Globalization part 2
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 10:20 AM on 11/22/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
1
New cards
David Harvey(time-space compression)
overcoming the distance barrier with advances of transportation and information technology
2
New cards
costs of overcoming distance
goods trade, communication, face-to-face
3
New cards
rebundling
mainly producing for domestic consumption during 1914-1945
4
New cards
costs of overcoming distance
goods trade, consumption, face-to-face
5
New cards
first unbundling
steam&industrial revolution, 1820-1980
6
New cards
old international division of labour
Ricardo‘s world of comparative advantage, but many of them are artificially created within colonial trading systems
7
New cards
the Great Divergence
Europe&US overgrowing the Global South
8
New cards
Global South
China, India, Africa
9
New cards
second unbundling
lower ICT cost; starts after 1945, but accelerates since mid-1980s
10
New cards
new international division of labor
enables a more detailed global division of labor, knowledge and information spillovers, crossing North-South borders
11
New cards
RTA
regional trade agreement
12
New cards
tacit knowledge
knowledge from personal experience, not taught
13
New cards
GVC
global value chain
14
New cards
task outsourcing in old division of labor
intra-factory flow of ideas/goods; competition between firms and their products
15
New cards
task outsourcing in new division of labor
international flow of ideas/goods; competition between individual occupations and tasks
16
New cards
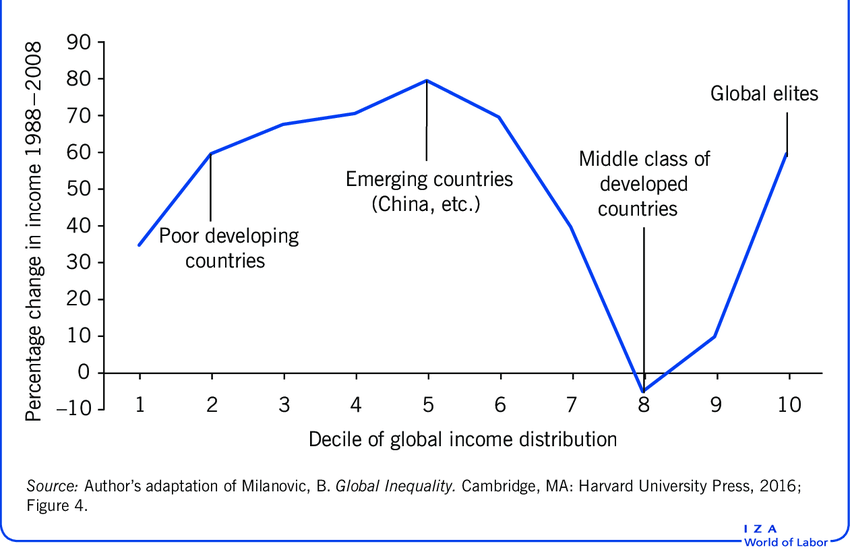
the elephant graph
relative gain per income by global income level
17
New cards
winners of globalisation
Asian poor and middle classes; "head of the graph"
18
New cards
losers of globalisation
lower middle class of the rich world (OECD countries); lower points of the graph
19
New cards
global plutocrats
top 1 percent of rich economies; highest point of the graph
20
New cards
what do changes in output and prices in Stolper-Samuelson theorem lead to
strong re-distributive implications of free-trade models
21
New cards
Stolper-Samuelson theorem traces out the effects...
of price changes on the material well-being of different groups
22
New cards
free trade can benefit countries as a whole even though ...
within countries there will be winners and losers individuals
23
New cards
who are worse as a result of trade liberalization
unskilled workers in developed countries
24
New cards
If politicians go after the remaining, low barriers, then...
trade agreements
become more about redistribution than about expanding the economic pie
become more about redistribution than about expanding the economic pie
25
New cards
Polanyi's main idea
there are political countermovements against the negative
consequences of commodification processes
consequences of commodification processes
26
New cards
Polanyi's double movement
movement of laissez-faire (to expand and influence self-regulating markets) and movement of protection (to protect social life from destructive effects of market pressure)
27
New cards
precarity
situation when one's job or career is in danger of being lost (=economic insecurity)
28
New cards
political reactions to precarization
rise of populist election polls; turns against immigration,EU or global finance
29
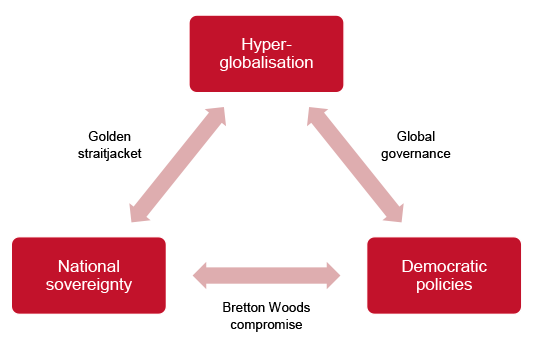
New cards
Daniel Rodrik's trilemma
impossibilty of achieving three policy goals (national sovereignty, hyper-globalisation and democratic policies) simultaneously, two must be chosen
30
New cards
golden straightjacket
national sovereignty+hyperglobalisation; authoritarian state with global integration - China
31
New cards
global governance
hyperglobalisation+democratic policies; open borders for trade, democratic institutions at a global scale - EU
32
New cards
Bretton Woods compromise
national sovereignty+democratic policies; giving up some trade for strong welfare state - UK's Brexit
33
New cards
Summers
"let them eat pollution", neoclassical school
34
New cards
Nelson
Feminist Economics
35
New cards
Decker
from de-growth to de-globalization; ecological school
36
New cards
Sheng
different shape of globalization; omplexity/evolutionary/behavioral school
37
New cards
Rodrik
globalization after Covid-19; global rules and policies (beggar-thy-neighbour and public goods); institutional school
38
New cards
Hecksher-Ohlin Theory: factor endowments give a country...
comparative advantage over other countries