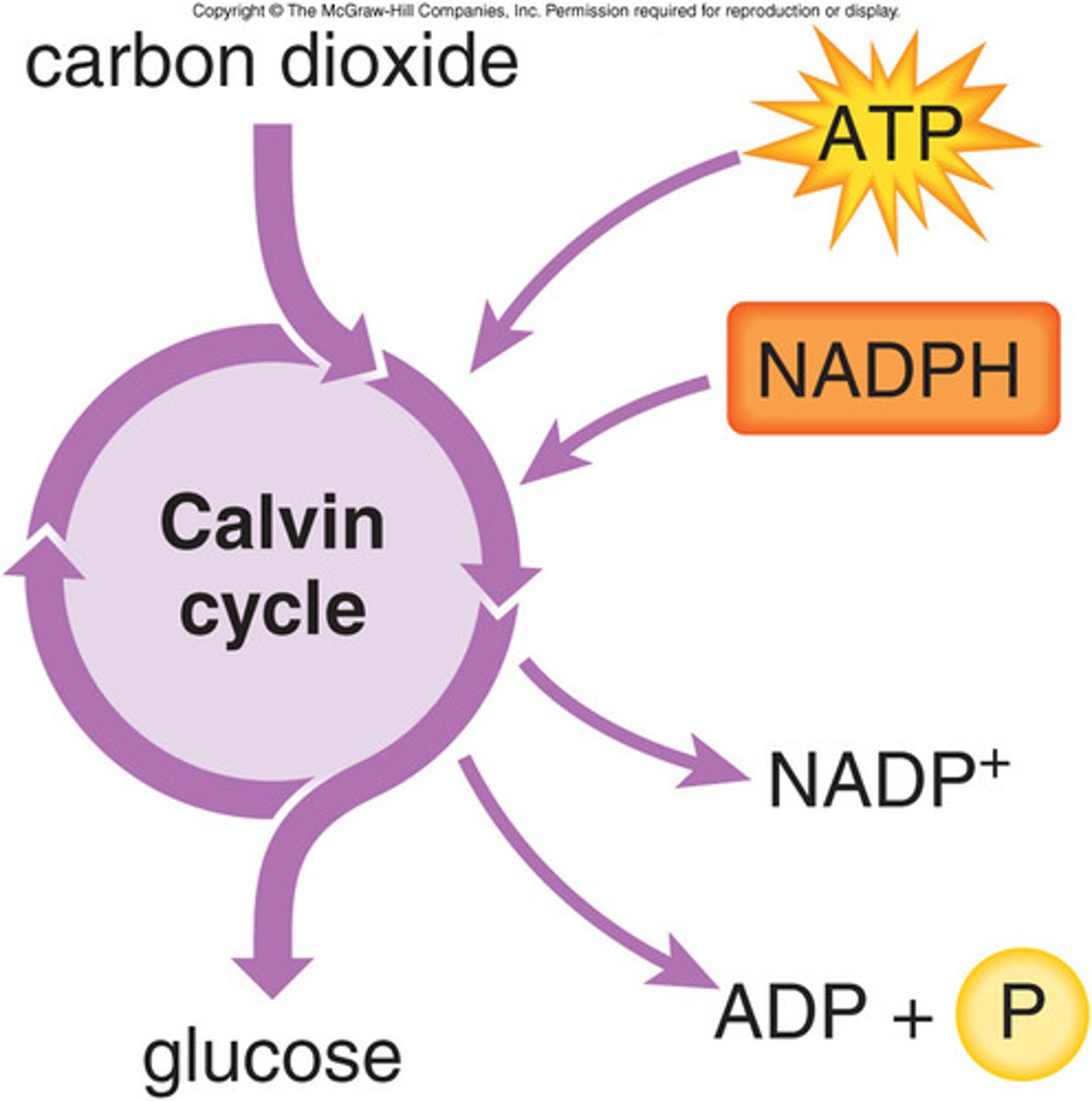
What sugar is made from carbon dioxide in the Calvin Cycle?
glucose
What pigment in the plant processes light energy?
Chlorophyll
What are ATP and NADPH used for in the Calvin Cycle?
to convert the three-carbon compound, 3-PGA, into another three-carbon compound called G3
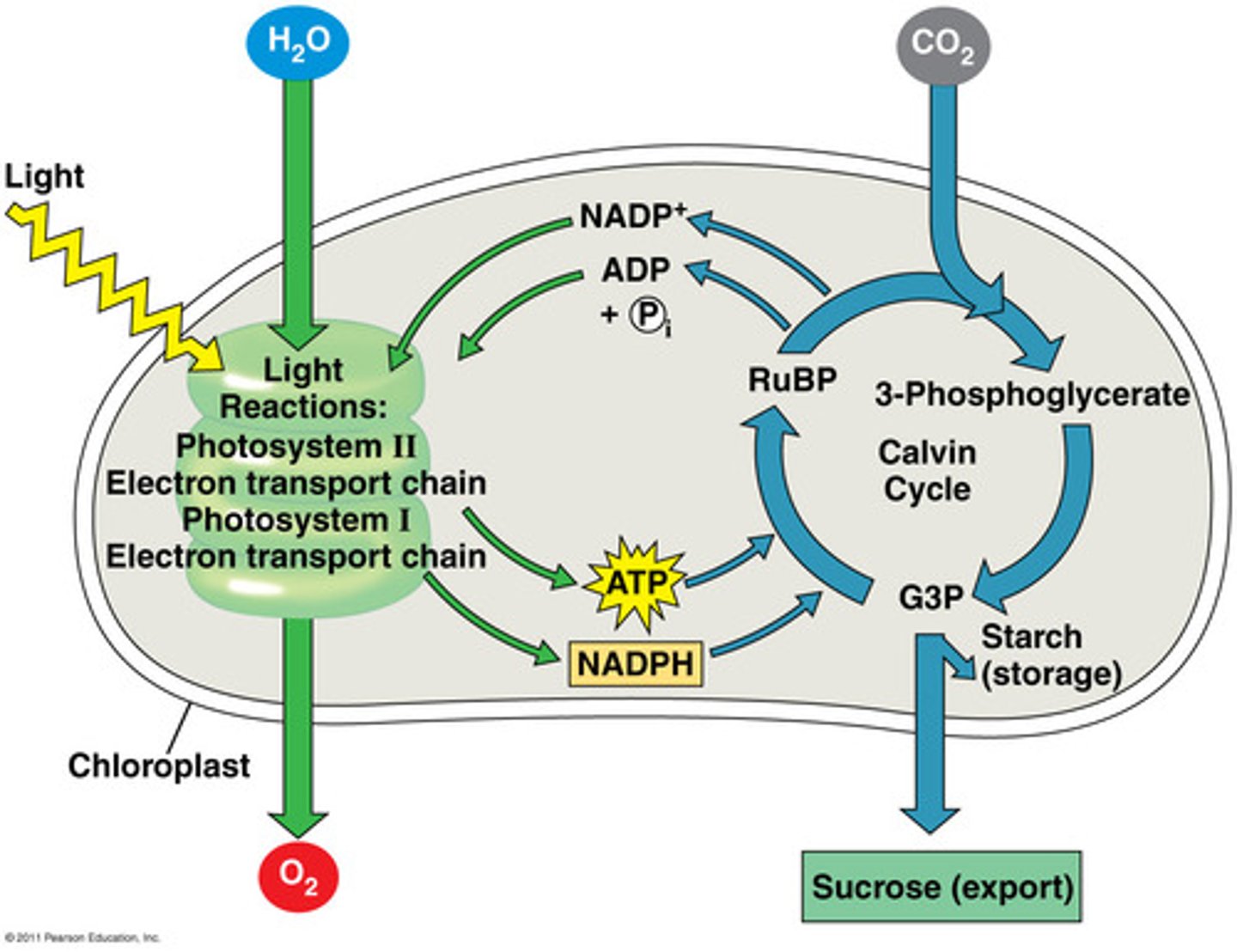
Where do the Light reaction and the Calvin Cycle take place in the chloroplast? Be familiar with the structure of a chloroplast.
Light reaction inside the thylakoid membrane, Calvin cycle in the stroma.
How/when is Oxygen created during photosynthesis?
When water splits
What is a redox reaction? How does this apply to photosynthesis and respiration? What molecules are electron donors/acceptors?
a chemical reaction where electrons are transferred between molecules. one molecule being oxidized (losing electrons) and the other molecule being reduced (gaining electrons). NADH and FADH are electron donors. NAD+ and FAD+ are electron acceptors.
What are the three main events in cellular respiration?
Glycolysis - Krebs cycle (citric acid cycle) - Oxidative phosphorolation
What role does Glycolysis play in Cellular Respiration?
it is the beginning step for all forms of anaerobic/aerobic respiration routes and provides the essential Pyruvic acid.
What are the 2 main events within oxidative phosphorylation
Chemiosmosis and the Electron transport chain
How many net ATP's are produced in glycolysis? Citric Acid Cycle? Oxidative Phosphorylation?
2 net ATP made during glycolysis, 2 ATP made in Citric acid cycle, and 32 ATP made in oxidative phosphorylation
Where does glycolysis take place in the cell? Is this process aerobic or anaerobic?
cytoplasm and is anaerobic
Where does aerobic respiration take place in the cell?
Mitochondrion
What are two types of fermentation? What are the products of each?
2 types are alchoholic fermentation with results in the production of ethanol, and the other form is lactic acid fermentation which results in the product of lactic acid.
What is the purpose of pyruvic acid? In what step is pyruvic acid made?
Pyruvic acid is made during glycolysis. Pyruvic Acid enters the citric acid cycle for aerobic respiration or is converted into lactate or ethanol for anaerobic respiration.
What are the reactants and products of each phase of cellular respiration?
Glycolysis- Reactants are glucose, 2 NAD+, and 2 ATP, products are 2 Pyruvate, net gain of 2 ATP, and NADH
Krebs cycle- Reactants-NAD+, ADP Products- 4 CO2, 2 ATP, FADH, NADH
Oxidative Phosphorylation- ???
What is the purpose of ATP Synthase and during what stages/processes is it used?
ATP synthase turns ADP into ATP by performing phosphorylation, and is used in oxidative phosphorylation in cellular respiration and the light reactions of photosynthesis.
Why is it important that oxygen is the final receptor in the Electron Transport Chain?
ensures the continuous flow of electrons, allowing ATP production and preventing a backup in the system.
What is the importance of NADH "dumping" electrons? (Mystery of the Seven Deaths Case Study)
NADH "dumping" electrons is crucial for ATP production in the etc, regenerating NAD⁺, and maintaining cellular redox reaction balance.
Which cellular processes produce ATP?
cellular respiration, including glycolysis, Krebs cycle and oxidative phosphorylation
What organisms require cellular respiration?
all organisms
What is the importance of the H+ concentration gradient in the ETC?
it powers the electron transport chain through electrons from the NADH and FADH
What is phosphorylation and what provides the energy to produce ATP?
Phosphorylation is the process of adding a phosphate group to ATP, the energy to produce ATP primarily comes from the breakdown of glucose during cellular respiration.