instrumental chap 11
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
atomic mass spectroscopy
quantitative and qualitative detection of elements in parts per million and parts per billion concentrations
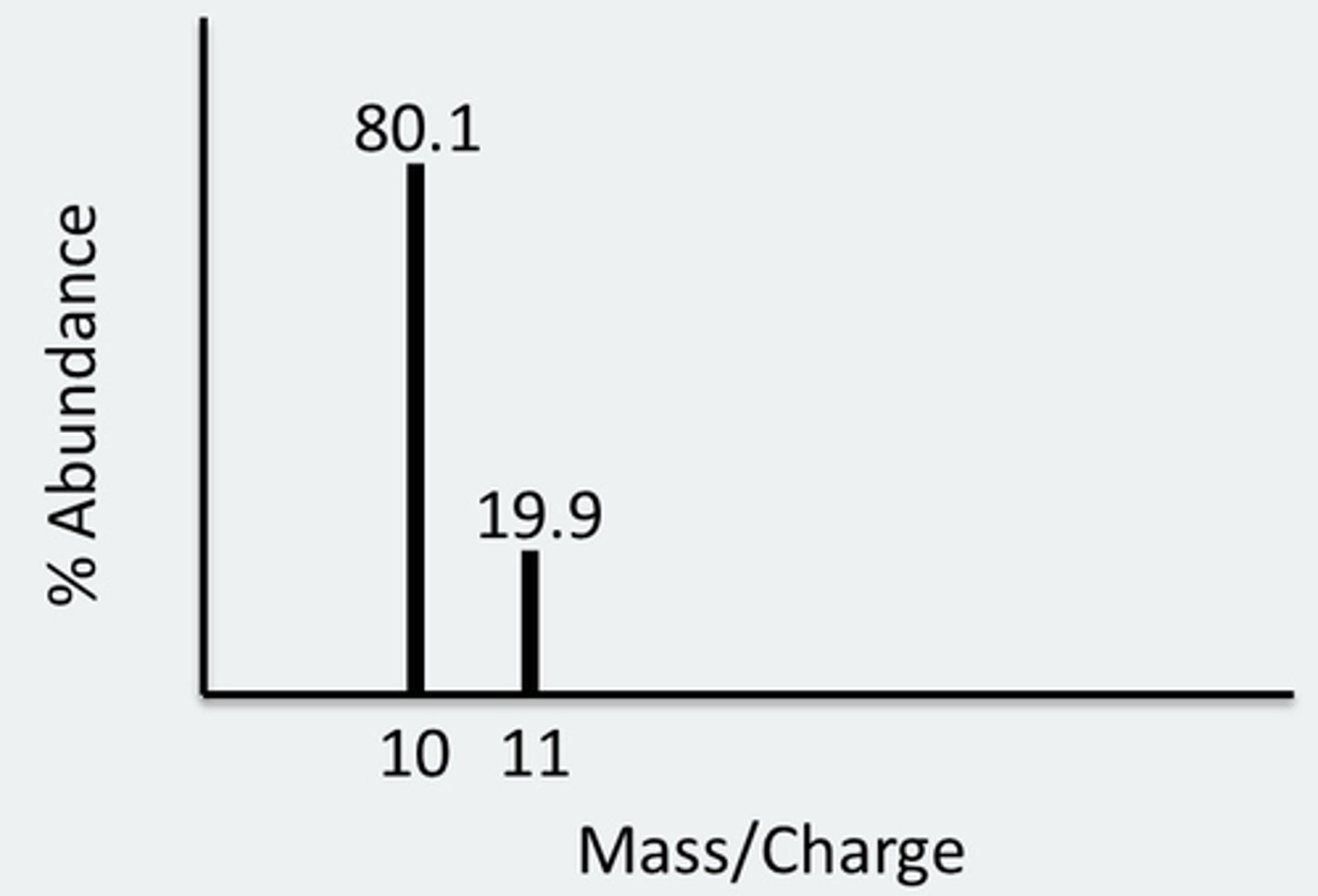
detection limits higher than optical methods, simple spectra, measures atomic isotopic ratios
advantages
expensive, instrumental drift, interference
disadvantages
atomization, formation of ions, separation of ions based on m/z, counting number of ions
processes involved
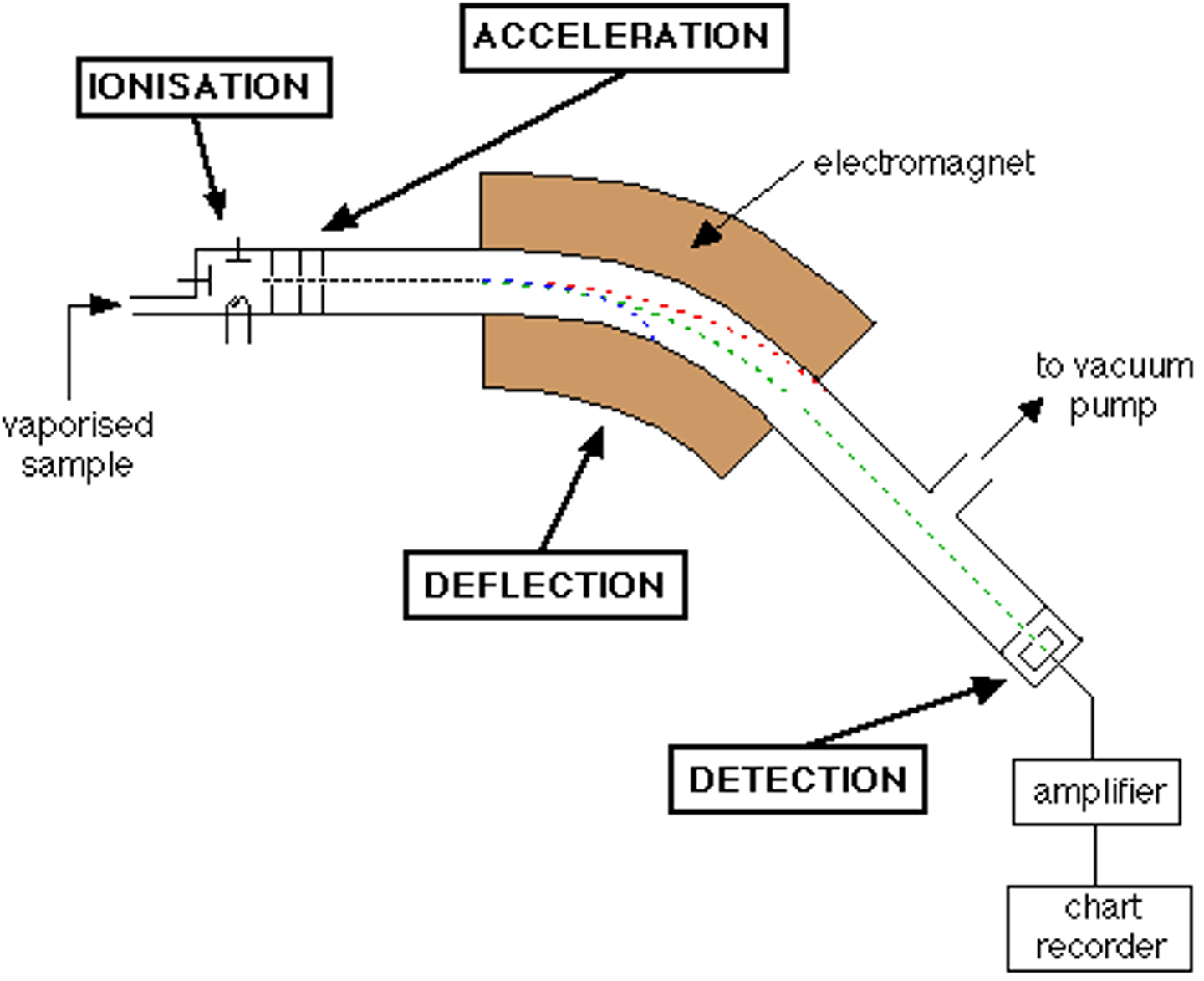
mass spectrometer
an instrument used to determine the relative masses of atoms by the deflection of their ions on a magnetic field
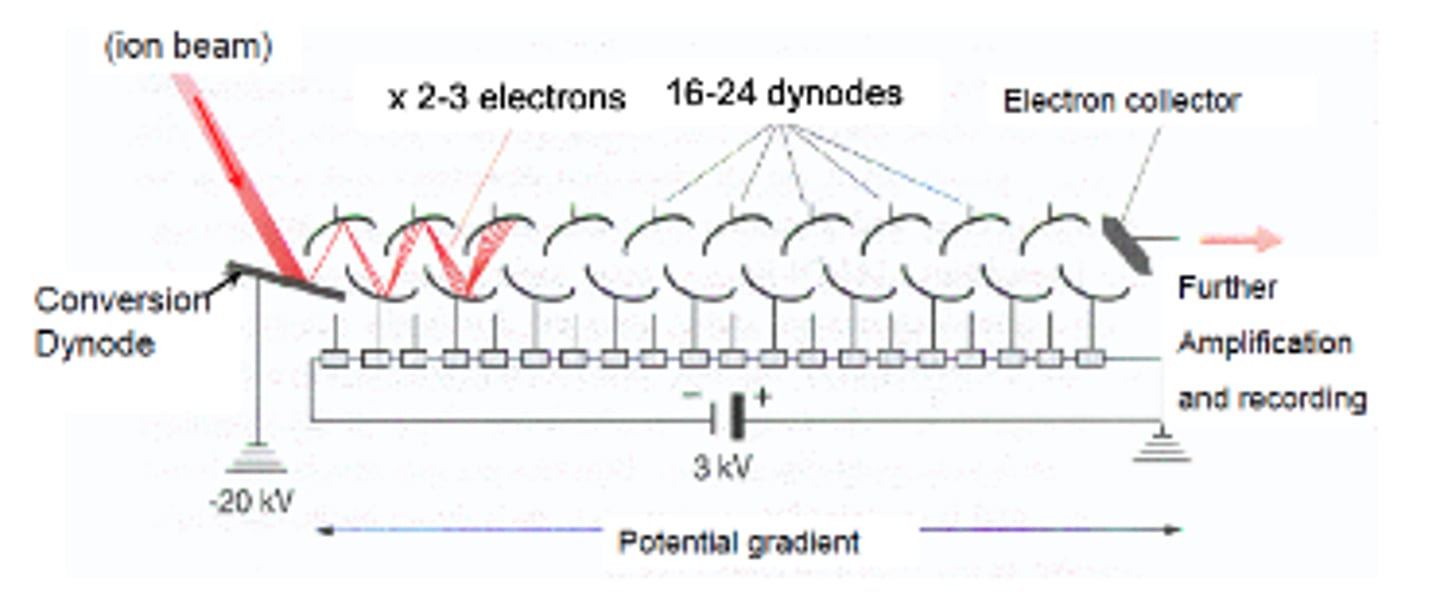
electron multipliers
ions hit metal surface or semiconductor and breaks off to make secondary electrons. secondary electrons also fragment and make more secondary electrons. 1 electron can make 1x10^6 electrons, destructive detection. good for ion trap and quadrupole
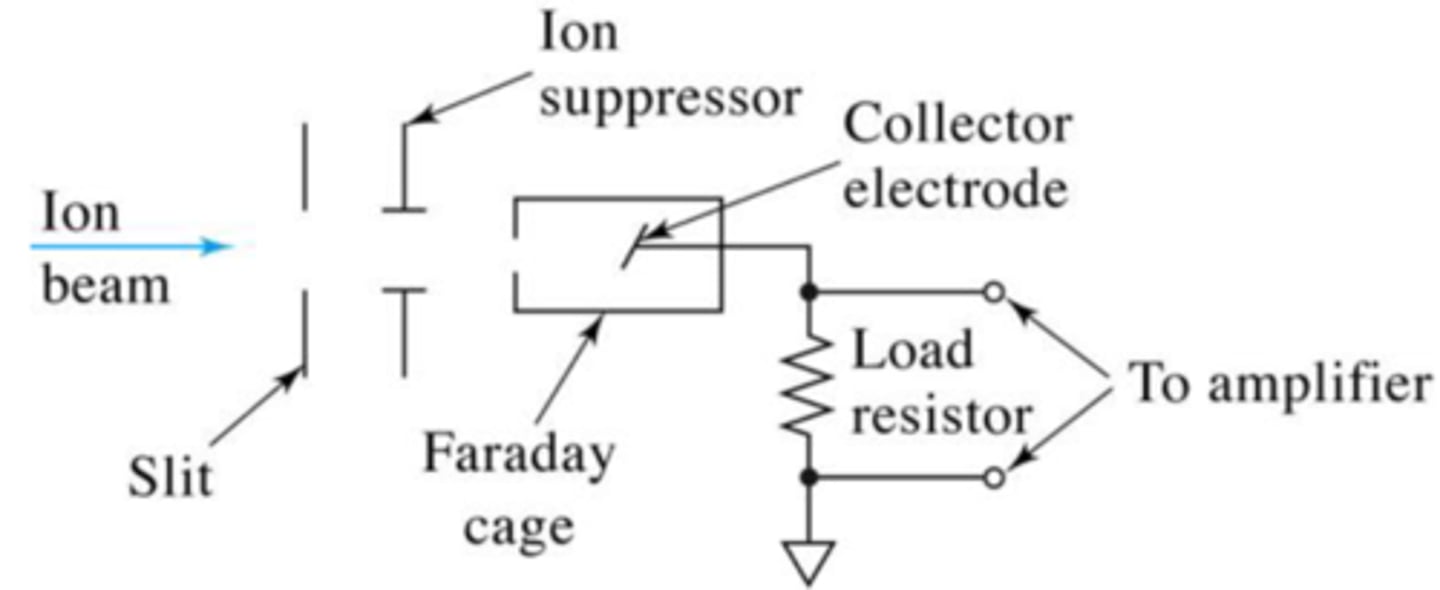
faraday cup
Relatively simple MS detector; uses an aligned or tilted collector electrode that is connected to ground through a resistor; voltage drop is amplified using high impedance amplifier; main disadvantage is the slow response of the detector due to the high impedance amplifier.
electron multipliers, faraday cup
transducers for mass spectrometry
quadrupole mass analyzer
A set of 4 conducting rods, each with an oscillating voltage.
This establishes an oscillating electric field between the rods.
Frequency of voltage oscillations is varied, to select for ion with
an m/Z that can successfully pass between the rods.
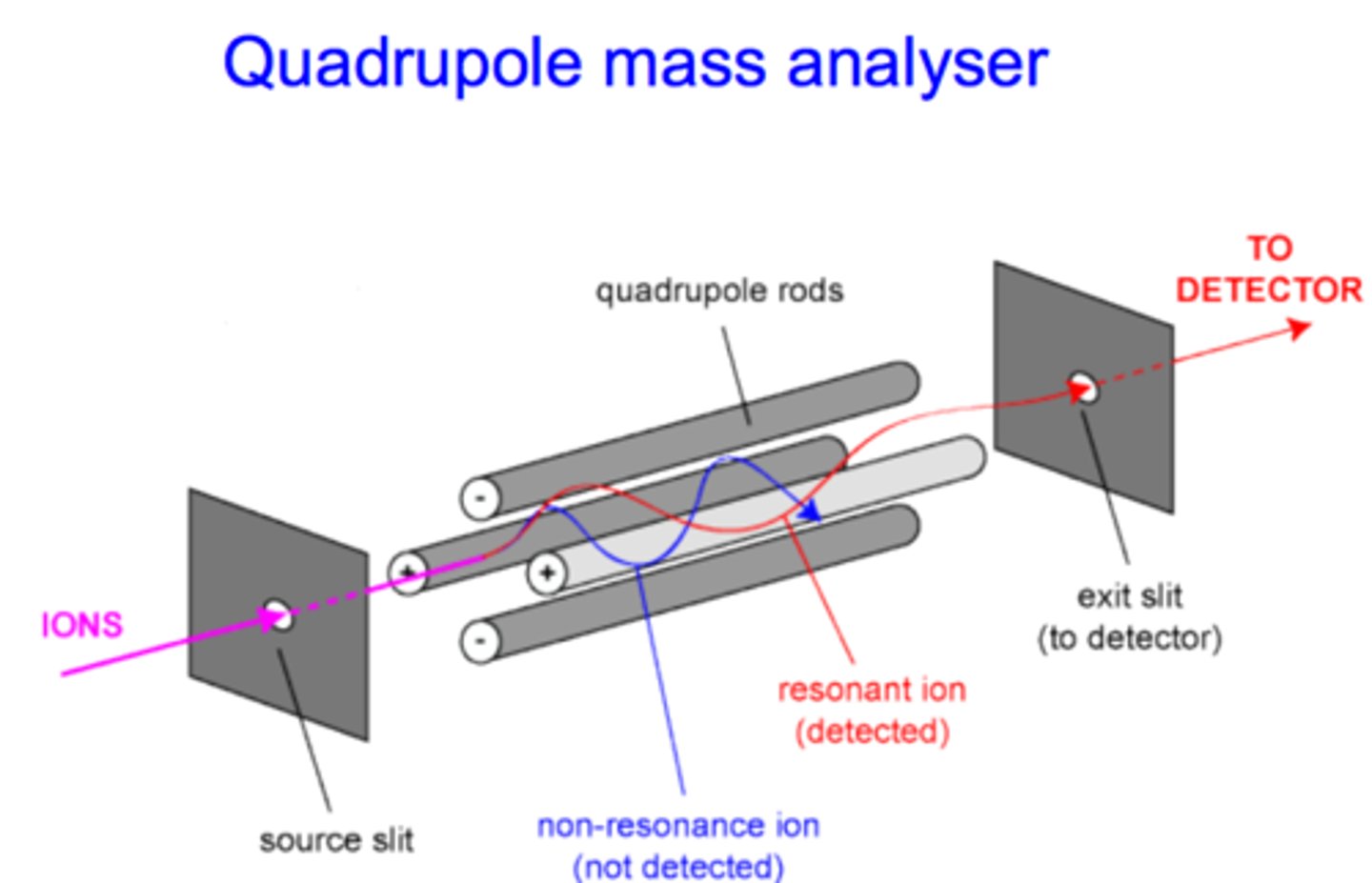
separates ions of different mass based on m/z through 4 rods
quadrupole mass analyzer
Time of flight mass analyzer
Equal kinetic energy ions enter the tube. Drift velocity and thus arrival time at the detector depend on mass
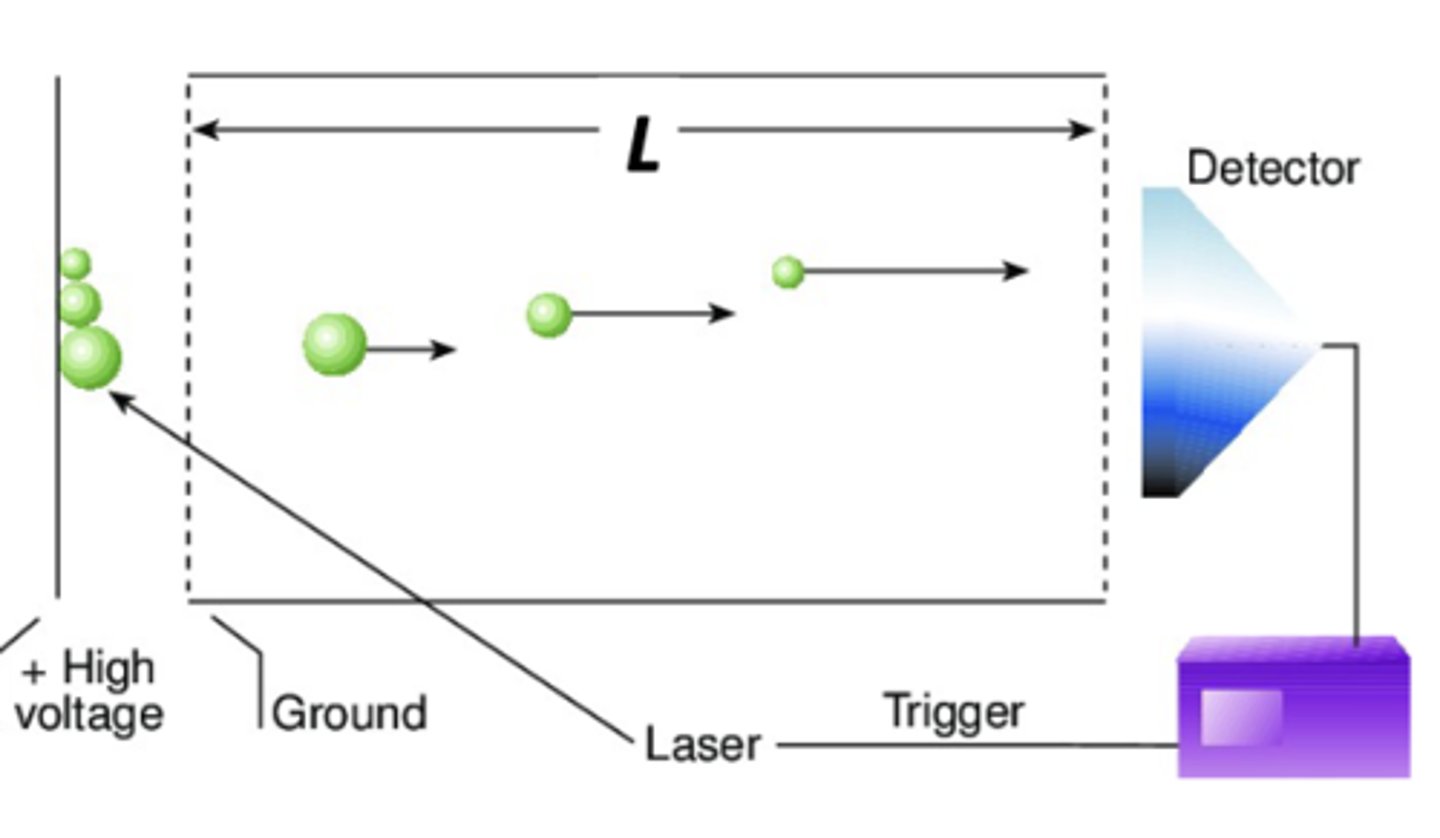
ions are accelerated into field free drift tube, lighter ions arrive first
time of flight
double focusing mass analyzer
Electrostatic focusing followed by magnetic field detection. Trajectories depend on m/z values.
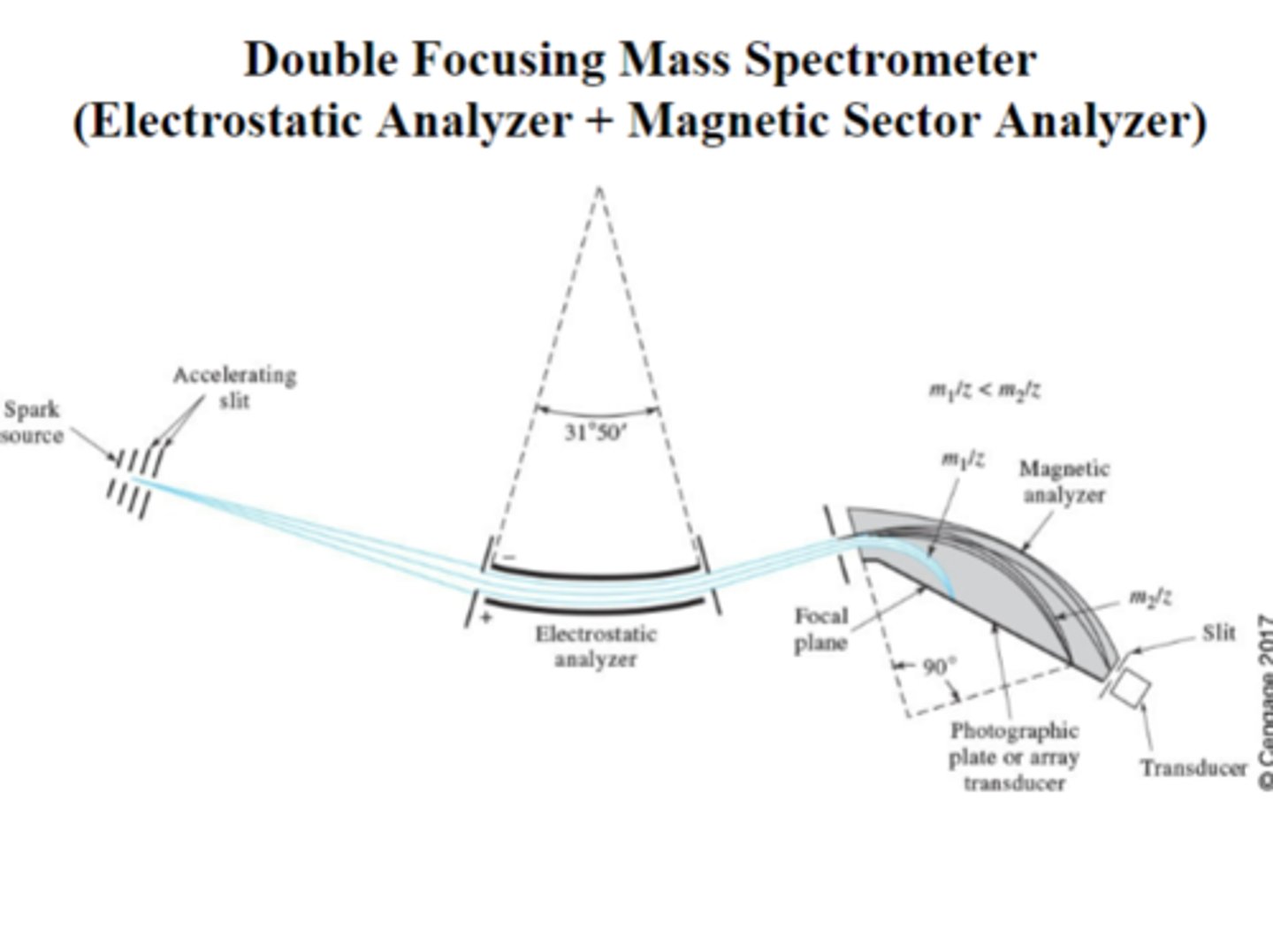
ions accelerated into electrostatic field and magnetic, lightest deflected and dispersed on plane
double focusing
more compact, less expensive, more rugged, m/z needs to be less than 2000
quadrupole traits
unlimited mass range, simple rugged
TOF advantages
limited resolution, limited sensitivity, requires fast eletronics
TOF disadvantages
ICP-MS
a form of mass spectrometry used to detect inorganic materials and metals. the best and most modern technique for metal analysis
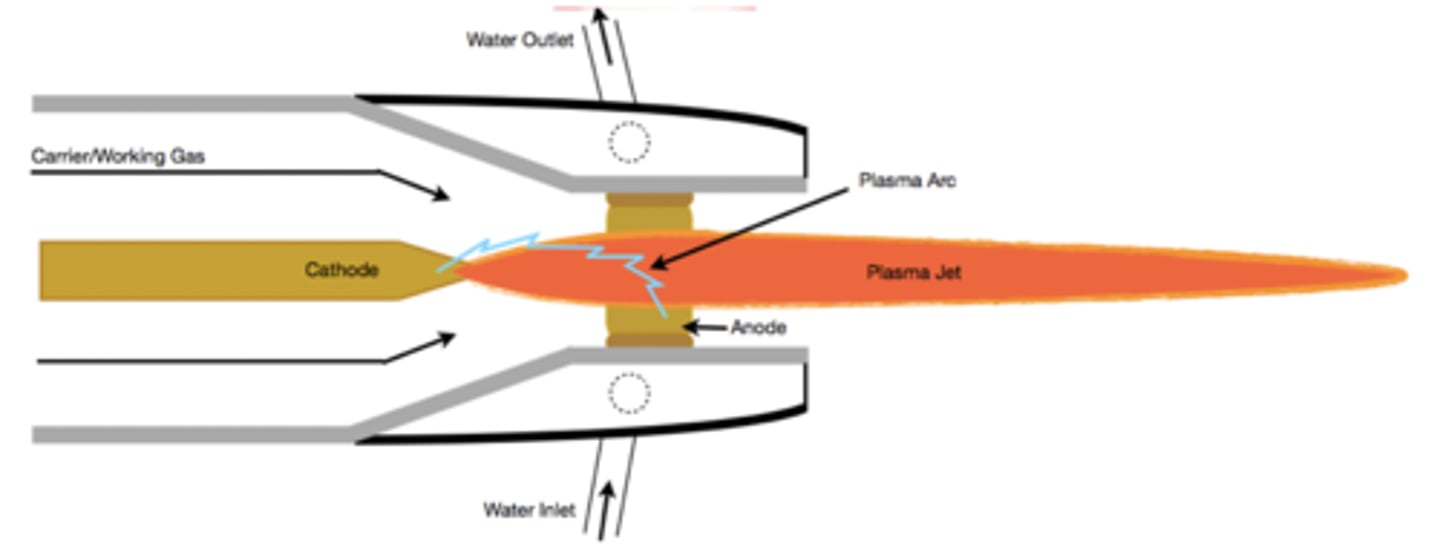
nebulizer creates microdroplets, argon carries to plasma torch, atomization takes place, taken to quadrupole
ICPMS
atomic is complex, mass is simple, clear
atomic emission spectra vs mass spectra
isobaric ions, polyatomic or adduct ions, doubly charged ions, refractory oxide ions
ICPMS spectroscopic interferences
high sensitivity, selectivity, determines most elements in periodic table
why is ICPMS widely used