halogenoalkanes
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
What makes halogenoalkanes reactive
Hydrocarbons contain only hydrogen and carbon atoms which have similar electronegativities so the bonds are almost non polar
Halogenoalkanes have a halogen atom with an electronegativity higher than carbon, forming a polar bond. C hs delta positive, halogen is delta negative
These carbons attract nuceophiles
Nucleophile
A nucleophile is a species that donates a lone pair of electrons to form a covalent bond with an electron-deficient atom
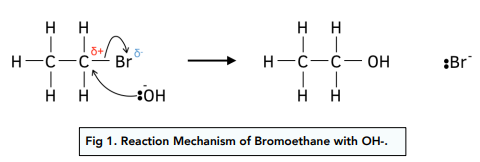
Halogenoalkane to alcohol
Nucleophilic substation
Heat with aqueous potassium hydroxide under reflux
CH3CH2CH2Cl + KOH → CH3CH2CH2OH + KCl
Ionic equation:
CH3CH2CH2CL + OH- → CH3CH2CH2OH + Cl-
Need to know mechanism
Halogenoalkanes to nitrile
Nucleophilic substation
Heat with potassium cyanide dissolved with ethanol under reflux
CH3CH2Br → CH3CH2CN + KBr
-has one more carbon atoms- way of extending carbon chain
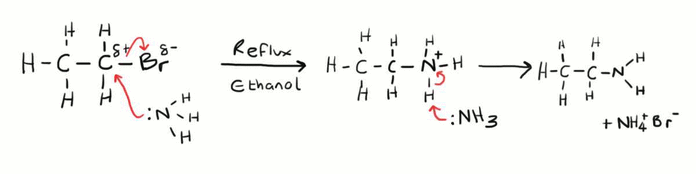
Halogenoalkanes to primary amines
Nucleophilic substitution
Heating with ammonia solution in sealed tube- needed because ammonia is a gas which could escape
CH3CH2Cl + NH3 → CH3CH2NH3+ + Cl-
CH3CH2NH3+ +NH3 → CH3CH2NH2 + NH4+
CH3CH2Cl + 2NH3 → CH3CH2NH2 + NH4+Cl-
Need to know mechanism
Halogenoalkanes to Alkene
Elimination reaction
Halogenoalkanes reacted with ETHANOIC potassium hydroxide, OH- acts as base not nucleophile
-hydrogen reacts with OH-
-must be the hydrogen attached to te carbon atom next to the C in the C-Br bond
CH3-CHBr-CH3 +KOH → CH2=CH-CH3 +H20 +KBr
Hydrolysis with water
CH3CH2Br + H2O → CH3CH2OH + H+ + Br-
Slow- water is a poor nucleophile
Practical hydrolysis- why is silver nitrate used
Used as a test for halide ion, silver ions react with halide ions to form a precipitate
How are rates of different halogens different
Fastest: -1-iodobutane
-1 bromobutane
Slowest: -1 cholobutan
C-Cl has the highest bond enthaply so is stronger and requires more energy to break
C-I is weakest so the I+ ion forms quickly and forms precipitate
Different structure and rate on halogenoalkanes
Fastest: 2-bro o- 2 -methylpropane (tertiary)
2 bromobutane (secondary)
1 bromobutane (primary)