OPT 311 Midterm 1 part 1 (history + pupil exam)
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
98 Terms
What are some things that can cause acute painful vision loss?
GCA (older pt)
optic neuritis (younger pt)
classic migraine prodrome (younger pt, w/ flashing lights, nausea, emesis, head pain)
What are some things that can cause acute painless vision loss?
CRA occlusion
RD
What are some things that can cause transient vision loss?
amaurosis fugax of CV disease = unilateral
vertebral basilar insufficiency = bilateral
visual obscurations = momentary brown outs or blur outs of vision due to disc edema
classic migraine prodrome (younger pt, w/ flashing lights, nausea, emesis, head pain)
What are some things that can cause double vision?
paralytic strabismus = issues with CN 3, 4, 6
VF defects
polyoplia aka monocular diplopia from polycoria, bifocal CL, uncorrected astig
nystagmus
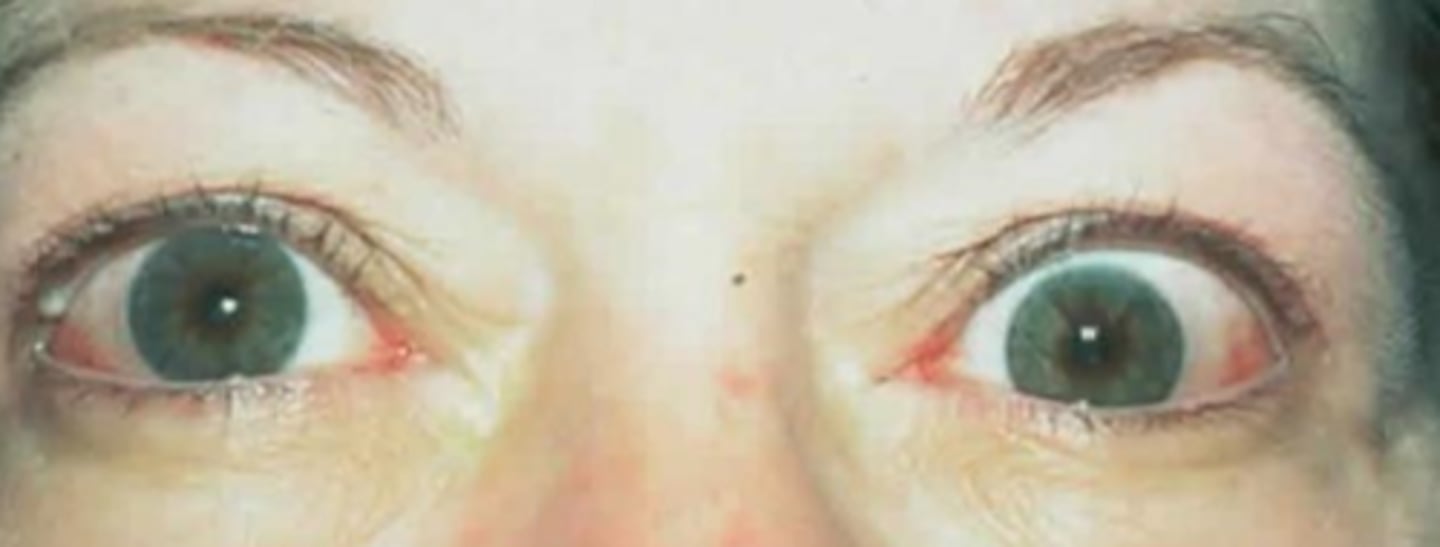
What are some things that can cause flashing lights?
BRAO or CRAO
resolving optic neuritis
classic migraine prodrome (younger pt, w/ flashing lights, nausea, emesis, head pain)
something pulling on retina like PVD, VMT

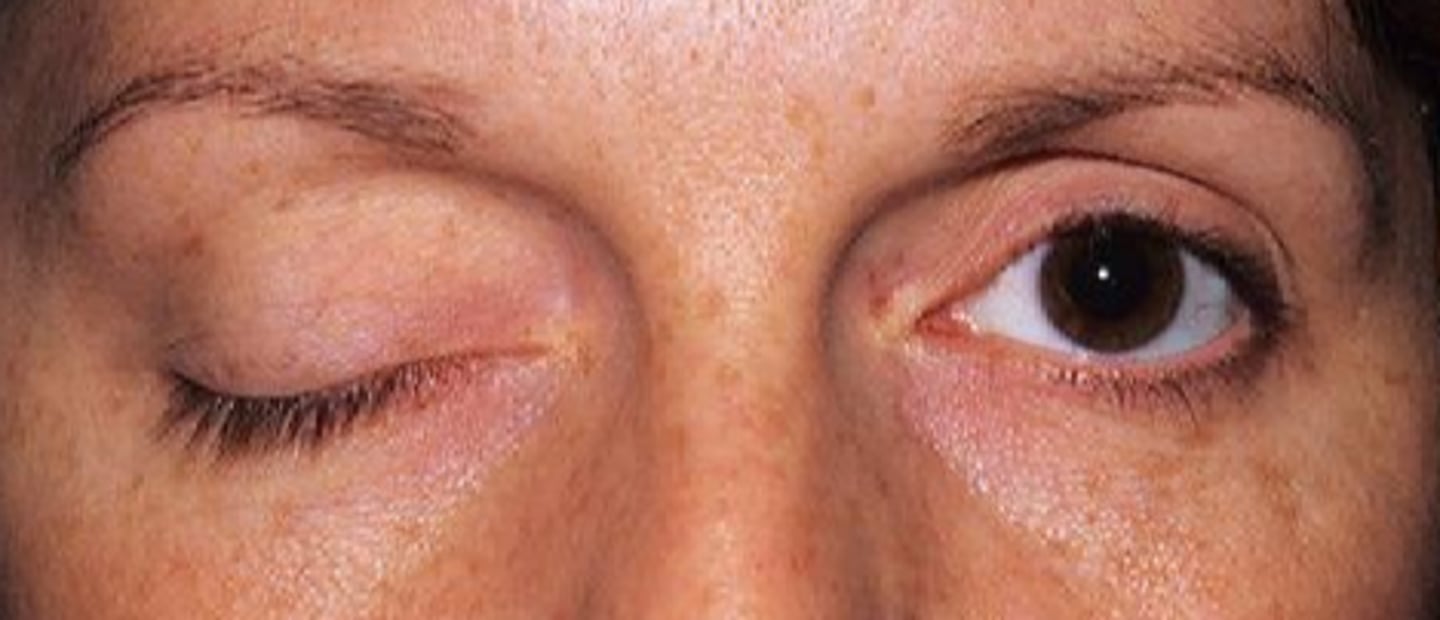
What are some things that can cause eyelids to not open?
CN 3 palsy = lids completely shut
Horner's syndrome = subtle ptosis
MG = lid droop that fatigues with sustained upgaze, later in day
hemifacial spasm
hyperkinetic lid syndrome
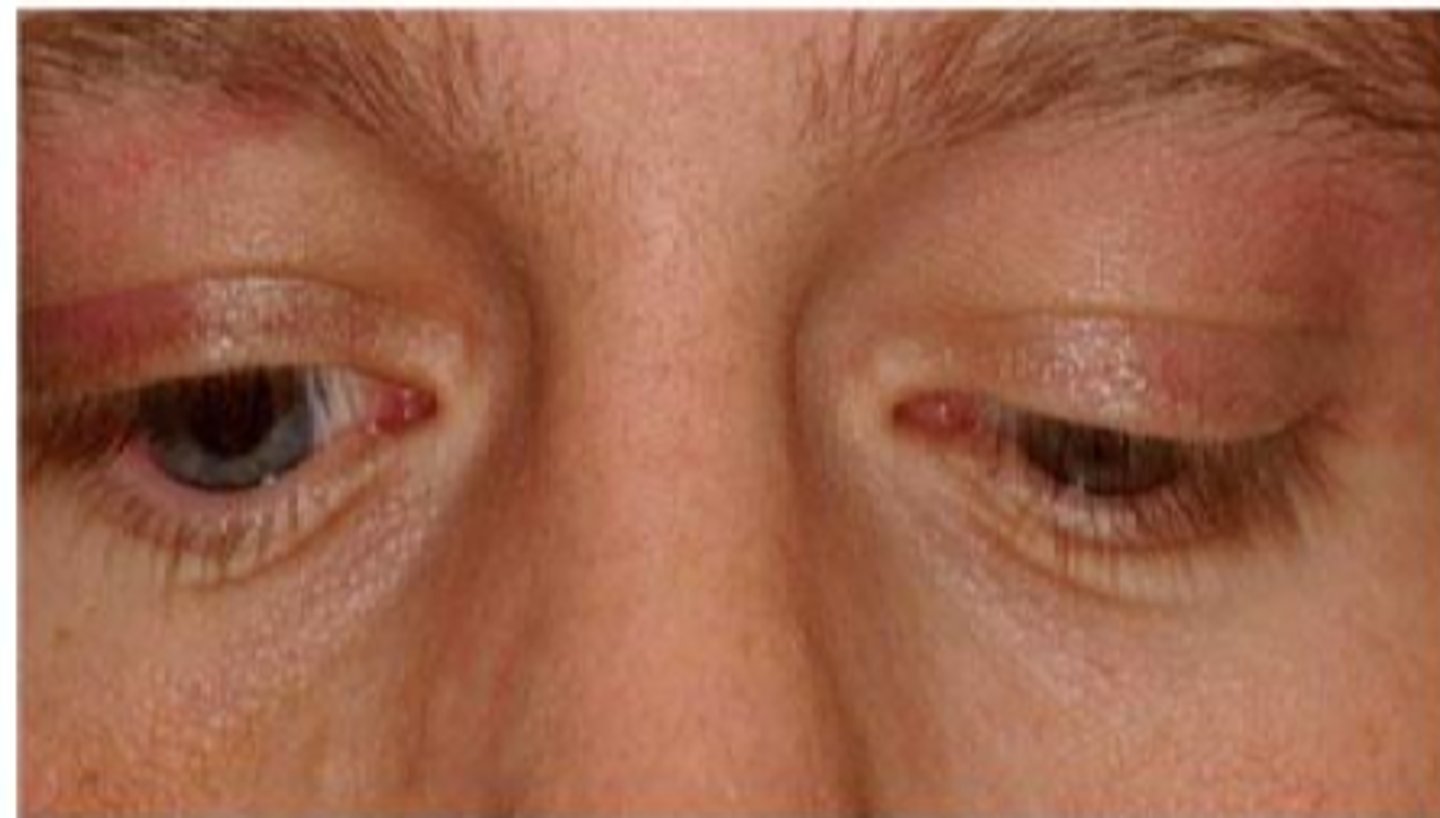
What are some things that can cause eyelids to not close?
facial palsy like Bell's CN 7 palsy
myotonic dystrophy = once pt opens eyes, lids remain up there
TED = UL infiltration and retraction
aberrant regeneration of CN 3
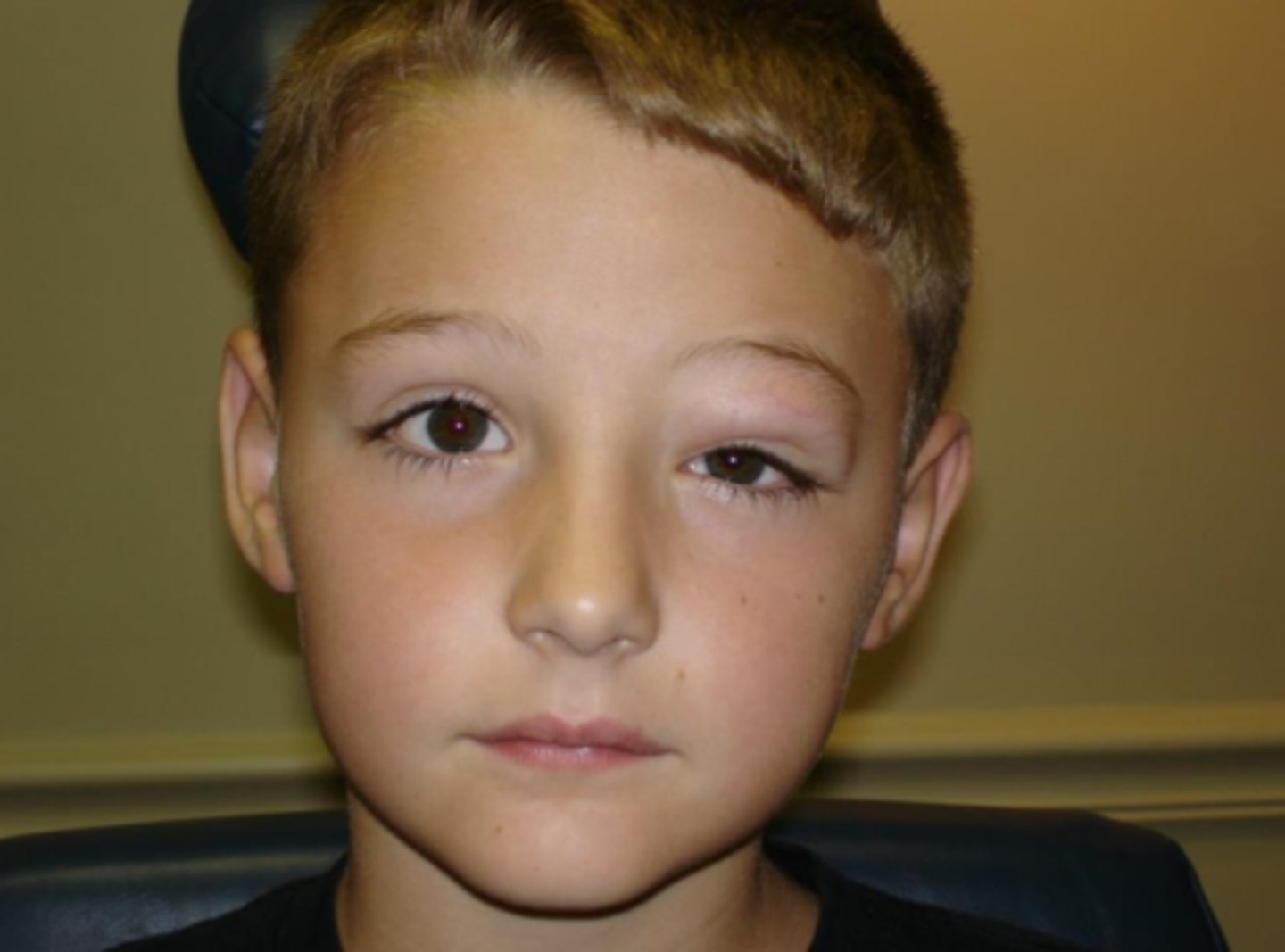
What are some things that can cause misaligned eyes?
paralytic strabismus
TED = infiltration restrains eye movement
orbital tumors push on eye
orbital inflam
What are some things that can cause bulged eyes?
TED = most common cause of exophthalmos
orbital tumors
orbital inflam
carotid-cavernous fistula = ICA rupstures in cavernous sinus, blood enters orbit

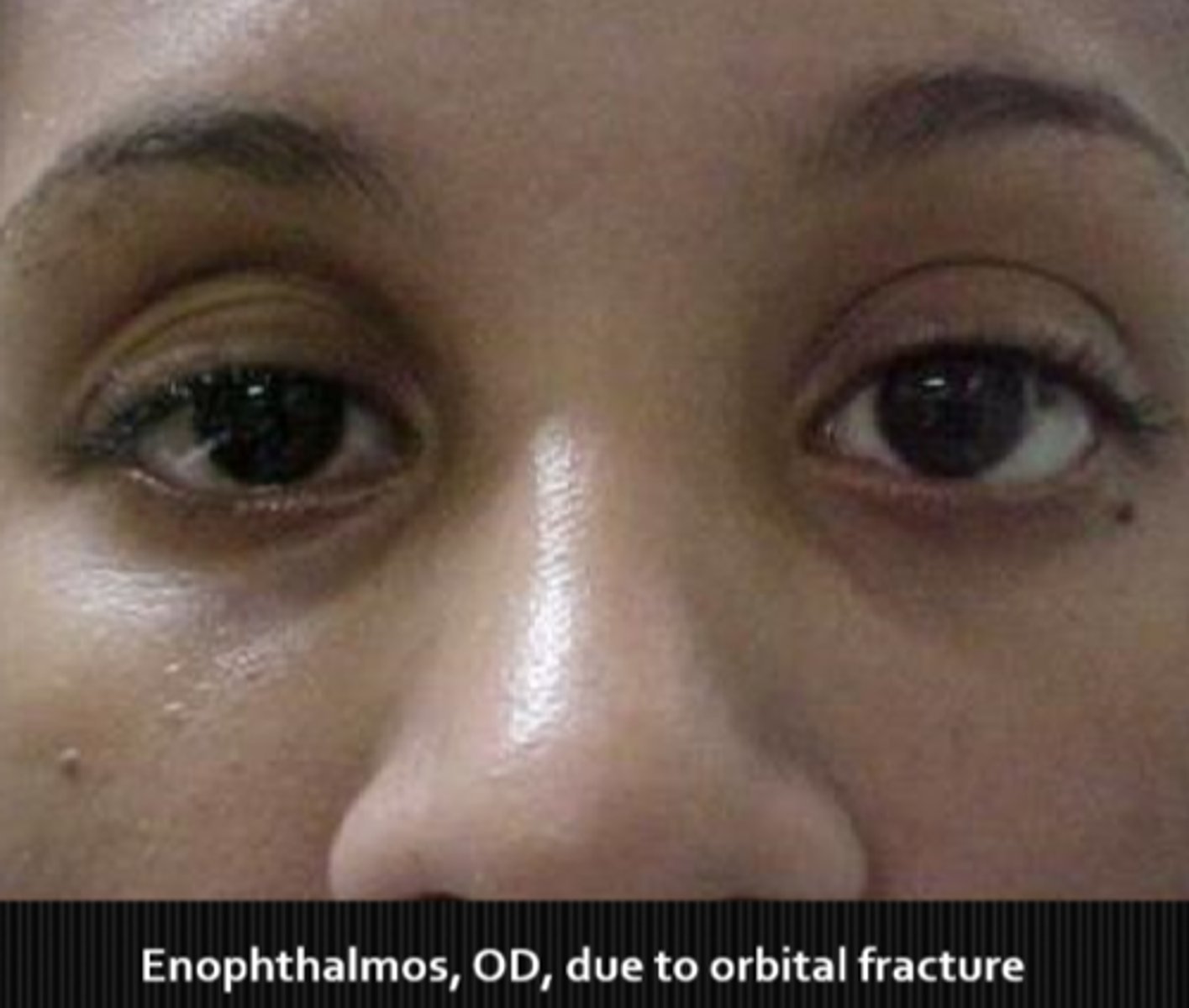
What are some things that can cause sunken eyes?
orbital fractures
scirrhous carcinoma = dehiscence of orbital tissue
Duane's retraction syndrome = retracts globe as eye adducts
What are some things that can cause anisocoria?
pharmacological
Horner's pupil
tonic pupil
CN 3 palsy
What are some things that can cause pupils to not respond to light?
pharmacological
tonic pupil
CN 3 palsy

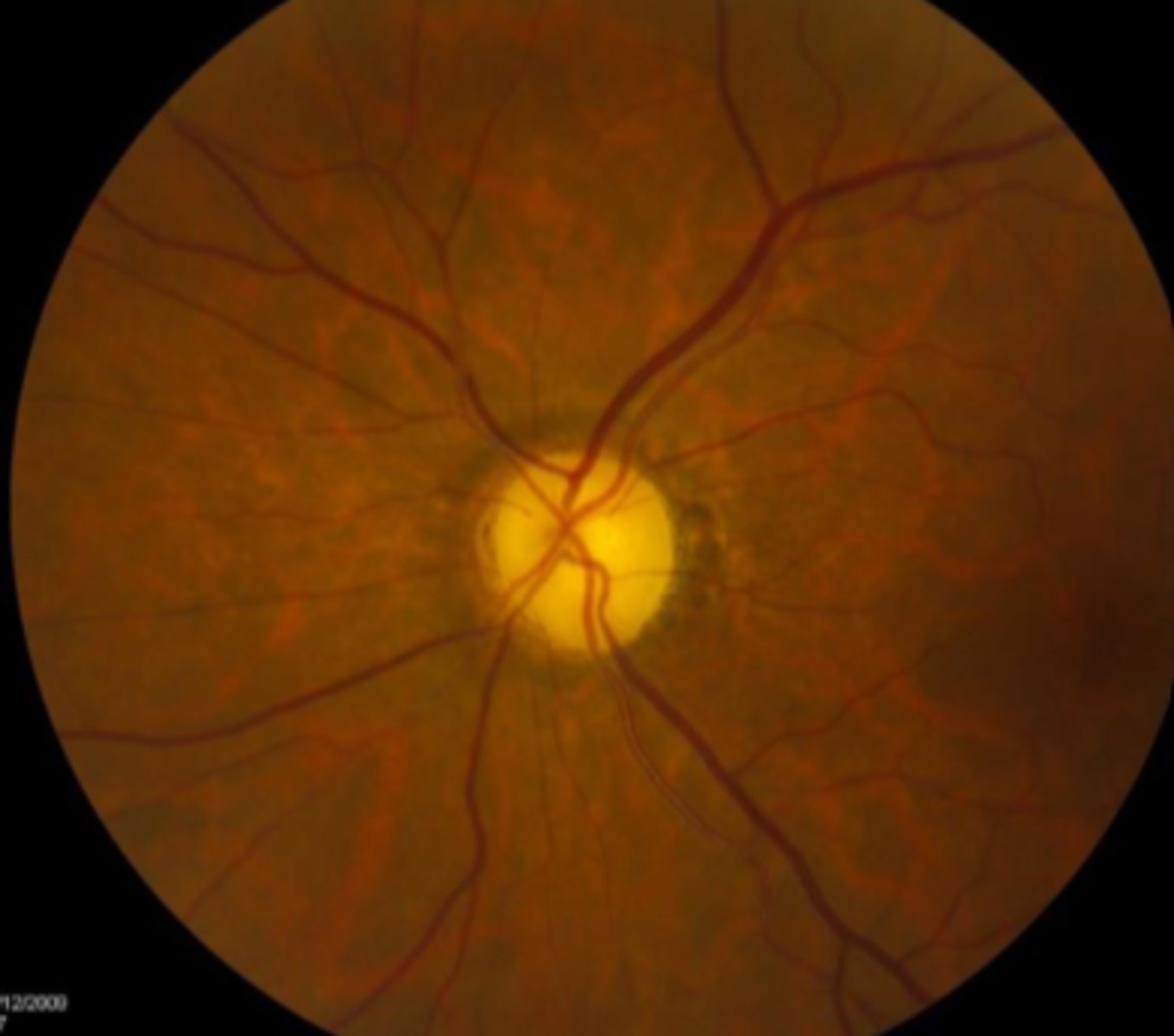
What are some things that can cause pale ONH?
optic atrophy
myopic discs
neonates discs
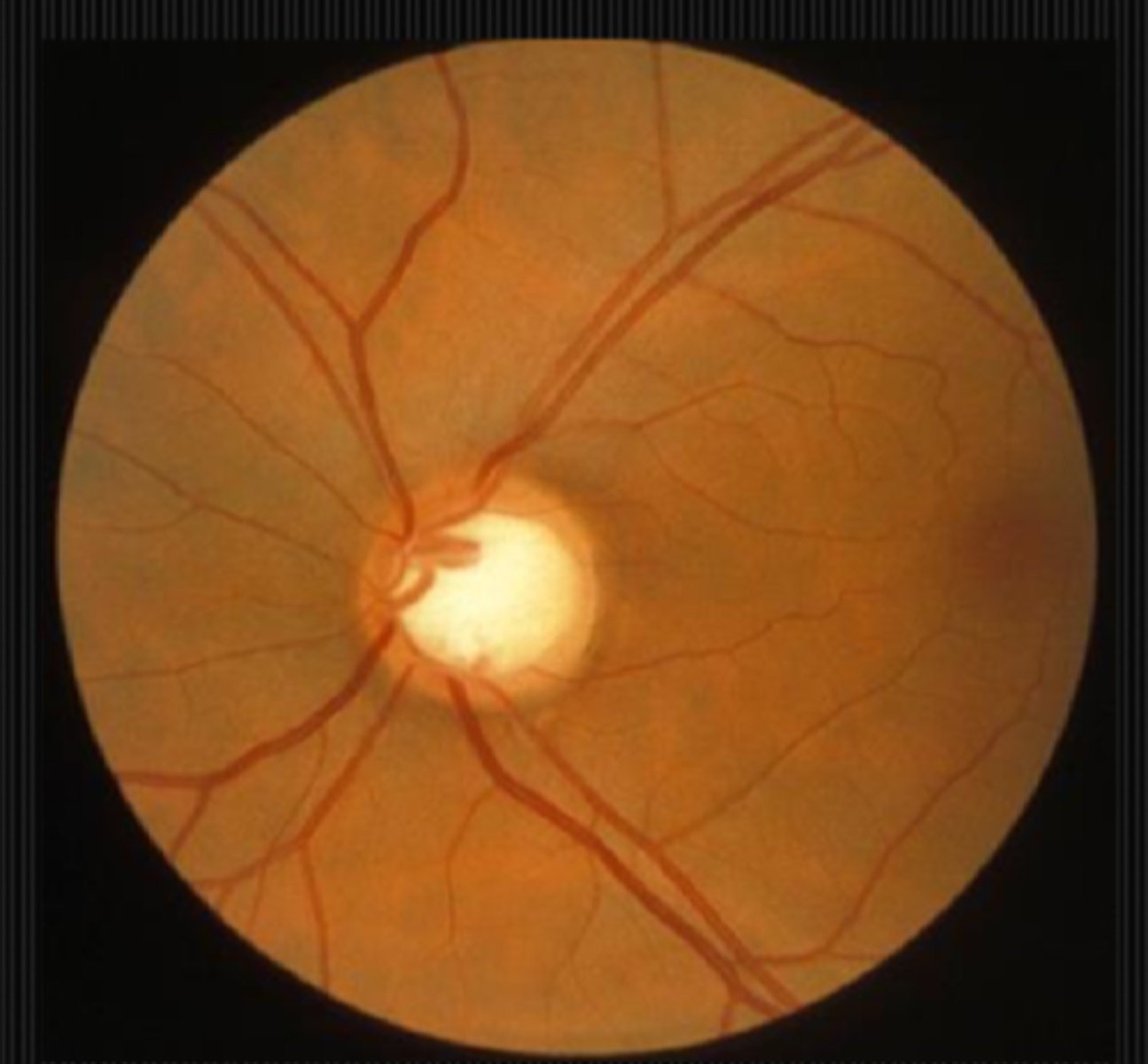
What are some things that can cause cupped discs?
other than the obvious, glaucoma...
trauma
ischemia
compression
inflam
What are some things that can cause swollen discs?
disc edema
drusen
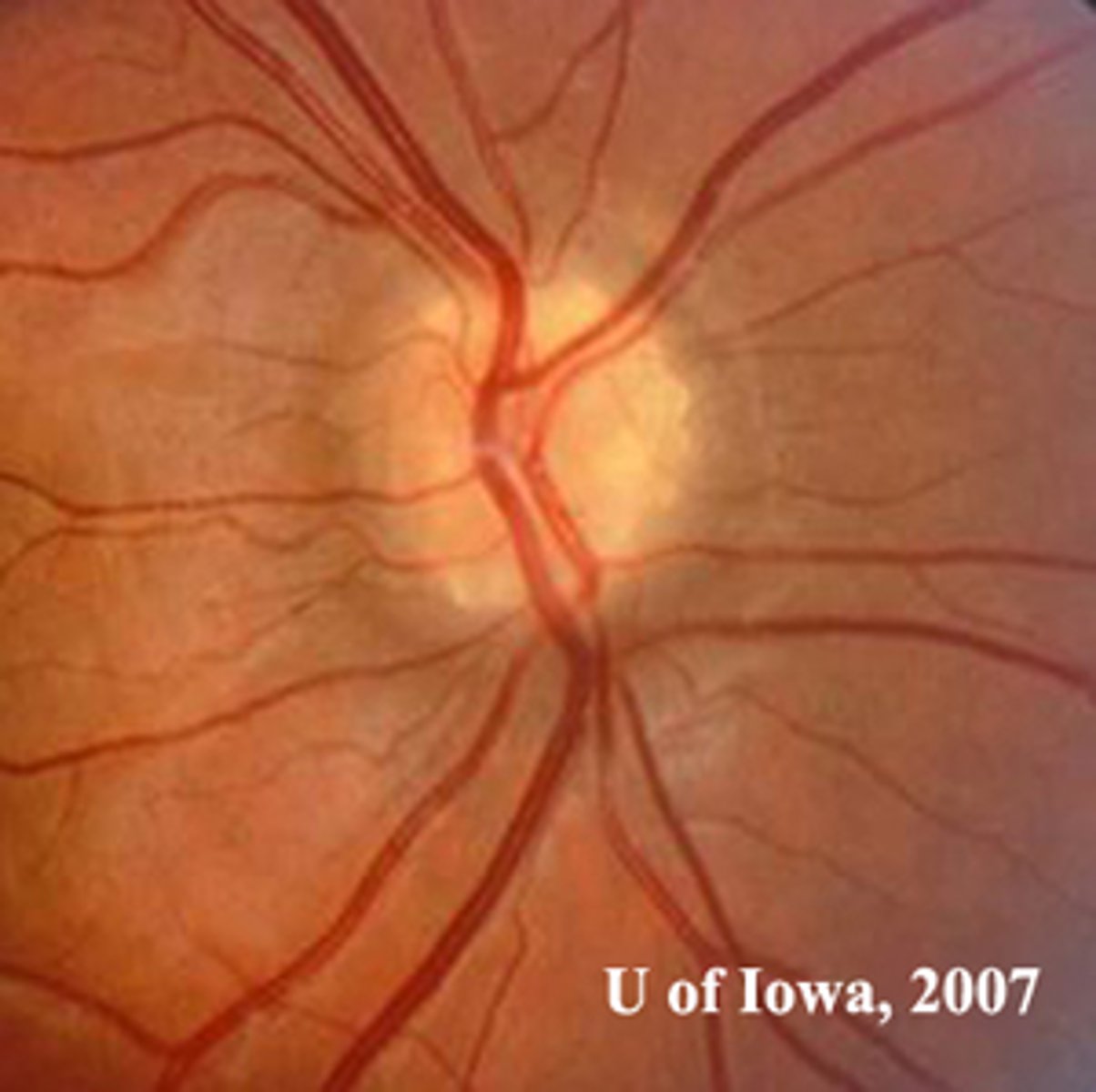
What are some things that can cause funny-looking discs?
congenital anomalies like tilted disc, coloboma, optic pits, morning glory nerve
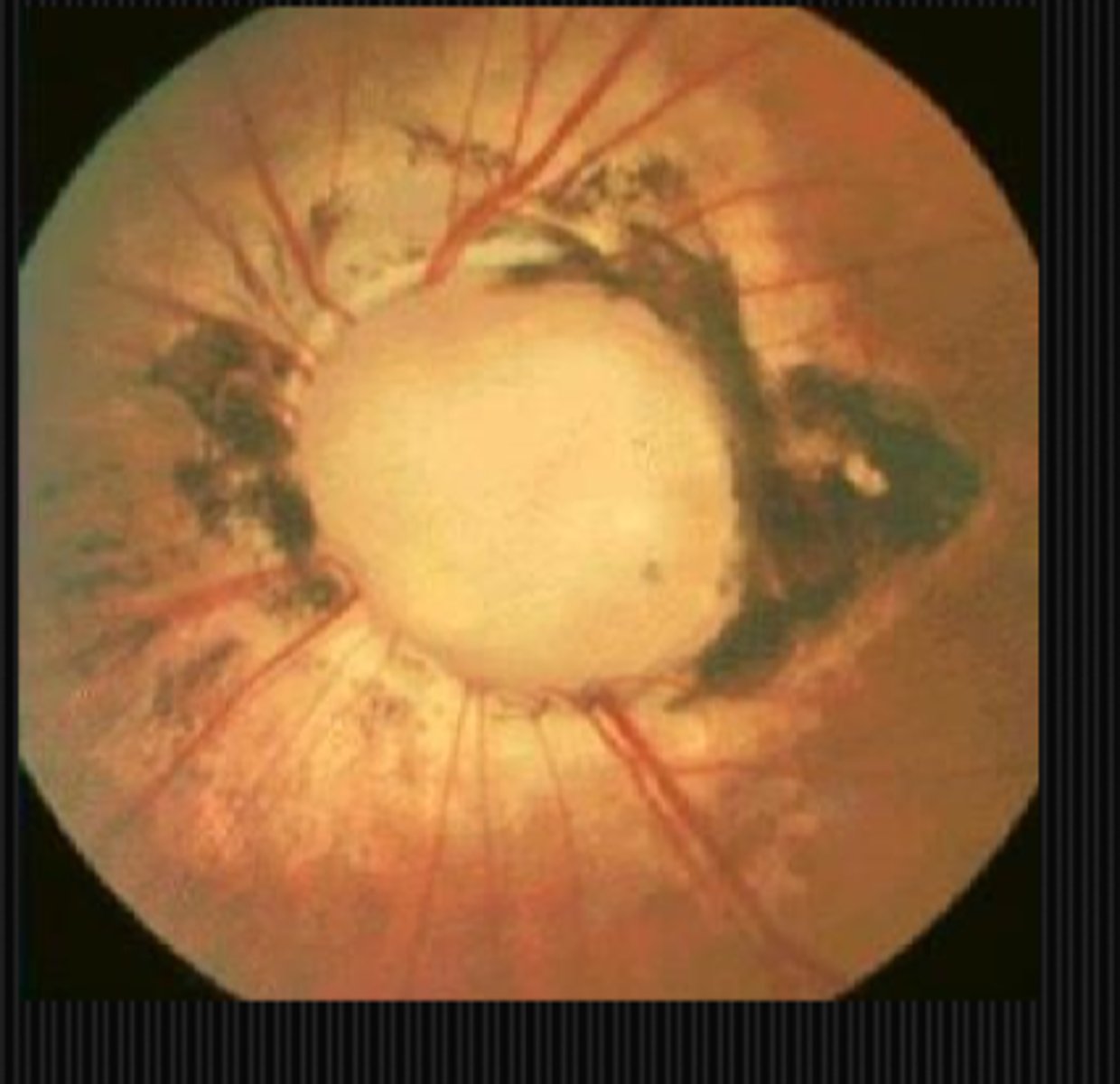
What are some things that can cause prechiasmal VF defects?
glaucoma
toxic/nutritional
demyelinating
ischemic/vascular
compressive
traumatic
What are some things that can cause chiasmal VF defects?
compressive
demyelinating (rare)
traumatic (rare)
What are some things that can cause postchiasmal VF defects?
ischemic/vascular
compressive
How does age play into neuro eye disease for things like a CN 6 palsy?
child = neoplasm in posterior fossa
adult = ischemic/vascular

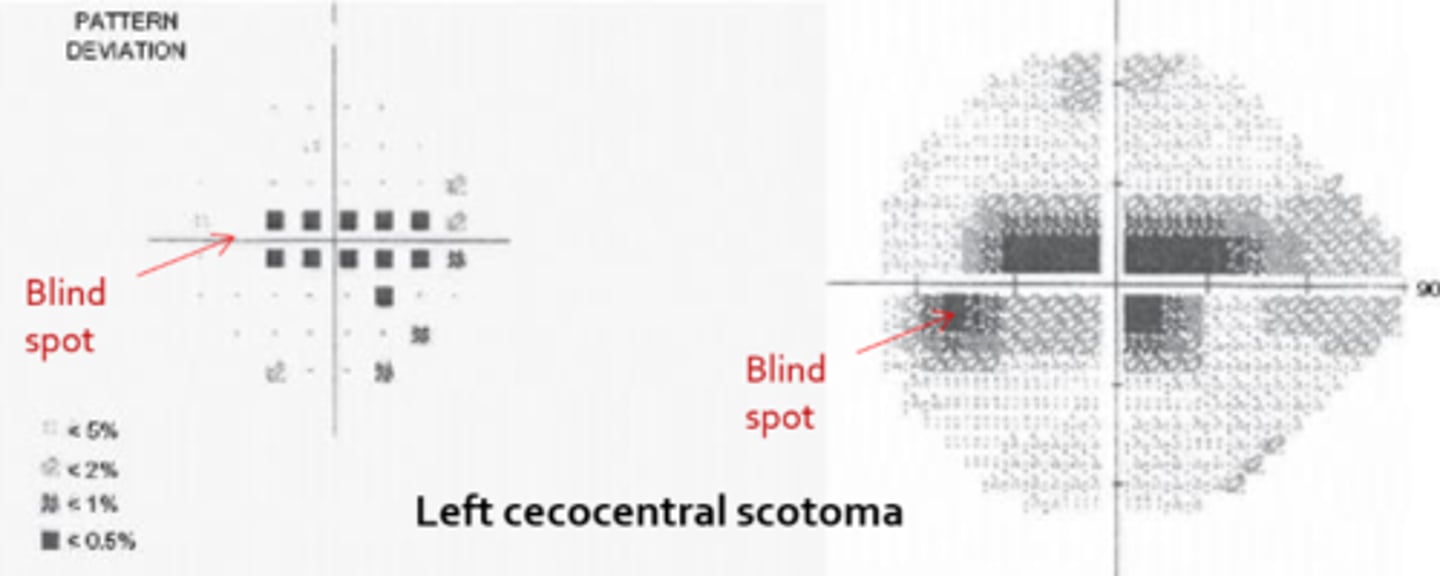
How does age play into neuro eye disease for things like a cecocentral scotoma?
child = congenital defect like optic pits, Leber's optic atrophy
adult = toxic/nutritional
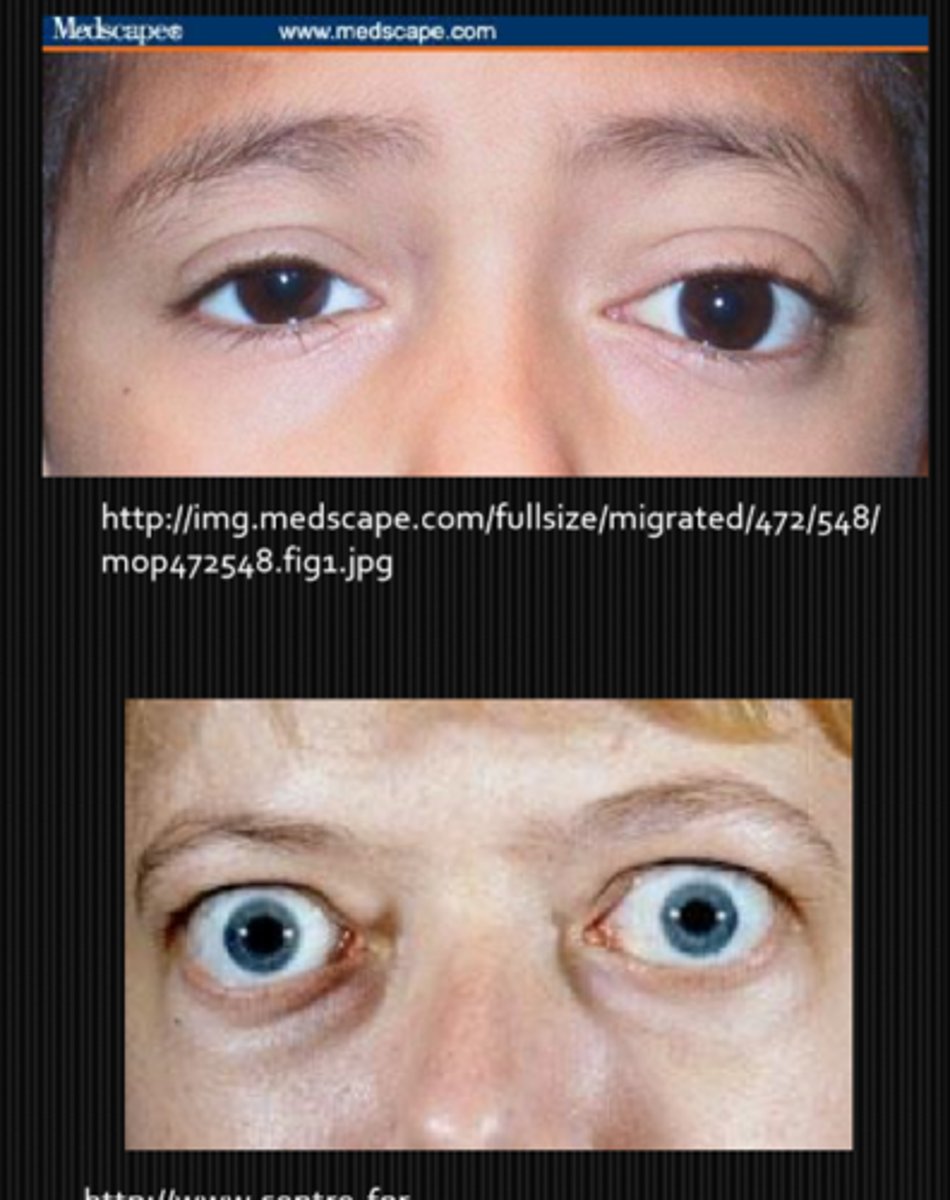
How does age play into neuro eye disease for things like a proptosis?
child = orbital cellulitis, tumors
adult = TED
How does age play into neuro eye disease for things like a swollen disc?
teenage female = collagen vasc disease like lupus
middle aged female = ischemic optic neuropathy
elderly female = ischemic optic neuropathy, GCA
What is the gender and/or race preference for IIH?
young obese women
What is the gender and/or race preference for GCA?
old Caucasian women
What is the gender and/or race preference for Raeder's paratrigeminal syndrome?
males >>>>>>> females by 7:1
What is the gender and/or race preference for MG?
old men
young women
What is the nationality/race preference for nasopharyngeal carcinoma?
Asian
What is the nationality/race preference for sickle cell disease?
black
What is the nationality/race preference for Sarcoidosis?
black
What is the nationality/race preference for Bechet's disease?
arabic
What is the nationality/race preference for Tay Sachs disease?
Jewish
What condition is linked to the medication enterovioform, used in Mexico for amoebic dysentery or gastroenteritis?
central scotoma OU
What condition is linked to the medication chloroquine, used for inflammatory conditions?
ring-shaped scotomas
What condition is linked to the medication bromide, sometimes used for epilepsy?
upbeat nystagmus
What condition is linked to the medication nalidixic acid, used for UTIs?
IIH
What condition is linked to the medication tetracycline/minocycline used for inflam or bacterial infections?
IIH
How can diet in social history impact neuro status?
Vitamin A intoxication can cause IIH
toxic-nutritional disease can cause optic atrophy
How can occupation in social history impact neuro status?
nitrous oxide used by surgeons and dentists can deplete B12 stores = central scotoma
How can religion in social history impact neuro status?
tx and meds that some religions may not believe in
What might we be looking at during the inspection of clothing part of a neuro exam?
how do clothes fit = weight loss may indicate GCA, weight gain may indicate IIH
ring fit = enlarged hands from acromegaly may indicate a pituitary tumor
dressed poorly for weather = thyroid disease causing heat/cold intolerance
hat/sunglasses = photophobia
bizarre colour combos = acquired colour deficiency
asymmetrical clothes/makeup = paresis on one side, visual neglect
What might we be looking at during the inspection of makeup part of a neuro exam?
heavy makeup may be covering white lashes (poliosis), loss of lashes/brows (alopecia), skin lesions (Sturge-Weber, nevus of ota, cafe-au-lait spots, sarcoid nodules)

What might we be looking at during the inspection of hair part of a neuro exam?
toupee/hair loss w/ bilateral optic neuritis = syphillis
receded hair line w/ hatchet-shaped face, myotonic eyelids = myotonic dystrophy
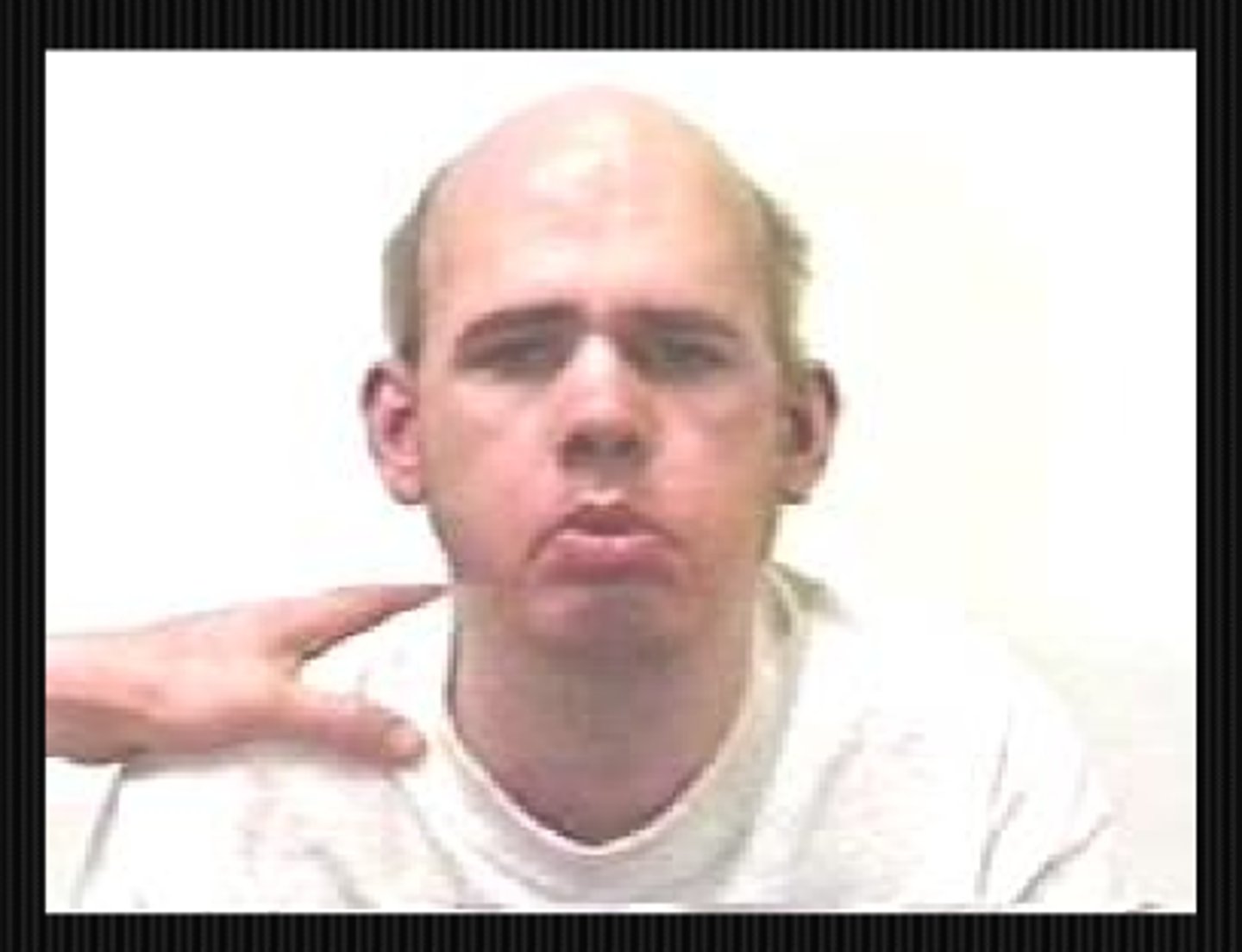
What might we be looking at during the inspection of mouth part of a neuro exam?
CN 7 palsy may cause unilateral drooping mouth
MG snarl when orbicularis oris fatigues and mouth corners cannot raise
hemifacial spasm = involuntary twitching or contraction of the facial muscles on one side of the face
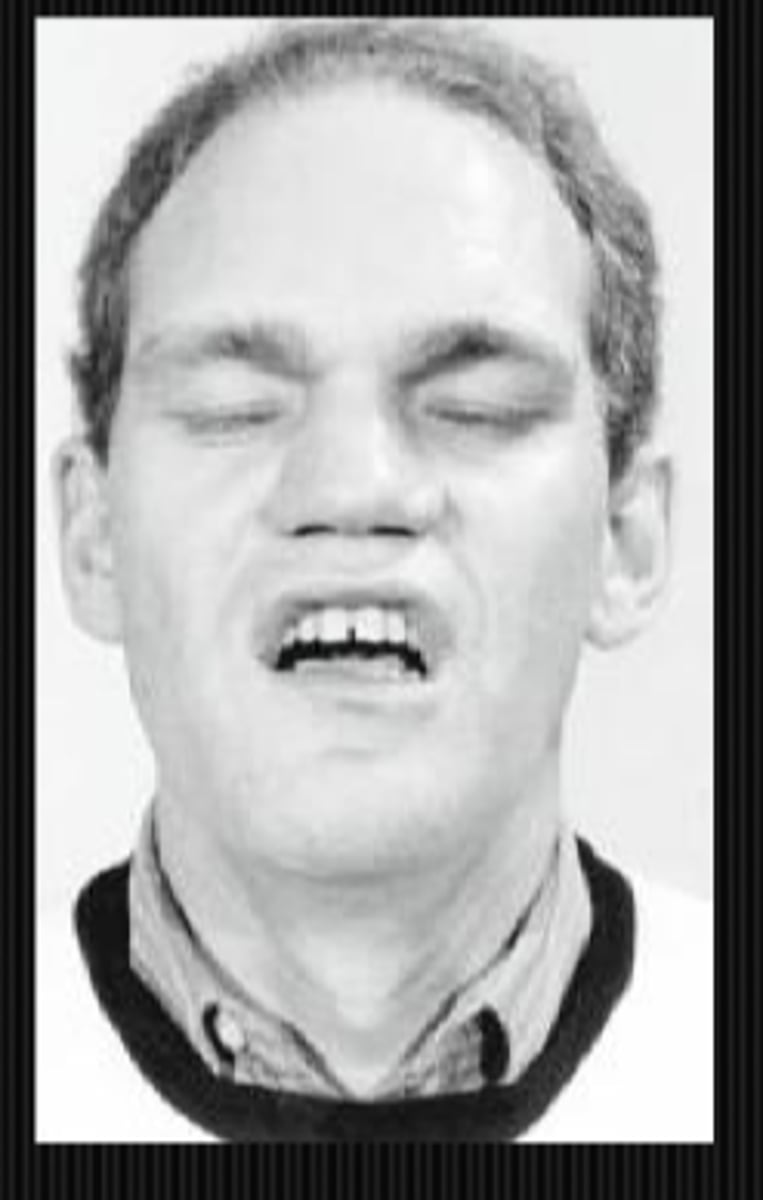
What might we be looking at during the inspection of chin part of a neuro exam?
chin elevation in a ptosis
chin depression in a CN 4 palsy
A or V syndromes
prognathism = marked protrusion of the jaw

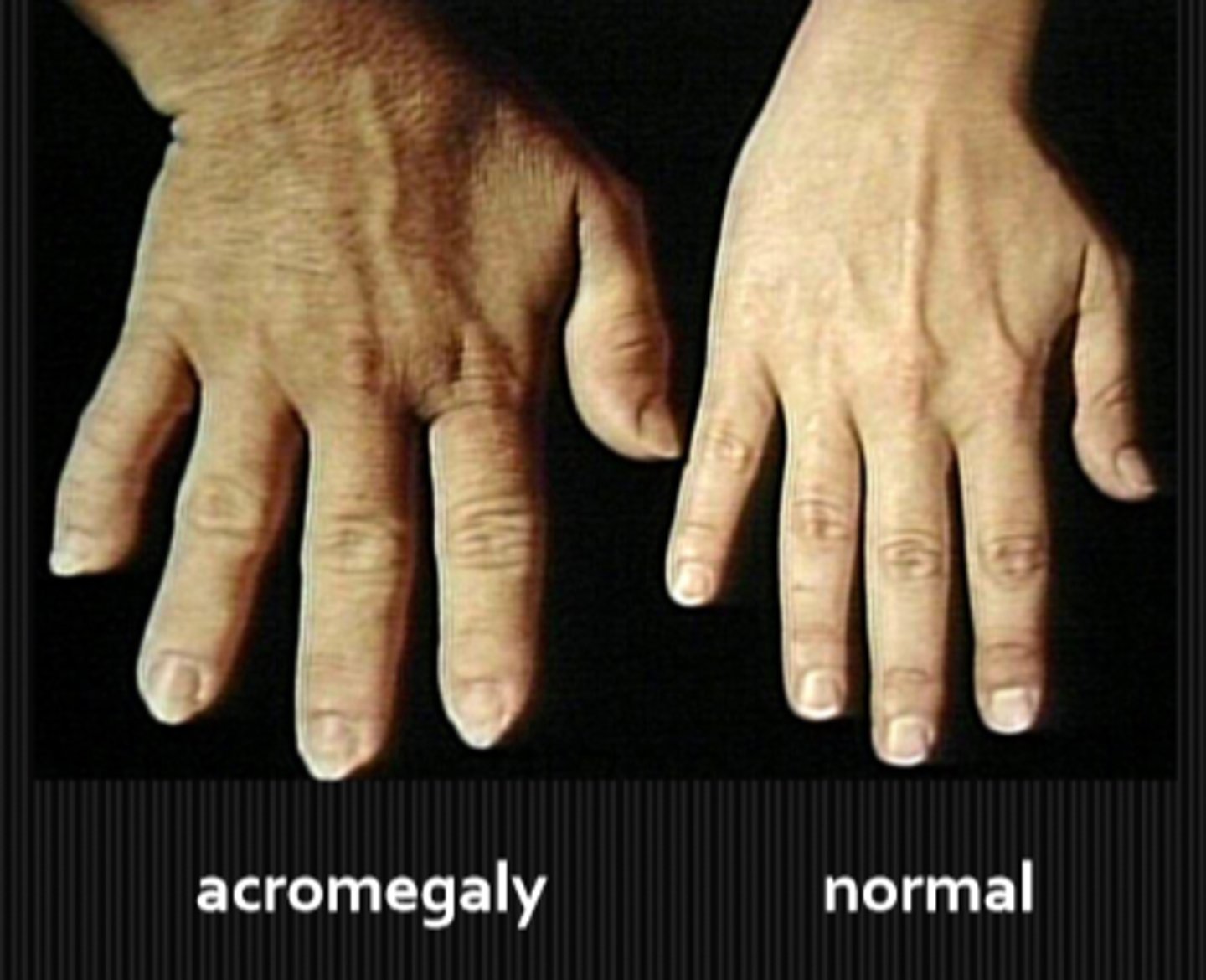
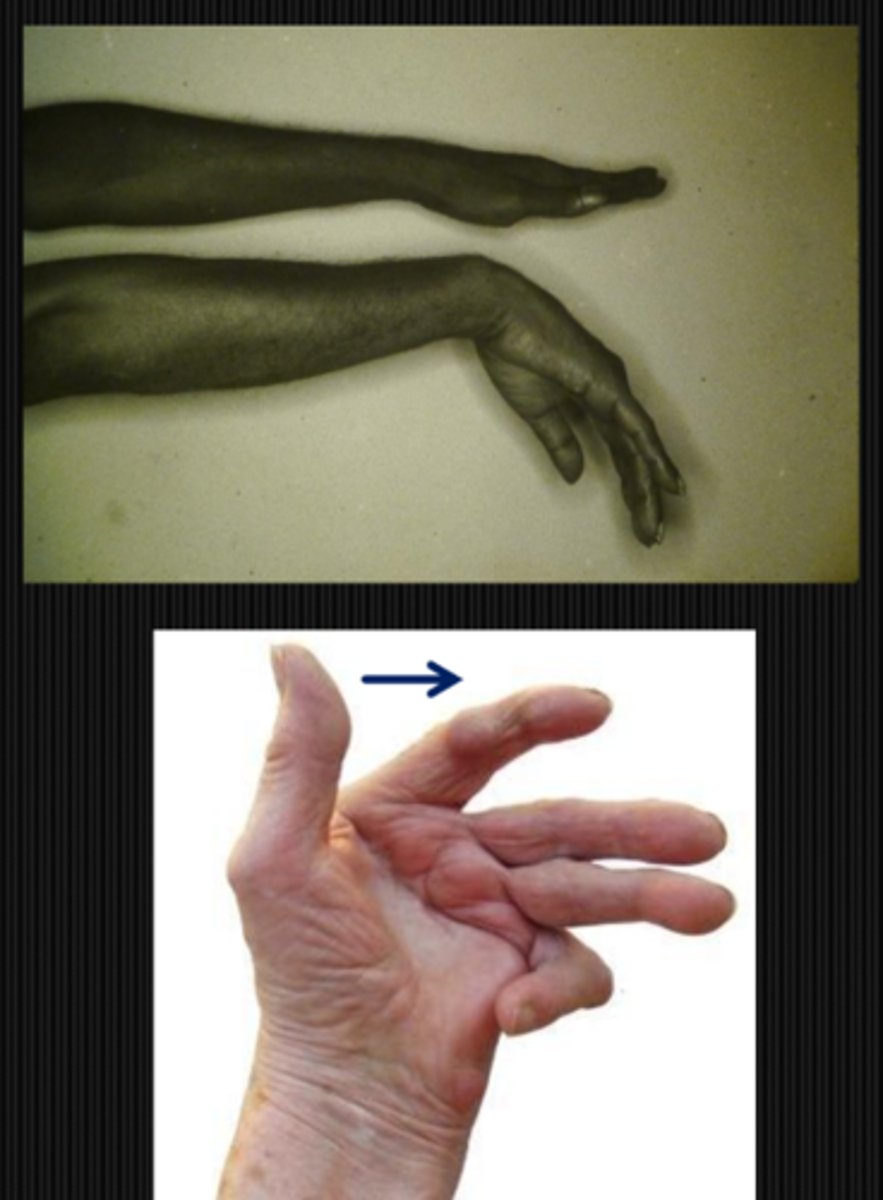
What might we be looking at during the inspection of hands part of a neuro exam?
wrist drop w/ optic neuropathy and decreased VA = pt may have a radial nerve palsy associated with lead, arsenic, alcohol poisoning
ulnar deviation = fingers deviated towards ulna in rheumatoid arthritis
acromegaly
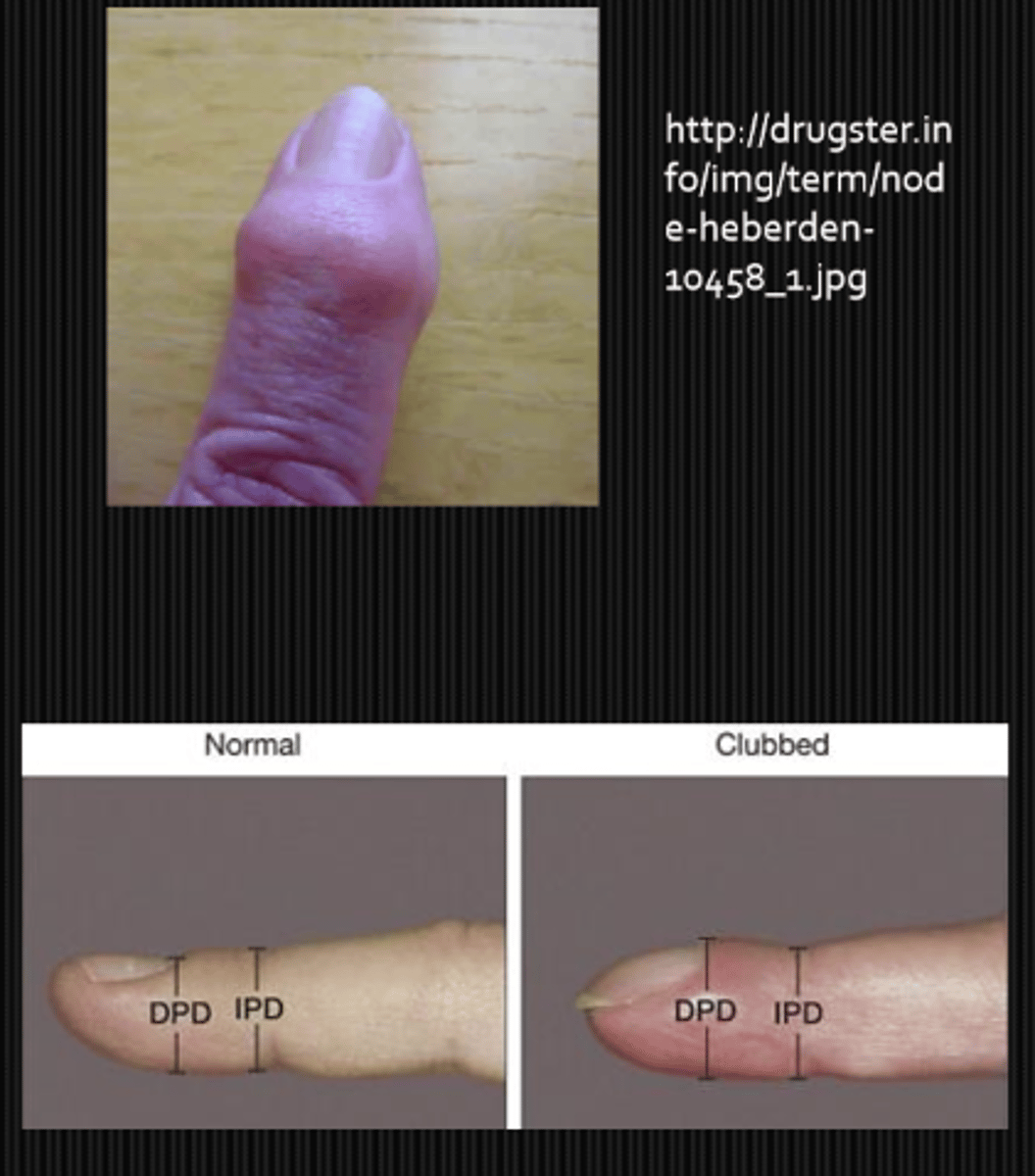
What might we be looking at during the inspection of fingers part of a neuro exam?
Haygarth's nodes = dilated inflam joints on the proximal portion of finger in rheumatoid arthritis
Heberden's (distal) and Bouchard's (proximal) nodes = dilated non-inflam joints on the distal portion of finger in osteoarthritis
clubbing = angle between nail and finger is lost (floating fingernail) in CV disesae, thyrotoxicosis, hepatic cirrhosis
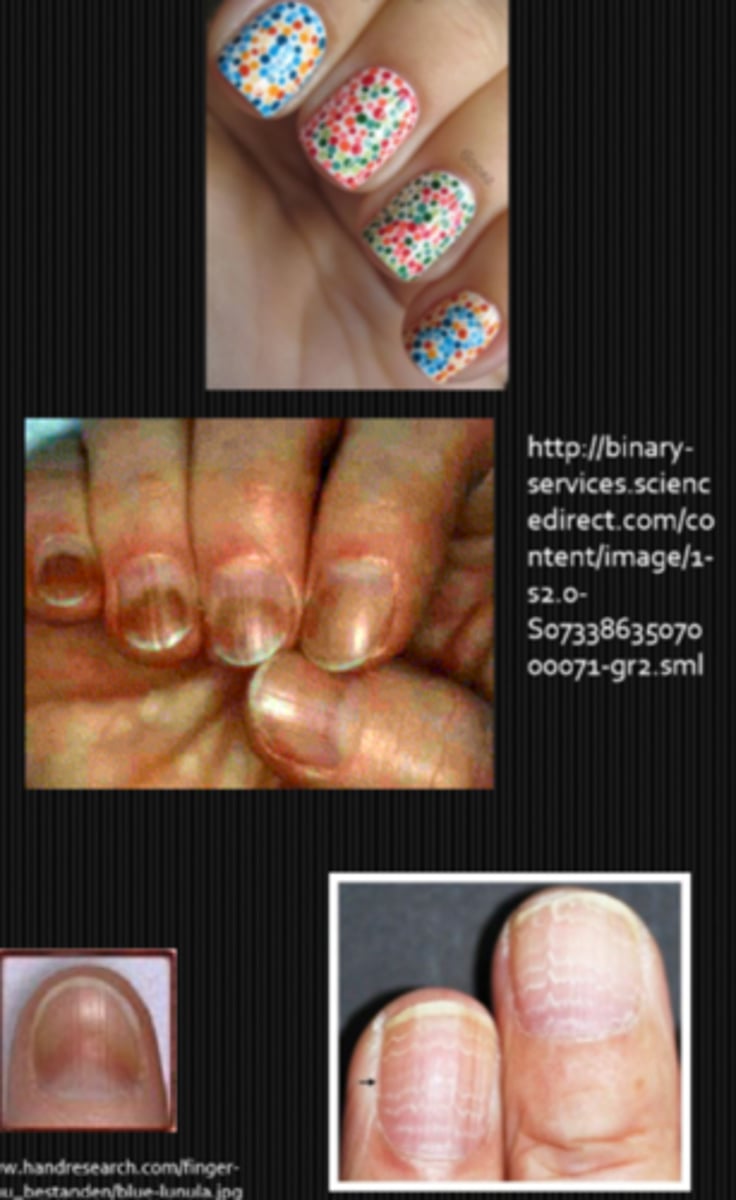
What might we be looking at during the inspection of nails part of a neuro exam?
nail polish neatly applied or messy?
subungual hemorrhages in trichinosis, subacute bacterial endocarditis
azure lunula = Wilson's disease (hepatolenticular degen)
Beau's lines = white lines on nails due to poisioning, toxicity, nutritional problems
What might we be looking at during the inspection of odours part of a neuro exam?
acetone = ketoacidosis
sweet breath = diptheria
bad breath = amphetamine abuse
bitter almond odor = cyanide
What might we be looking at during the best-corrected Snellen VA part of a neuro exam?
compare distance and near = can tell you about Rx, accom, VF defects, PSC, macular disease, etc.
PH improvment indicates Rx issue, keratoconus, light scattering opacities, HOA
PHNI from central media opacity, media haze, central scotoma, ambylopia

What might we be looking at during the qualitative VA part of a neuro exam?
missing one side of chart letters = VF defects

What might we be looking at during the colour vision part of a neuro exam?
Kollner's rule = acquired R/G defecit is ONH disease, acquired B/Y defecit is CATs or retinal disease
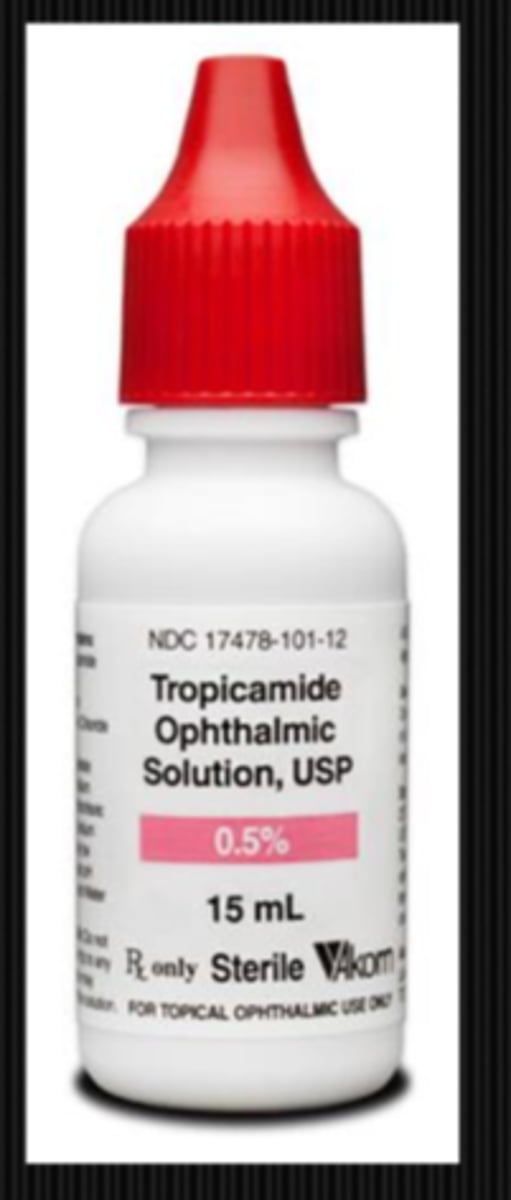
What might we be looking at during the VA w/ ND filter part of a neuro exam?
VA with filter is the same as without = amblyopia
VA with filter is worse by 2 lines or so = pathology

What might we be looking at during the 4 BO prism test part of a neuro exam?
used to detect small paracentral scotoma:
BO prism over abnormal eye = eye does not move
BO prism over normal eye = eyes move nasally

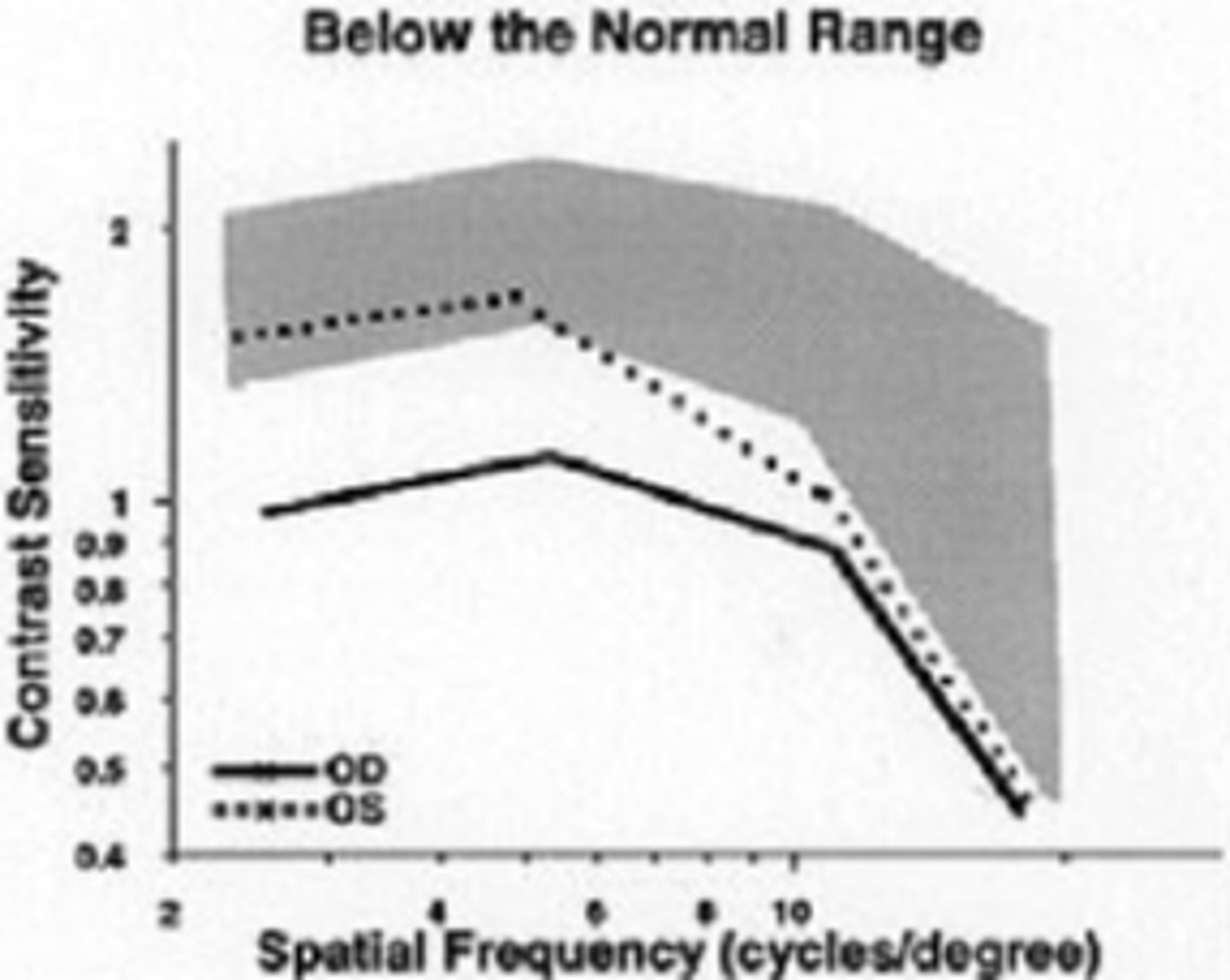
What might we be looking at during the contrast sensitivity part of a neuro exam?
loss at SF other than 20/20 equivalent
can check CS for 1 point on the curve: at 5 cpd (20/100 Snellen letter; peak of CSF function), reduce contrast until last detected letter
What might we be looking at during the confrontation VF part of a neuro exam?
facial amsler = assess whether pt can see whether 1 eye is closed, mouth is open, etc.
quadrant vertical finger counting
simultaneous finger counting = parietal lobe extinction
hemifield comparison for bitemporal or altitudinal hemianopia
plot the blindspot
fingernail comparison for central scotoma
red targets = which one looks more pink/red
Bjerrum's zone
modified Armaly = have pt look at eye, move your finger to pt blindspot, fingertip should disappear
nasal step

What might we be looking at during the Amsler VF part of a neuro exam?
at 30cm, each square subtends 1 deg of retina = good for central scotomas, etc

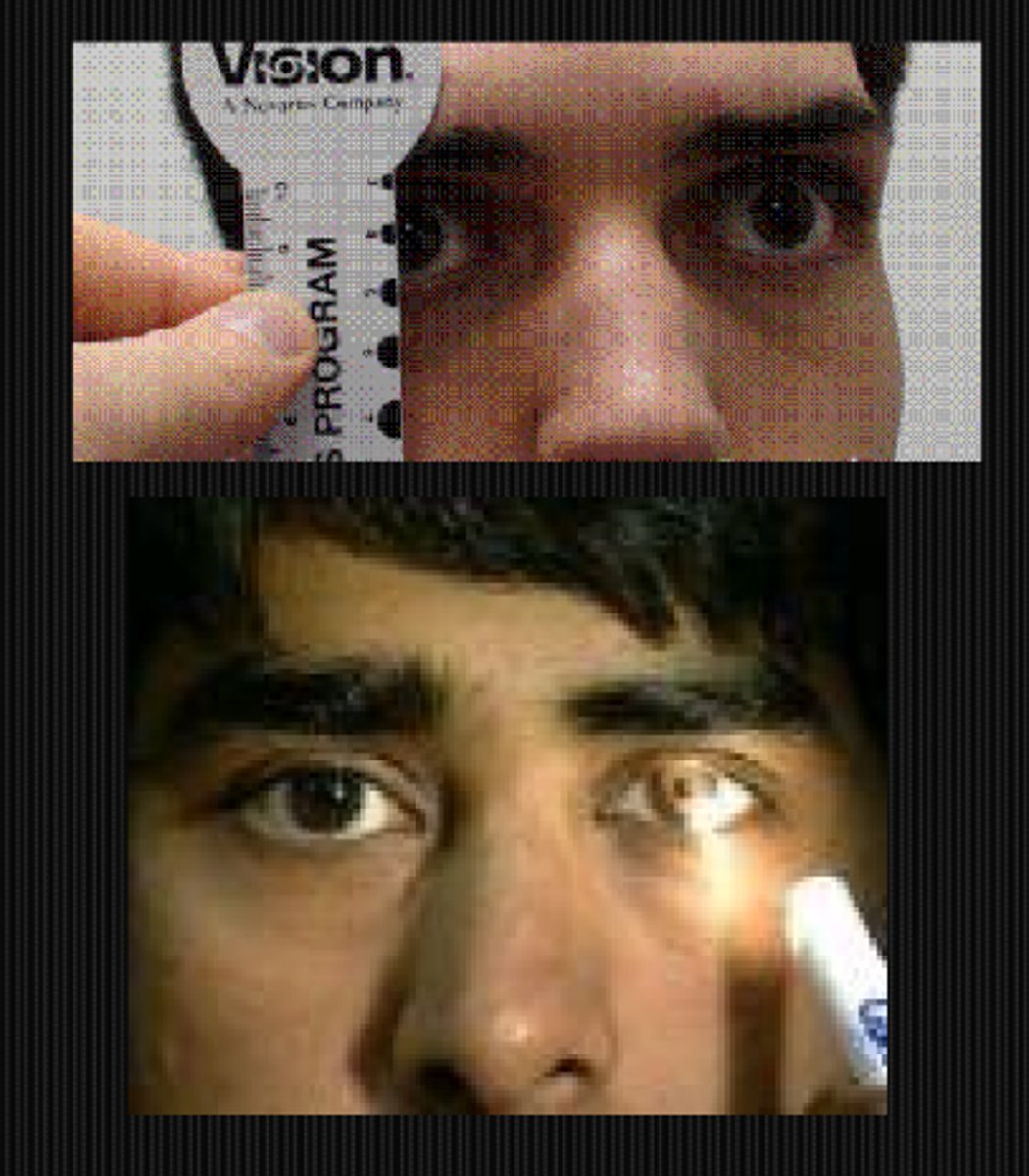
What might we be looking at during the pupil testing part of a neuro exam?
APD
anisocoria = physiological if equal in bright and dim light, parasymp issue if aniso greater in bright light, symp issue if ansio greater in dim light, tonic pupil if same pupil is larger in bright and smaller in dim
What might we be looking at during the eyelid testing part of a neuro exam?
ptosis = is it due to an issue with the mm, NM junction, nerve, or brain?
eyelid retraction = is it due to an issue with the mm (TED), NM junction (pharm), nerve (aberrant regeneration of CN 3), or brain (Collier's sign in brainstem depression)?
What might we be looking at during the orbit testing part of a neuro exam?
exophthalmos due to lesion, TED
enophthalmos due to trauma
globe displacement down and out (most orbital tumors/lesions), nasal (lacrimal gland), temporal (ethmoid sinus)

What might we be looking at during the diplopia testing part of a neuro exam?
monocular or binocular?
horizontal or vertical?
worse in 1 gaze?
greater at distance or near?
paralytic strab of CN 3, 4, 6 = palsy, brainstem issue, NM junction issue
decompensating phoria
eye restriction due to mechanical cause like tumors

What are the 5 steps of the pupil exam?
1. is there anisocoria and is it greater in light or dark?
2. what are the eyelid positions?
3. what is the direct response to light?
4. is there a RAPD?
5. is the near response greater than the direct response?
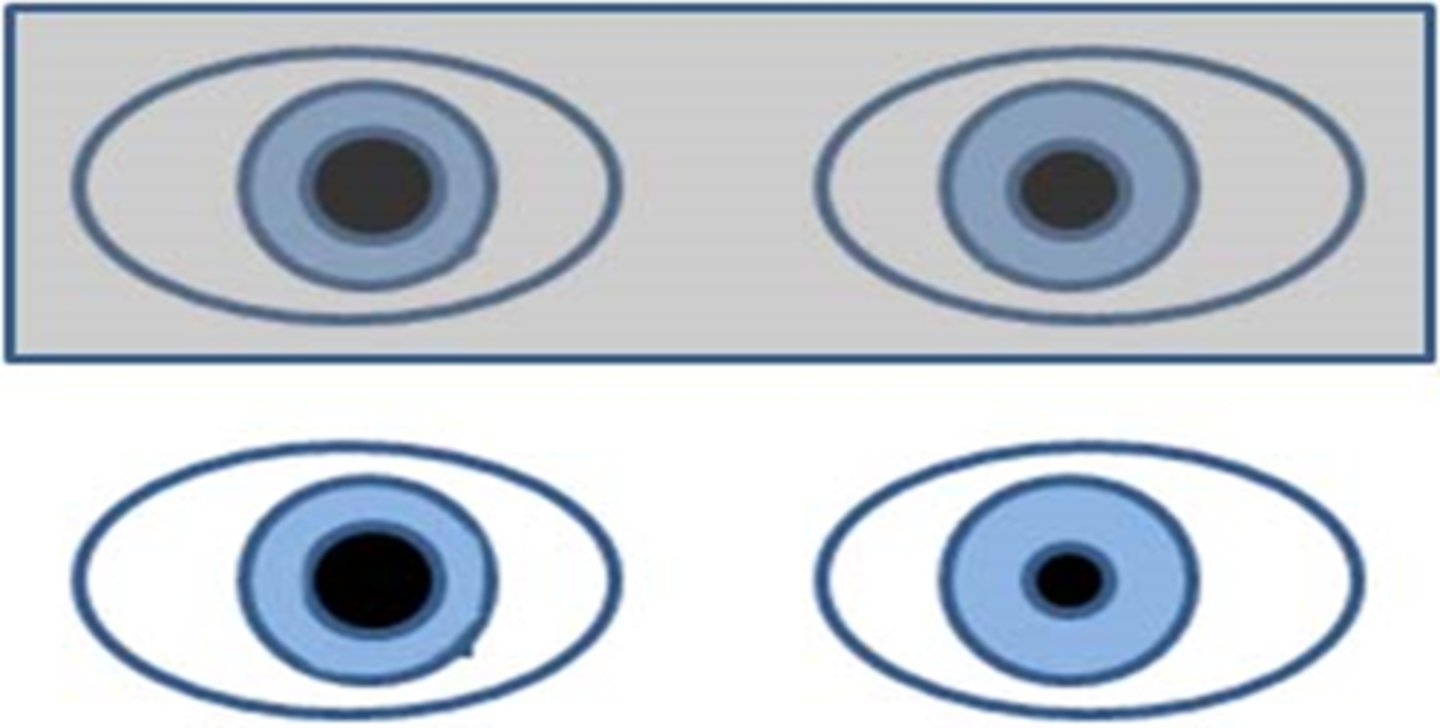
What does it mean if the anisocoria is greater in the dark?
iris cannot dilate = sympathetic issue
ex) Horner's syndrome
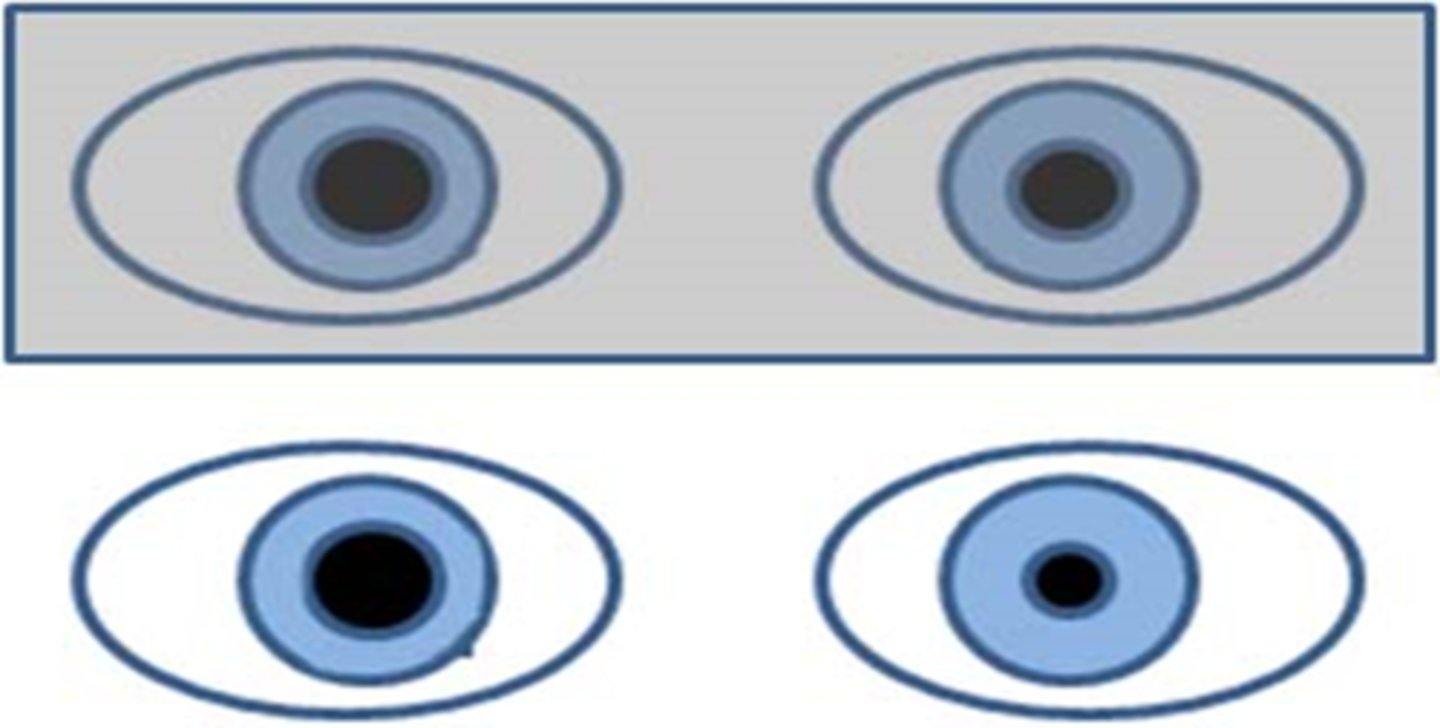
What does it mean if the anisocoria is greater in the light?
iris cannot constrict = parasympathetic issue
ex) internal ophthalmoplegia
What does it mean if the anisocoria is the same in the light and the dark?
physiologic aka benign anisocoria
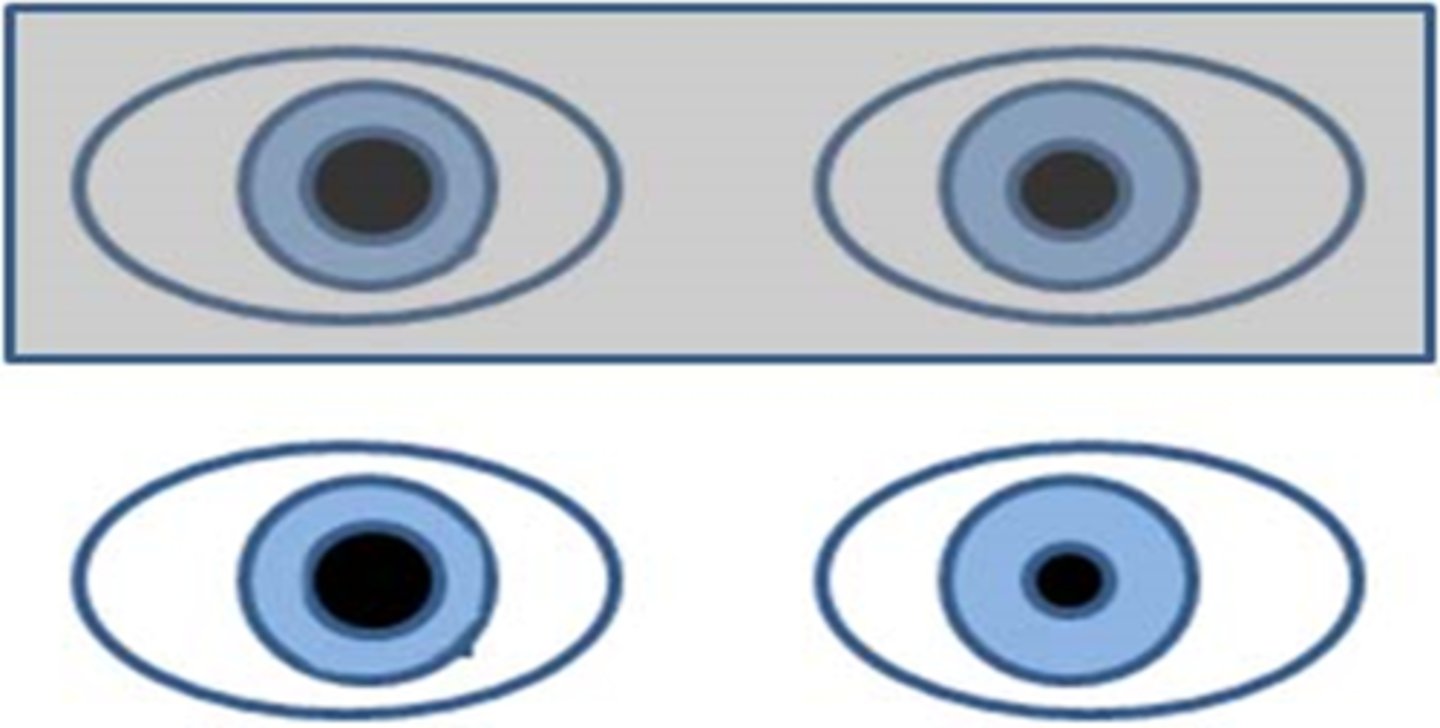
What does it mean if the anisocoria will switch in the dark vs light?
iris is not changing/moving at all = tonic pupil
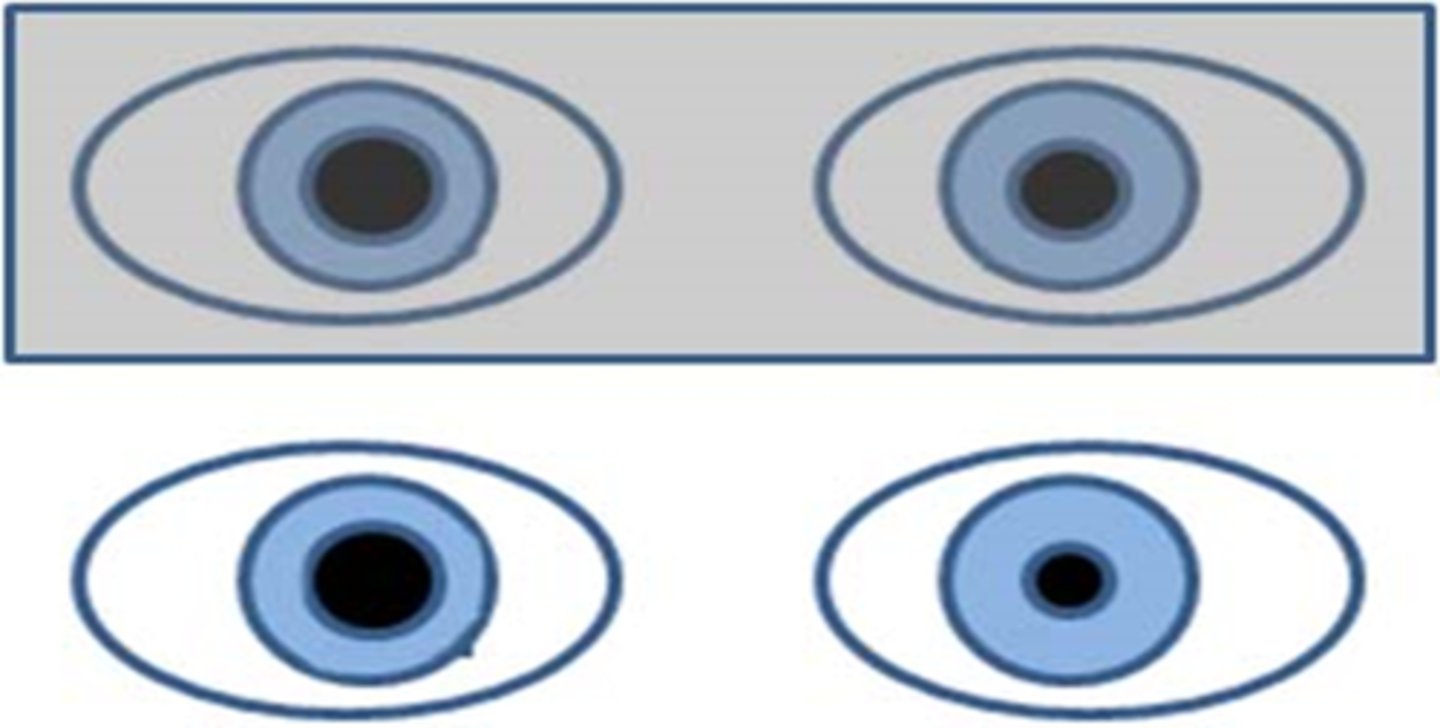
What amount of change between anisocoria difference in the light and dark (or between years ago vs today) is considered clinically significant?
0.5mm
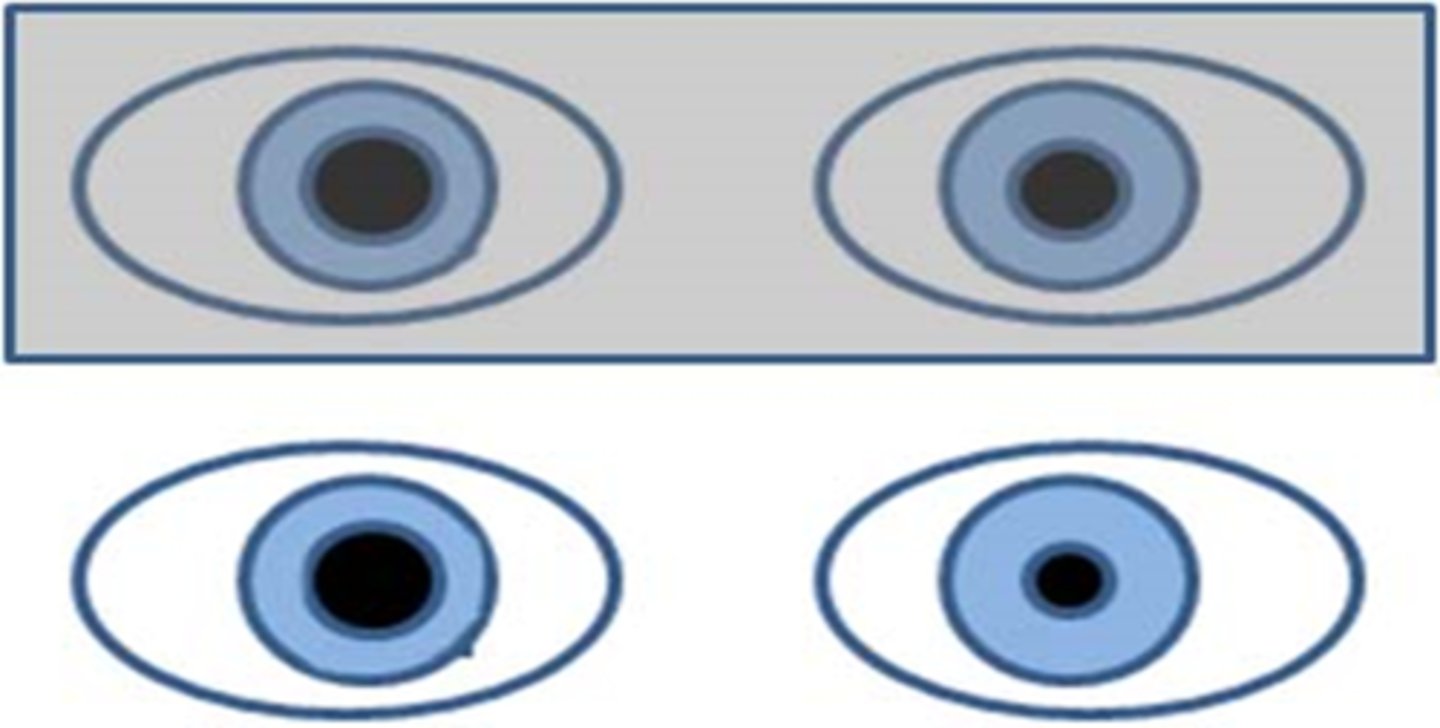
When doing pharmacologic testing of the pupil, when should we record pupil size?
before and after instilling the drugs

When seen with a large pupil, what might a ptosis indicate?
CN 3 palsy (parasymp issue) will show...
ptotis
eye is "down and out"
large pupil
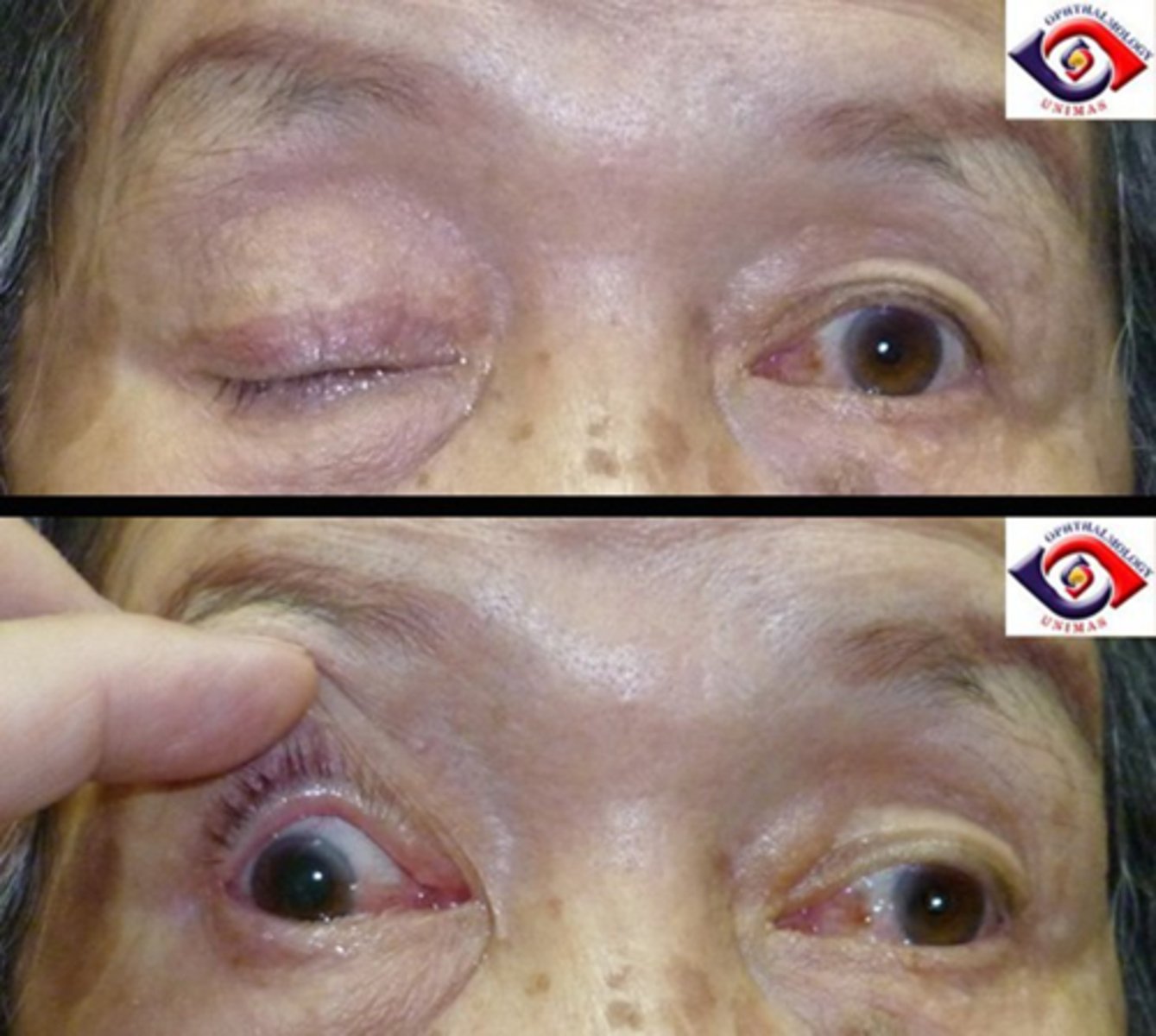
When seen with a small pupil, what might a ptosis indicate?
Horner's syndrome (symp issue) will show...
ptosis due to Muller's affected
small pupil = miosis
anhydrosis
What does it mean when the direct response to light is inhibited?
amaurotic pupil reaction = total blindness in the eye that has no direct response...
no direct response in bad eye
no consensual response in good eye
direct response in good eye
consensual response in bad eye
near response intact OU
In what conditions may the direct response to light be absent?
severe head trauma
cardiac arrest
medical coma
brain death
Aside: what are 3 possible tests for malingerers?
1. have pt cover good eye, then throw a tennis ball to see if pt reacts
2. Troost's test = have pt cover good eye, pass a mirror in front of their face to see if there is an OKN movement
3. pass an offensive word written on a card in front of the pt to see if there is any facial expression/pupil dilation

What is the Au sign test for assessing consensual response, often used in determining whether or not pt has anterior segment inflam or malingering?
pt occludes light sensitive, painful eye and shine light in normal eye = if consensual response is intact, the bad eye pupil will constrict and will increase the pain
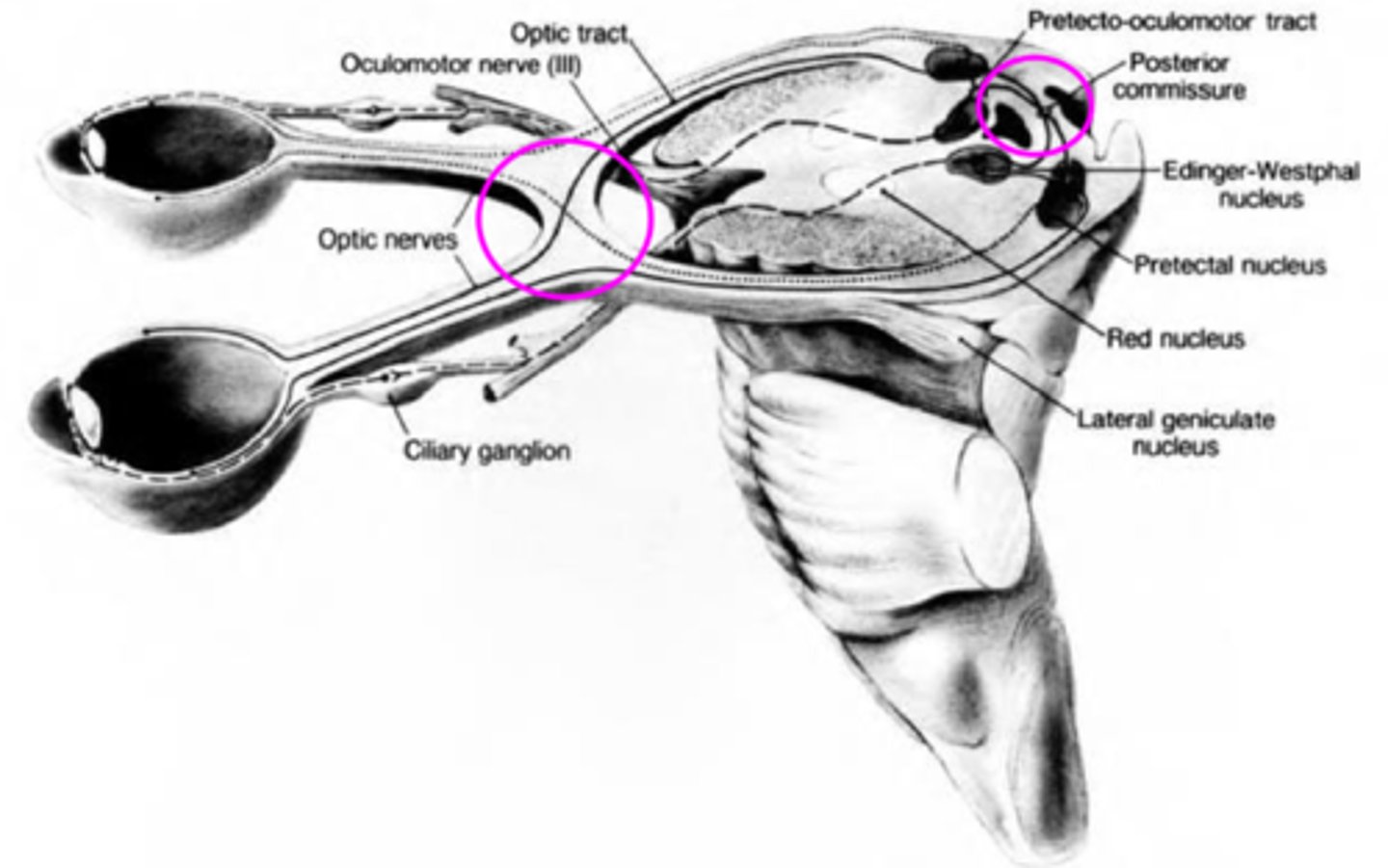
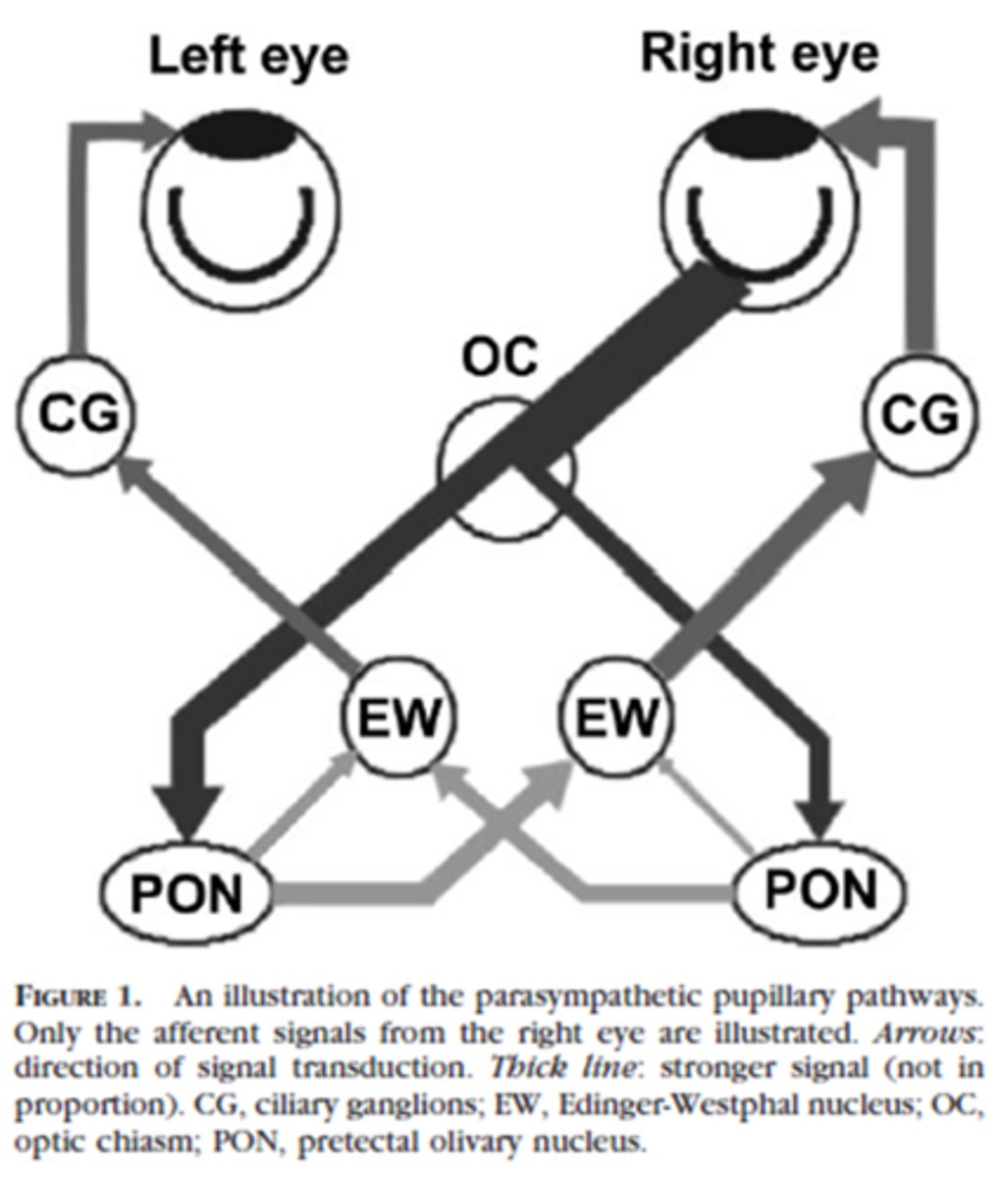
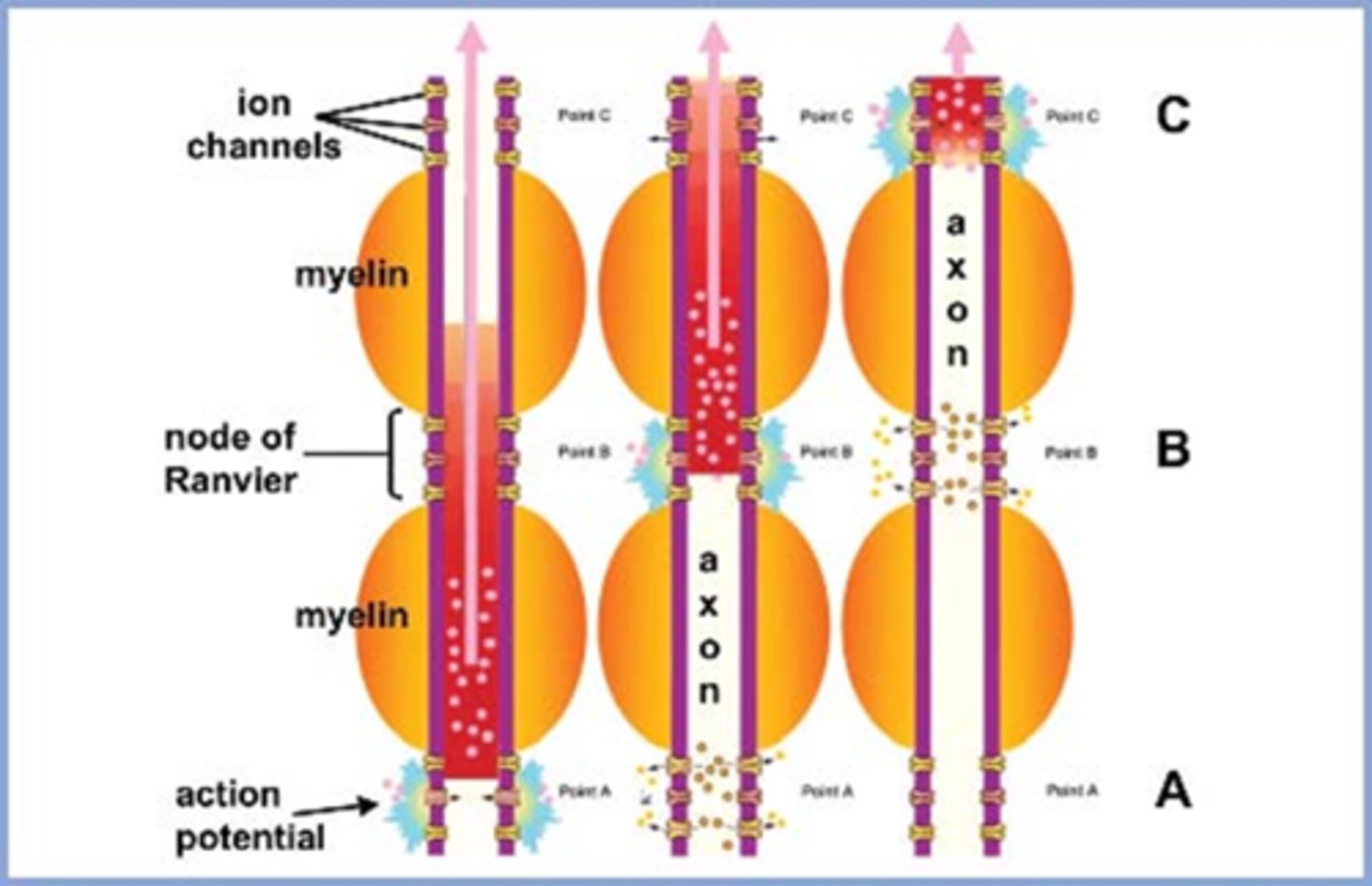
Explain the pathway of neural signals that is responsible for the pupil response.
RGC fibers travel to optic tract = some fibers separate and synapse in midbrain pretectal nucleus (superior colliculus) before reaching LGN = some of these fibers go to the ipsilateral E-W nucleus and others cross at the posterior commissure to the contralateral E-W nucleus.
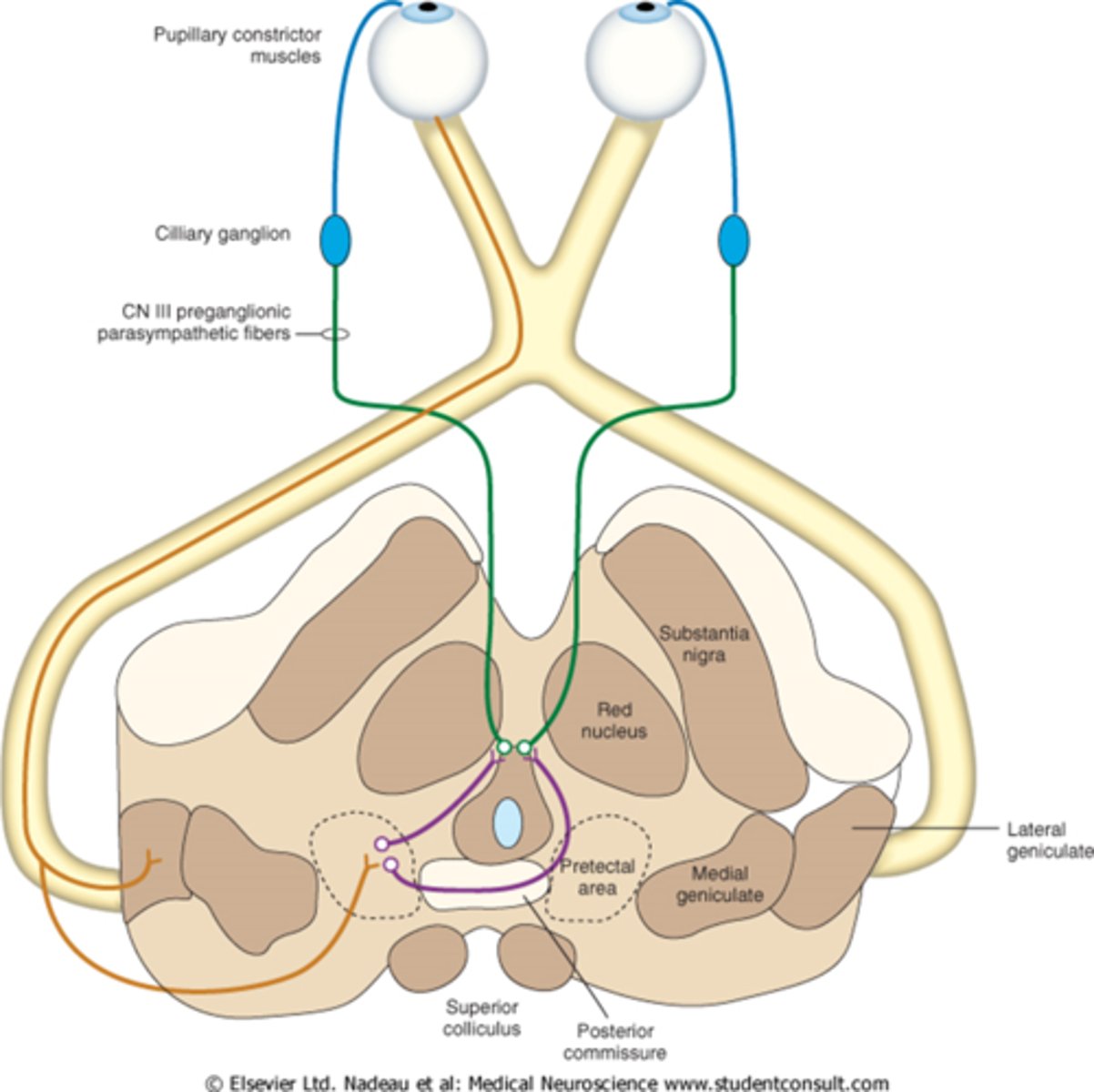
Where are the 2 decussations of fibers involved in the pupil response?
chiasm where all nasal retinal fibers cross
posterior commissure where some fibers go to the ipsilateral E-W and others to the contralateral E-W
In a normally functioning system, pupil reactions are always __________________ when light is directed into either eye.
grossly equal
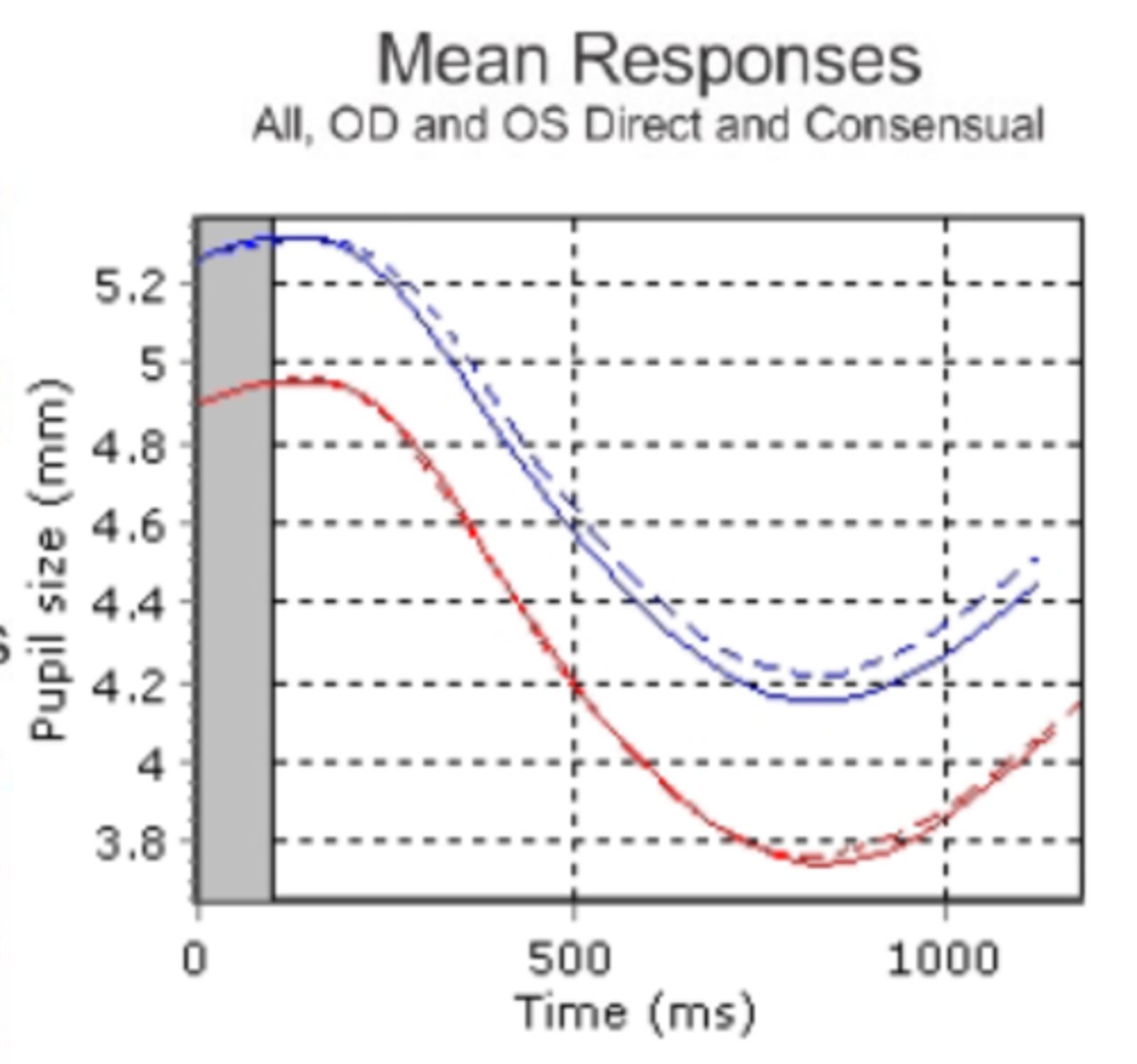
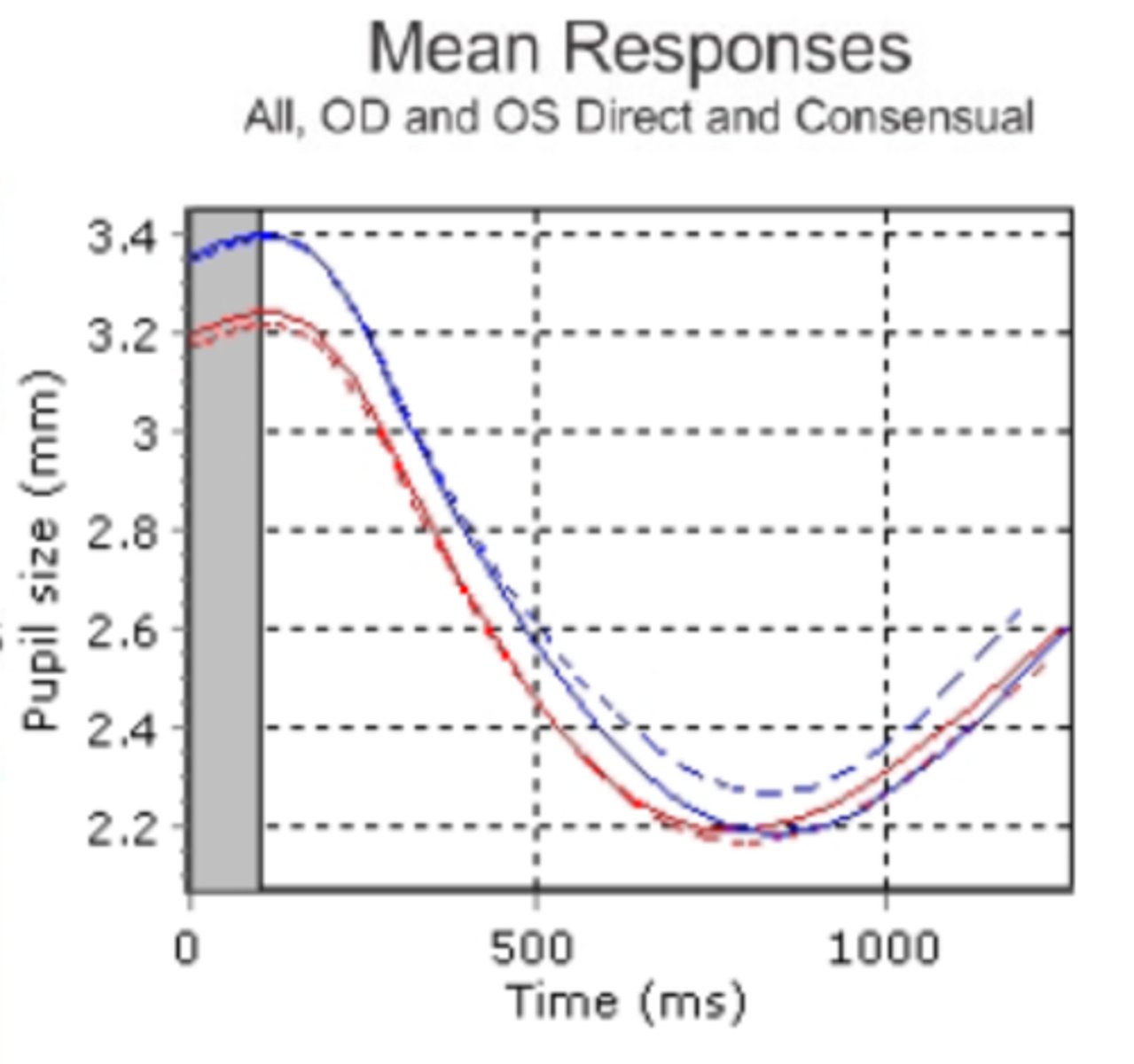
Is there an anisocoria and/or an APD shown here?
anisocoria is present bc of unequal pupil sizes, but both pupils show the same latency and velocities so there is no APD
What is contraction anisocoria?
pupil size obtained when shining light into direct eye is different than the consensual response obtained in the other eye (even if you didn't see aniso before this)
can be bilateral (doesn't matter which eye) or unilateral (ony occurs in one eye)
What is shown here?
OD consensual is slightly smaller than the OD direct response, but this is a normal variation!
What does a positive RAPD (aka Marcus Gunn pupil) look like?
direct response is less than the consensual response in the same eye
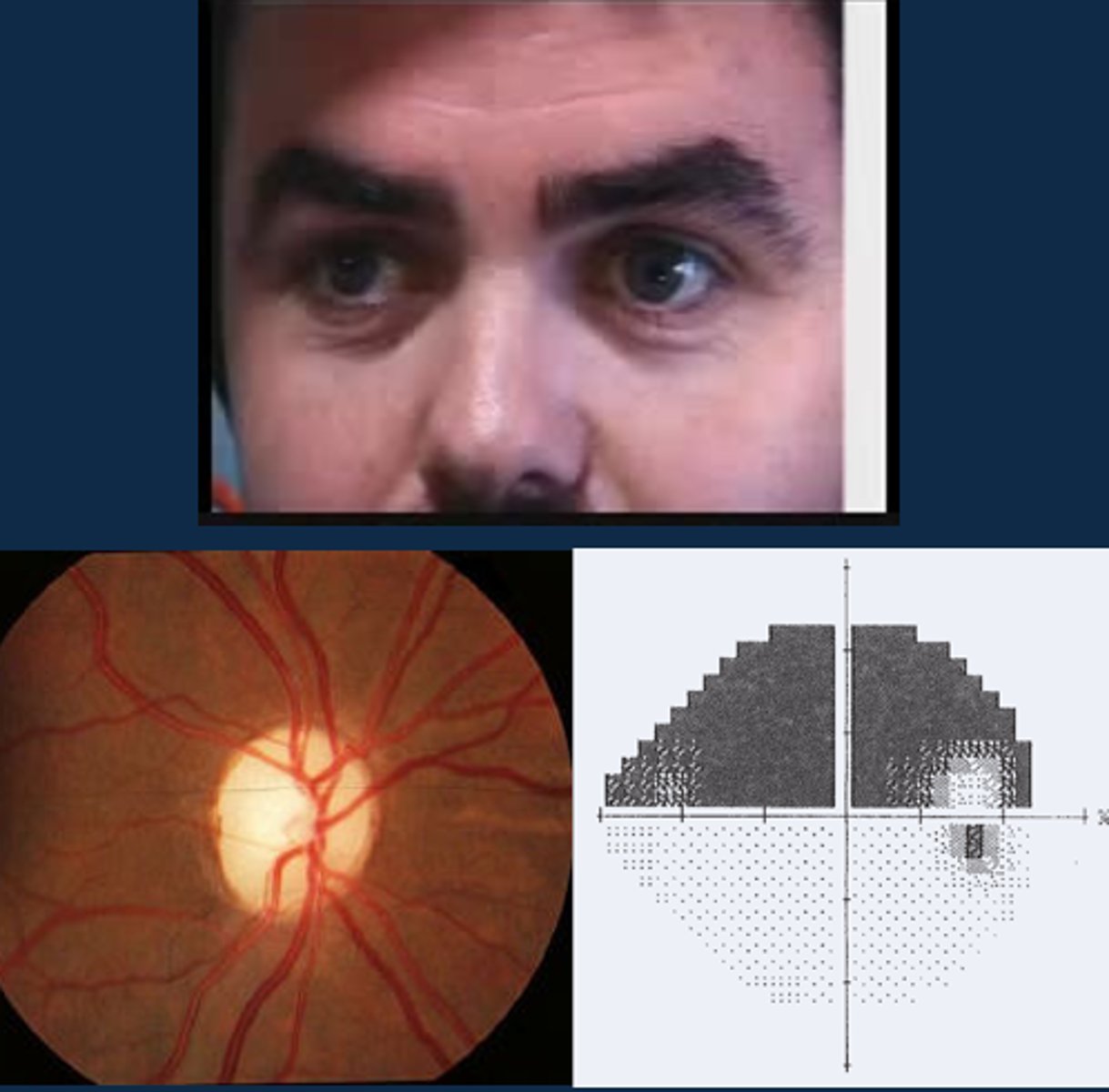
What does a positive RAPD (aka Marcus Gunn pupil) mean?
issue with the afferent pathway of information getting to brain = ONH disease like optic atrophy, optic neuritis, optic neuropathy, glaucoma, OR pt already bleached
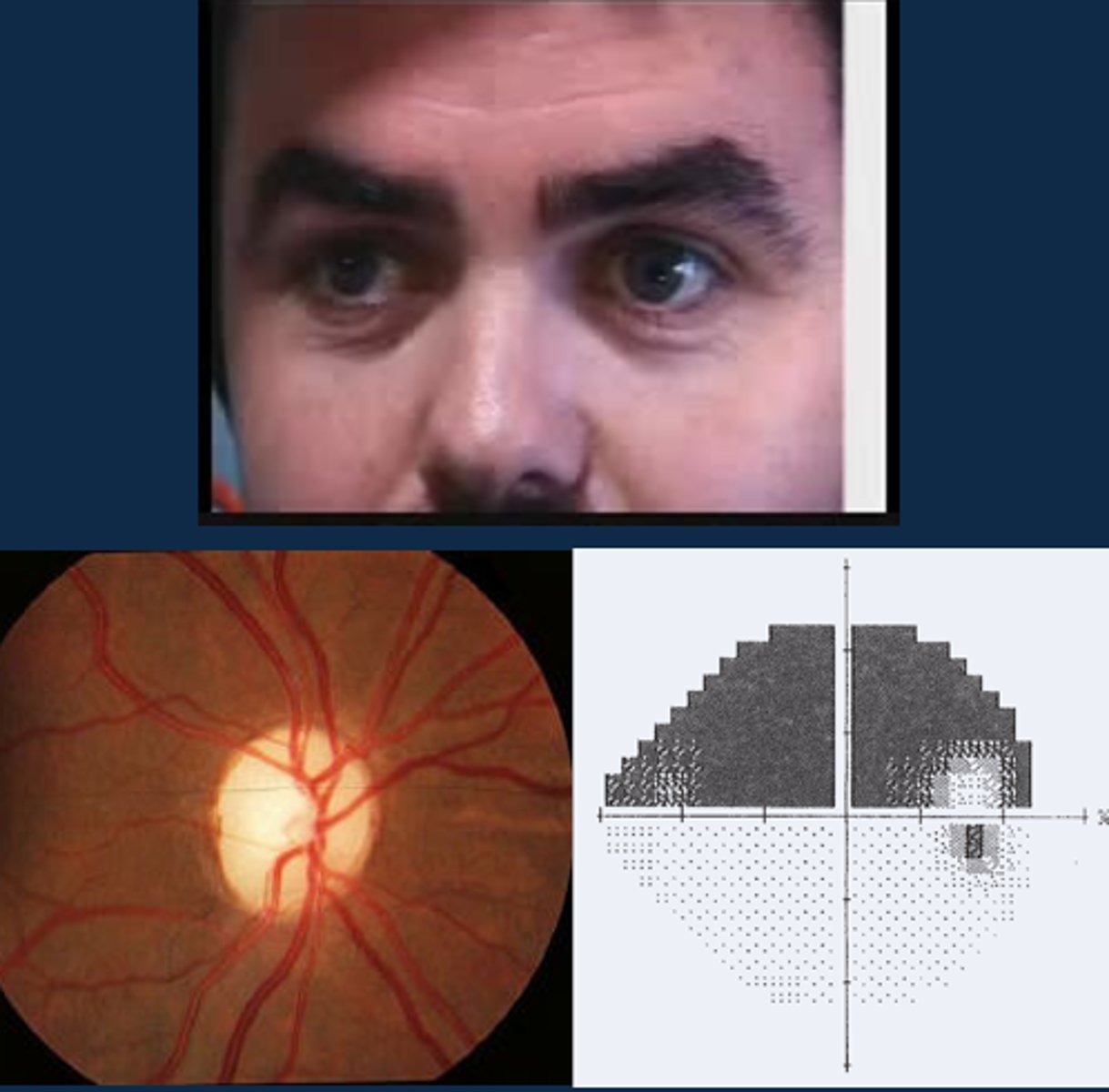
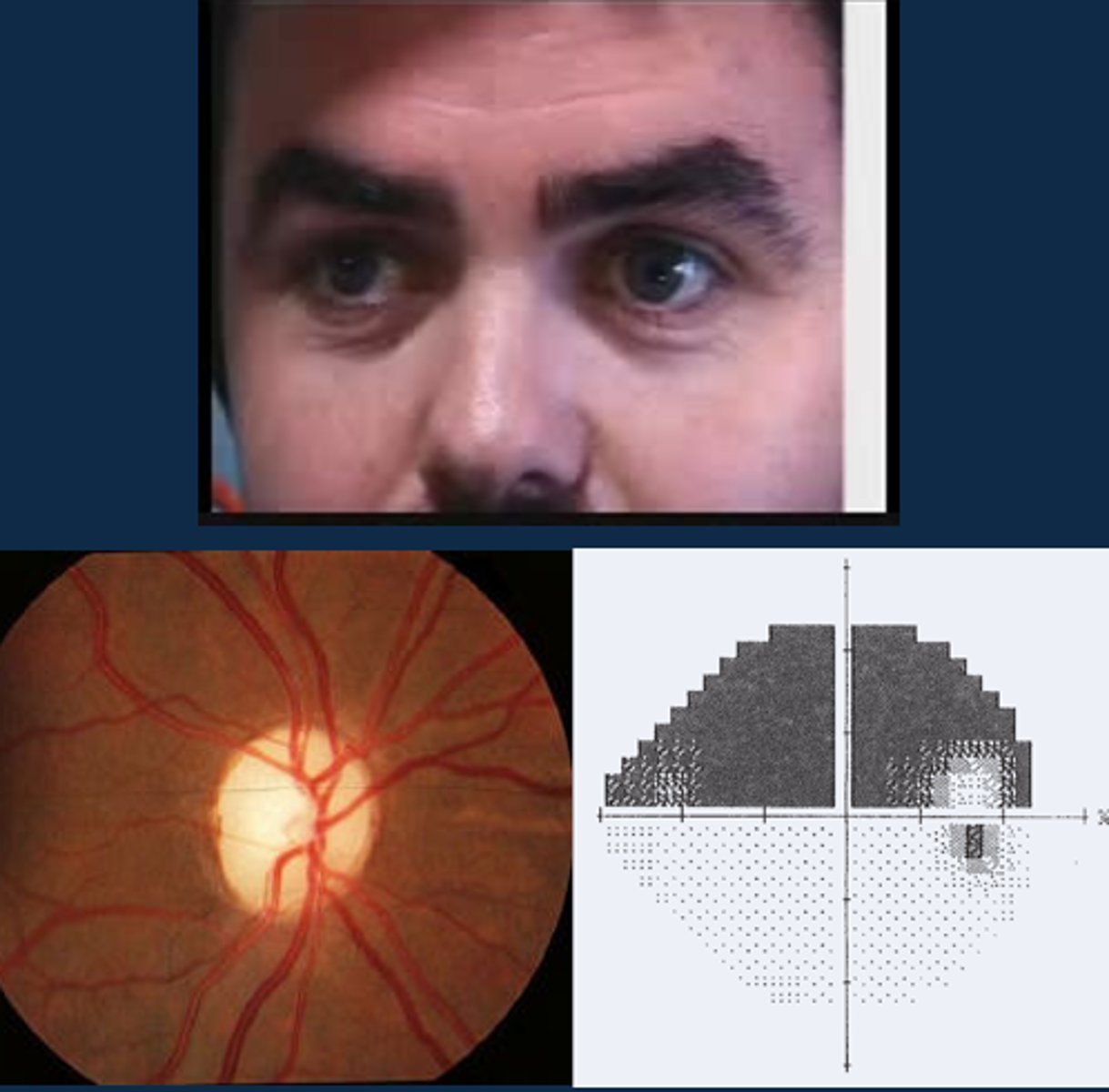
Aside from a positive RAPD, what other signs might indicate optic atrophy?
ONH pallour
dyschromatopsia
altitudinal VF defect
ONH NFL dropout
What are some tips for performing an APD test?
pt should fixate across the room
perform in dim illumination
use a bright, cool light
check for aniso first
don't bleach eye beforehand
avoid eyedrops beforehand
What is the subjective luminosity test to verify an APD?
ask pt "if this penlight is worth $100 of brightness with your good eye, what is it now worth looking with the bad eye?"
similar to red-cap test

What should we expect to see on the subjective luminosity test if there is an APD?
bad eye should see things more dimly by a difference of at least $15 due to a slower, less intense AP in that diseased eye
What is the indirect APD test?
when we compare the consensual response and the direct response in the normal eye
When might we use the indirect APD test?
to check for an APD in an eye where the pupil doesn't work/is fixed in position due to posterior synechiae, CN III palsy
Ex) Your pt has a Hx of trauma causing an OD efferent pupil defect. How would you perform the indirect APD test here?
OD does not react directly or consensually = look at OS direct and consensual responses = if OS constricts when pupil is shined into either eye, then there is NO APD in either eye
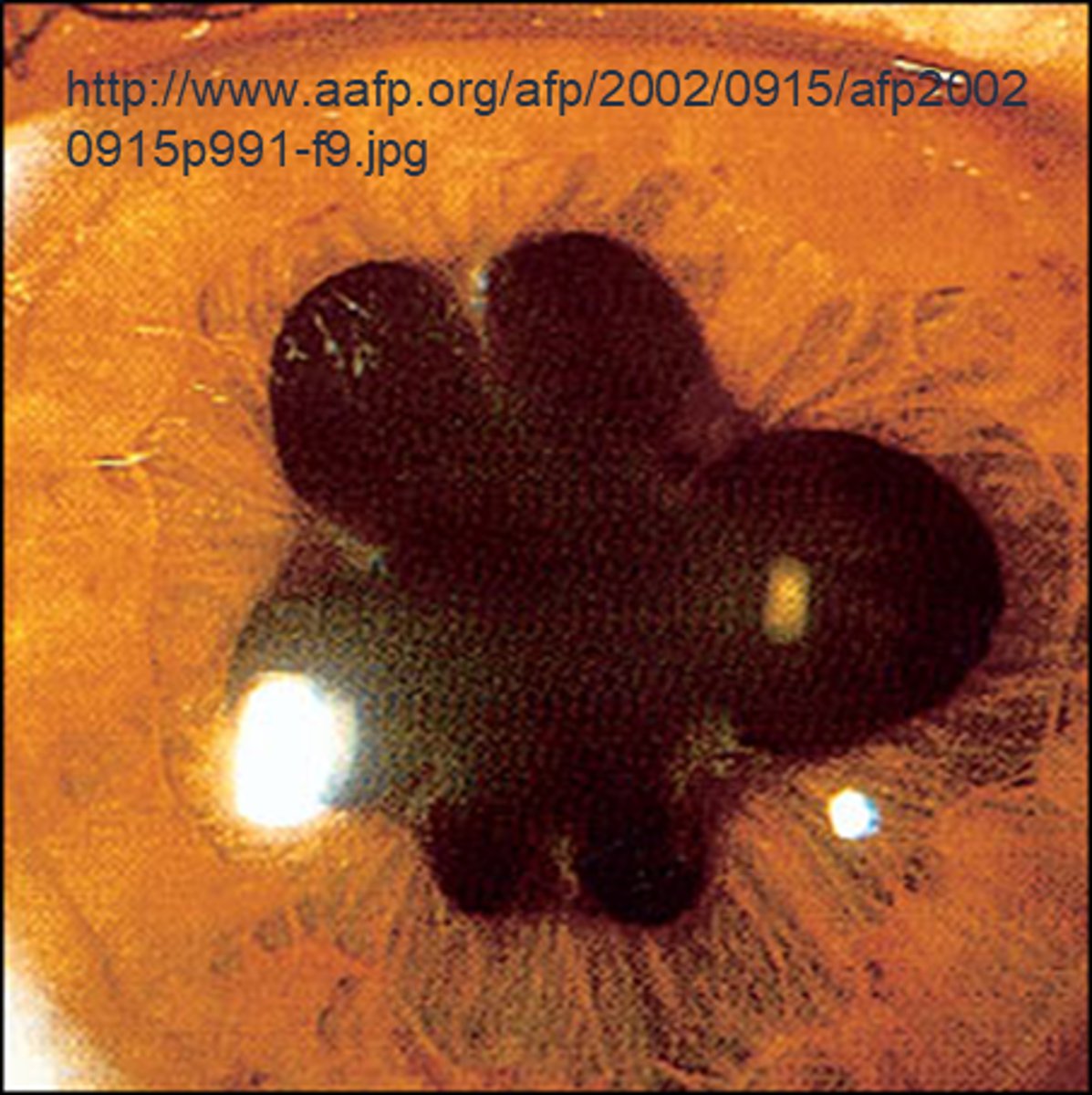
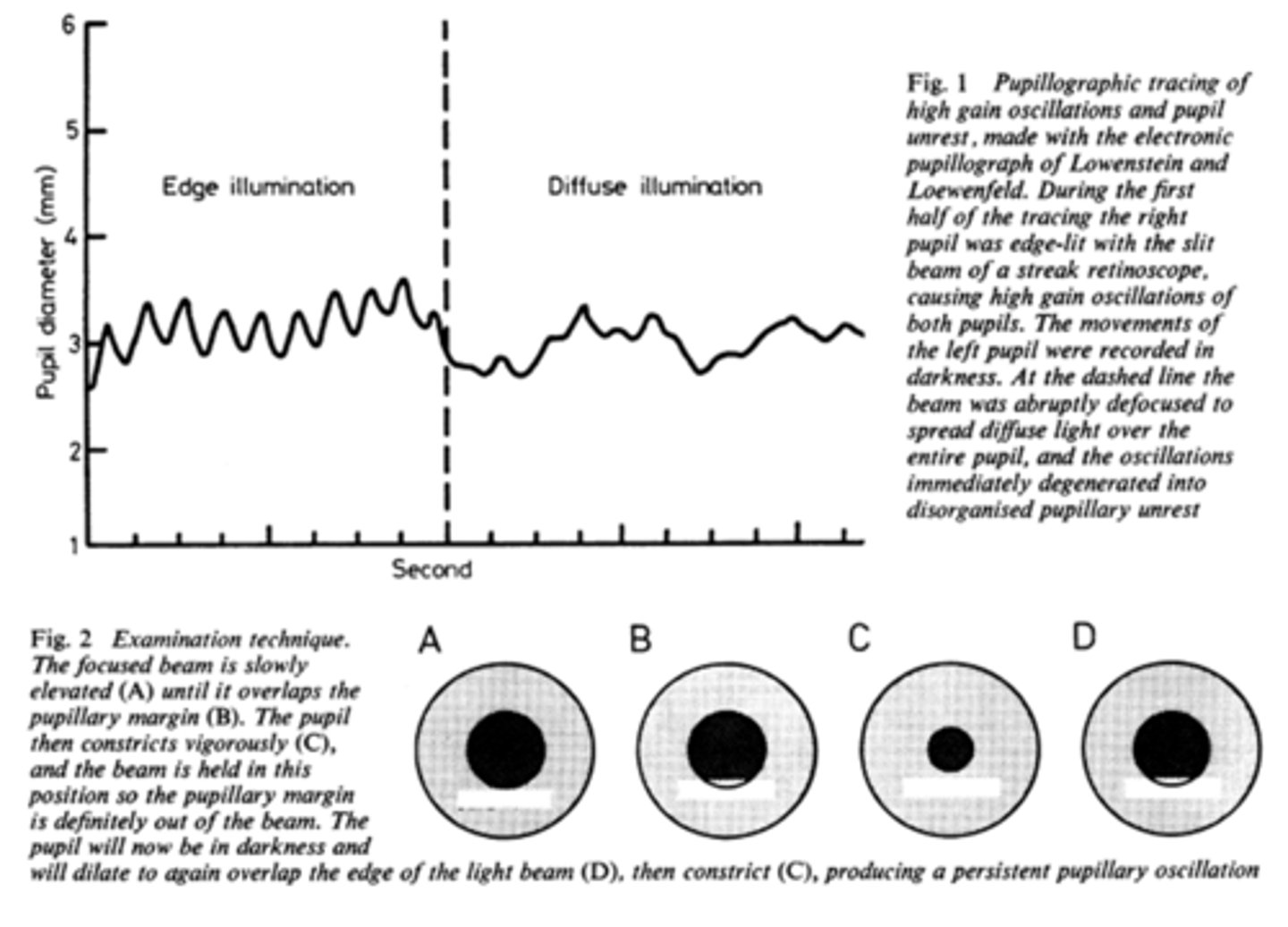
What is pupil cycle time?
playing peek-a-boo with the pupil = position slit lamp bream on edge of iris causing pupil to oscillate between constrict, dilate, constrict, dilate
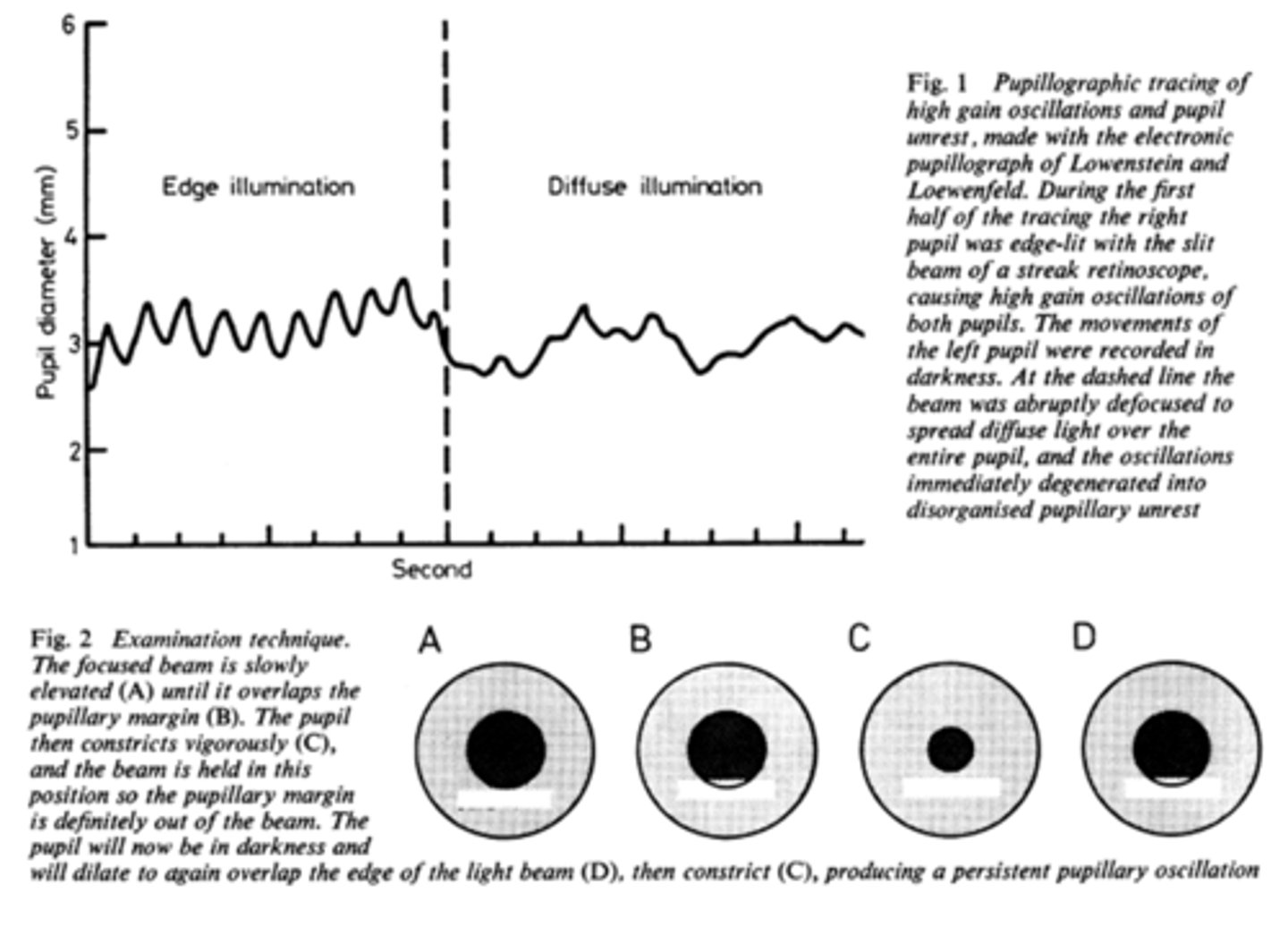
How do we obtain/measure a pupil cycle time?
time 100 cycles of oscillations and convert time to msec = this tells us how many msec per cycle
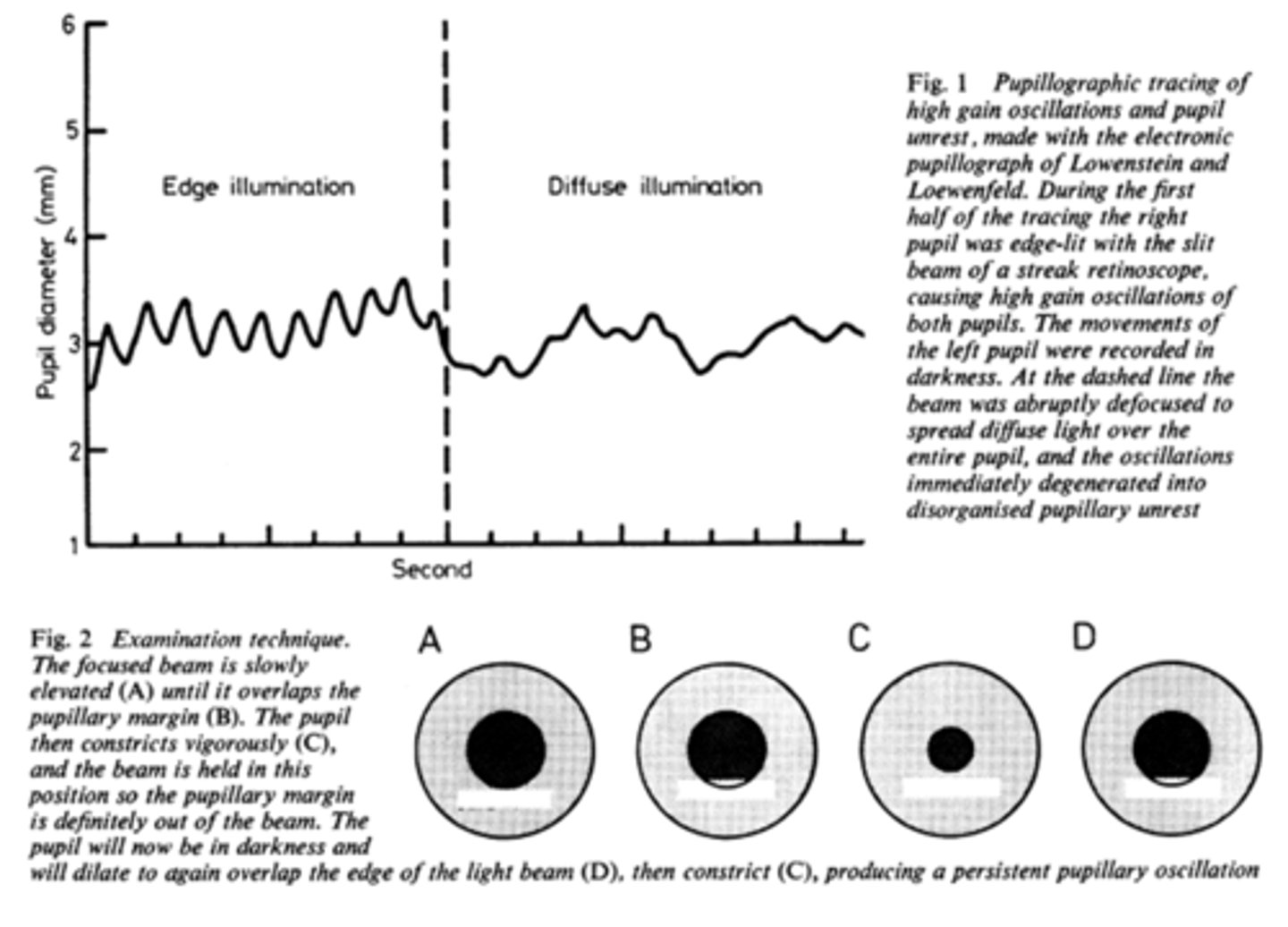
What does pupil cycle time tell us?
tells us how much impulse is getting to the E-W nucleus = another indicator of ONH function
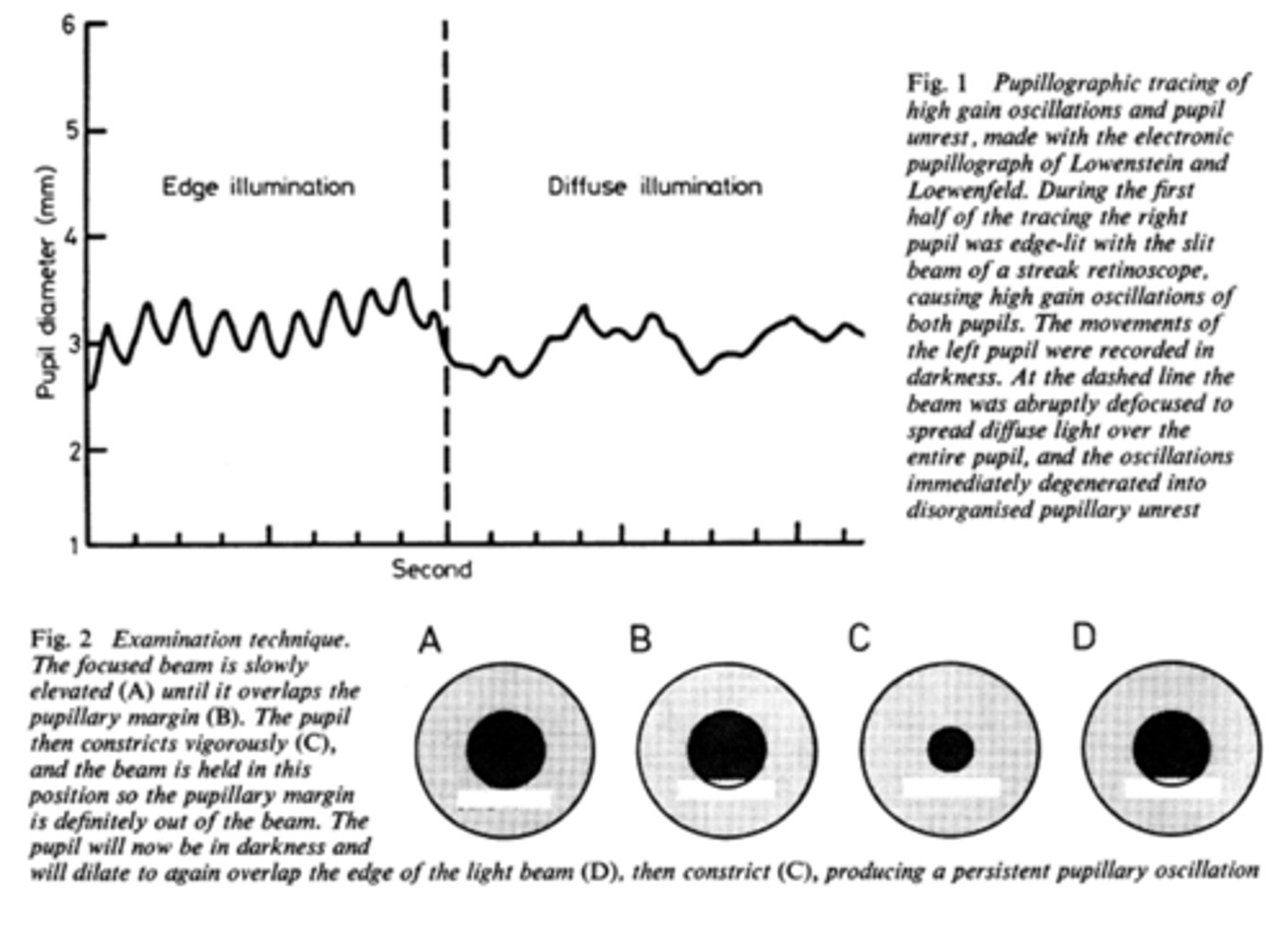
What is a normal pupil cycle time?
954 msec
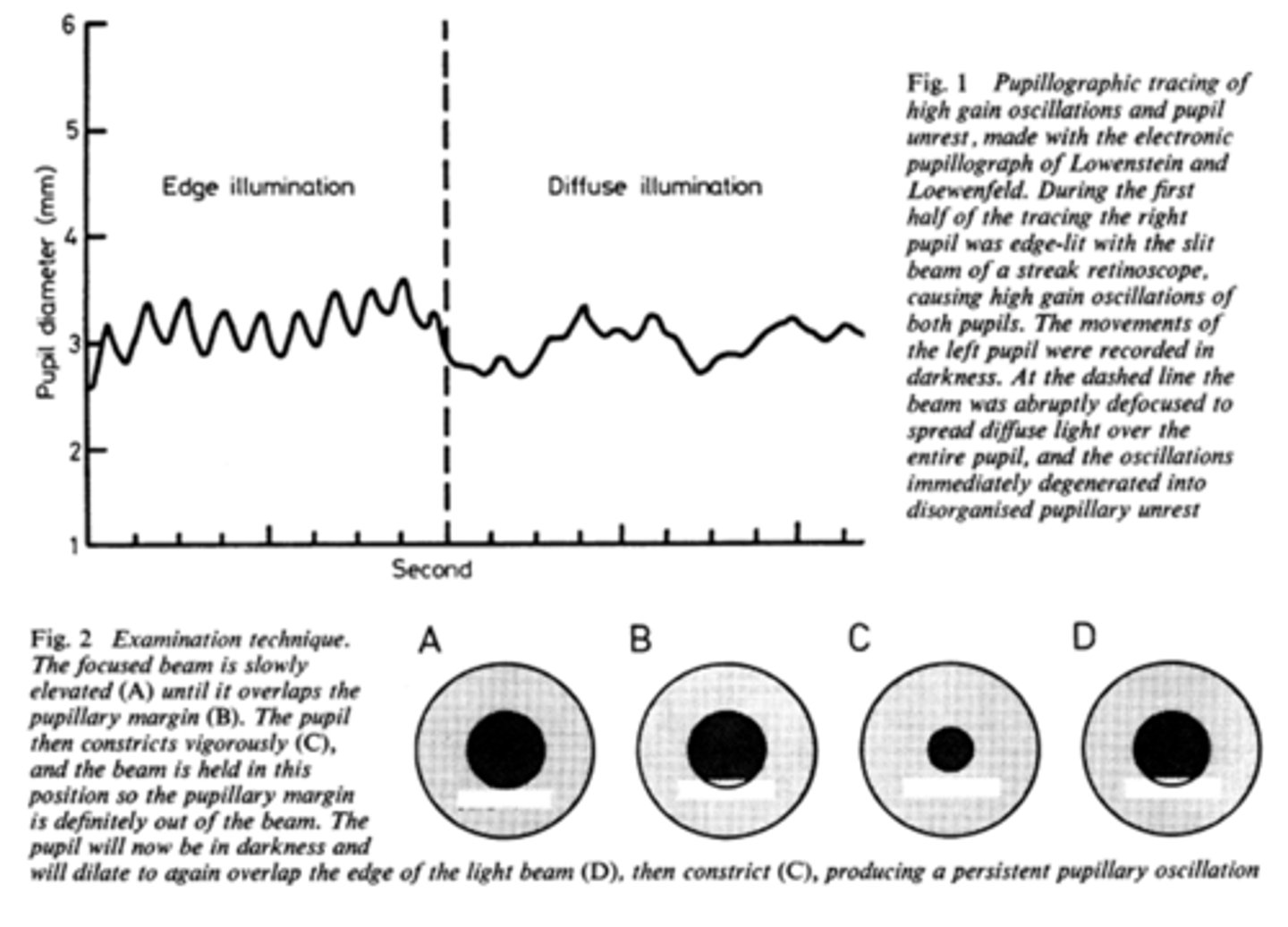
What does a prolonged pupil cycle time tell us?
APD or afferent lesion of ONH
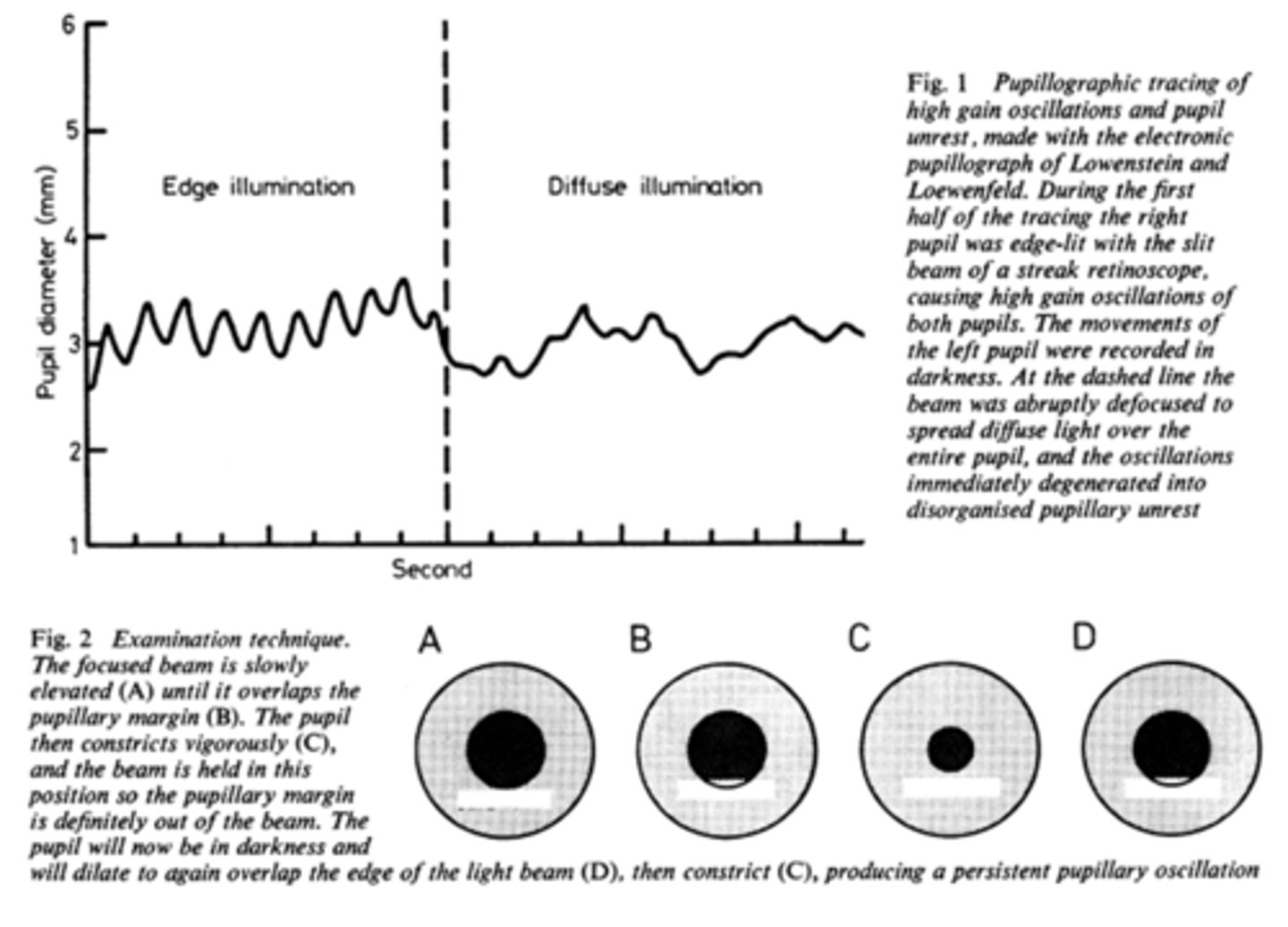
What does an asymmetric (40 msec difference between eyes) pupil cycle time tell us?
prolonged cycle time = APD or afferent lesion of ONH
Is it more likely to have a poorer near repsonse or direct response when assessing pupils in a normal pt?
near reponse is typically worse than direct response in a normal pt
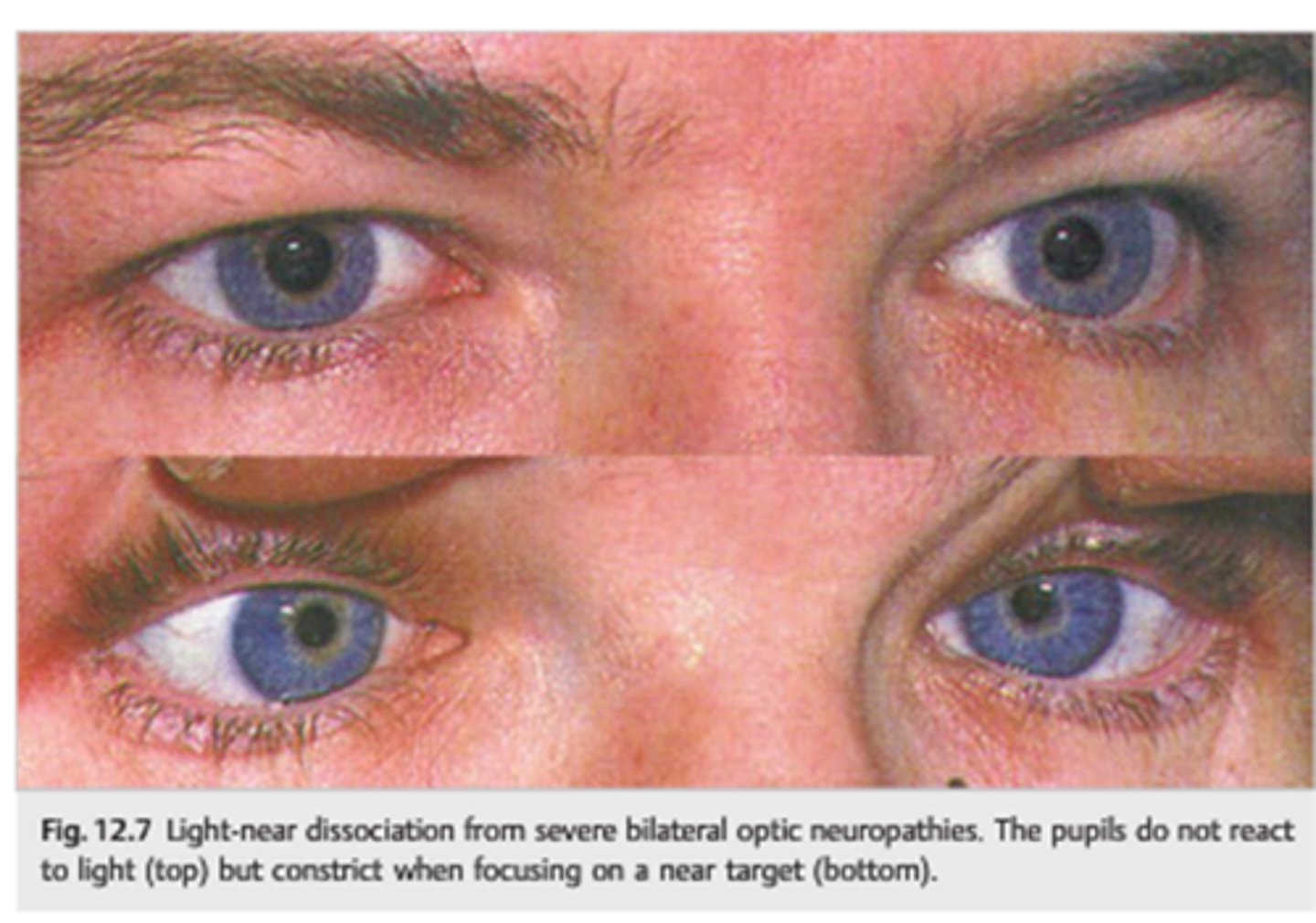
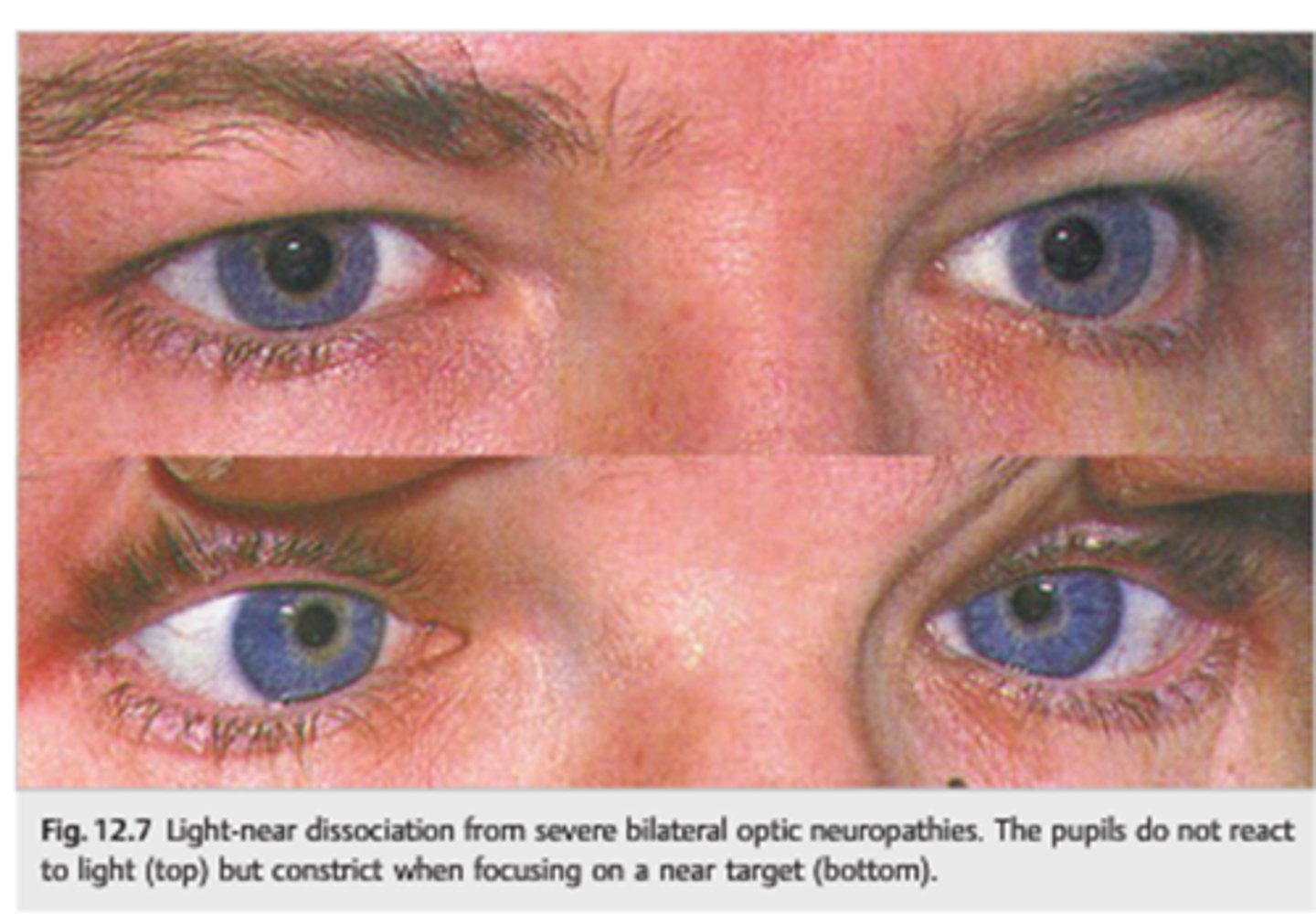
What is a light-near dissociation pupil?
pupil that does NOT respond to light, but does have a near response
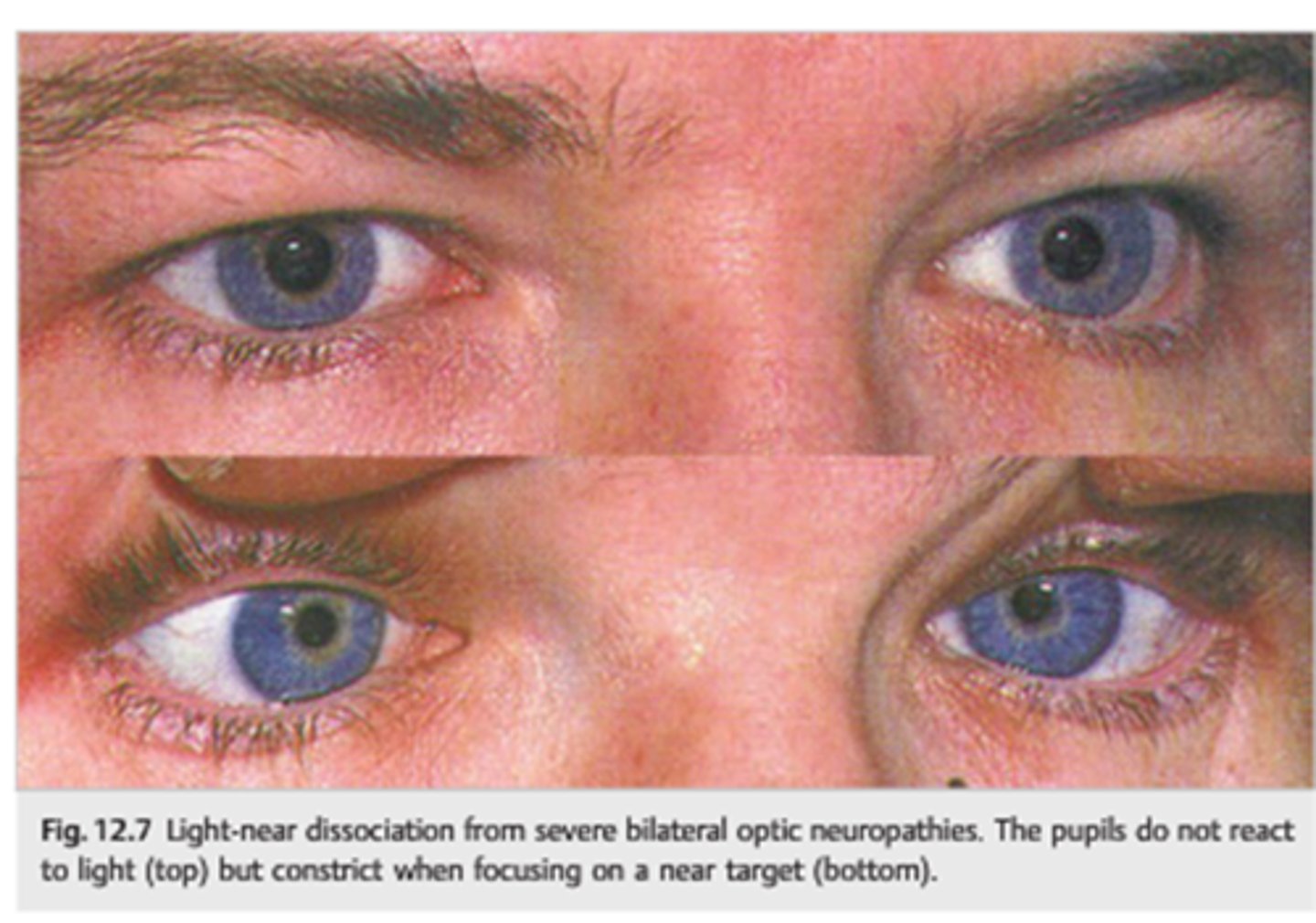
What can cause a light-near dissociation pupil?
Argyll-Robertson (CNS syphillis)
amaurotic pupil
aberrant regeneration of CN III
tonic pupil
tectal pupils (upper midbrain)
tabes diabetica (posterior spinal columns in DM)