W13: ALCOHOLS. PHENOLS, AND THIOLS
1/92
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Alcohols, Phenols, Thiols
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
93 Terms
How many electrons Oxygen have?
6
How many covalent bonds oxygen have when interacting with organic compound?
2 covalent bonds
An organic compound in which an —OH group is bonded to a saturated carbon atom.
Alcohol
What is saturated carbon atom?
Carbon atom that is bonded to four other atoms
The functional group that is characteristic of an alcohol called hydroxyl group.
-OH group
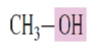
What is the common name for the alcohol:
Methyl alcohol
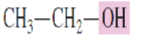
What is the common name for the alcohol:
Ethyl alcohol
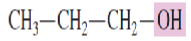
What is the common name for the alcohol:
Propyl alcohol
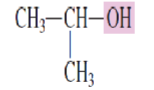
What is the common name for the alcohol:
Isopropyl alcohol
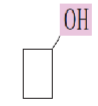
What is the common name for the alcohol:
Cyclobutyl alcohol
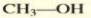
Give the IUPAC name of the alcohol:
methanol
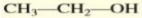
Give the IUPAC name of the alcohol:
ethanol
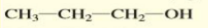
Give the IUPAC name of the alcohol:
1-propanol
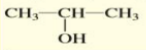
Give the IUPAC name of the alcohol:
2-propanol
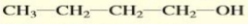
Give the IUPAC name of the alcohol:
1-butanol
Give the condensed structure formula of:
2-methyl-1-propanol
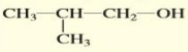
Give the condensed structure formula of:
2-butanol
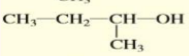
Give the condensed structure formula of:
2-methyl-2-propanol
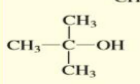
Give the IUPAC name of the following alcohol:
3-methyl-3-hexanol
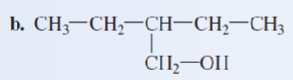
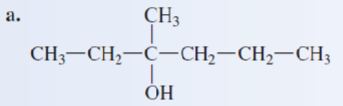
Give the IUPAC name of the following alcohol:
2-ethyl-1-butanol
Give the IUPAC name of the following alcohol:
3,4-dimethylcyclohexanol
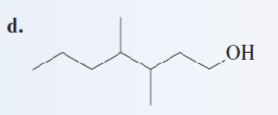
Give the IUPAC name of the following alcohol:
3,4-dimethyl-1-heptanol
Alcohols that possess more than one hydroxyl group
Polyhydroxy alcohols
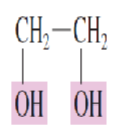
Name the Polyhydroxy alcohol:
two hydroxyl groups are present
1,2-ethanediol
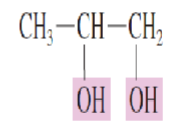
Name the Polyhydroxy alcohol:
two hydroxyl groups are present
1,2-Propanediol
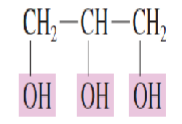
Name the Polyhydroxy alcohol:
three hydroxyl groups are present
1,2,3-Propanetriol
Commonly encountered alcohols:
One carbon atom and one -OH group, simplest alcohol
Good fuel for internal combustion engines
Excellent solvent properties (solvent for: paints, shellacs, and varnishes)
sometimes called wood alcohol
Methyl alcohol
Methyl alcohol was oxidized by the liver enzyme called ____________.
alcohol dehydrogenase
Methyl alcohol produces toxic metabolites _____________ when oxidized by the liver enzyme alcohol dehydrogenase.
formaldehyde and formic acid
Formaldehyde can cause ________________.
blindness
Formic acid causes _____________.
acidosis
Commonly encountered alcohols:
two-carbon monohydroxy alcohol, is the alcohol present in alcoholic beverages and is commonly referred to simply as alcohol or drinking alcohol.
less toxic than those of methyl alcohol
can be produced through yeast fermentation of sugars found in plant extracts
often called grain alcohol
Ethyl alcohol (ethanol)
Ethyl alcohol produces _____________ when oxidized by livers enzyme alcohol dehydrogenase.
Acetaldehyde
Responsible for the symptoms of hangover after drinking.
Acetaldehyde
ethyl alcohol that has been rendered unfit to drink by the addition of small amounts of toxic substances
type of ethyl alcohol that is mostly used for industrial purposes
Denatured alcohol
A 70% isopropyl alcohol, 30% water solution is marketed as _____________.
rubbing alcohol
It’s rapid evaporation rate creates a dramatic cooling effect when it is applied to the skin.
Isopropyl alcohol
The two simplest alcohols possessing two -OH groups.
diol
Ethylene glycol and Propylene glycol
A diol in which the two -OH groups are on adjacent carbon atoms.
glycol
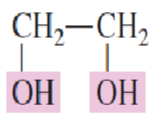
Name the following structure:
1,2-Ethanediol
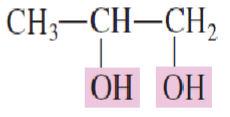
Name the following structure:
1,2-Propanediol
Both of these glycols are __________, __________, __________ liquids that are completely _________ with water.
1.) colorless, odorless, high boiling
2.) miscible
Ethylene glycol is extremely toxic when ingested. In the body, liver enzymes oxidize it to ________________. A calcium salt crystallizes in the kidneys, which leads to renal problems.
oxalic acid
Glycol that is essentially nontoxic and has been used as a solvent for drugs.
Propylene glycol
A clear, thick liquid that has the consistency of honey.
Its molecular structure involves three —OH groups on three different carbon atoms.
-triol
Glycerol
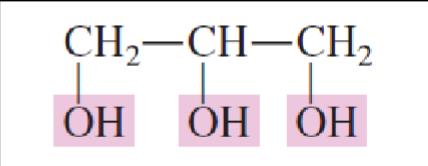
Name the chemical structure:
1,2,3-Propanteriol
Glycerol is normally present in the human body because it is a product of ____________.
fat metabolism
Glycerol is present, in combined form, in all ___________ and _________.
animal fats
vegetable oils
In some Arctic species, glycerol functions as a “________________”
biological antifreeze
Because glycerol has a great affinity for water vapor (moisture), it is often added to pharmaceutical preparations such as ___________ and _______.
skin lotions
soap
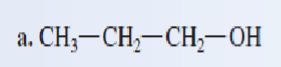
Classify each of the following alcohols as a primary secondary, or tertiary:
primary
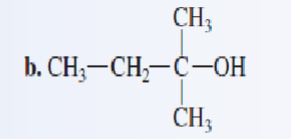
Classify each of the following alcohols as a primary secondary, or tertiary:
tertiary
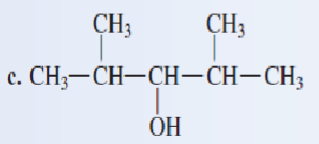
Classify each of the following alcohols as a primary secondary, or tertiary:
secondary
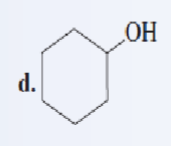
Classify each of the following alcohols as a primary secondary, or tertiary:
secondary
________________ of all types undergo combustion in air to produce carbon dioxide and water.
Hydrocarbons
A chemical reaction in which the components of water (H and OH) are removed from a single reactant or from two reactants (H from one and OH from the other).
Dehydration
In _________________, both water components are removed from the same molecule.
intramolecular dehydration
Reaction conditions for the intramolecular dehydration of an alcohol are a temperature of _____ and the presence of ________ as a catalyst.
180 °C
sulfuric acid
what is the product of intramolecular alcohol dehydration?
alkene
Intramolecular alcohol dehydration is an example of an ___________________.
elimination reaction
At a lower temperature (140 °C) than that required for alkene formation (180°C), an _______________ rather than an intramolecular alcohol dehydration process can occur.
intermolecular
Product of intermolecular alcohol dehydration process.
ether
A reaction in which two groups or two atoms on neighboring carbon atoms are removed, or eliminated, from a molecule, leaving a multiple bond between the carbon atoms.
elimination reaction
Intermolecular alcohol dehydration process is an example of what type of reaction?
condensation reaction
A chemical reaction in which two molecules combine to form a larger one while liberating a small molecule, usually water.
condensation reaction
Alcohols undergo ______________ in which a halogen atom is substituted for the hydroxyl group, producing an alkyl halide.
halogenation reactions
A ________ is an organic compound in which an —OH group is attached to a carbon atom that is part of an aromatic carbon ring system.
phenol
The general formula for phenols is?
Ar-OH
an aromatic carbon ring system from which one hydrogen atom has been removed.
Aryl group (Ar)
the functional group for both phenols and alcohols
hydroxyl group
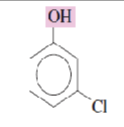
Name the following phenols:
3-chlorophenol
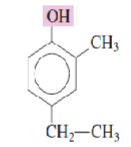
Name the following phenols:
4-Ethyl-2-methylphenol
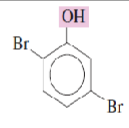
Name the following phenols:
2,5-Dibromophenol
Methylphenols are called _______.
cresols
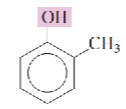
Name the isomeric methylphenols:
ortho-cresol
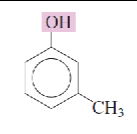
Name the isomeric methylphenols:
meta-cresol
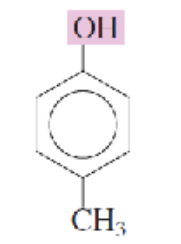
Name the isomeric methylphenols:
para-cresol
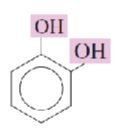
Name the hydroxyphenols:
catechol
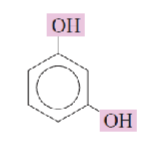
Name the hydroxyphenols:
resorcinol
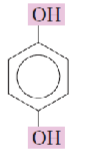
Name the hydroxyphenols:
Hydroquinone
Phenols are generally low-melting solids or oily liquids at ____________.
room temperature
Many phenols have _________ and ________ properties.
antiseptic
disinfectant
What is the melting point of phenols?
41 C
What is the naturally occurring phenolic antioxidant in the human body?
vitamin E
A number of phenols found in plants are used as ______________ and/or
_____________.
flavoring agents
antibacterials
Obtained from herb thyme
Possesses both flavorant and antibacterial properties. It is used as an ingredient in several mouthwash formulations.
Thymol
Responsible for the flavor of cloves.
Dentists traditionally used clove oil as an antiseptic
Eugenol
Thiols, the sulfur analogs of alcohols, contain _______________ instead of —OH functional groups.
—SH functional groups
The thiol functional group is called a _______________.
sulfhydryl group
An older term used for thiols is ___________.
mercaptans
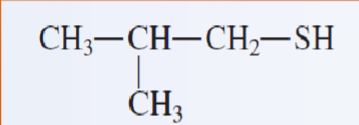
name the following thiols:
2-methyl-1-propanethiol
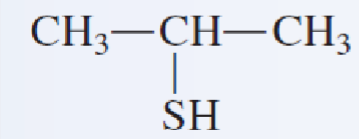
name the following thiols:
2-propanethiol
Two important properties of thiols are ______________________ than alcohols of similar size and a strong, disagreeable odor
lower boiling points
strong, disagreeable odor