(z-Scores, Normal Curve, Probability, and Sampling Techniques)
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Z- Score
- Number of standard deviations that a score is
above (or below, if it is negative) the mean of its
distribution
- It is an ordinary score transformed so that it better
describes the score’s location in a distribution
-standardizing a score to a predetermined value (μ= 0, σ= 1)
STANDARDIZED DISTRIBUTION
- is composed of scores that have been transformed
to create predetermined values for μ and σ
- used to make dissimilar distributions comparable
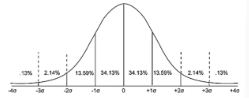
THE NORMAL CURVE
- specific, mathematically defined, bell-shaped
frequency distribution that is symmetrical and
unimodal; distributions observed in nature and in
research commonly approximates it
- also called the Gaussian Distribution (Carl Friedrich
Gauss)
THE NORMAL CURVE TABLE
- table showing percentages of scores associated
with the normal curve
- also called the z Table
PROBABILITY
- the extent to which an event is likely to occur as
determined by the the fraction or proportion of
successful outcomes to all the possible outcomes
- outcome – term used in discussing
probability for the result of an experiment
(or almost any event)
-what connects the population to the sample
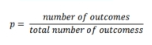
FRACTION:
Probability of getting Ace of Spade in a deck of card
p(ace of spade)= 1/52
PERCENTAGE:
Probability of getting three dots in a dice
p(3)= 16.67%
DECIMAL/PROPORTION:
Probability of getting a head in heads or tails
p(heads)= 0.50
RANDOM SAMPLING
- requires that each individual in the population has
an equal chance of being selected
- a sample obtained by this process is called simple
random sample
SAMPLING WITH REPLACEMENT
- keeping the probabilities from changing from one
selection to the next by returning each individual to
the population before you make a selection
ADDITION RULE
- “or rule”
- Is used when there are two or more mutually
exclusive outcomes
Example:
- Heads or tails on a single flip or a coin
- Getting a 3, 4, 5 in a single roll of dice
- You want to pick a random student from your
university. With 30% are seniors and 20% are juniors,
what is the probability of getting either a senior or a
junior?
MULTIPLICATION RULE:
- “and rule”
- It is used when figuring probability of getting both
of twoo (or more) independent outcomes
Example:
- Getting a head on the second flip of the coin?
- Getting a 5 on two throws of a dice?
- Getting two questions correct on a 4-option
multiple choice exam?
SAMPLING FRAME
- Specific list of the members of the population in
order to select a subset of that population
ELEMENT
Basic unit that
represents whatever is
Being sampled and
from which
survey data are
to be gathered
PROBABILITY SAMPLING
- uses randomization to make sure that every
element of the population gets an equal chance to
be part of the selected sample.
SIMPLE RANDOM SAMPLING
- Participants has an equal chance of getting
selected to be the part sample
STRATIFIED RANDOM SAMPLING
- divides the elements of the population into small
subgroups (strata) based on the similarity in such a
way that the elements within the group are
homogeneous and heterogeneous among the
other subgroups formed.
CLUSTER SAMPLING
- The entire population is divided into clusters or
sections and then the clusters are randomly
selected. All the elements of the cluster are used for
sampling.
Single Stage
- entire cluster is selected
randomly for sampling.
Two Stage
– first,
we randomly select clusters and then from
those selected clusters we randomly
select elements for sampling
SYSTEMATIC SAMPLING
- a probability sampling method where the elements
are chosen from a target population by selecting a
random starting point and selecting other
members after a fixed ‘sampling interval’
MULTISTAGE SAMPLING
- It is the combination of one or more methods
described above.
NON-PROBABILITY SAMPLING
- a sampling technique where the samples are
gathered in a process that does not give all the
individuals in the population equal chances of
being selected.
CONVENIENCE SAMPLING
- The samples are selected based on the availability.
PURPOSIVE SAMPLING
- Sampling technique that is based on the intention
or the purpose of study
QUOTA SAMPLING
- sampling technique wherein the assembled
sample has the same proportions of individuals as
the entire population with respect to known
characteristics, traits or focused phenomenon.
REFERRAL/SNOWBALL SAMPLING
- this technique is used in the situations where the
population is completely unknown and rare