Histology- special senses
1/53
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
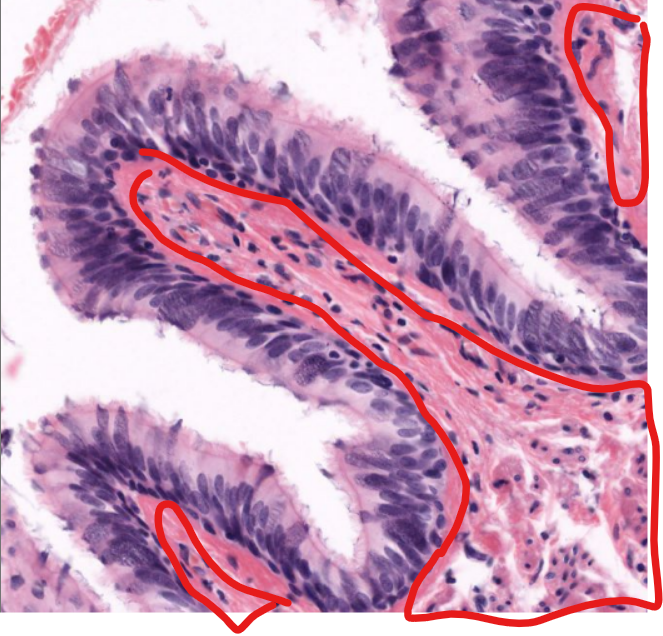
tissue type
respiratory epithelium, aka pseudostratified columnar epithelium
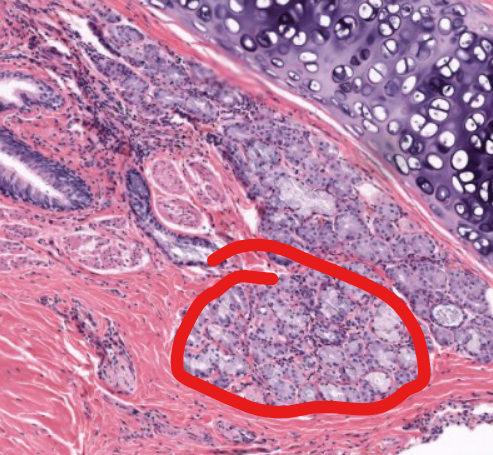
tissue type
sero-mucous glands of the lungs
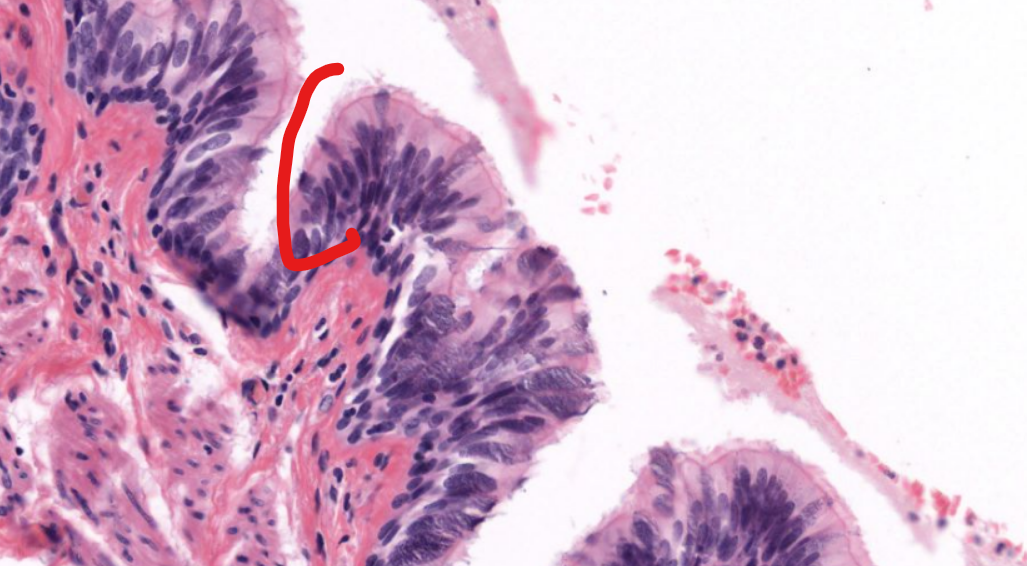
layer
lamina propria
the layer of connective tissue that is under respiratory epithelium’s basement membrane
made of loose irregular CT
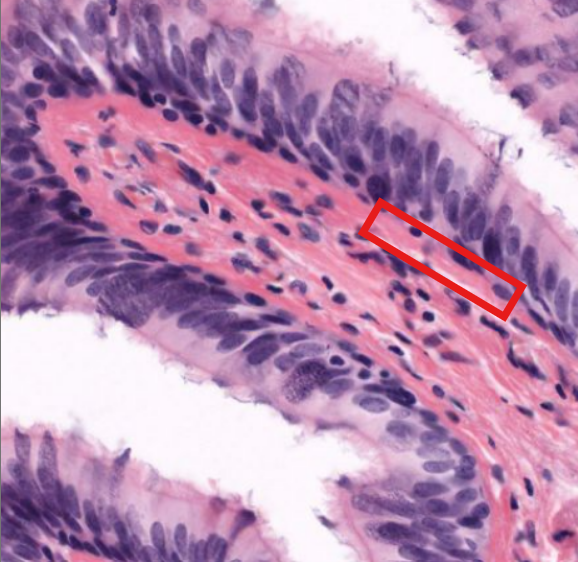
layer
basement membrane
supports respiratory epi
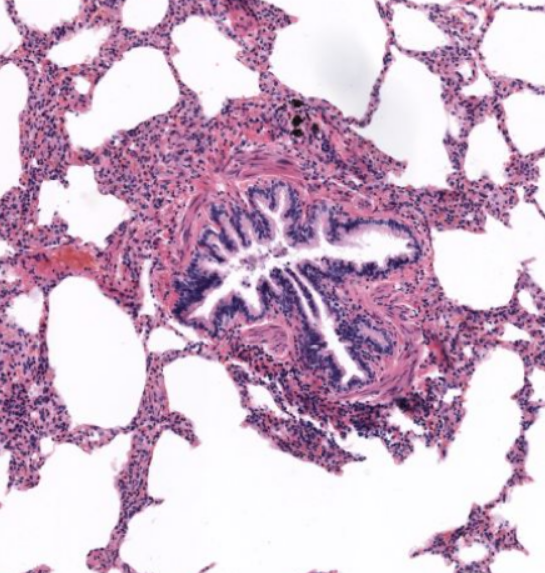
structure
terminal bronchiole-
conducting airway, has simple columnarepi
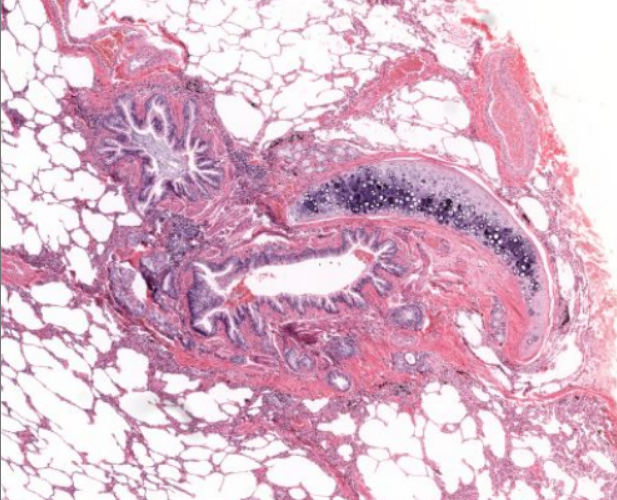
structure
primary bronchiole-
notice the bronchial cartilage
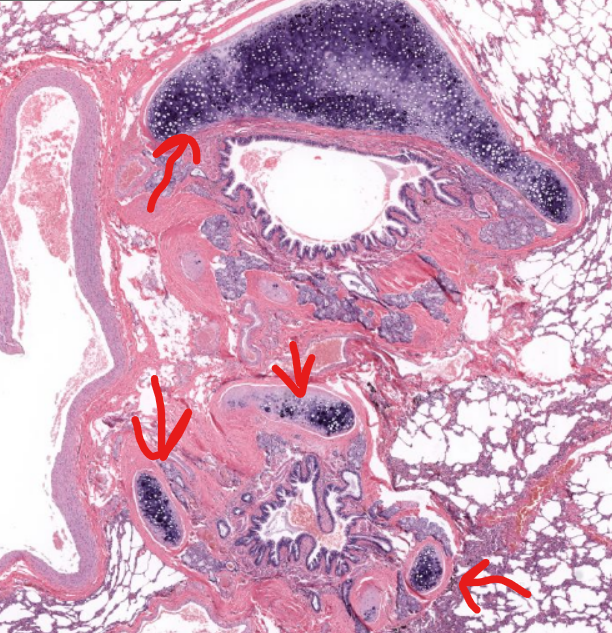
tissue type/structure
bronchiole cartilage-
found next to primary bronchi (just branched off of trachea)
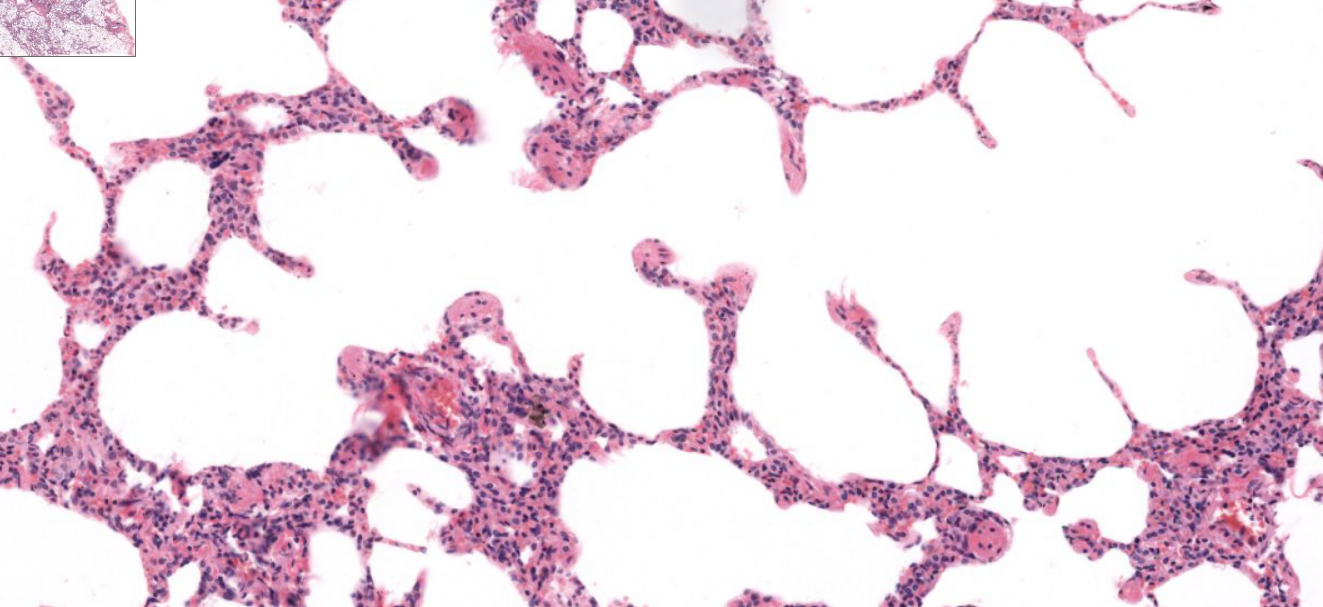
structure
alveoli-
blind ending sacs, location of gas exchange within lungs
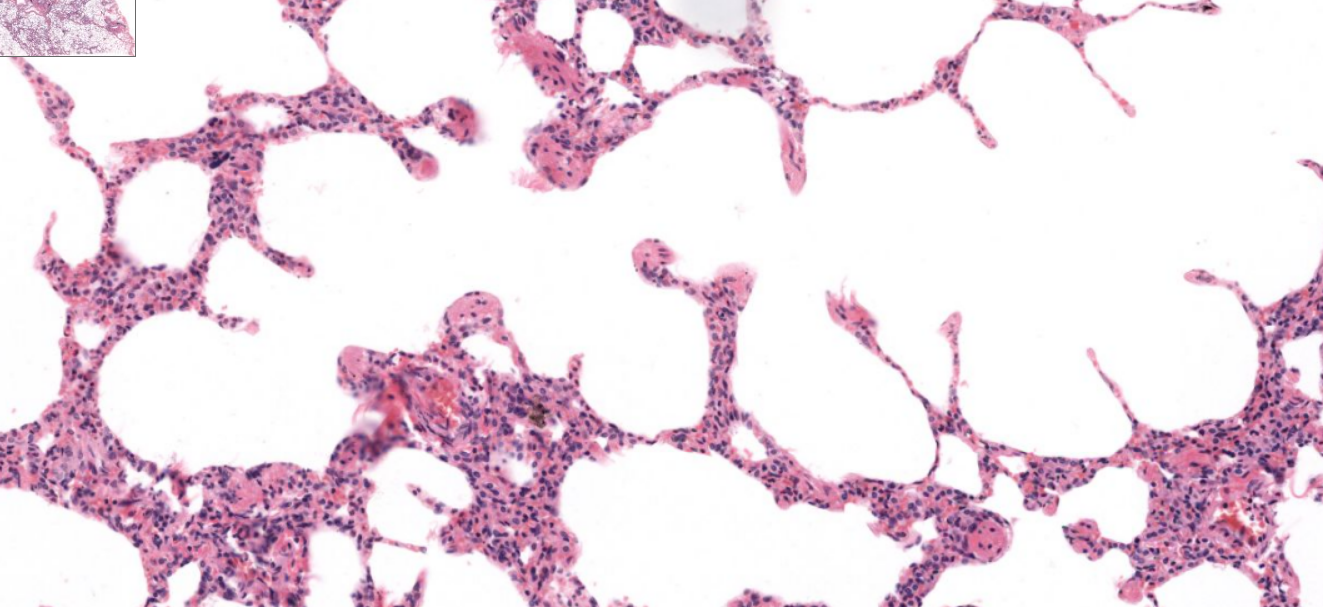
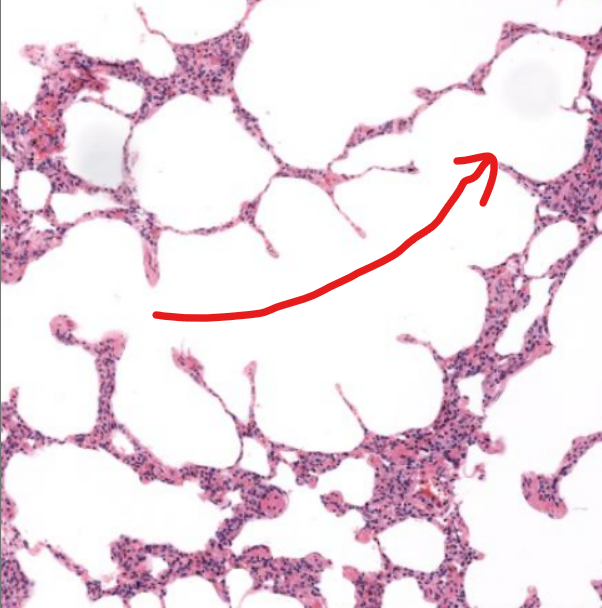
structure
alveolar sacs- spherical-like spaces where multiple alveoli connect to
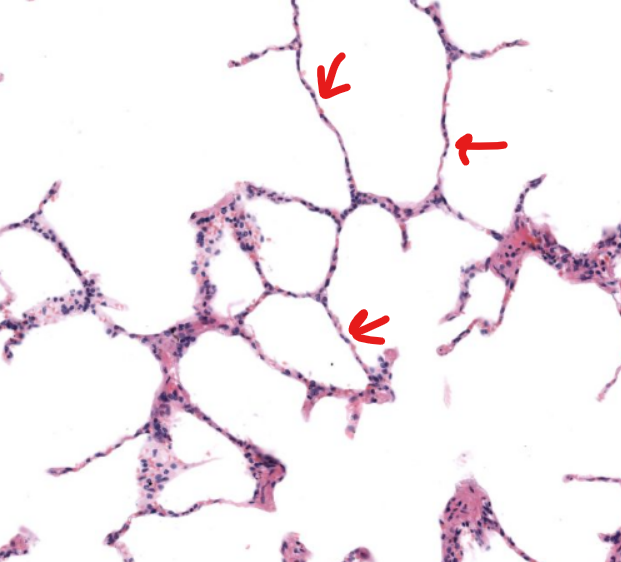
structure
alveolar duct-
arise from bronchioles and are passageways lined with alveoli
tissue type
type 1- simple squamous epi
gas exchange occurs here
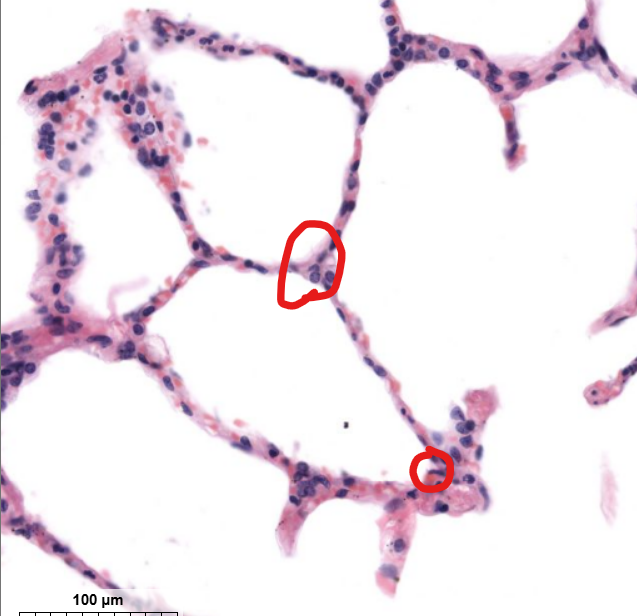
tissue type
alveolar type 2 cells-
secrete surfactant
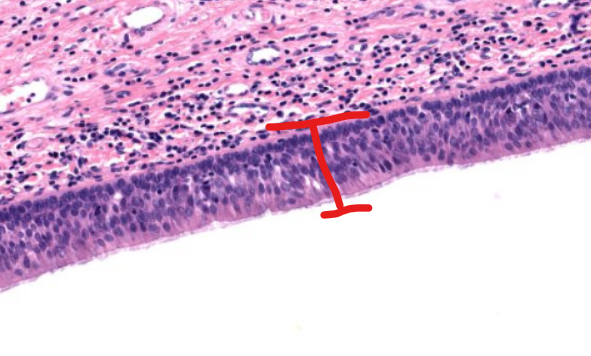
tissue type (on epiglottis)
respiratory epithelium
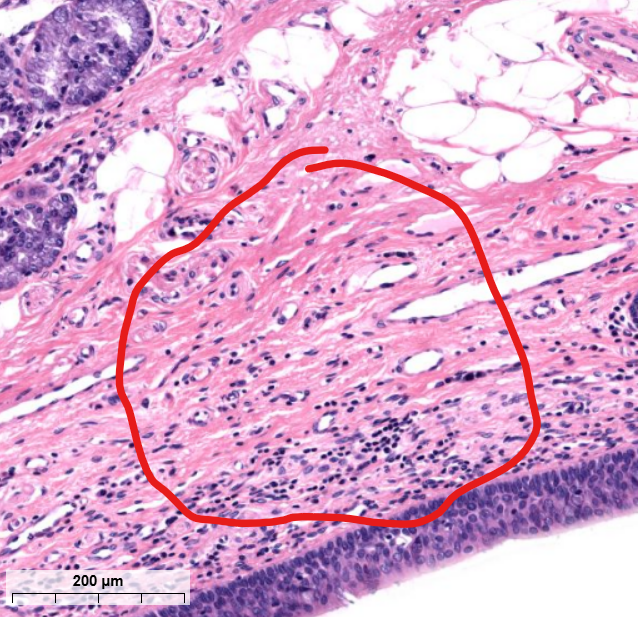
tissue type/layer?
lamina propria-
supporting respiratory epi
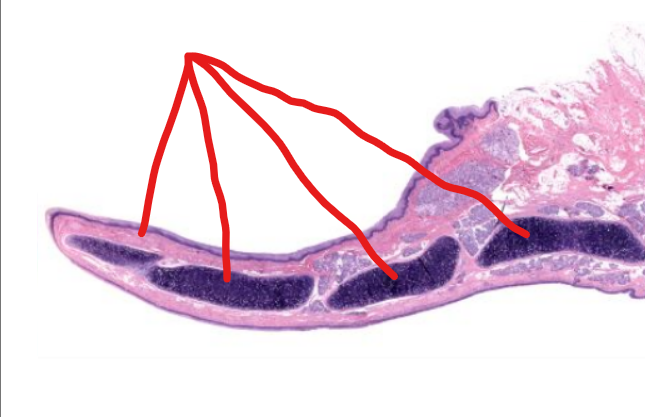
tissue type
elastic cartilage-
provides support to epiglottis
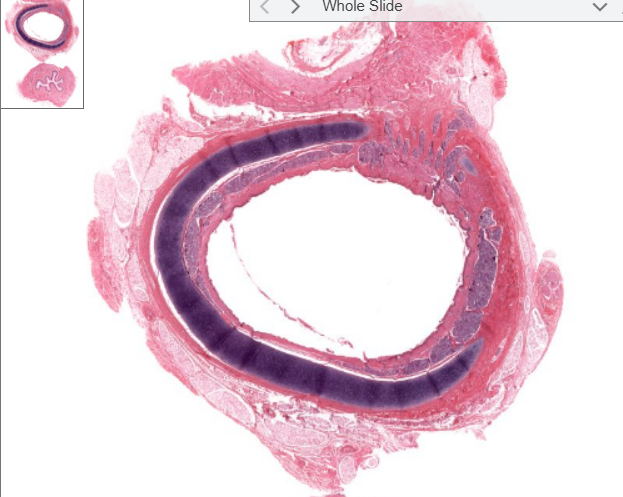
structure
trachea
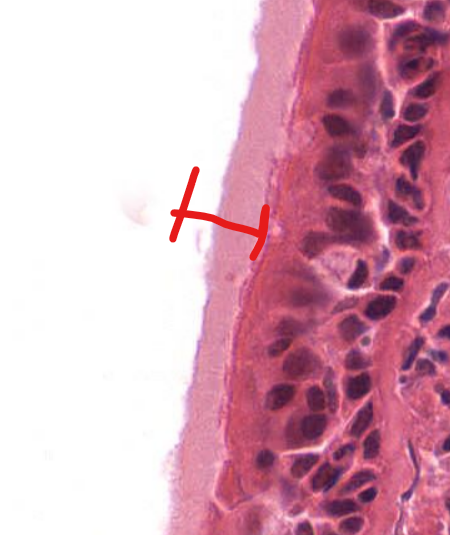
structure
cilia of respiratory epithelium
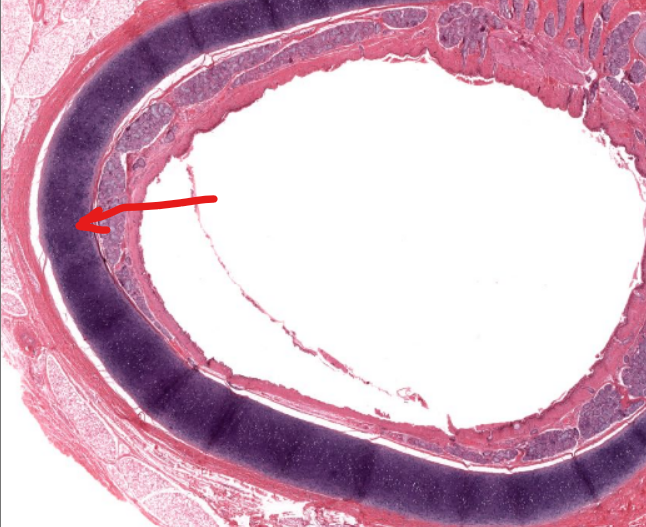
structure
tracheal cartilage-
made of hyaline cartilage, is open on the posterior aspect to allow the esophagus to expand
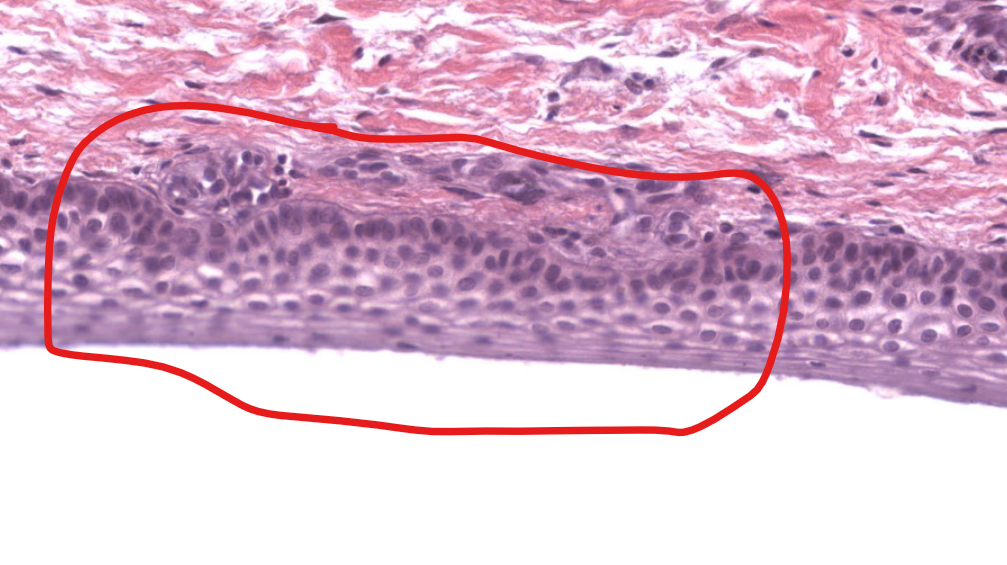
tissue type
stratified squamous epi, non-keratinized
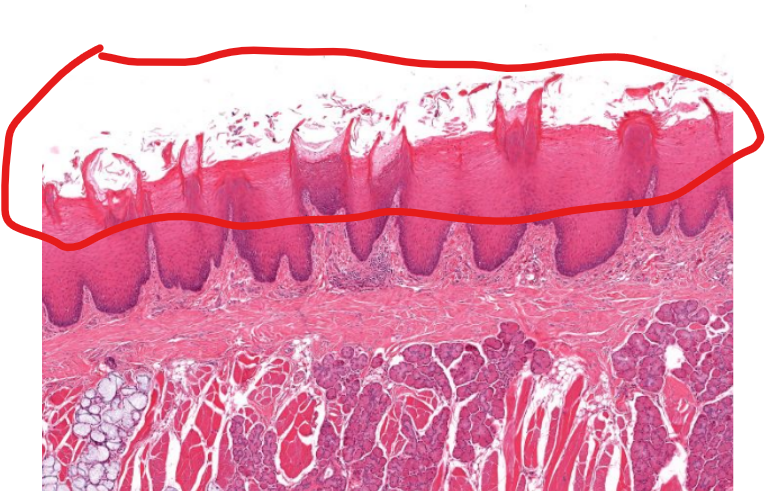
structure
filiform papillae-
“flam-like”, serve to move food on the tongue
do not contain taste buds
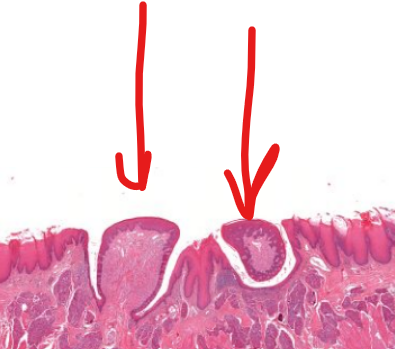
structure
circumvallate papillae-
8-12 dome shaped structures in a V shape on tongue
largest in size and smallest in number papillae on the tongue
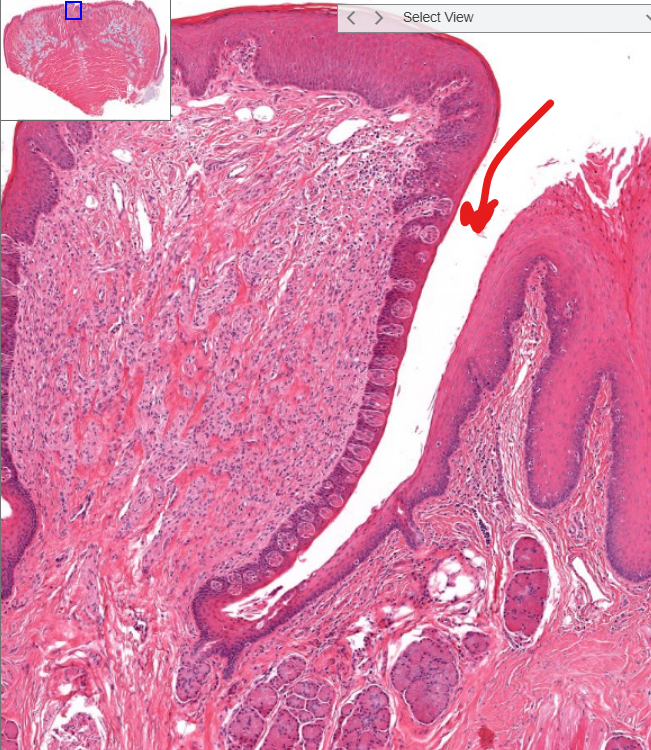
structure
furrow-
“moat” around circumvallate papillae, which receives saliva from minor salivary glands
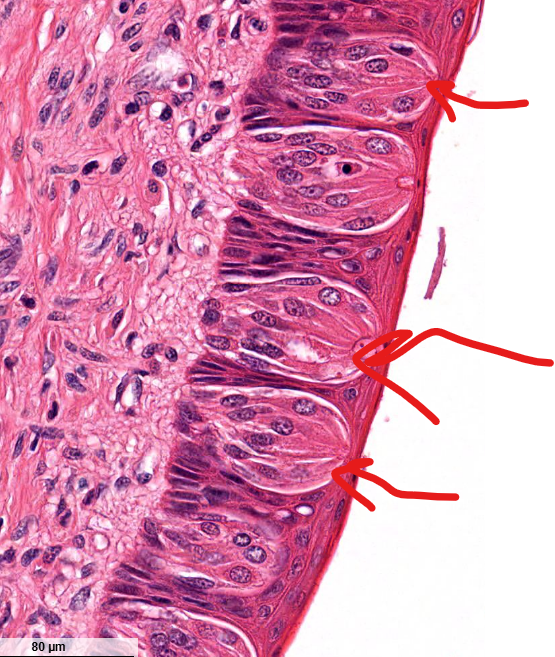
structure
taste buds-
found on the “side” of the moats, contain cells with taste receptors
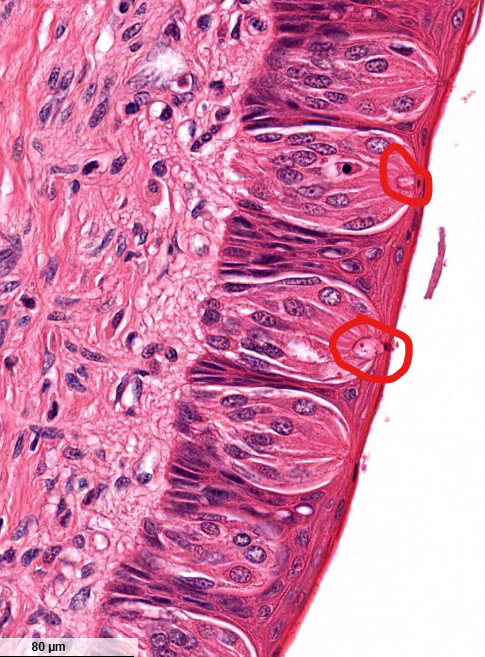
structure
taste pore
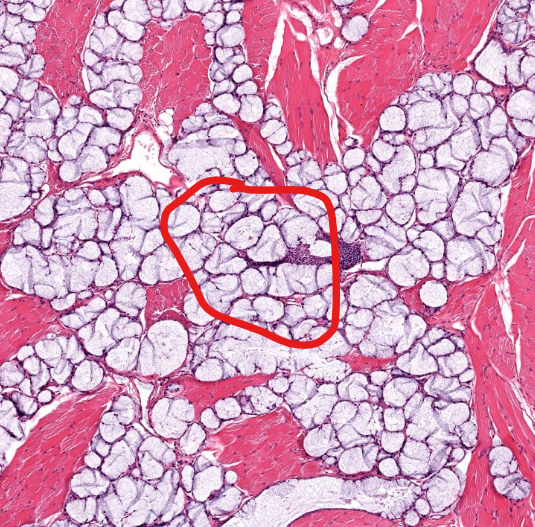
structure
mucous salivary gland
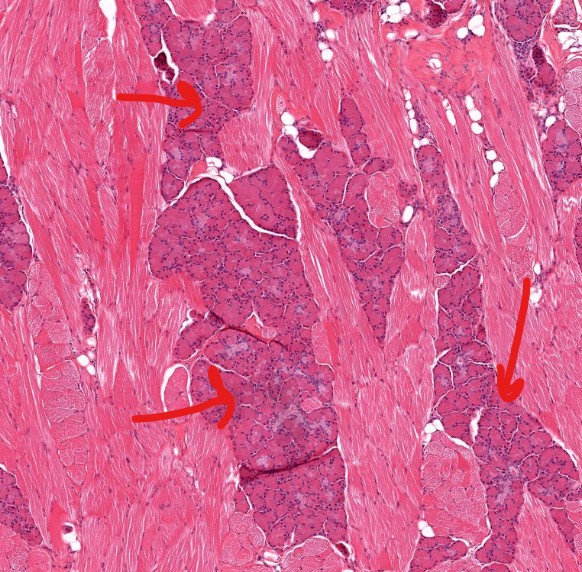
structure
serous salivary gland
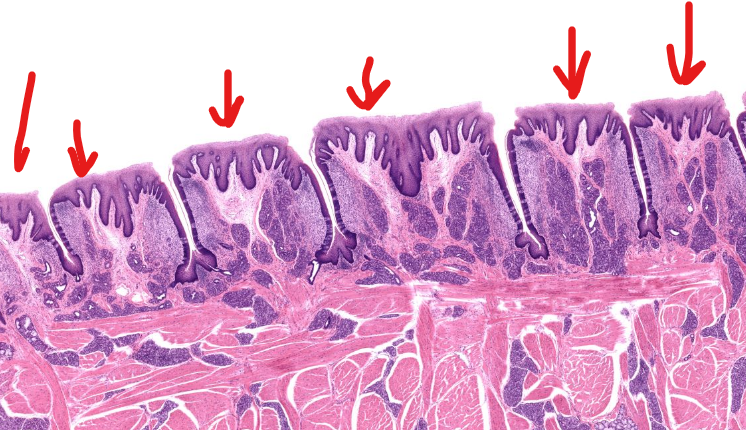
structure
foliate papillae-
parallel ridges on the lateral tongue, separated by deep moats
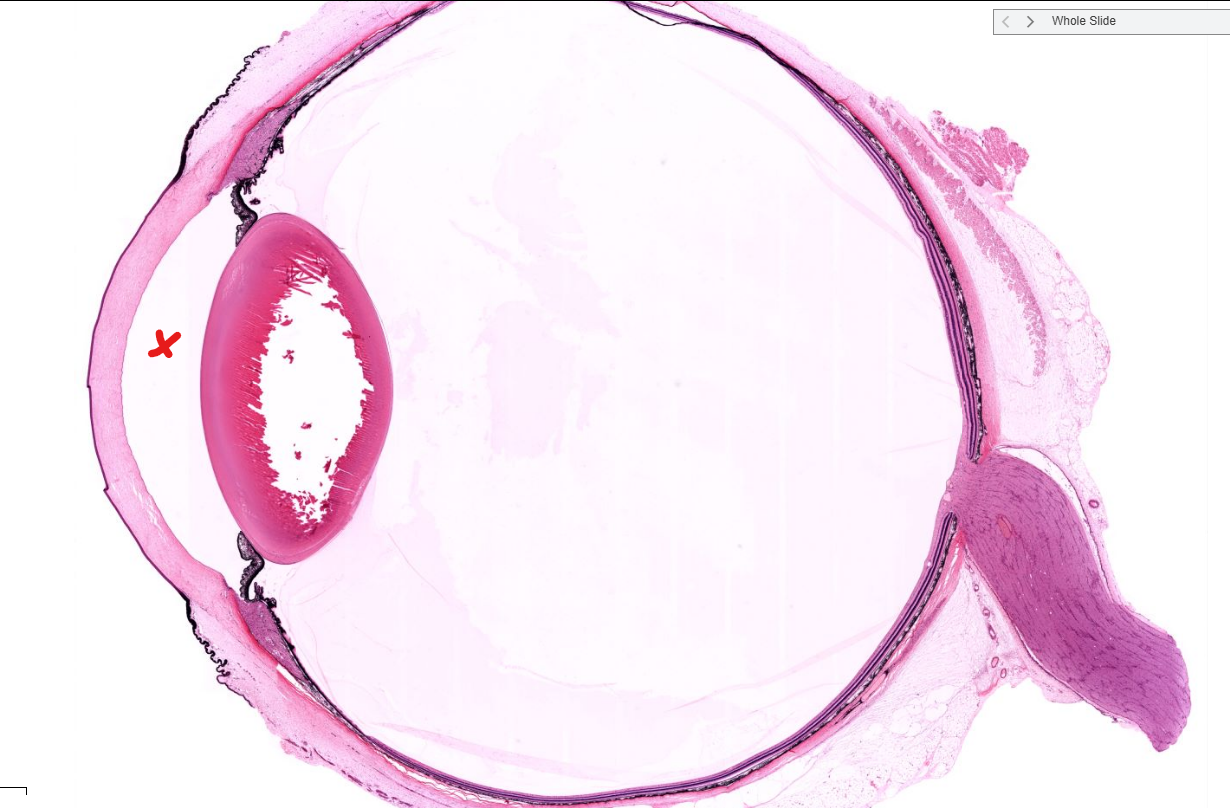
area
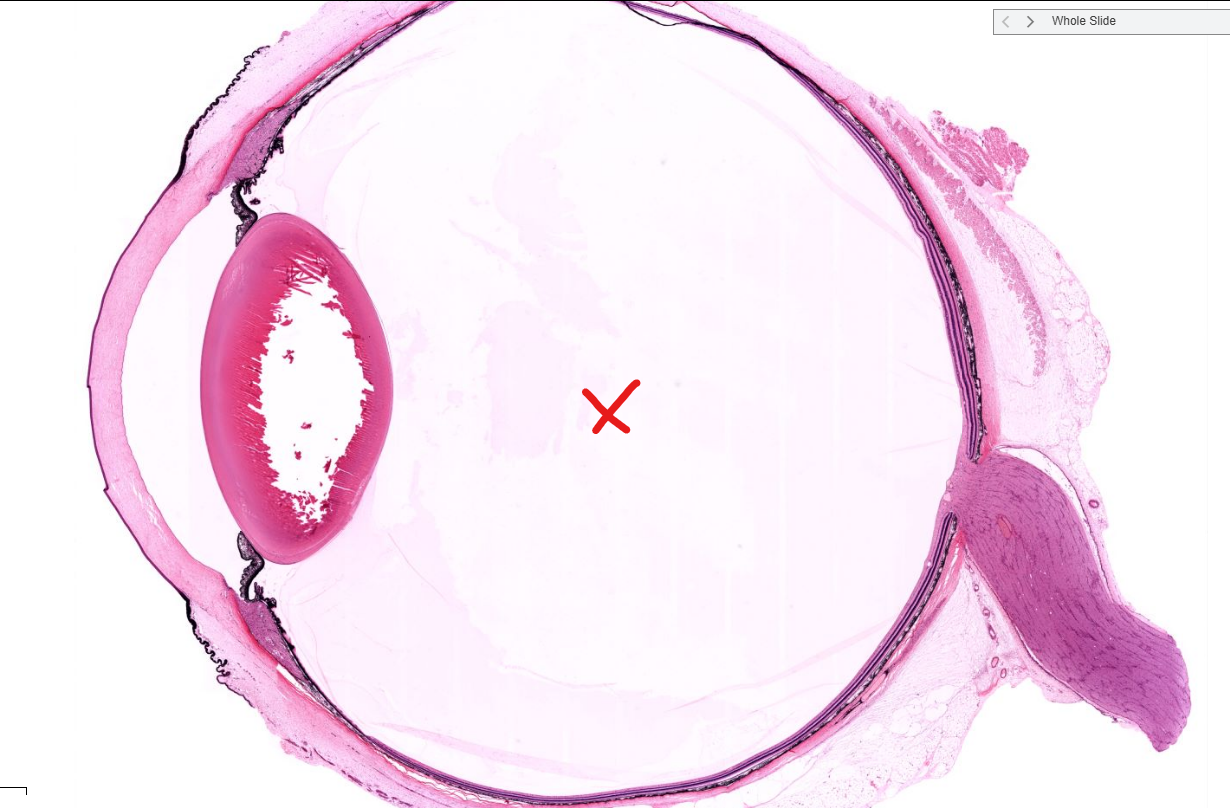
aqueous chamber of the eye
area
vitreous chamber of the eye
sclera
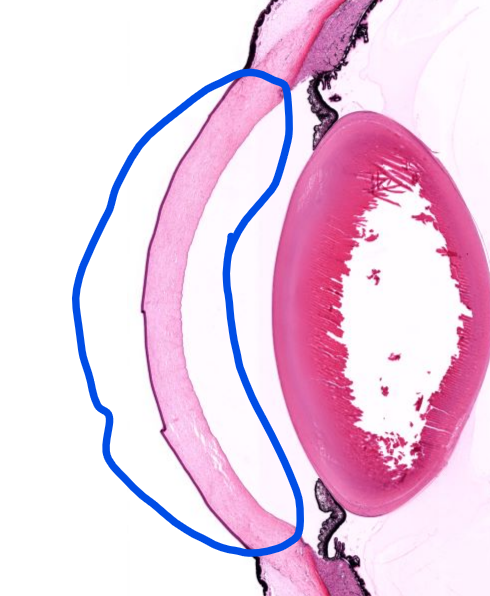
cornea
structure
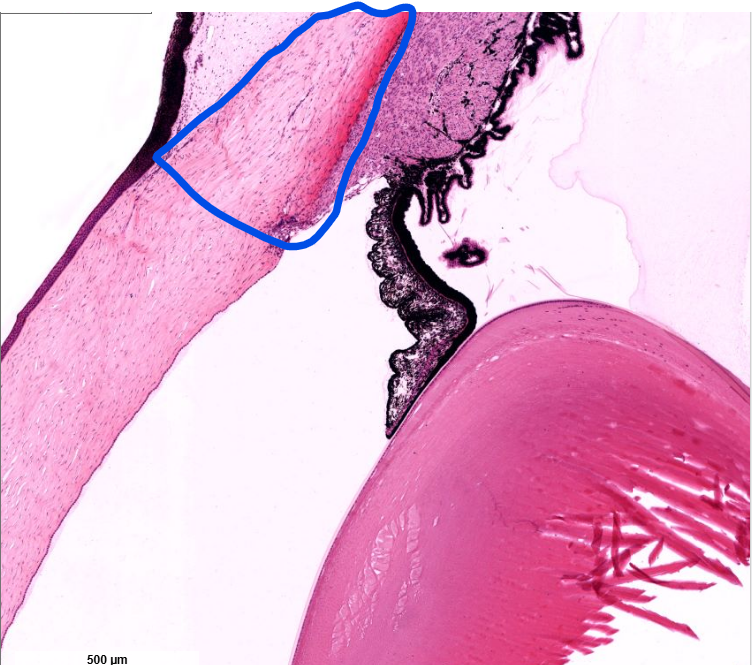
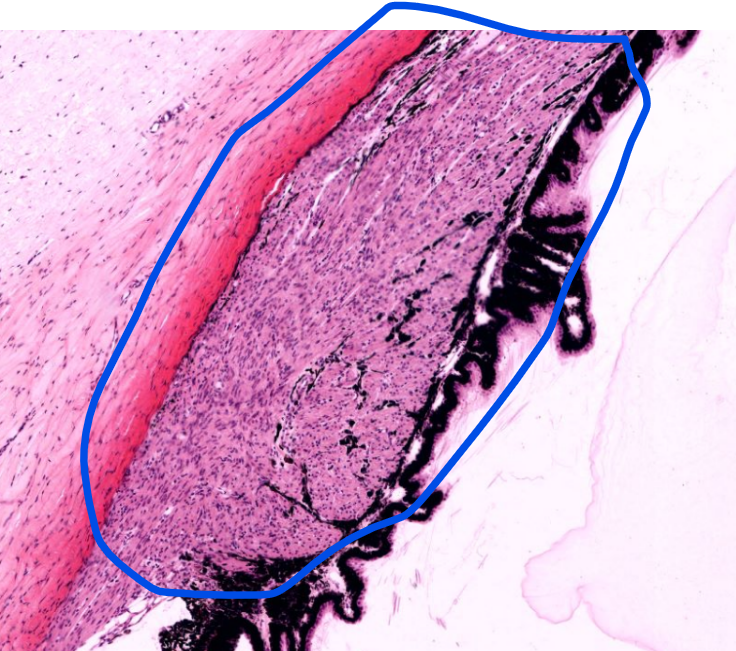
ciliary body
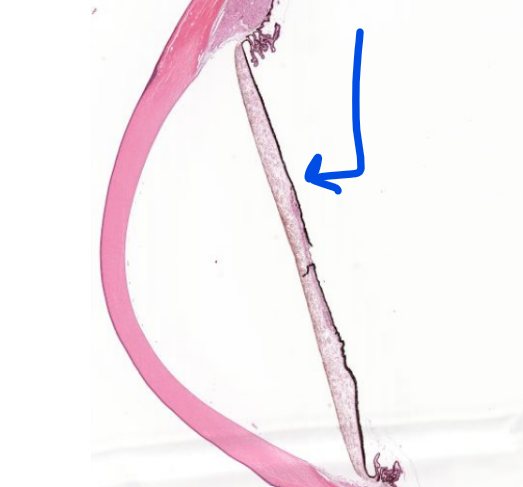
structure
iris
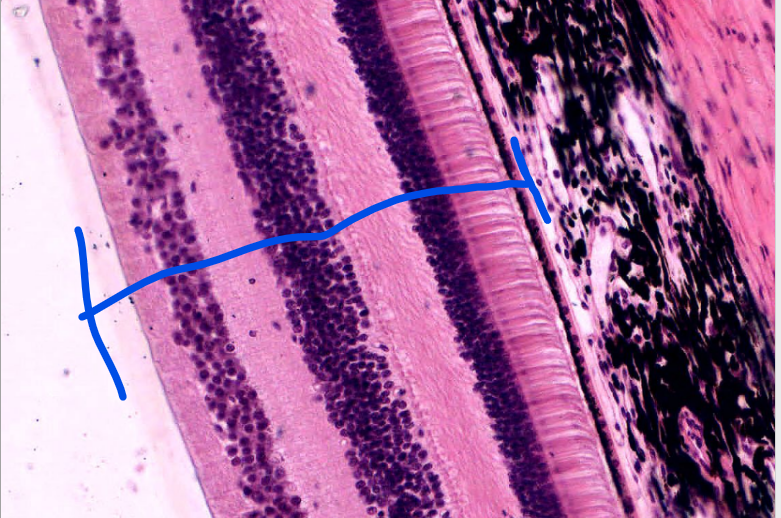
layer
retina- (see the pigment epi and rods/cones?
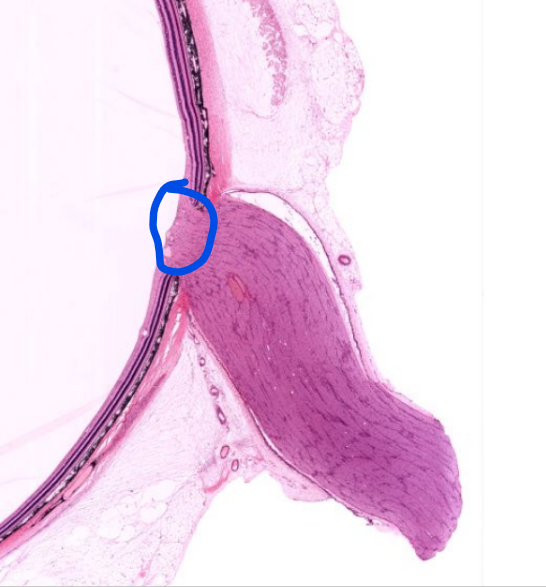
structure
optic disc- where there are to photoreceptor cells, “blind spot” where the axons of the neurons become the optic nerve and leave the eye
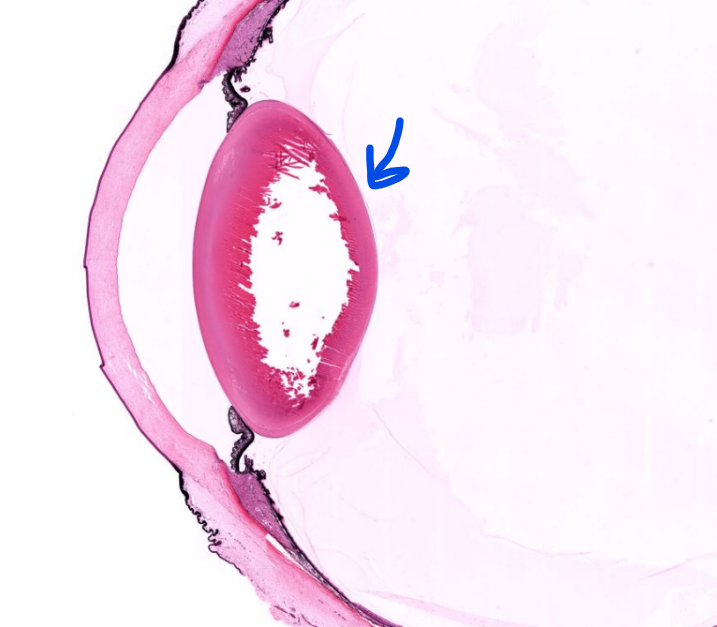
structure
lens
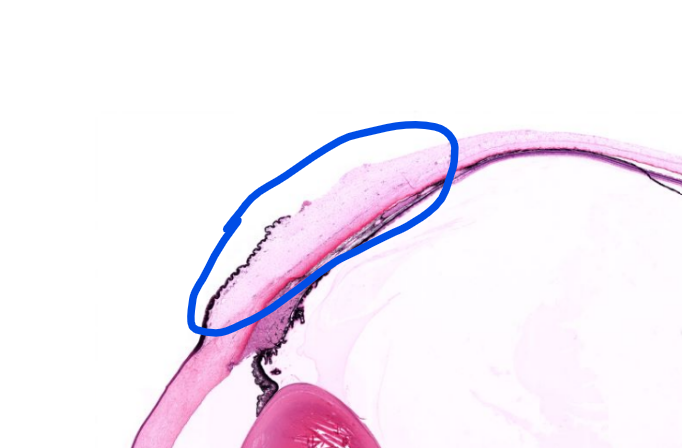
structure
conjunctiva-
the mucous membrane covering the anterior sclera
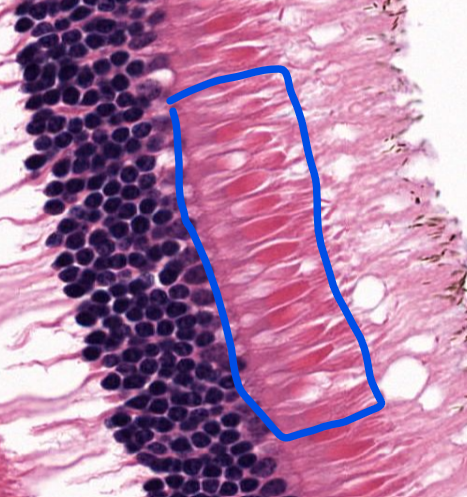
cell type
photoreceptor cells-
rods and cones, part of the retinal layer
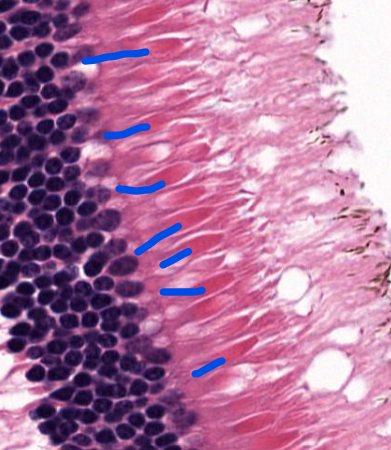
cell type
cones
cell type
rods
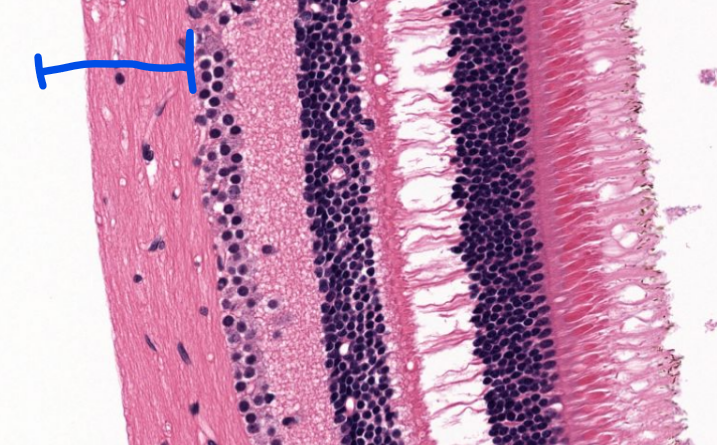
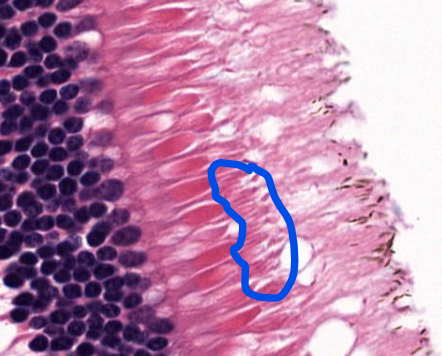
structure
axons that receive signals from rods and cones, lead to the optic nerve
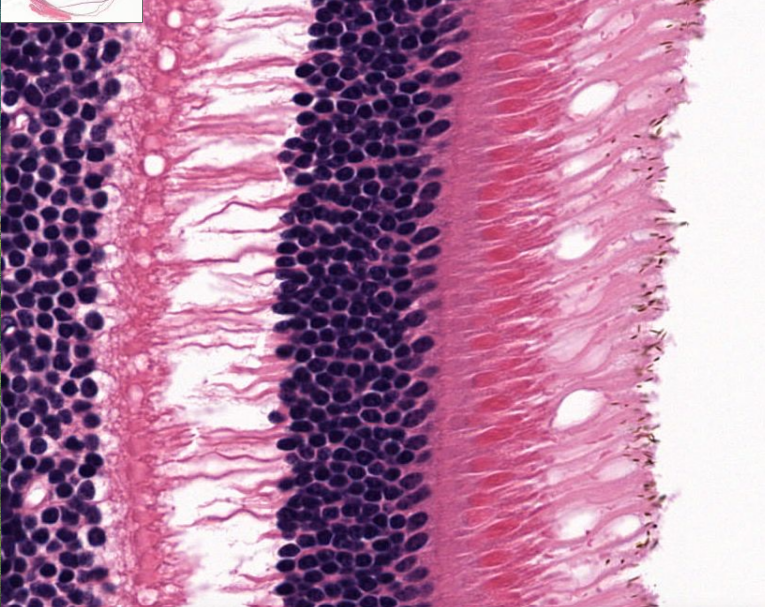
structure (look at photoreceptor cells
macula lutea-
area of the retina that has mostly cone cells
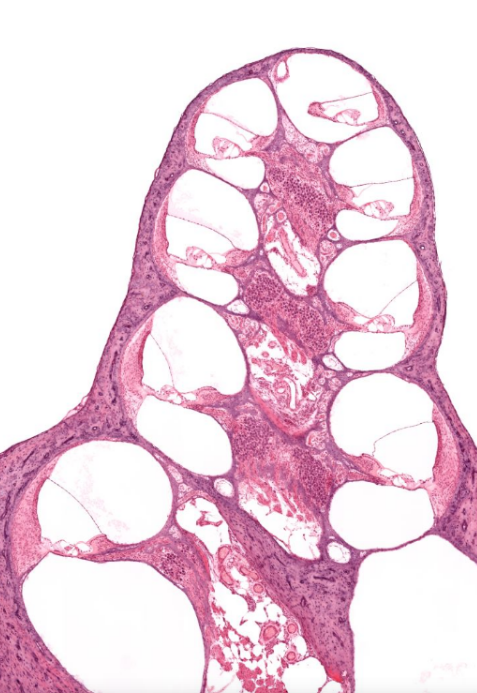
structure
cochlea of the inner ear- detects sound vibration
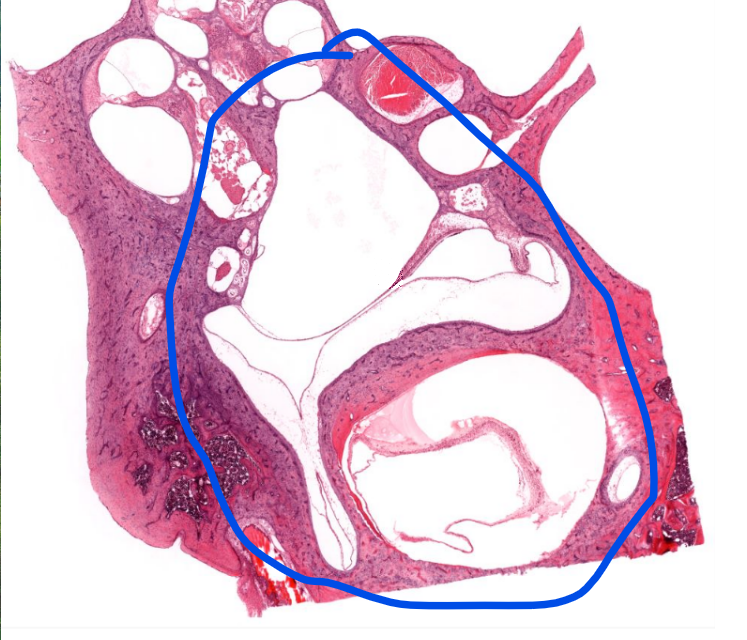
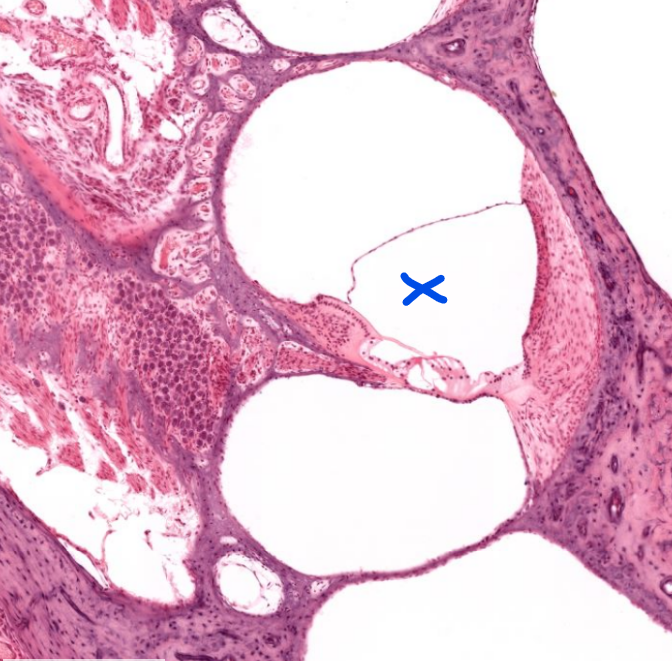
structure
vestibular apparatus- detects gravity/static position, and acceleration
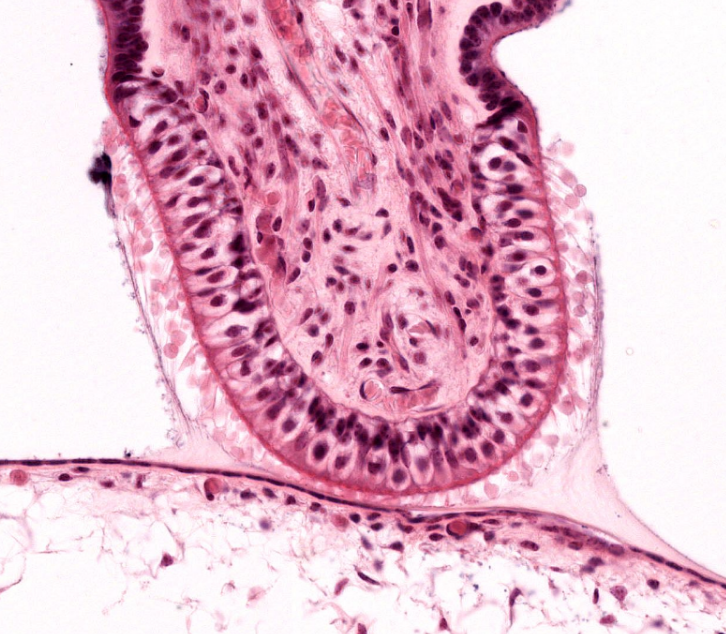
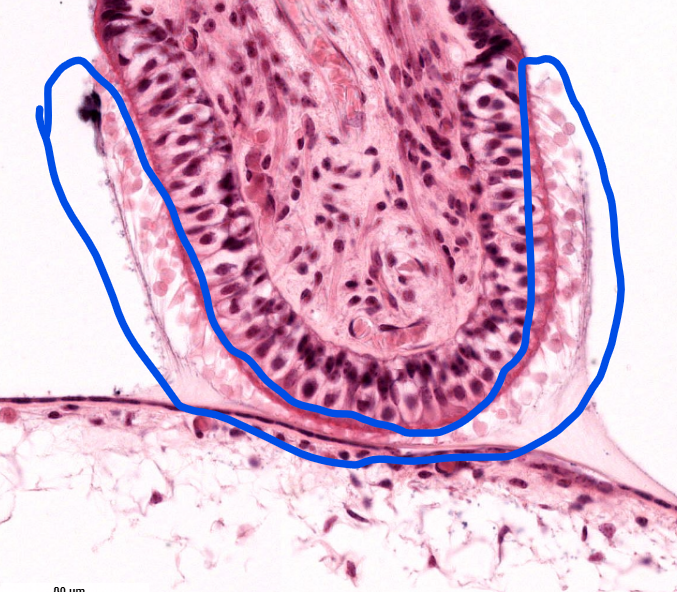
structure
crista ampullaris- the sensory region of the semi-circular canals
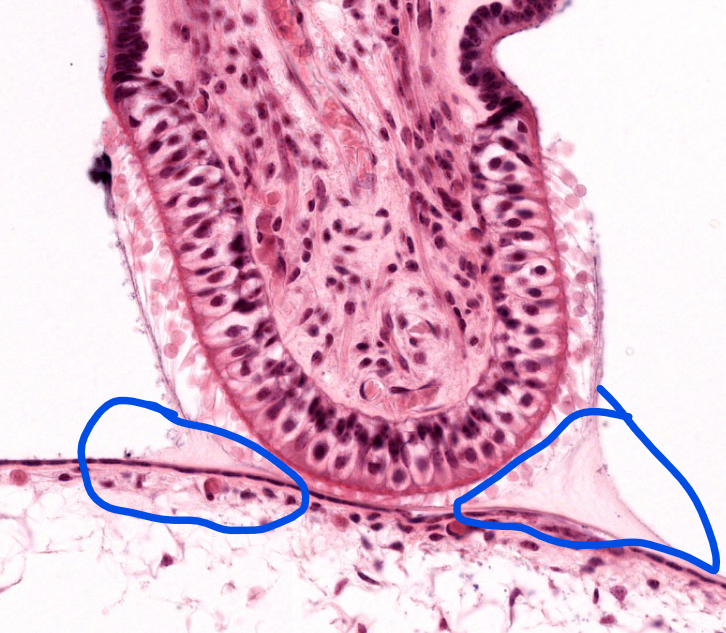
structure
cupula- of the inner ear
structure
hair cells
structure
scala media
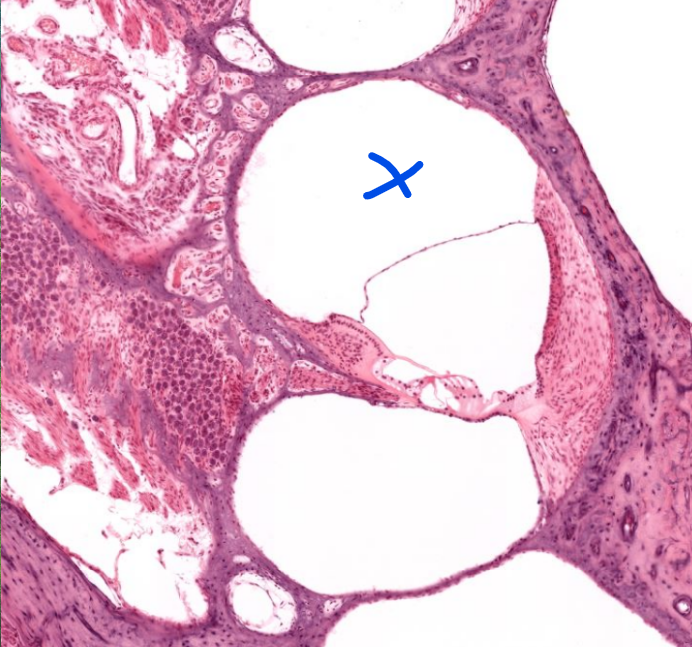
structure
scala vestibuli- the “first” part of the cochliea→ (vestibule)
notice the lame skinny layer of tissue dividing this and the scala media
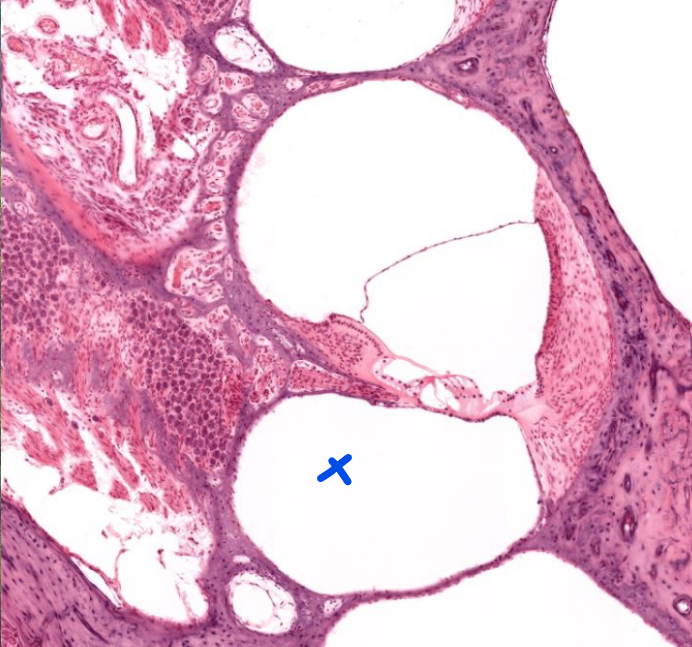
structure
scala tympani- the lower compartment- notice the complicated membrane between this and the scala media→ this is used to transmit hearing info
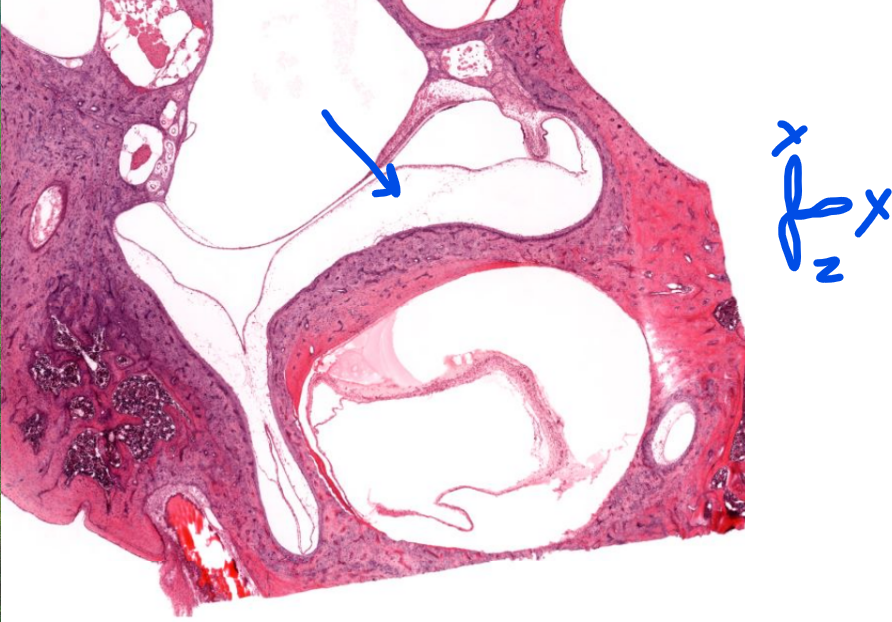
structure
semi-circular canals-
sense linear/directional acceleration
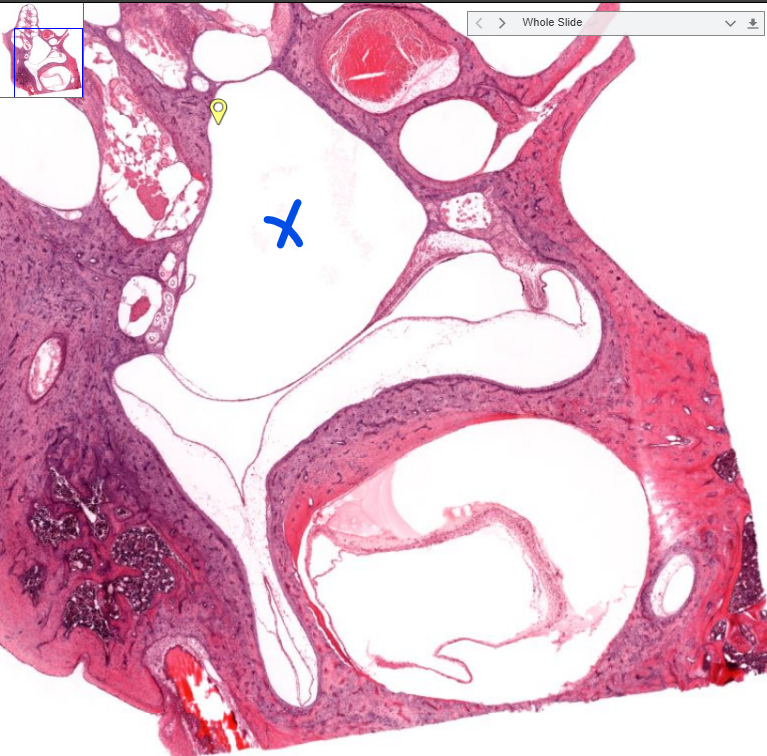
structure
utricule/saccule- impossible to say in this histology slide/one dimention
deal with sensing static position/gravity
structure
techtorial membrane