17.8 thyroid gland
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
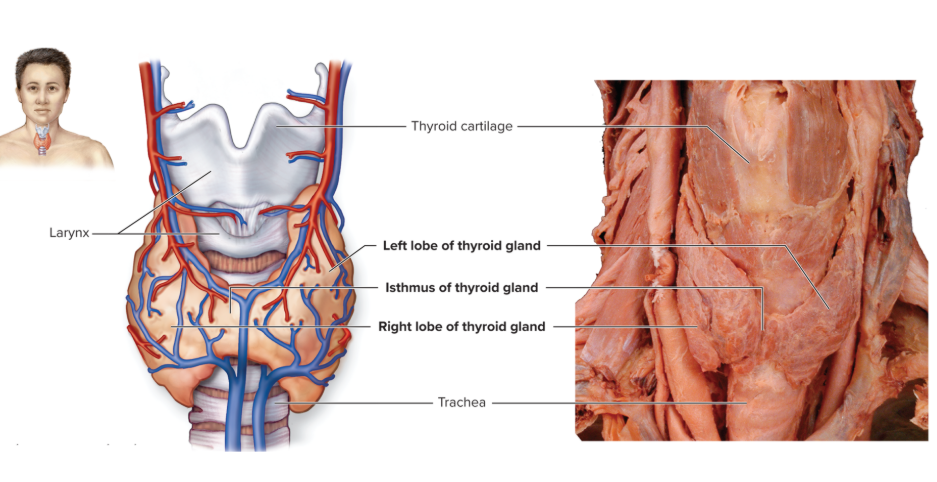
anatomy of thyroid gland
Inferior to thyroid cartilage of larynx, anterior to trachea
Left and right lobes
Connected at midline by isthmus
Rich vascularization gives it reddish color
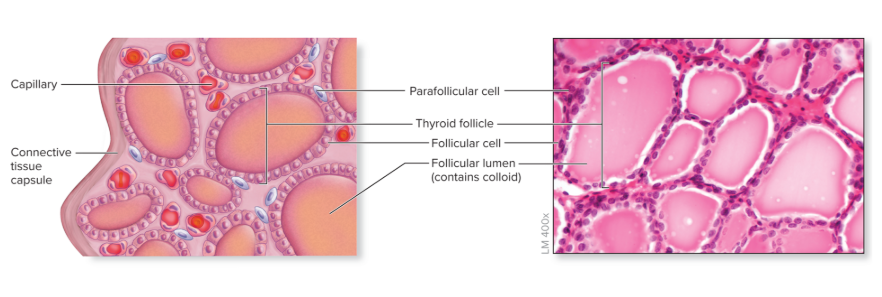
Composed of microscopic follicles
thyroid follicles
numerous, microscopic, spherical structures that make up the thyroid
Follicular cells—cuboidal epithelial cells that surround a central lumen, synthesize thyroglobulin (TGB)
Produce and release thyroid hormone (TH)
Follicle lumen houses colloid—a viscous, protein-rich fluid
Parafollicular cells— cells between follicles, make calcitonin
Hormone that decreases blood calcium levels
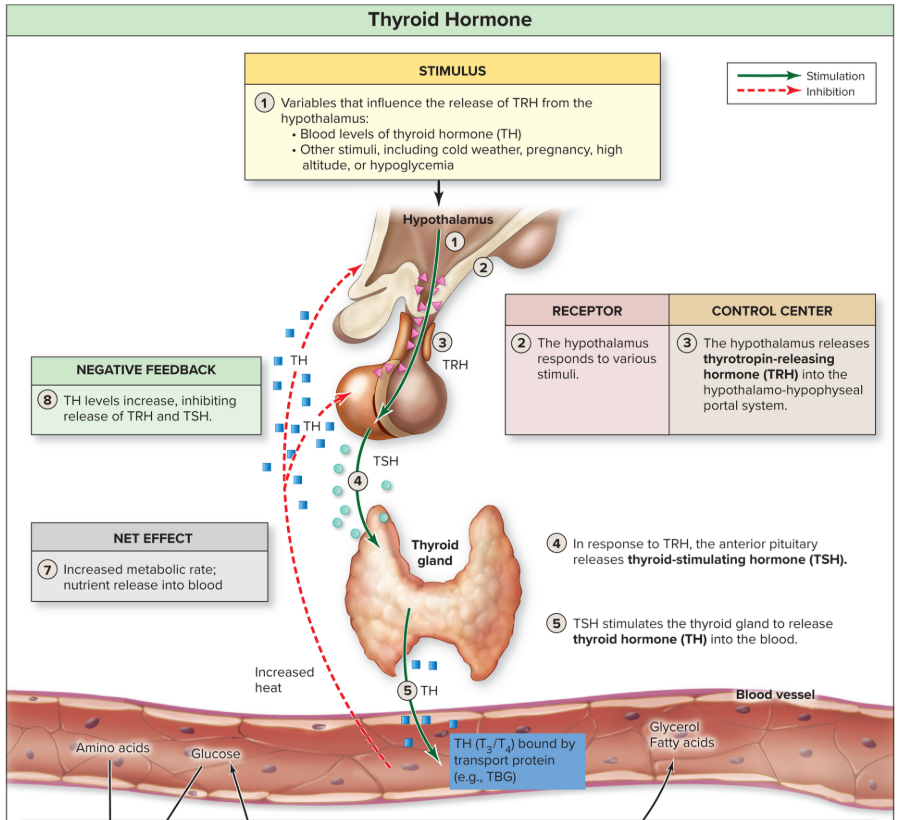
steps in regulation of thyroid hormone release
stimuli monitored by the hypothalamus
stimuli detected by hypo. the receptor
hypo. releases thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH)
anterior pit. responding to TRH releases TSH
TSH stimulates the thyroid gland to release TH in forms T3 and T4, lipid soluble and needs transport proteins
TH stimulates effectors
increased metabolic rate and release of nutrients into the blood to supply energy needed for higher metabolism
regulated by negative feedback
stimuli regulating release of TRH
TH levels low, needs to maintain a set point
set point determined by:
a. genetics
b. aging
c. environmental factors
effects of thyroid hormone TH
increases metabolism and initiates release of nutrients
lipid soluble, needs transport proteins
two forms: T3 and T4
T3: active form
T4: typically converted to T3 inside of cell, greater amount made at first
TH effect on all cells
TH increases metabolic rate of all cells
increases their synthesis of sodium potassium pumps Na+/K+
converts ATP to hear
this rise in temp is called calorigenic
heats body
makes pumps
gets pumps working
TH effect on liver
release of glucose into blood, increases:
glycogenolysis (breakdown of glycogen into glucose)
gluconeogenesis (synthesis of glucose from noncarb. resources)
glycogenesis is inhibited (synthesis of glycogen from glucose)
TH effect on adipose CT
increases glycerol and fatty acids into blood as an alternative to nutrients for cellular respiration
adipocytes respond to TH and increase lipolysis (breakdown of triglycerides into glycerol and fatty acids)
inhibits lipogenesis (formation of triglycerides)
saves glucose for brain (glucose sparing effect)
TH effect on respiratory and cardiovascular systems
respiration rate increases to meet additional oxygen demands
blood flow increases to deliver more nutrients and oxygen
indirect on heart
up regulation of B-adrenergic receptors
increase heart rate and contraction
calcitonin regulation and effects
from parafollicular cells, reduces blood calcium from blood into bone
activates when high calcium in blood
kidneys to increase loss of Ca urine