Exam 3 Study Guide: Cognition, Language, and Intelligence
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
Cognition
Mental activity associated with obtaining, converting, and using knowledge.
Thinking
Mental activity associated with coming to a decision, reaching a solution, or forming a belief.
Concepts
Mental representations of categories of objects, situations, and ideas that belong together based on their central features or characteristics.
Prototypes
The ideal or most representative example of a natural concept.
Hierarchies of Concepts
Categories organized from broadest to most specific, including superordinate, midlevel, and subordinate levels.
Superordinate
The broadest category that encompasses all objects in a group.
Midlevel
The basic level of categorization most often used in everyday experiences.
Subordinate-level
The narrow and specific level of categorization.
Mental Images
Descriptions of images from the 'mind's eye' that may be mentally manipulated in three dimensions.
Biology of Cognition
The study of how brain regions are involved in cognitive processes.
Left frontal lobe
Critical for a broad array of higher cognitive functions, processing emotions, controlling impulses, and making plans.
Broca's area
A language center in the brain associated with speech production.
Wernicke's area
A language center in the brain associated with language comprehension.
Formal Concepts
Mental representations of categories created through rigid and logical rules or through features.
Natural Concepts
Mental representations of categories resulting from experiences in daily life.
Availability Heuristic
A decision-making strategy that predicts the likelihood of something happening based on how easily a similar type of event from the past can be recalled.
Recency
An example of the availability heuristic where recent events are more easily recalled.
Frequency
An example of the availability heuristic that involves comparing the number of occurrences of different items.
Familiarity
An example of the availability heuristic based on personal experiences with similar events.
Vividness
An example of the availability heuristic where more vivid or dramatic events are more easily recalled.
Representativeness Heuristic
decision-making strategy that evaluates the degree to which the primary characteristics of a person or situation are similar to our prototype of that kind of person or situation.
Language
a system for using symbols (words, gestures, and sounds) to think and communicate.
Phonemes
the units of sound that serve a basic building block for all words.
Morphemes
consists of one or more phonemes, bringing meaning to a language.
Grammar
refers to the rules associated with both word and sentence structure.
Syntax
refers to collection of rules dictating where words and phrases should be placed.
Semantics
represents the rules used to bring meaning to words and sentences.
Pragmatics
social rules that help organize activity.
Functional Fixedness
a barrier to problem solving that occurs when familiar objects can only be imagined to function in their usual way.
Problem Solving
the variety of approaches that can be used to achieve our goals.
Infants' Phoneme Recognition
Infants between 6 and 8 months can recognize all phonemes from all languages, but diminishes at about 10 months.
Basic Elements of Language
Know the different components of language (ex: phonemes, morphemes, grammar, syntax, semantics, pragmatics) and know them in the order of most specific to most general.
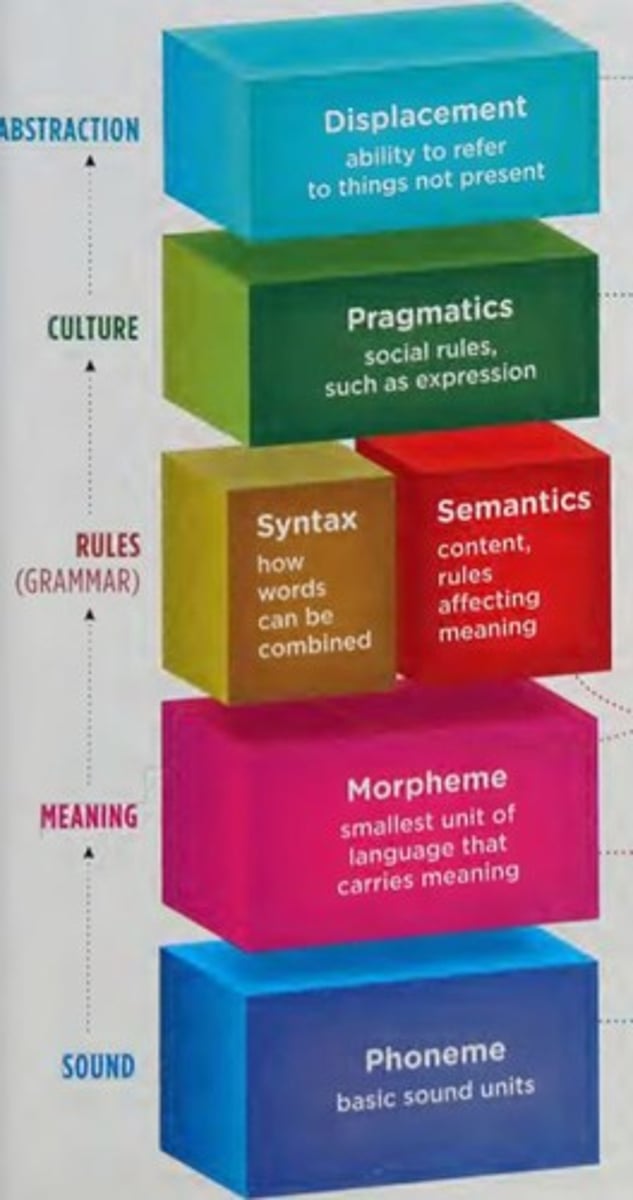
Example of Morphemes
Example: 'unimaginable' has 3 morphemes: un, imagine, able.
Grammar Components
tells how words are made from sounds, how sentences are formed with words, where to place punctuation, and which word tense to use.
Syntax Function
Guides both word choice and word order, providing consistency in sentence organization.
Semantics Context
Also refers to the context in which words appear.
Pragmatics in Social Interactions
Language used in social interactions, which are governed by certain norms and expectations.
Obstacles in Problem Solving
Obstacles that block path to solution.
Initial State to Goal State
The process of moving from the initial state to the goal state in problem solving.
Creative Use of Objects
This fixation can stop us from finding new, creative use for objects.
Example of Functional Fixedness
Ex: a tear in your pants occurs and you have tape and staples to fix it.
Intelligence
one's innate ability to solve problems, adapt to the environment, and learn from experiences
Validity
degree to which an assessment measures what it intends to measure
Reliability
ability of a test to provide consistent, reproductive results
Fairness
are these test differences
Cultural-fair intelligence tests
assessments are designed to minimize cultural bias
Phenotype
observable expression or characteristics of one's genetic inheritance
Epigenetics
field that examines the process involved in the development of phenotypes
Synaptic Pruning
Unused synaptic connections estimated
Language Explosion
At age of 5, most have amassed a vocabulary of approx. 13,000 words
30 million word gap
1990s, researchers published a study suggesting that the amount of language spoken at home correlates with socioeconomical status (SES)
Sequence of Language Acquisition
Across cultures, 'vocabulary explosion' tends to occur around 2 to 3 years of age
Piaget's concepts
specifically schema, assimilation, and accommodation
Piaget's levels of cognitive development
sensorimotor, preoperational, concrete operational, formal operational
Vygotsky's theories
differed from Piaget's theories
Cross-sectional method
a research method design used in developmental psychology
Longitudinal method
a research method design used in developmental psychology
Cross-sequential method
a research method design used in developmental psychology
Basic emotions
set of emotions that are universally recognized
Paul Ekman
psychologist known for research on emotional expressions in America and New Guinea
Positive psychology
emphasizes the study of positive aspects of human life
Need for Achievement
a psychological need to accomplish goals
Need for Power
a psychological need to influence or control others
Facial Feedback Hypothesis
suggests that facial expressions can influence emotional experiences
Amygdala
a part of the brain related to emotion
Abraham Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
a theory in psychology that prioritizes human needs
Theories of emotion
James-Lang, Cannon-Bard, Schachter-Singer, Cognitive Appraisal
Negative emotions
have survived throughout our evolutionary history and are more prevalent than positive emotions