Week 3: Inductance, LC, RL, LRC
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
What is the equation for back EMF created by an inductor?
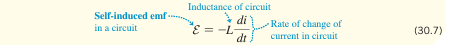
What is back EMF
The voltage induced in an inductor that opposes the change in current through the circuit.
What is Lenz’s Law?
States that the direction of an induced EMF and the resulting current always opposes the change in magnetic flux that produced it. This ensures conservation of energy.
What does the negative sign in the back EMF equation represent?
It represents Lenz's Law, indicating the induced EMF opposes changes in current.
How is energy stored in an inductor calculated?
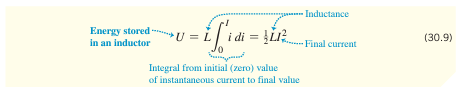
What is the equation for the time constant in an R-L circuit, and what does it indicate?
It represents the time it takes for current to grow to ~63% of its maximum value or decay to ~37% of its initial value.
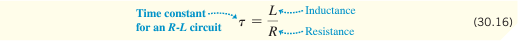
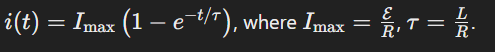
What is the equation for current growth in an R-L circuit?
What is the equation for current decay in an R-L circuit?
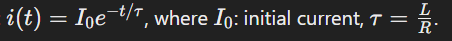
What is the natural frequency of an L-C circuit?
Where w is frequency, L is inductance, and C is capacitance
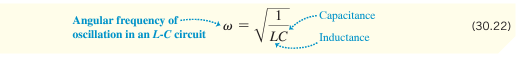
What is the equation for oscillatory current in an L-C circuit?
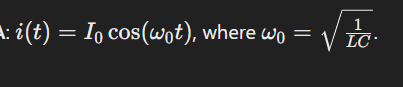
What is the equation for damped oscillations in an L-R-C circuit?
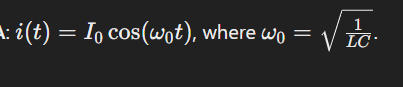
What happens in an L-R-C circuit when R= (2L/C)1/2
The circuit reaches critical damping, and oscillations stop.
How does energy decay in an L-R-C circuit?
U(t)=U0e-Rt/L, where U0 is initial energy