Metamorphic Rocks
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
Metamorphism can occur in the surrounding rock as an igneous pluton forms. Which type of metamorphism is most likely to occur in the surrounding rock?
Thermal or contact metamorphism
In a rock undergoing metamorphosis, which type of stress occurs when one part of a rock moves sideways relative to the rest of the rock?
Shear stress
Shale, a sedimentary rock, can be subjected to high heat and pressure through?
burial during continental collision
Which process brings metamorphic rocks to the surface over time?
Exhumation
Which nonfoliated metamorphic rock forms from the metamorphism of limestone?
Marble
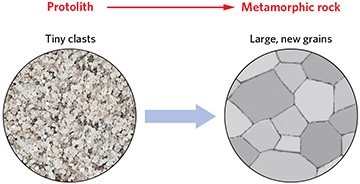
Identify the metamorphic process that is shown in the image.
Recrystallization
The temperature range for the formation of low-grade metamorphic rocks is __________ degrees C.
250 to 400
Which statement about the pathways of the rock cycle is TRUE?
Granite that is eroded, transported, deposited, and lithified will become a sedimentary rock.
When a rock is subjected to compressional pressure, the grains will?
Elongate perpendicular to the direction of stress.
Identify the metamorphic process that causes grains to warp and/or elongate but not melt or dissolve.
Plastic deformation
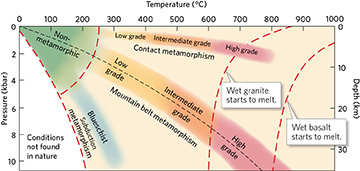
Using the graph, determine what type of metamorphism (related to its geologic setting) a rock would likely be experiencing if it was at a depth of 20 km and heated to a temperature of 500 degrees C.
Mountain belt metamorphism
What type of metamorphism would occur at a plate boundary where two continents are colliding?
Dynamothermal or regional metamorphism
Which agent of metamorphism involves hot water moving ions?
Interaction with hydrothermal fluids
Metamorphic rocks differ from igneous rocks in their formation because metamorphic rocks?
Do not form from molten rock.
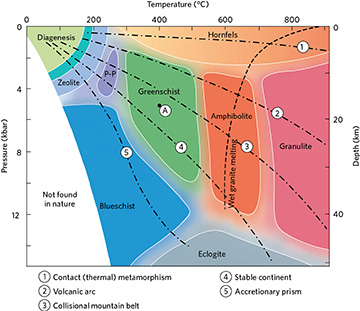
Different temperature and pressure ranges create specific sets of metamorphic minerals that are called metamorphic facies. Using the graph, determine what facies a rock would be found in if it was buried 30 km deep and heated to a temperature of approximately 200 degrees C.
Blueschist
Which of the following describes an igneous to metamorphic to sedimentary path through the rock cycle?
A granite becomes buried and heated to form gneiss, and is then uplifted and eroded to make sand.
During metamorphism, the process that changes the crystal structure of a mineral without changing its chemical composition is called?
Phase change
Metamorphic grade is determined mainly by?
Temperature
The fine-grained foliated metamorphic rock formed from the metamorphism of shale or mudstone is called?
Slate
A rock experienced melting then cooling, burial to deep depths during mountain building, and then uplift and weathering. Which pathway did this rock take through the rock cycle?
Igneous → metamorphic → sedimentary
Which type of foliation does gneiss have?
Compositional layering
Within a single mountain range,
It is possible to find a variety of metamorphic rocks produced in distinct facies, including high-, intermediate-, and low-grade rocks.
Geologists classify metamorphic rocks primarily according to?
Whether they are foliated or nonfoliated.
Which of the following commonly serves as a protolith in the formation of marble?
Limestone
A nonfoliated metamorphic rock that is composed entirely of calcite is called?
Marble
Slaty cleavage, schistosity, and compositional banding are all examples of?
Foliation
Which of the following processes is NOT involved in metamorphism?
Cementation and compaction of grains during diagenesis
Regional metamorphism?
Is another name for dynamothermal metamorphism.
Thermal (contact) metamorphism occurs?
In areas surrounding igneous intrusions.
Foliated rock is created by a preferential stress oriented __________ the foliation.
Perpendicular to
Which of the following processes CANNOT occur in the formation of metamorphic rock?
Complete melting of the rock, followed by solidification to form a new rock

The figure below shows the application of
Shear stress
In the formation of gneiss (from a granite protolith), distinctive compositional bands form because of?
Crystals dissolving, with atoms and ions migrating and reorganizing as new crystals.
Rocks subjected to __________ feel a squeezing motion
Compression
The application of __________ during metamorphism causes elongated crystals to align parallel with each other. When this happens, the rock develops __________.
differential stress; foliation
Which of the following is a common protolith involved in the formation of slate?
Shale
Foliated metamorphic rocks possess?
Mineral grains in preferred orientations or patterns of association such as banding.
Which of the following is a common foliated metamorphic rock?
Gneiss
A buried body of shale is subjected to differential stress, causing clay minerals to realign and produce slate. This is an example of?
Metamorphism
What is a primary difference between phyllite and schist?
Mica crystals within schist are larger than those within phyllite
Thermal (contact) metamorphism produces?
Nonfoliated rocks only
A type of foliation defined by the preferred orientation of large crystals of mica is termed?
Schistosity
Which list properly orders these foliated metamorphic rocks from lowest grade to highest grade?
slate, phyllite, schist, and gneiss
Clay minerals within a buried body of slate are recrystallized at high temperatures and pressures to form mica, producing a rock called phyllite. This is an example of?
Metamorphism.
Elongated or “smeared” mineral grains indicate that a rock was subjected to?
Shearing
Which of the following is a common protolith involved in the formation of quartzite?
Sandstone
Nonfoliated metamorphic rocks are mainly classified based on their?
Mineral composition
Two common metamorphic rocks that typically lack foliation are __________ and __________.
quartzite; marble

What was the direction of compression that formed the foliation in the image below?
top and bottom, pressing inward
Which of the following is a high-grade metamorphic rock?
Gneiss
Foliation may include the alignment of __________ in a metamorphic rock.
Minerals
The application of __________ during metamorphism causes elongated crystals to align parallel with each other. When this happens, the rock develops __________.
differential stress; foliation
Within a single mountain range,
it is possible to find a variety of metamorphic rocks produced in distinct facies, including high-, intermediate-, and low-grade rocks.
A buried body of shale is subjected to differential stress, causing clay minerals to realign and produce slate. This is an example of?
Metamorphism
Foliated rock is created by a preferential stress oriented __________ the foliation.
perpendicular to
Regional metamorphism?
Is another name for dynamothermal metamorphism.
Which of the following is a common protolith involved in the formation of quartzite?
Sandstone
Elongated or “smeared” mineral grains indicate that a rock was subjected to?
Shearing
What are the textures of metamorphic rocks?
Clastic or detrital
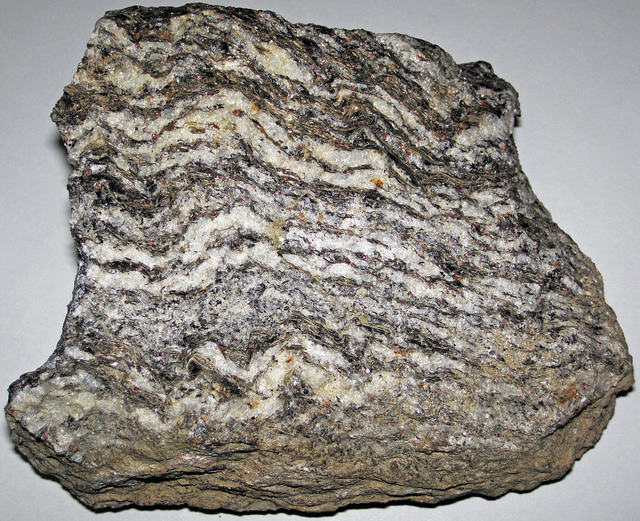

What is the texture of this metamorphic rock?
Nonfoliated
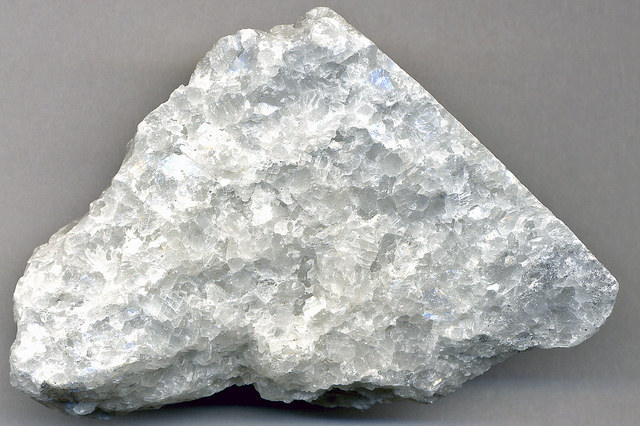

What is the texture of this metamorphic rock?
Foliated
Which of the following is true of metamorphic rocks?
They form as a result of intense heat and pressure.
Metamorphic rocks are created with the aid of ________.
Increased temperature, increased pressure, chemically active fluids, and the parent rock
Which type of metamorphism is responsible for the greatest amount of deformation?
Regional
Metamorphism includes a solid-state change in a rock caused by heat, pressure, and/or hydrothermal fluids. Explain what is meant by solid-state change.
A solid-state change takes place when all changes in size, shape, or composition of minerals are done while the rock remains solid. The rock does not form from a melt, nor has it been melted or weathered into a solution.
Describe the resulting metamorphism that occurs next to an igneous intrusion.
The metamorphism created by the intrusion is called thermal metamorphism or contact metamorphism and takes place in the absence of pressure. A metamorphic aureole forms next to an intrusion. Each layer of the aureole has progressively lower-grade metamorphism the farther away from the intrusion it is.

Draw the orientation of the preferential stress that created the foliation in the image below.

What is the difference between schist and phyllite?
Schist and phyllite are both foliated metamorphic rocks containing platy mica grains such as muscovite and biotite. Phyllite is a lower grade metamorphic rock and thus the mica grains are finer (smaller). Schist is a higher grade of metamorphic rock and thus the mica grains are coarser (larger).
What is an index mineral? What do metamorphic isograds indicate? What is a metamorphic zone?
An index mineral is a mineral that forms under a specific range of metamorphic conditions and is thus reminiscent of those conditions. Isograds are lines drawn on a geologic map to indicate the location at which index minerals first appear. A metamorphic zone is the region between two isograds and represents an area of metamorphic rock of a given grade.