Biology Unit 1
1/134
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
135 Terms
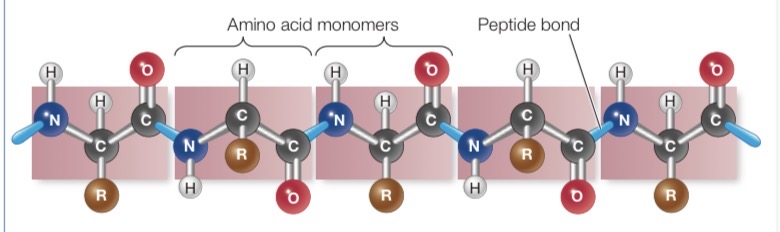
Primary Structure of Protein
Linear sequence of amino acids joined by peptide bond
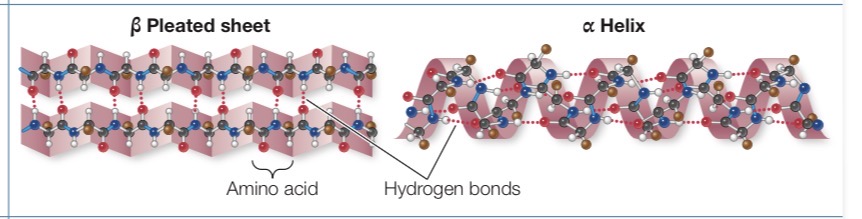
Secondary structure of protein
Regular repeated local spatial patterns. Form alpha helices and beta pleated sheets through hydrogen bonding.
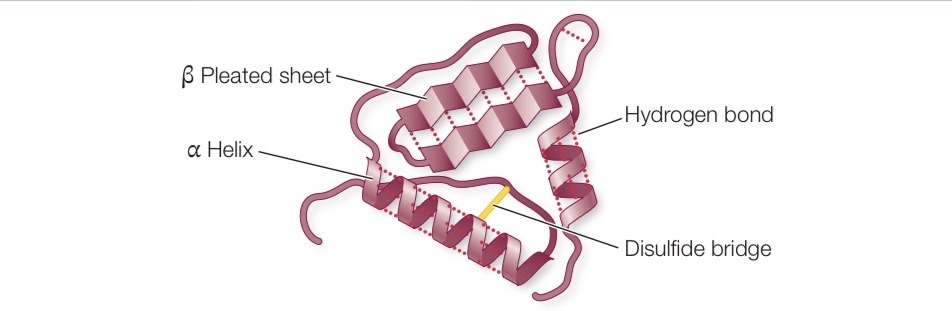
Tertiary structure of proteins
Bending path of polypeptide chain in 3D chain in three dimensional space
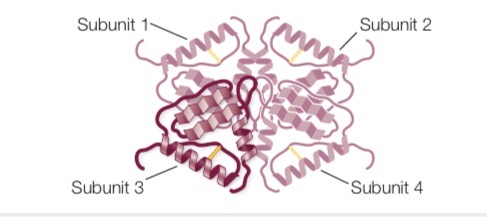
Quaternary structure of proteins
Spatial arrangement of polypeptide subunits in proteins made up of more than one polypeptide chain
Beta Pleated Sheet
Formed from two or more polypeptide chains that are almost completely extended and aligned side by side. Stabilizes between the N—H groups on one chain and the C=O groups on the other. A β pleated sheet may form between separate polypeptide chains or between different regions of a single polypeptide chain that is bent back on itself. 3.5 Angstroms per amino acid residue
Alpha Helices
Right handed coil. The R groups extend outward from the peptide backbone of the helix. The coiling results from hydrogen bonds that form between the δ+ hydrogen of the N—H of one amino acid an. 3.6 amino acids per turn. 1.5 amino acids per residue, 5.4 amino acids per turn
Alpha Helix Modifiers
Proline: Alpha helix breaker, no h because it loops so cannot form hydrogen bond required
Glycine: Too flexible
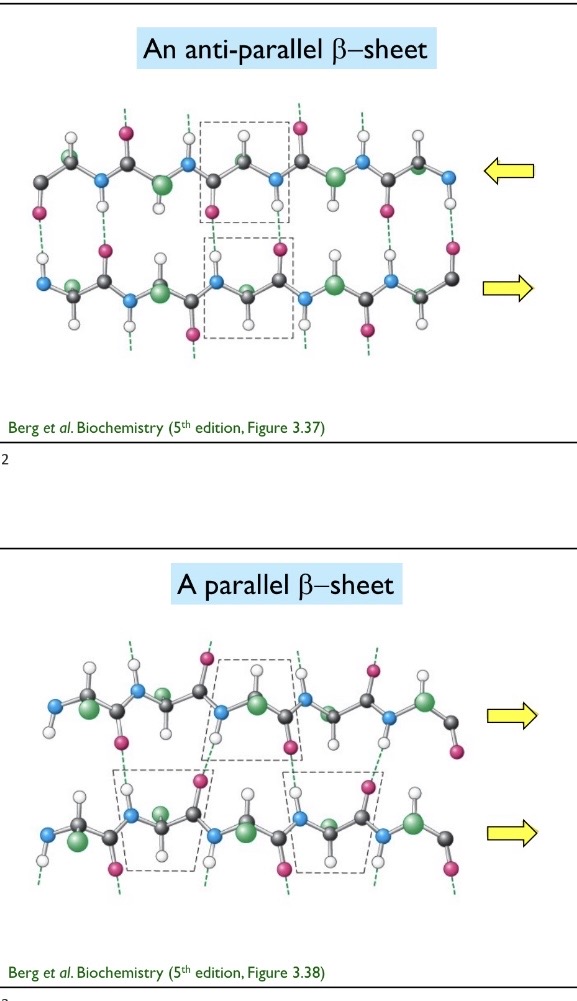
Parallel and anti parallel beta strands
Parallel beta strands are when both adjacent strands goes from N terminus to C terminus. Anti parallel beta strands are when proteins go in opposite direction. Parallel=zigzag and antiparallel=straight across
What defines a cell?
Interior of cell is separated from its environment, and the inside of the cell is chemically different from its environment.
Prokaryote
Bacteria and archaebacteria. No nucleus or membrane bound organelles. Genome is one circular molecule. Still need to do DNA replication, transcription, and translation
Micrometer
10^-6 meters
Nanometer
10^-9
Eukaryotic Nuclear Architecture
Has two layers that are contiguous with the endoplasmic reticulum. Encloses DNA and is the site of RNA production
Nucleolus
Site of ribosomal biogenesis (rRNA transcription and assembly)
Nucleoplasm
Filled with chromatin which are uncondensed chromosomes.
Nuclear Lamina
Proteins lining the inside of the nuclear envelope that provide structural support to the nucleus
Nuclear Pore
Regulates movement of ions and molecules between the nucleus and cytoplasm
Endomembrane System
Contains the rough ER, smooth ER, and golgi apparatus
Rough ER
Ribosomes are on the surface of the rough ER. Synthesize proteins that are destined for another cell organelle, the plasma membrane, or outside the cell. Proteins are inserted into the lumen, folded, and modified (ex: adding sugar group).
Smooth ER
Contiguous with the rough ER. Site of steroid and lipid synthesis. Detoxification and calcium ion storage.
Golgi Apparatus
Sorts, modifies, and packages proteins to their final destination. Proteins enter via vesicles on the “cis” side and leave outside the “trans” side. Vesicles are carried by motor proteins on cytoskeletal tracks. Lysosomes come from the golgi apparatus.
Lysosomes
Digestive enzymes that break down waste
Endocytosis
3 Types: Receptor mediated endocytosis, pinocytosis “cell drinking”, and phagocytosis. Matter is taken in via vesicles. The plasma membrane is pinched off and forms a vesicle.
Exocytosis
Vesicles carrying matter fuse with the plasma membrane and leave the cell.
Mitochondria
Site of cellular respiration and energy production. Site of steroid and heme synthesis. Contains ribosomes and circular DNA. Has a double membrane.
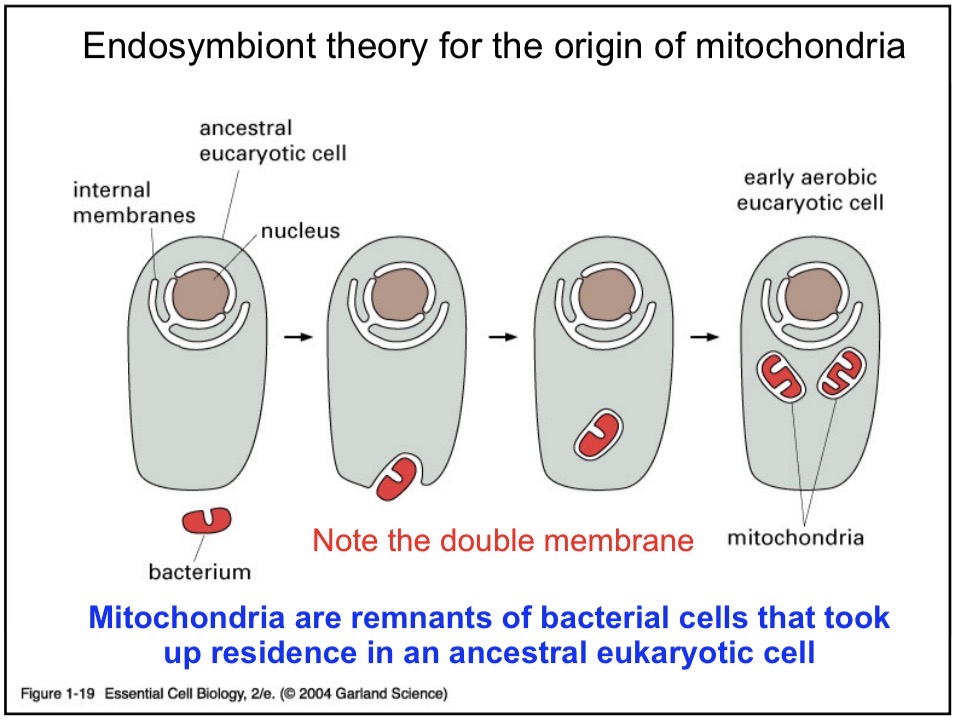
Endosymbiont Theory
Mitochondria are ancestral bacteria that got engulfed by an ancient eukaryotic cell. Developed a symbiotic relationship.
Plastids
Site of photosynthesis. Site of biosynthesis of fatty acid and starch synthesis. Have their own circular genome.
Actin Microfilaments
Cytoskeletal elements that help with cell shape and locomotion. Monomer: G-actin
Intermediate Filaments
Cytoskeletal elements that are fibrous proteins which provide support and make up nuclear lamina.
Microtubules
Cytoskeletal elements that are important for chromosome division and vesicle movement.
Motor Proteins
Ex: Kinesin. Drive movement down microtubule tracks
Six most common elements found in tissue
C, H, O, N, P, and S
Elements found at a lower level
Na, Mg, K, Ca, Mn, Fe, Co, Cu, Zn, Si, and Cl
Covalent Bond
Formed by the sharing of a pair of electrons between adjacent atoms. Strength 50-100 kcal/mol
Octet Rule
Tendency for atoms in stable molecules to have 8 electrons in their valence shell
Electronegativity
Attractive force an atomic nucleus exerts on electrons
Non-Covalent Bonds
Ionic interactions, hydrogen bond, van der waals, hydrophobic interactions
Ionic Interaction + Strength
Oppositely charged groups. Simple ions are elemental, such as Na+ or Cl-. Complex ions include R-COO- (carboxyl ion). 3-7 kCal
Salt Bridge
Between a R-COO- (carboxyl) and a R-NH3+ group (alkyl ammonium)
Hydrogen Bond + Strength
Between an electronegative atom and a hydrogen bond covalently bonded to it and another hydrogen atom bonded to another. 1-5 kCal
Van der Waals Interaction + Strength
Transient fluctuation induces a dipole in a neighboring atom. 0.5 to 1 kcal.
Hydrophobic Interaction
Nonpolar molecules group together, energetically favorable
Hydroxyl Group
Aldehyde
Keto
Carboxyl
Amino
Phosphate
Sulfhydryl
Condensation Reaction
Removing a water to form a bond
Hydrolysis
Inserting a water molecule to break a bond
Proteins
Involved in energy production, catalysis, cell structure, and regulation. Not involved in information or energy storage.
Zwitterion
A positive and negative charge on an amino acid
Special case amino acids
Cysteine, glycine, and proline
Disulfide Bridge
The —SH groups of two cysteine chain react to form a covalent bond between two sulfur atoms
Four macromolecules found in living things
Proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and lipids
Trans Configuration
Alpha Carbon and R groups are on opposite sides of a peptide bond
What types of interactions drive tertiary structures
Hydrophobic interactions, ionic interaction, hydrogen bonding, disulfide bridges
Denaturation
Disrupts the tertiary and secondary structure of a protein and destroys the protein’s biological functions
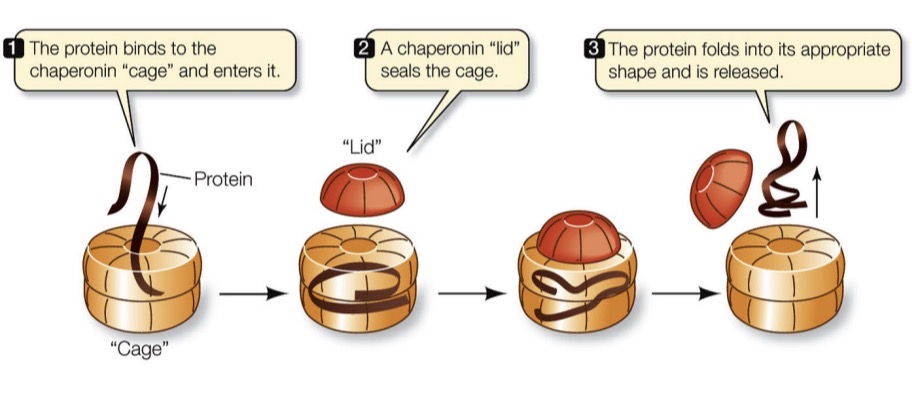
Chaperonins
A protein that helps other proteins fold correctly. Step 1: Protein binds to the “cage” and enters it. Step 2: Chaperonin “lid” seals the cage
Induced Conformational Change of Protein Examples
Metal binding protein/metal, enzyme/substrate, hormone receptor/hormone, transcription factor/DNA
Prion Diseases
Kuru, Creutzfeldt-Jacob Disease, Mad Cow Disease, Scrapies
What makes the alpha helix rich version convert to the beta version
Normal endogenous PrP^C. PrP^SC converts PrP^C into a mutated version. PrP^SC comes from a random mutation or inoculation to PrP^SC
Sickle Cell Disease
Glutamic Acid to Valine substitution in the Beta hemoglobin protein. Result is the change in the shape of red blood cells
Insulin
Disulfide bridge holds together 2 polypeptides (quatenary structure) and is also within the same polypeptide chain.
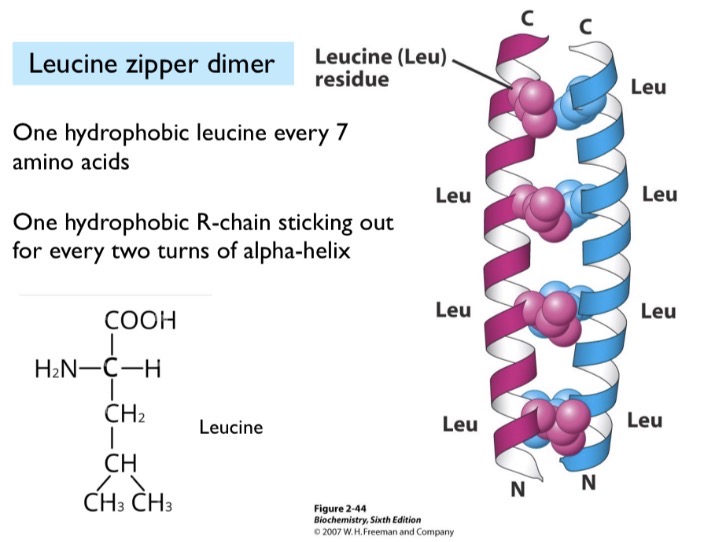
Leucine
Held together by hydrophobic interactions. One hydrophobic leucine held together every 7 amino acids (two turns).
B Cell
Contains antigen and antigen receptor. Antigen binds to antigen receptor, activating the B cell. The B cell then proliferates (multiple copies of B cell) and differentiates (becomes unique) and releases antibodies.
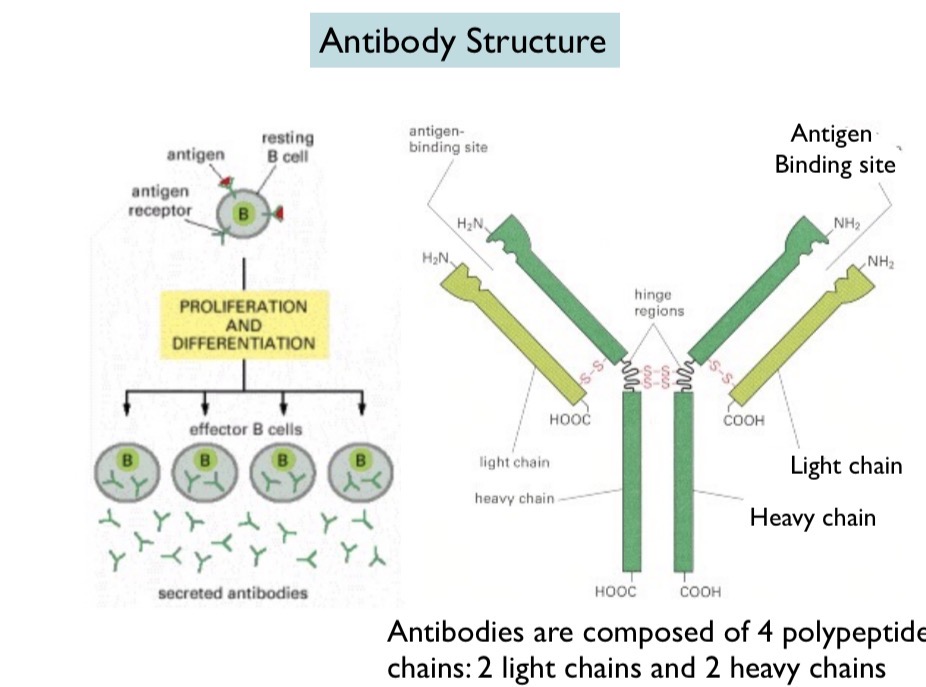
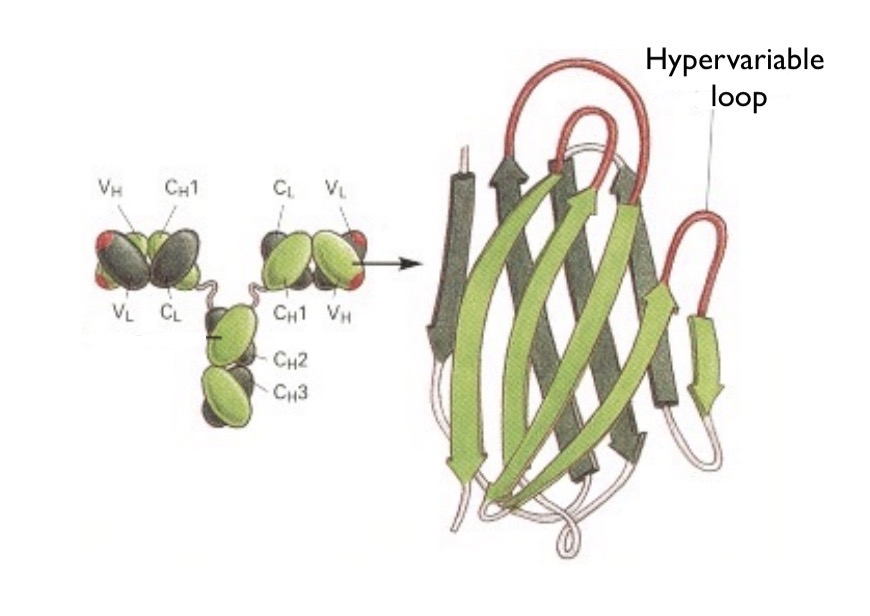
Antibody Structure
Made up of 4 chains: two heavy chains and two light chains. Disulfide bonds hold together the heavy and light chains and the hinge regions in the heavy chains
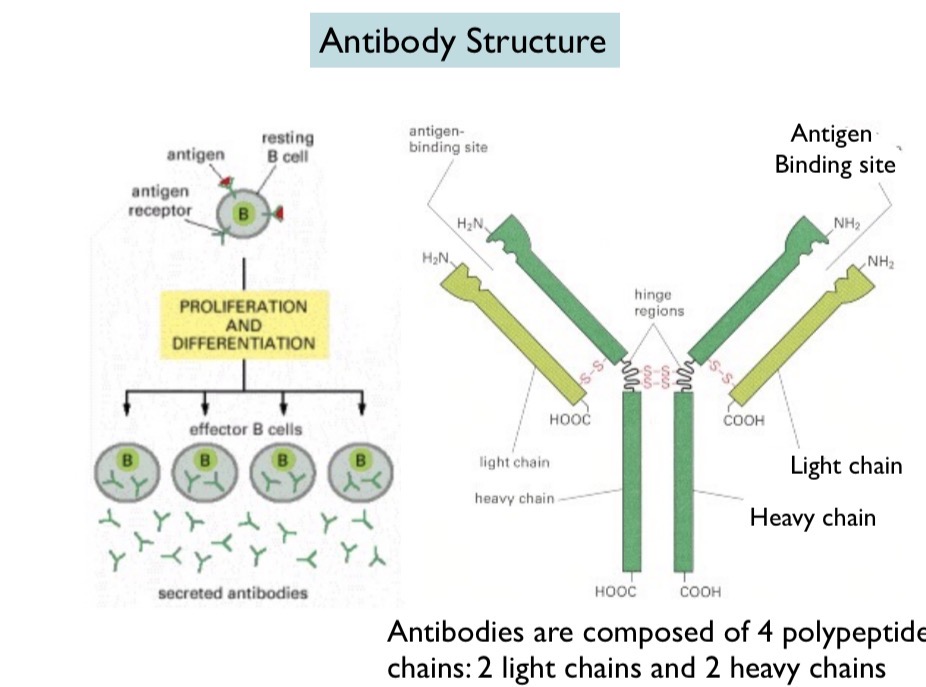
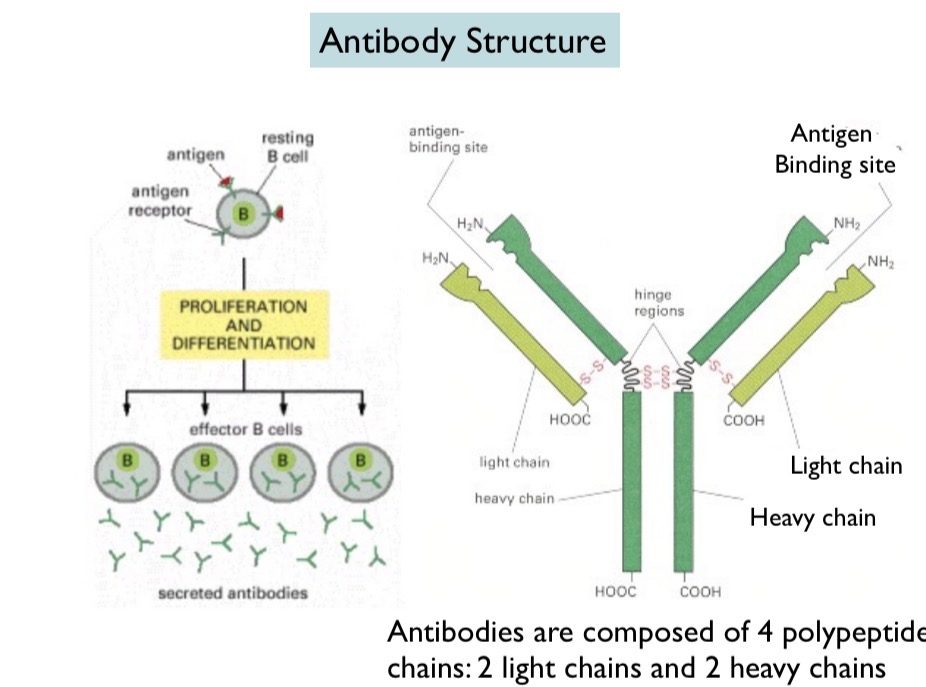
What do both heavy and light chains contain?
Variable region and constant region. The variable region is unique for each B cell and is on the tips of the Y. The hypervariable region is where the cell binds. The constant region is on the Stem of the Y and is the same for antibodies of the same class.
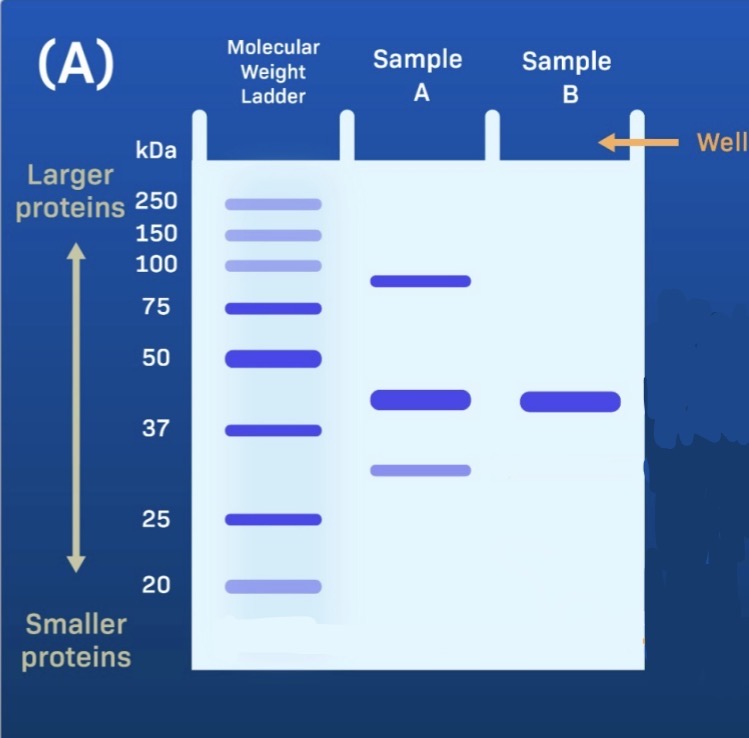
Gel Electrophoresis
Separation by size. Smaller proteins move farther and larger proteins move less. Compare to the molecular weight ladder.
Beta Turn (AKA Hairpin Turn)
A tight turn of ~4 amino acids. An example of this is a sucrose porin, which is made of beta sheets and hairpin turns.
Hyper variable Region
Where antigens bind. Created through beta sheets with loops. Lots of variation within loops which make it hyper variable
Properties of Proteins that can be used to seperate
Solubility, size, charge, hydrophobicity, affinity
Protein Purification
Isolating a protein from a mixture based on charges.
Assay
Controlled experiment used to measure a biological thing or activity
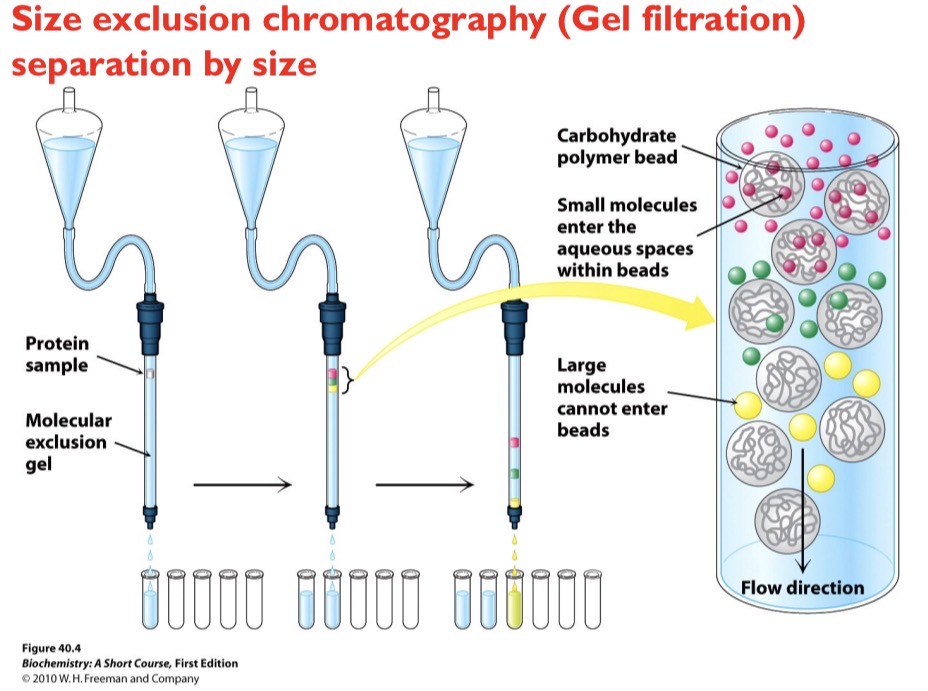
Size Exclusion Chromatography
Separation by size. Smaller molecules become trapped in porous beads while larger molecules bypass the pores and elute from the column first.
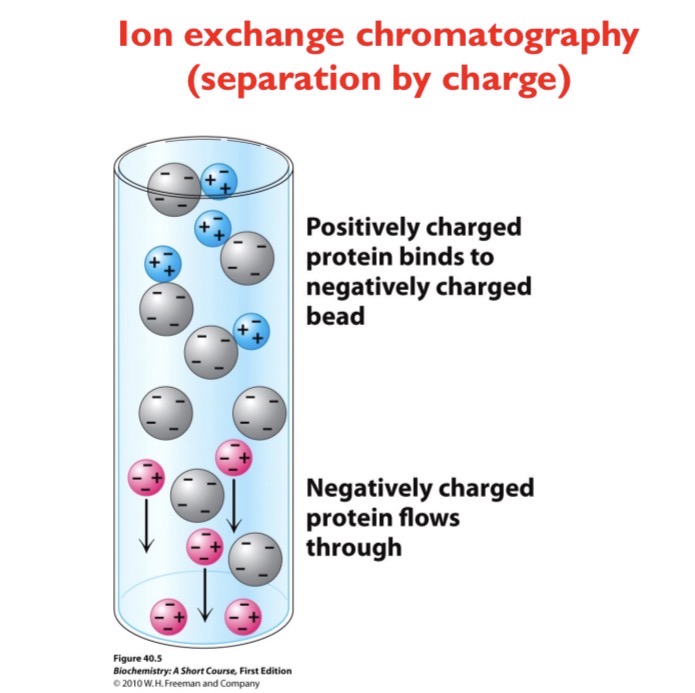
Ion Exchange Chromatography
Separation by charge. A positively charged protein will bind to a negatively charged bead while a negatively charged protein will flow through
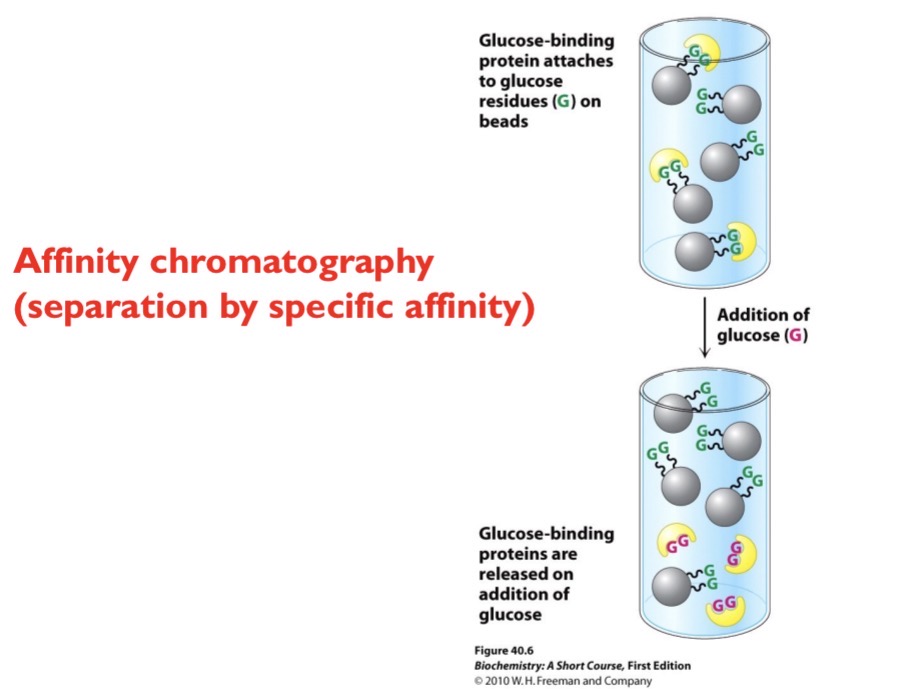
Affinity Chromatography
Separation by specific affinity. Beads are attached to a specific molecule (ex glucose). Any protein that can bind to that specific molecule will get stuck. Then, you add more of that molecule (ex glucose) so the protien binds to the excess molecule added.
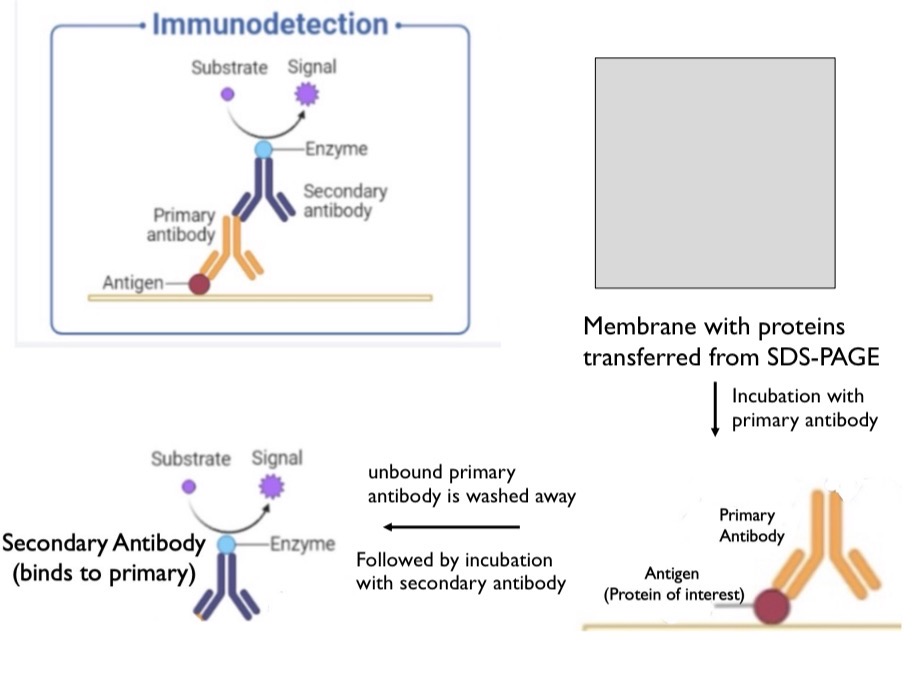
Western Blot (What it is and the process of it)
An optional step after SDS PAGE to identify a specific protein. Used to confirm the protein band is a protein of interest and not just another protein of the same size. Press gel against membrane and the proteins will move from the gel to the membrane. A primary antibody will be mixed with this membrane and bind to the antigen (your protein of interest). Unbound antibodies will be washed away. Then, a secondary antibody will bind to the primary antibody and send a signal. Secondary antibody can bind to the constant regions on the primary antibody.
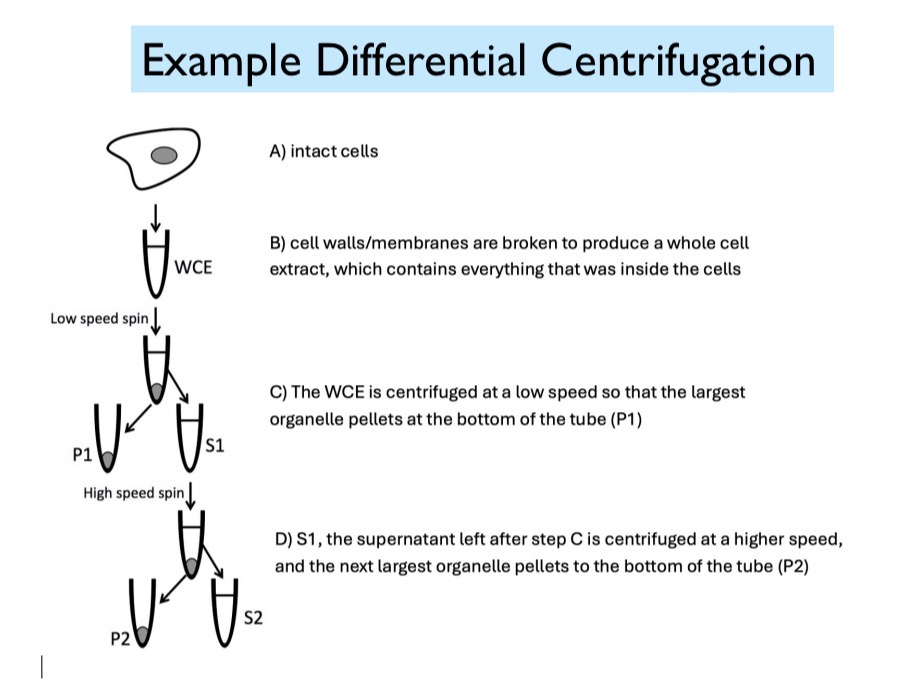
Differential Centrifugation
Start with intact cells. (1) These intact cells are then broken to produce a whole cell extract, which contains everything that was inside the cells. (2) After a low-speed spin, the heaviest organelles pellet at the bottom of the tube. (3) The supernatant and pellet are separated. (4) The supernatant is then centrifuged at a higher speed and the next largest organelle pellet to the bottom of the tube.
Metabolism
Network of biochemical pathways with each reaction catalyzed by an enzyme
Gibb’s Free Energy
Delta G<0, the reaction proceeds spontaneously. Delta G>0, energy has to be put into the energy to proceed
Kinetics
Rate at which a reaction will occur
Catalysts
Substances that speed up a reaction without being permanently altered by a reaction
Catalysts
Substances that speed up a reaction without being altered by the reaction. Change the kinetics of a reaction, not the thermodynamics
Enzymes
Specific biological catalysts, typically proteins but can be RNA. Lower the activation energy for a biochemical reaction. Facilitate the formation of a transition state
Active Site
3D cleft or crevice where enzyme and substrate interact, and catalysis occurs. Typically a small part of the enzyme. E+S —> ES—> ES* (Transition state) —> EP —? E+P.
Active Site
Unique microenvironments where substrates are bound by multiple weak interactions. 1) Orients substrates 2) Physically strains substrates 3) Adding chemical charges to substrates
Lock and Key Model
Substrate fits exactly into enzyme
Induced Fit Model
When the substrate binds, it induces a shape change in the enzyme, so the active site fits the substrate more precisely during the reaction
Michaelis-Menten Kinetics
V0=Vmax*(S)/(S+Km)
Vmax
Maximum initial velocity of the reaction at high substrate concentrations
Km
How efficiently an enzyme binds to a substrate and converts it to a product. Measure of the substrate concentration required for significant catalysis to take place. Lower Km= maximal catalytic efficiency at low substrate concentration. Unique for each enzyme/substrate pair
Competitive Inhibition
Substrates binds to enzyme at active site. Km increases and Vmax stays the same
Noncompetitive inhibition
Enzyme binds to substrate at an allosteric site and changes the shape of the enzyme, so the substrate can no longer bind to the active site. Km stays the same and Vmax decreases
Lipid
Made up of hydrocarbons, making them hydrophobic. Form macromolecular aggregates in aqueous environments through hydrophobic interactions
Roles of lipids in biology
Major component of the plasma membrane, energy source and energy storage, signaling molecules (ex: steroid hormones), structural/architectural
3 Types of Lipids and Function
Triglycerides (energy storage), phospholipids (membranes), steroids (membranes and signaling)
Triglycerides
Made up of 2 components: 1) Glycerol 2) 3 Fatty Acids
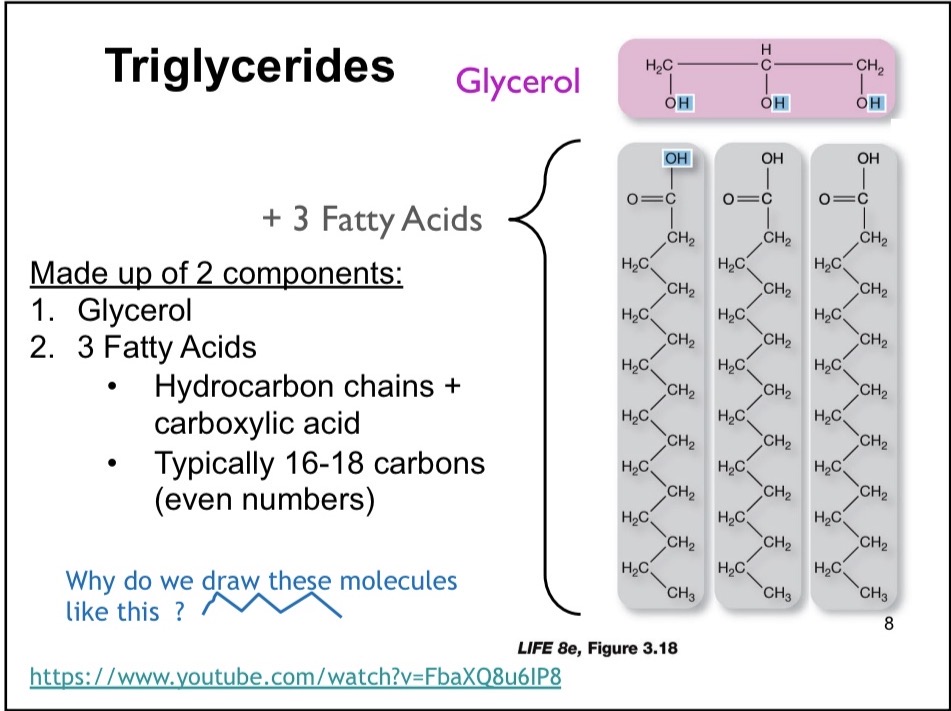
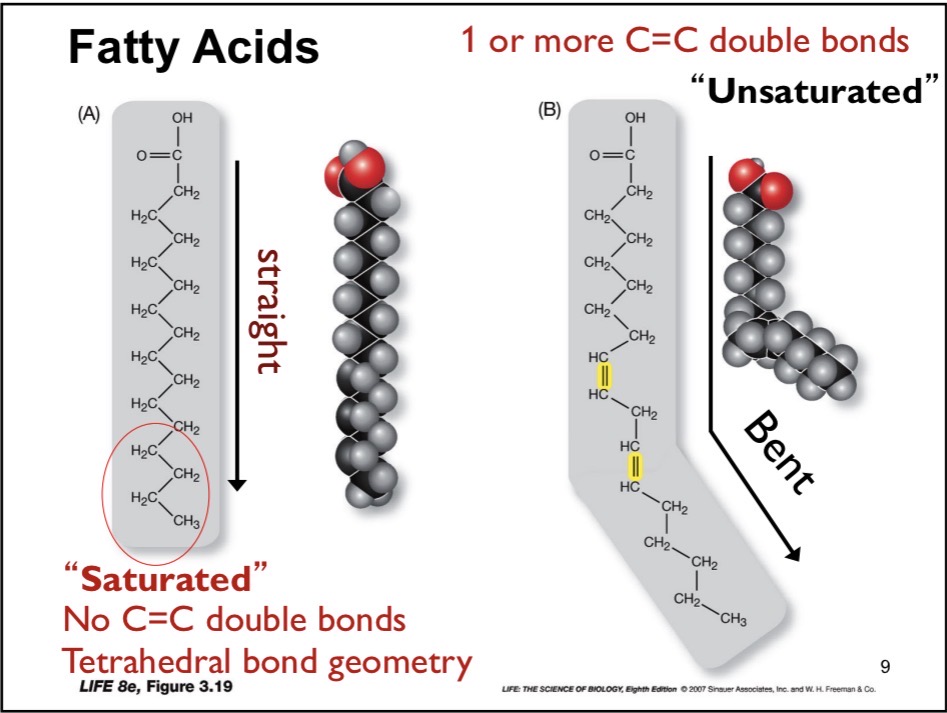
Fatty Acid
Hydrocarbon chains + Carboxylic acid. Typically 16-18 carbons (even numbers)