Bio Test 8.4/8.5/ 8.6 AJ likes Men
4.5(2)
Card Sorting
1/71
Earn XP
Last updated 1:30 PM on 4/4/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
1
New cards
DNA contains the information to _______?
Build proteins
2
New cards
Proteins are needed for __________?
Structure, function, and regulation of the body.
3
New cards
Steps of Central Dogma?
1\. DNA Replication
2\. Transcription: Converts the DNA into a mRNA (message)
3\. Translation: Interprets an RNA message into a string of amino acids, called a polypeptide, which makes up a protein.
2\. Transcription: Converts the DNA into a mRNA (message)
3\. Translation: Interprets an RNA message into a string of amino acids, called a polypeptide, which makes up a protein.
4
New cards
In transcription RNA (Ribonucleic acid) acts as a __________?
Middleman between DNA and protein synthesis.
5
New cards
What is RNA?
A chain of nucleotides, each made of a sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogen base.
6
New cards
__RNA differs from DNA in three major ways__?
RNA has a ribose sugar.
RNA has uracil instead of thymine. ( A pairs with U)
RNA is a single-stranded structure. (This single stranded structure allows some types of RNA to form complex 3D shapes, and as a result, some RNA molecules can catalyze reactions much as enzymes do.)
Additionally, DNA codes for proteins, while RNA makes proteins.
RNA has uracil instead of thymine. ( A pairs with U)
RNA is a single-stranded structure. (This single stranded structure allows some types of RNA to form complex 3D shapes, and as a result, some RNA molecules can catalyze reactions much as enzymes do.)
Additionally, DNA codes for proteins, while RNA makes proteins.
7
New cards
Transcription/where
Nucleus
8
New cards
Transcription/purpose
Copy a sequence of DNA to produce a complementary strand of RNA.
9
New cards
Transcription/definition
Process of copying a sequence of DNA to produce a complementary strand of RNA.
10
New cards
RNA polymerase/definition
Enzymes that bond nucleotides together in a chain to make a new RNA molecule.
11
New cards
RNA polymerase moves in a ____________?
5'-3' direction
12
New cards
RNA polymerase also unwinds and unbinds the __________?
DNA double helix
13
New cards
RNA polymerase adds nucleotides to a new strand of _________?
RNA
14
New cards
Transcription produces three major types of RNA molecules?
mRNA
rRNA
tRNA
rRNA
tRNA
15
New cards
mRNA?
Intermediate message that is translated to form a protein.
16
New cards
rRNA?
Forms part of ribosomes, a cell’s protein factories.
17
New cards
tRNA?
Brings amino acids from the cytoplasm to a ribosome to help make the growing protein.
18
New cards
Steps in transcription?
1\. INITIATION
2\. ELONGATION
3\. TERMINATION
2\. ELONGATION
3\. TERMINATION
19
New cards
(Honors) Initiation: TATA Box -
Promoter Sequence
20
New cards
(Honors) RNA polymerase binds to a region of a gene called the_________?
Promoter
21
New cards
(Honors) Promoter/Definition?
A segment of DNA that allows a gene to be __found and transcribed__
22
New cards
(Honors) The promoter tells the RNA polymerase where on the DNA to begin______?
Transcribing
23
New cards
A TATAA box is?
A DNA sequence that indicates where a genetic sequence can be read and decoded. It is a type of promoter sequence, which specifies to other molecules where transcription begins.
24
New cards
Elongation?
Using the DNA strand as a template the RNA polymerase makes a complementary strand of RNA.
__Elongation__ is the stage when the RNA strand gets longer, thanks to the addition of new nucleotides.
__Elongation__ is the stage when the RNA strand gets longer, thanks to the addition of new nucleotides.
25
New cards
Termination?
After a gene has been transcribed, RNA polymerase will encounter a __terminator sequence__ and the RNA strand will be released.
26
New cards
Termination/ End result
mRNA
Before the mRNA can leave the nucleus and be used it needs to be edited (__mRNA splicing__).
Before the mRNA can leave the nucleus and be used it needs to be edited (__mRNA splicing__).
27
New cards
(Honors) Pre-mRNA Splicing?
RNA splicing is a process in molecular biology where a newly-made precursor messenger RNA (pre-mRNA) transcript is transformed into a mature messenger RNA (mRNA). It works by removing all the introns (non-coding regions of RNA) and splicing back together exons (coding regions).
mRNA must be processed before leaving the nucleus.
mRNA must be processed before leaving the nucleus.
28
New cards
(Honors) mRNA Splicing process?
Exons are nucleotide segments that __code__ for parts of the protein.
Introns are __non-coding__ nucleotide segments that intervene, or occur, between exons.
5' cap tail is added which helps preserve the mRNA and helps ribosomes bind to it.
Poly-A tail is added to help the mRNA leave the nucleus.
Introns are __non-coding__ nucleotide segments that intervene, or occur, between exons.
5' cap tail is added which helps preserve the mRNA and helps ribosomes bind to it.
Poly-A tail is added to help the mRNA leave the nucleus.
29
New cards
(Honors) 1.3' poly-A tail protects _________?
Protects mRNA from degradation
Aids in exporting the mature mRNA to the cytoplasm.
Involved in binding proteins to initiate translation.
Aids in exporting the mature mRNA to the cytoplasm.
Involved in binding proteins to initiate translation.
30
New cards
(Honors) The 5' cap protects the __________?
newly-synthesized mRNA from degradation.
It also assists in ribosome binding to help initiating translation.
It also assists in ribosome binding to help initiating translation.
31
New cards
__Translation/Definition__
The process which translates an mRNA message into a polypeptide chain (__protein__).
32
New cards
__Translation/Where__
Cytoplasm
33
New cards
Primary?
Amino acid sequence
34
New cards
Secondary structure?
Alpha helix, beta sheet and loops
35
New cards
Tertiary?
Phi-Psi angle
36
New cards
Quaternary?
Arrangement of several Polypeptide chains
37
New cards
The human genetic code only directly encodes _______?
20 amino acids
38
New cards
__Codon/definition__
A sequence of 3 nucleotides that codes for an amino acid
39
New cards
The genetic code matches each mRNA codon with its _________?
Amino acid or function
40
New cards
The __first two letters are the most important__ in coding for ____________?
Amino acids
41
New cards
Stop codons/definition
Signal the end of an amino acid chain.
42
New cards
Stop codons?
__UAA,UGA, and UAG__
43
New cards
Start codons/definition
Signals the start of translation. AUG which codes for methionine is the start codon.
44
New cards
Reading frame
It's crucial that the mRNA is read correctly.
A misread mRNA could change the protein completely.
Could lead to mutations.
In molecular biology, a reading frame is a way of dividing the sequence of nucleotides in a nucleic acid (DNA or RNA) molecule into a set of consecutive, non-overlapping triplets.
Where these triplets equate to amino acids or stop signals during translation, they are called __codons.__
A misread mRNA could change the protein completely.
Could lead to mutations.
In molecular biology, a reading frame is a way of dividing the sequence of nucleotides in a nucleic acid (DNA or RNA) molecule into a set of consecutive, non-overlapping triplets.
Where these triplets equate to amino acids or stop signals during translation, they are called __codons.__
45
New cards
Universal Language
The genetic code is shared by almost all living organisms.
Codons are said to be universal throughout all living organisms. This allows crossing species and genetic modification.
The genetic code is universal means the same codons code for the same amino acids in all forms of life that exists today.
Codons are said to be universal throughout all living organisms. This allows crossing species and genetic modification.
The genetic code is universal means the same codons code for the same amino acids in all forms of life that exists today.
46
New cards
How to read the mRNA?
The mRNA is read by a ribosomal subunit (rRNA) and a transfer RNA (tRNA).
The __rRNA__ is composed of 2 subunits a large and small, together they pull the mRNA through reading one codon at a time.
The __large subunit__ holds onto the growing protein chain, while the __small subunit__ holds onto the mRNA.
tRNA carry free-floating amino acids from the cytoplasm to the ribosome.
It's L shaped, (tRNA) one side has an amino acid attached; the other has a code called the anticodon.
The anticodon is a set of three nucleotides complementary to the mRNA.
mRNA: GGG
tRNA: CCC (this is the anticodon for GGG)
The __rRNA__ is composed of 2 subunits a large and small, together they pull the mRNA through reading one codon at a time.
The __large subunit__ holds onto the growing protein chain, while the __small subunit__ holds onto the mRNA.
tRNA carry free-floating amino acids from the cytoplasm to the ribosome.
It's L shaped, (tRNA) one side has an amino acid attached; the other has a code called the anticodon.
The anticodon is a set of three nucleotides complementary to the mRNA.
mRNA: GGG
tRNA: CCC (this is the anticodon for GGG)
47
New cards
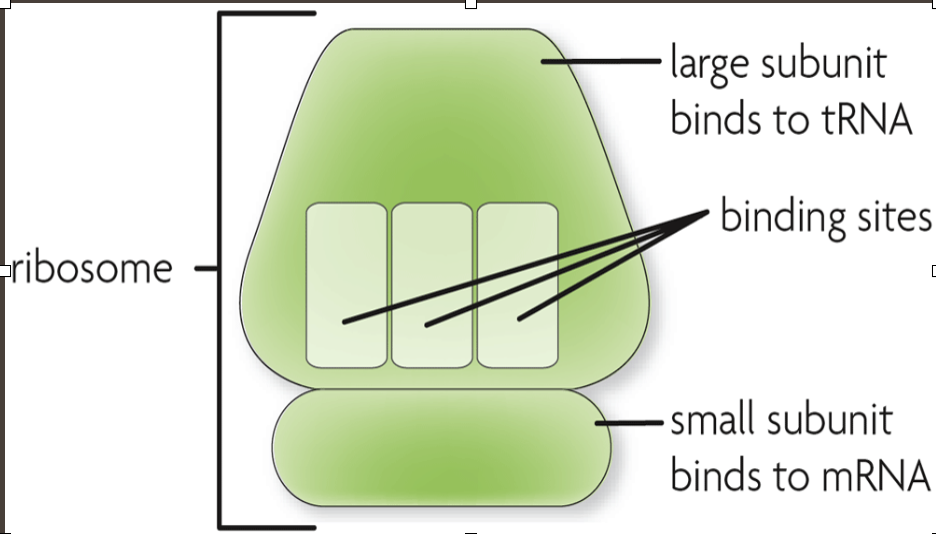
Ribosome
Large Subunit
Binding sites
Small subunit binds to mRNA
Binding sites
Small subunit binds to mRNA
48
New cards
tRNA
Amino acid
Anti-codon
Anti-codon
49
New cards
What happens when proteins fail to work?
When dietary protein is in short supply, the body tends to take protein from skeletal muscles to preserve more important tissues and body functions. As a result, lack of protein leads to muscle wasting over time.
The skin might also be affected—proteins enable skin regeneration, and if they do not work adequately, the skin might become dry and cracked.
The skin might also be affected—proteins enable skin regeneration, and if they do not work adequately, the skin might become dry and cracked.
50
New cards
Mutation/definition
DNA change
51
New cards
Mutations can affect a __________?
single gene or an entire chromosome.
Mutations can be good, bad, or neither.
Mutations can be good, bad, or neither.
52
New cards
Proteopathy?
The condition when proteins fail to work.
53
New cards
__Point mutations/ Definition__
Substitute one nucleotide for another. This means that an incorrect nucleotide is put in the place of the correct nucleotide.
54
New cards
__Sickle Cell anemia/ Definition__
Instead of coding for Glutamic acids, Valine is coded for when making the hemoglobin protein.
55
New cards
Examples of Gene mutations?
__Cystic Fibrosis__ __Tay-Sachs__ __Cancer__
56
New cards
Silent Mutation:
Silent mutations are mutations in DNA that do not have an observable effect on the organism's phenotype.
57
New cards
Missense Mutation:
A missense mutation is a mistake in the DNA which results in the wrong amino acid being incorporated into a protein because of change, that single DNA sequence change, results in a different amino acid codon which the ribosome recognizes.
58
New cards
Nonsense Mutation
A nonsense mutation, or its synonym, a stop mutation, is a change in DNA that causes a protein to terminate or end its translation earlier than expected.
59
New cards
__Frameshift mutations__:
Delete/insert nucleotides that don't belong
60
New cards
__Frameshift mutations/ examples__
Ex. THE CAT ATE THE RAT, delete the first E
THC ATA TET HER AT
Ex. THE CAT ATE THE RAT
Insert an extra C
THE CCA TAT ETH ERA T
THC ATA TET HER AT
Ex. THE CAT ATE THE RAT
Insert an extra C
THE CCA TAT ETH ERA T
61
New cards
Insertion mutation examples:
Fragile X Syndrome
Huntington's disease
Huntington's disease
62
New cards
Deletion mutation examples:
Cri du Chat
Male infertility
Prader Willi syndrome
Male infertility
Prader Willi syndrome
63
New cards
__Chromosomal mutations:__
Changes in structure or number of chromosomes.
64
New cards
__a.Duplication:__
One chromosome may have two copies of a gene(s).
65
New cards
__b.Translocation:__
A piece of one chromosome moves to a non-homologous chromosome
66
New cards
Duplications and Translocations occur in _________?
germ cells during Prophase I of meiosis.
67
New cards
Duplication/ examples
Klinefelter syndrome
XXY syndrome
Affects men only
XXY syndrome
Affects men only
68
New cards
Translocation/ example
Down syndrome
Edwards syndrome
Edwards syndrome
69
New cards
Not all mutations have an effect on an _________?
Organisms phenotype
70
New cards
Mutations that do not affect a resulting protein are called ___________?
__silent mutations__
71
New cards
Mutations can occur in all types of cells, but ________?
to affect an offspring it has to occur in __germ cells__ (gametes).
72
New cards
__Mutagens/ defintion__
Agents in the environment that can change DNA.
ndustrial chemicals
They can speed up replication rate or break DNA strands.
Some mutagens occur naturally. Ex. : UV rays from sunlight, pesticides, nicotine, bacteria, viruses, etc...
ndustrial chemicals
They can speed up replication rate or break DNA strands.
Some mutagens occur naturally. Ex. : UV rays from sunlight, pesticides, nicotine, bacteria, viruses, etc...