biological molecules
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
define polymer
Large, complex molecule made up of different/repeating units called monomers
how are polymers formed
formed through condensation reactions
what’s a condensation reaction
chemical process where a chemical/covalent bond forms between monomers which release a molecule of water
define a monomer
small, basic molecular units that join together in long chains to form polymers
give examples of some monomers and the polymer that they form
amino acids form proteins
monosaccharides form carbohydrates
nucleotides form DNA and RNA
what’s a hydrolysis reaction
breaks the chemical bond between monomers using a water molecule
name the 3 main biological molecules
carbohydrates, protein and lipids/fats
what’s the monomer of a carbohydrate
monosaccharides
define monosaccharides
simplest form of carbohydrates, consisting of a sing unit of sugar. Its the basic sub unit that makes up the polymer.
examples of monosaccharides
Fructose, galactose and glucose
what is the chemical formula for glucose
C6 H12 O6
what two types of glucose is there
Alpha glucose and Beta glucose
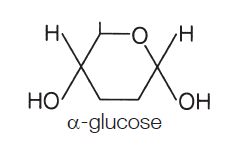
where is the OH (hydroxyl group) in alpha glucose
bottom right
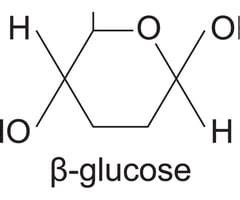
where is the OH (hydroxyl group) in beta glucose
top right
define a disaccharide
when two monosaccharides join together
when monosaccharides join together what reaction takes place and what happens
condensation reaction meaning a bond of water (H2O) forms and is released leaving oxygen by itself
Because Oxygen is left due to a condensation reaction when monosaccharides join- what bond does it make
glycosidic bond
what monosaccharides join to form maltose
alpha glucose and alpha glucose
what monosaccharides join to form lactose
alpha glucose and galactose
what monosaccharides join to form sucrose
alpha glucose and fructose
define a polysaccharide
complex carbohydrates made up of many monosaccharides joined via glycosidic bonds
what are the 3 main polysaccharides
starch, glycogen and cellulose
where is starch found
only found in plant cells
how do plant cells make glucose - what’s it stored as
make glucose in photosynthesis where its stored as starch
why is glucose stored as starch in plants
because glucose is soluble so can effect osmosis causing cells to loose water therefor its stored as starch which is insoluble
when starch is eaten to provide energy what’s it broken down into and stored as
broken down back into glucose to be stored as glycogen
what two different polysaccharides is starch made off
amylose and amylopectin
what are the main points about starch
suited for an energy store
compact
insoluble
easily hydrolysed
what are the monosaccharides of amylose and amylopectin
alpha glucose
What’s the main points about amylose (polysaccharide that makes up starch)
linear structure made of alpha glucose
glycosidic bonds
twist into helix shape making it compact to store more glucose
what are the main points about amylopectin (polysaccharide that makes up starch)
chains of alpha glucose linked by glycosidic bonds
branched molecule meaning its easily hydrolysed for use during respiration