peripheral & central nervous systems
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
ganglia definition
collection of neurons outside the CNS
spinal ganglia definition
where cell bodies of sensory neurons associated with spinal nerves are located
dorsal root ganglia definition
alternate name for spinal ganglia, which are part of the dorsal root of the spinal nerve
where cell bodies of sensory neurons associated with spinal nerves are located
in spinal ganglia
autonomic ganglion definition
the location of the cell body of the second neuron in a 2-neuron chain of autonomic nerves
where the spinal cord begins
at the foramen magnum
the spinal cord extends to the level of the disc between vertebrae ___ and ____
L1, L2
the spinal cord is a continuation of ___
the brainstem
the spinal cord is located in the ____ of the vertebral canal
upper 2/3
spinal segment definition
the length of the spinal cord to which one pair of spinal nerves is attached
up until ___, nerve roots emerge ____ (superior/inferior) to their respective vertebrae
C8, superior
T1 exits ___ (superior/inferior) to the T1 vertebrae
inferior
where C8 exits from the spinal cord
inferior to the C7 vertebrae
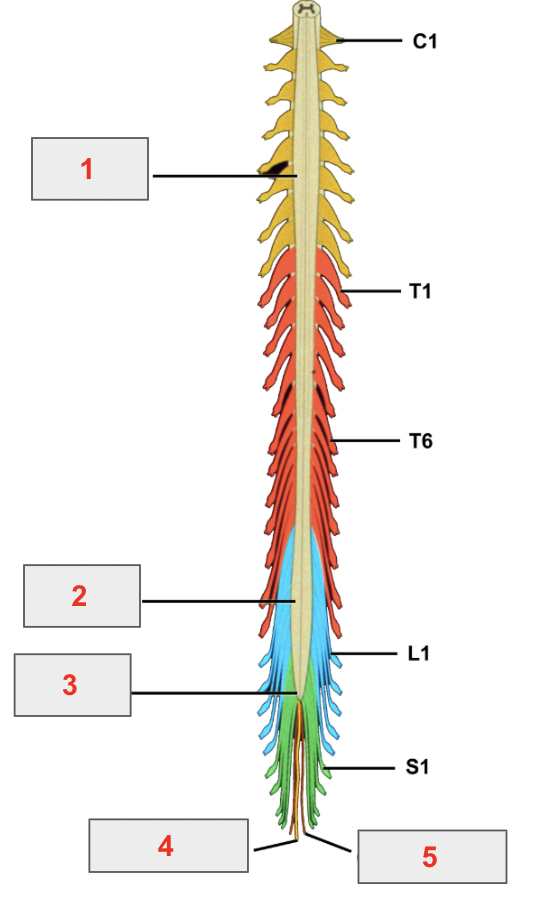
identify 1
cervical enlargement

identify 2
lumbar enlargement

identify 3
conus medullaris

identify 4
filum terminale

identify 5
coccygeal nerve
where nerves exit the vertebral column from
intervertebral foramina, between vertebrae
spinal nerves are vulnerable to injury by a ____ or pathological ____ as they exit the vertebral column
herniated intervertebral disk, narrowing of the intervertebral foramen
motor rootlets converge to form ___
ventral roots
what the ventral roots innervate
skeletal muscle in the neck, trunk, and limbs
ventral roots carry ____ (motor/sensory/mixed) information ____ (to/from) the spinal cord
motor
from
sensory rootlets converge to form ____
dorsal roots
dorsal roots carry ____ (motor/sensory/mixed) information ___ (to/from) the spinal cord
sensory
to
dorsal roots send information toward the cell body located in the ___, then through the dorsal root to the spinal cord
dorsal root ganglion
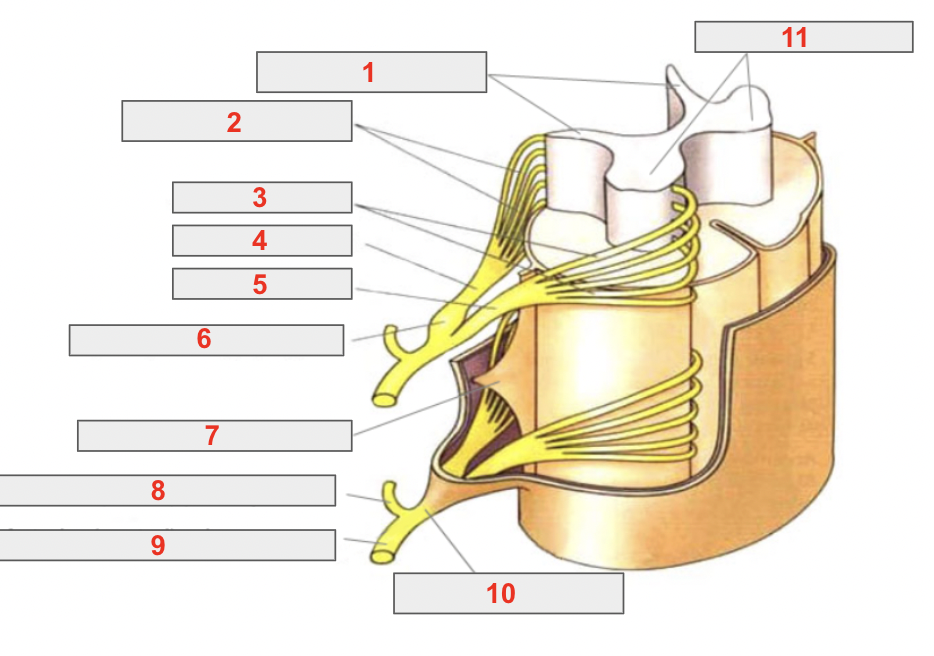
identify 1
posterior/dorsal gray horns

identify 2
posterior/dorsal rootlets

identify 3
anterior/ventral rootlets

identify 4
posterior/dorsal root

identify 5
anterior/ventral root

identify 6
spinal (sensory/dorsal) ganglion

identify 7
denticulate ligament

identify 8
posterior/dorsal ramus

identify 9
anterior/ventral ramus

identify 10
mixed spinal nerve

identify 11
anterior gray horns
spinal nerve is made by the combination of ____
a ventral root and a dorsal root
the spinal nerve is ___ (long/short)
short
the spinal nerve divides into a ___ and ____
posterior/dorsal ramus and an anterior/ventral ramus
the dorsal ramus innervates _____
the muscles and skin of the back
the ventral rami innervate ___
the muscles and skin of the other anterior + lateral aspects of the neck and trunk
T/F: the ventral rami are larger than the dorsal rami
true
the ventral form ___ to innervate the limbs
plexuses
T/F: the dorsal rami branch to form cervical, brachial, lumbar, and sacral plexuses
false
only ventral rami do
the ____ provides the bulk of innervation for the upper extremity
brachial plexus
the ____ provide the bulk of innervation for the lower extremity and pelvis
lumbar and sacral plexuses
sensory information is sent to the CNS via ____
dorsal roots
motor information is sent out from the CNS via ___
ventral roots
the dorsal root is connected to the ____ of the spinal cord
dorsal/posterior horn
the ventral root is connected to the ____ of the spinal cord
ventral/anterior horn
the ventral root joins the dorsal root distal to the ___ to form the spinal nerve
ganglion
muscles in the head are innervated by ____
cranial nerves
reflex pathway definition
where sensory and motor neurons are connected within the CNS
example of reflex pathway + describe
patellar reflex
tap on patellar ligament → detected by sensory neurons in femoral nerve → transmit info to spinal cord → motor neurons in femoral nerve respond → contract quads muscle
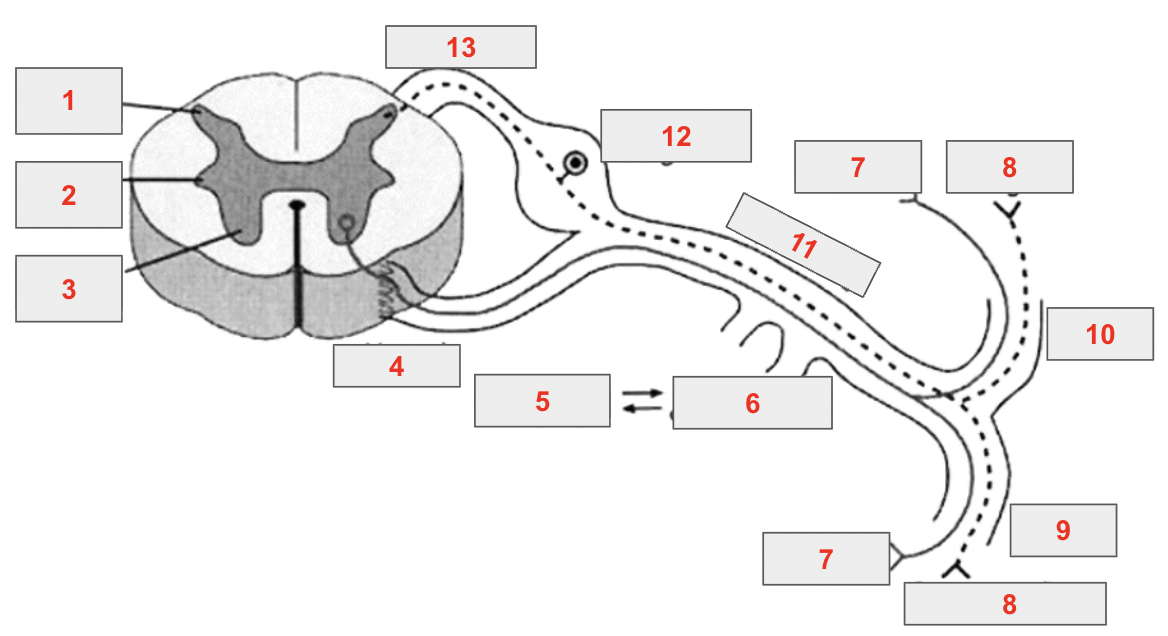
identify 1
posterior horn

identify 2
lateral horn

identify 3
anterior horn

identify 4
ventral root

identify 5
sympathetic chain ganglia

identify 6
rami communicantes

identify 7
skeletal muscles

identify 8
sensory endings

identify 9
ventral ramus

identify 10
dorsal ramus

identify 11
spinal nerve

identify 12
spinal ganglion

identify 13
dorsal root
T/F: only dorsal roots send information through spinal ganglion
true
vemtral spinal ganglion don’t exist
C6 key dermatome
thumb
C7 key dermatome
index and middle fingers
C8 key dermatome
ring and little fingers
C5-T2 key dermatome
upper limb
T4 key dermatome
nipple
T10 key dermatome
umbilicus
the 3 meninges, from outermost to innermost
dura mater, arachnoid mater, pia mater
dura mater extends to the ___ level
S2
arachnoid mater extends below to the ___ level
S2
at __, the pia mater continues as the filum terminale
L2
the filum terminale is an extension of the ___
pia mater
the filum terminale perforates the ___ and ___ at S2 and continues within the coccygeal ligament
arachnoid mater and dura mater
the spinal cords ends at the level of the disc between the ___ and ___ vertebrae
L1, L2
cauda equina definition
the descending roots of the lower spinal nerves, since the spinal cords end before their exit
location of spinal tap/lumbar puncture (space and level)
subarachoid space between L3-L4 or L4-L5, after termination of the spinal cord
landmark used for spinal taps
an imaginary line connecting the highest points on the iliac crests, corresponding to L4 spine
polio is an example of a ___ lesion
purely motor
polio occurs especially in the ___ part of the spinal cord
lumbosacral
herpes zoster lays dormant in the ___
dorsal root ganglia
herpes zoster re-emerges in ___
peripheral sensory nerves
herpes zoster is an example of ___ lesion
purely sensory
herniated discs most often herniate in the ___ direction
posterolateral
a herniated disc is an example of a ___ lesion
mixed motor and sensory lesion
the preganglionic neuron is located ____ and the postganglionic neuron is located ___
in the CNS
in autonomic ganglia outside the CNS
T/F: only the autonomic system and pre- and post-ganglionic neurons
true
the cell bodies of sympathetic preganglionic neurons are located _____ (level and location)
the T1-L2 spinal cord segments, in the lateral horn of the gray matter
axons of sympathetic preganglionic neurons leave the spinal cord through ___ and enter the ____
ventral roots
sympathetic trunk
sympathetic innervation of muscles and glands in the head come from postganglionic neurons in the _____
superior cervical sympathetic ganglion
sympathetic postganglionic neurons innervating the head have axons that follow the ___ to reach the head
internal and external carotid arteries
parasympathetic preganglionic neurons are located in ____ (level and location)
the brain stem and S2-S4 spinal cord segments
parasympathetic preganglionic neurons travel in ______ and ____ nerves
cranial nerves III, VII, IX, X
spinal nerves S2-S4